热带海洋学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (3): 155-165.doi: 10.11978/2023002CSTR: 32234.14.2023002
南海北部涠洲岛边缘珊瑚礁的生物侵蚀实验研究
江绿苗1,2( ), 陈天然1(
), 陈天然1( ), 赵宽3, 张婷1,2, 许莉佳4
), 赵宽3, 张婷1,2, 许莉佳4
- 1.中国科学院边缘海与大洋地质重点实验室, 中国科学院南海海洋研究所, 广东 广州 510301
2.中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
3.中国海洋大学三亚海洋研究院, 海南 三亚 572024
4.生态环境部华南环境科学研究所, 广东 广州 510530
-
收稿日期:2023-01-03修回日期:2023-03-26出版日期:2024-05-10发布日期:2023-04-13 -
作者简介:江绿苗(1998—), 女, 海南省三亚市人, 硕士研究生, 主要从事珊瑚礁沉积学研究。email: jianglvmiao.mf@outlook.com
-
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(42076065); 中央级公益性科研院所基本科研业务专项(PM-zx703-202105-176); 中央级公益性科研院所基本科研业务专项(PM-zx703-202004-143)
Experimental study on bioerosion of marginal reefs in the Weizhou Island, northern South China Sea
JIANG Lyumiao1,2( ), CHEN Tianran1(
), CHEN Tianran1( ), ZHAO Kuan3, ZHANG Ting1,2, XU Lijia4
), ZHAO Kuan3, ZHANG Ting1,2, XU Lijia4
- 1. Key Laboratory of Ocean and Marginal Sea Geology (South China Sea Institute of Oceanology), Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3. Sanya Oceanographic Institution, Ocean University of China, Sanya 572024, China
4. South China Institute of Environmental Sciences, MEE, China, Guangzhou 510530, China
-
Received:2023-01-03Revised:2023-03-26Online:2024-05-10Published:2023-04-13 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(42076065); Central Public-Interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund(PM-zx703-202105-176); Central Public-Interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund(PM-zx703-202004-143)
摘要:
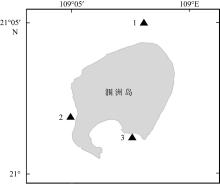
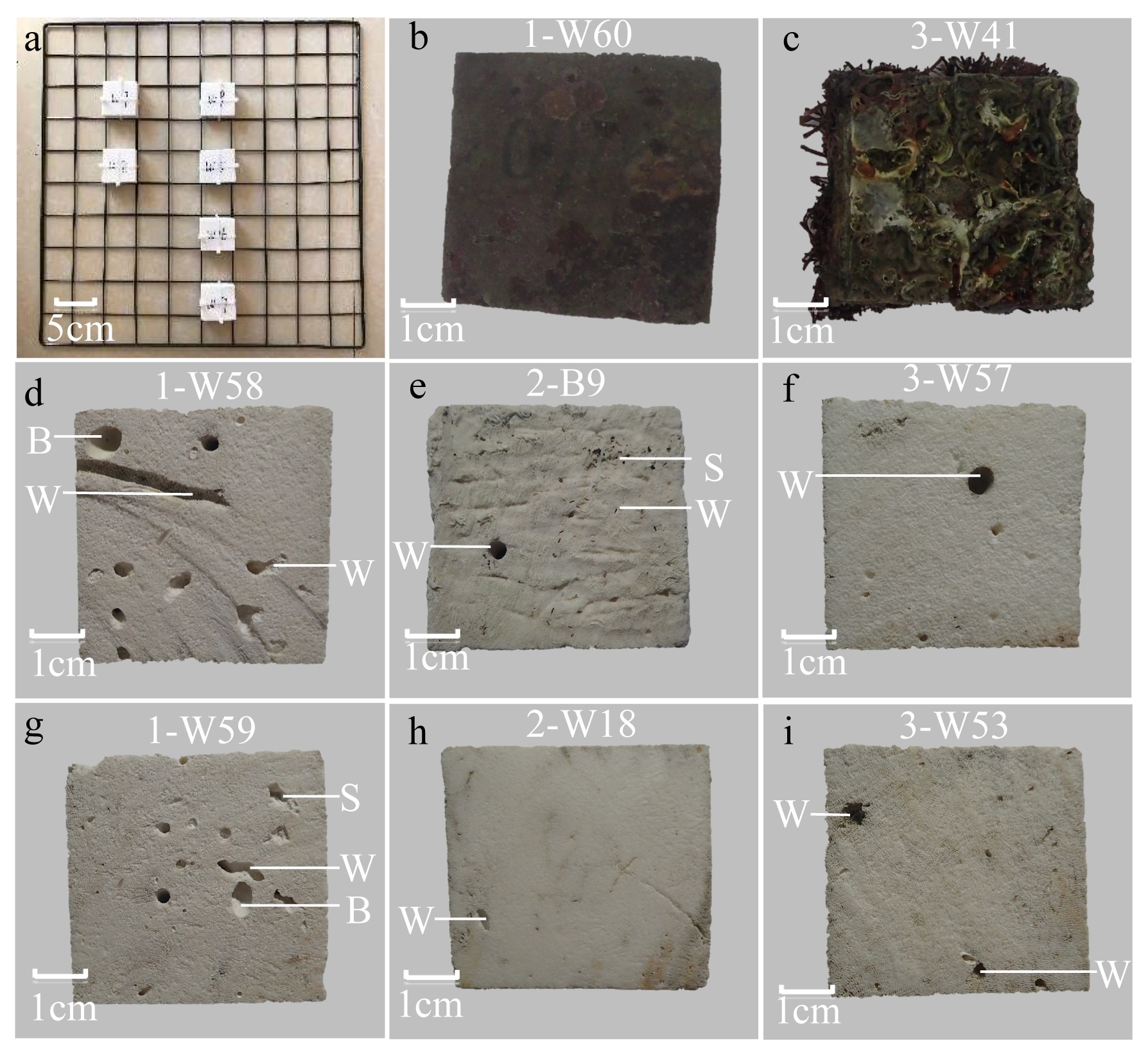
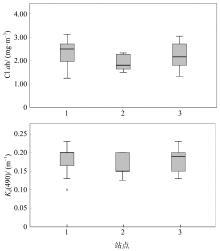
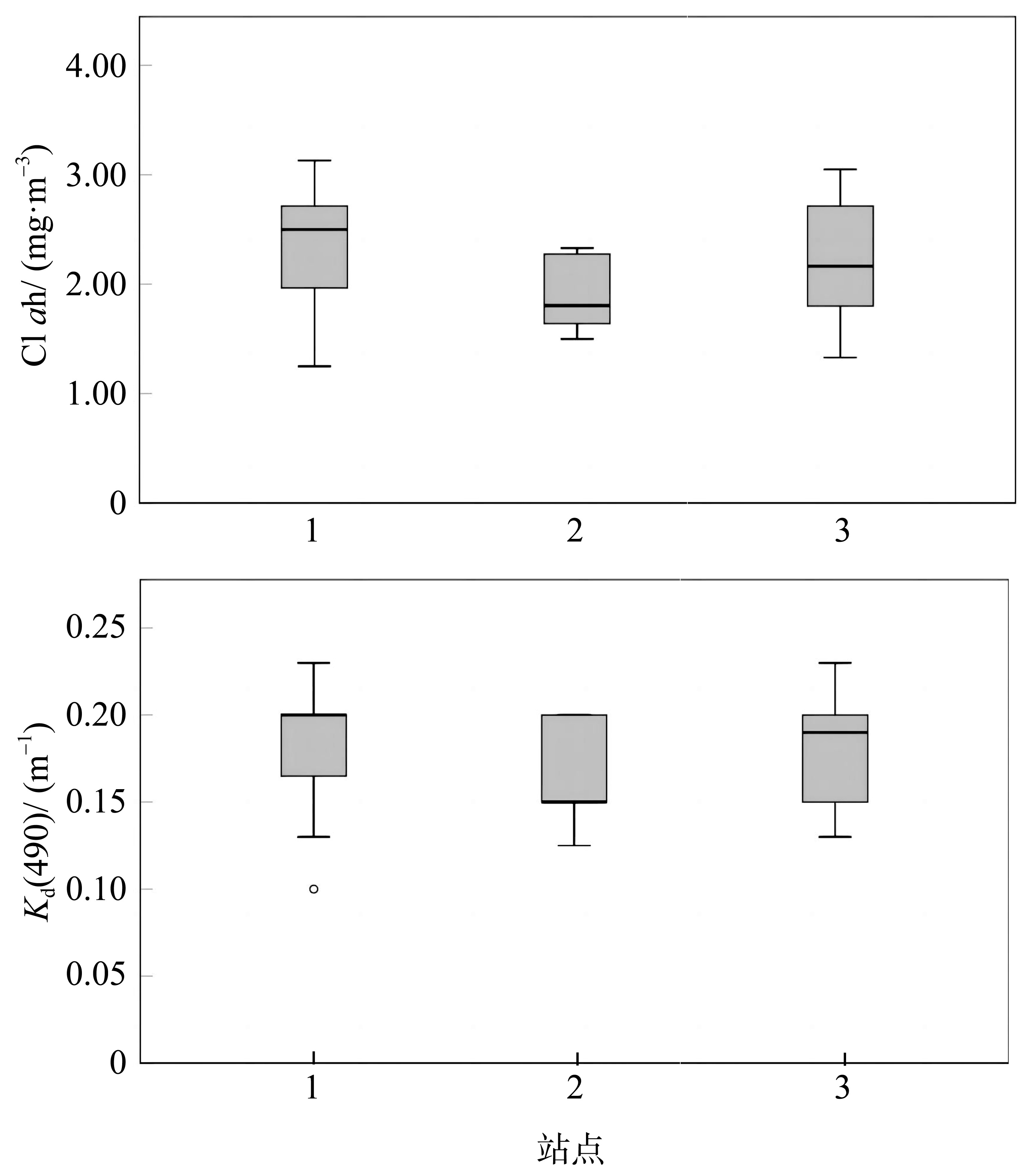
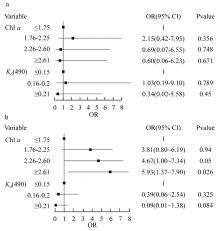
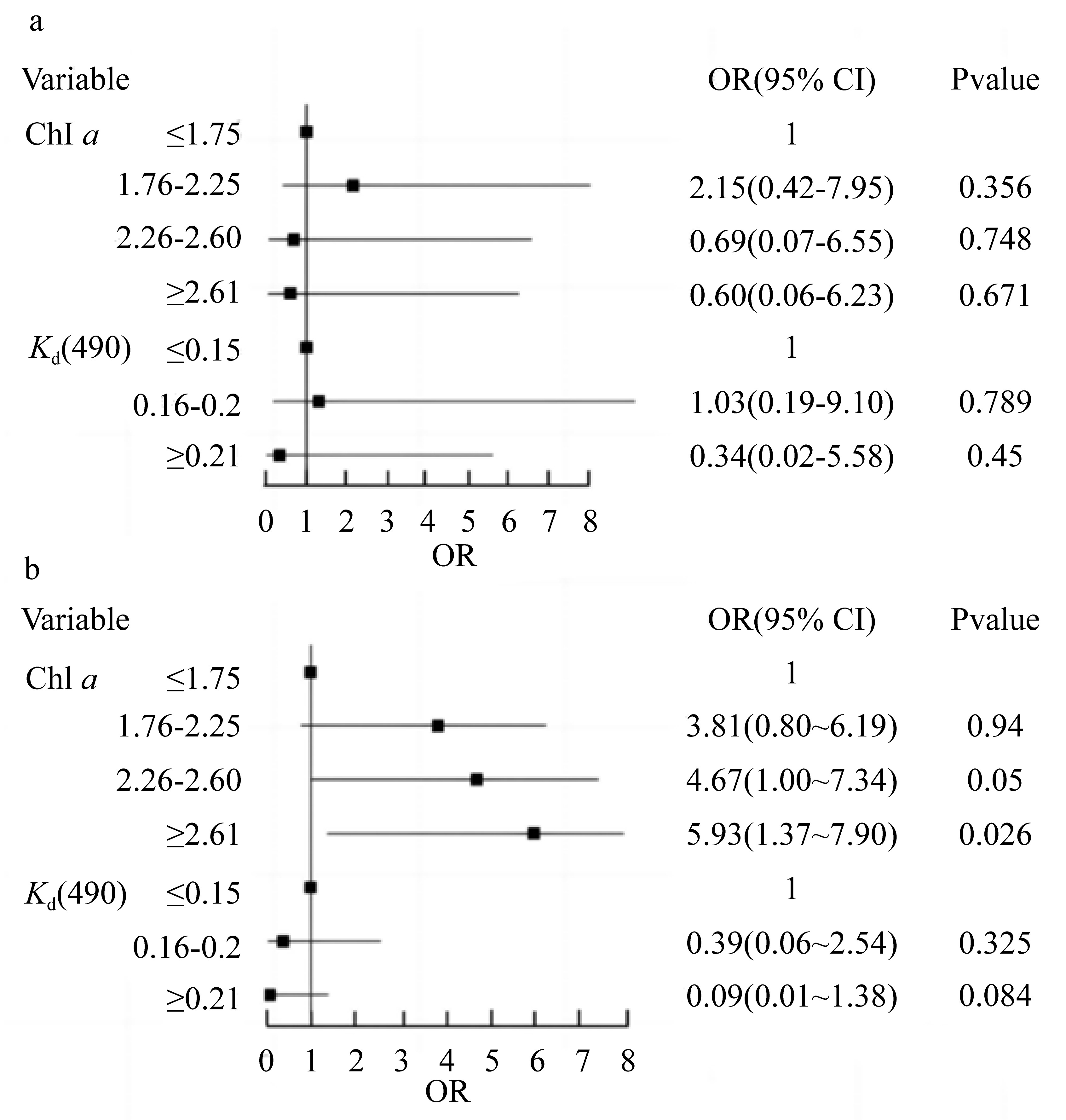
在全球变化背景下, 边缘珊瑚礁面临着来自自然与人类的双重压力。海水富营养化引起的生物侵蚀加剧, 虽然较为隐蔽, 但却会对珊瑚群落的发育以及礁格架的稳定性产生不良影响, 是边缘珊瑚礁潜在的危害之一。本研究在南海北部涠洲岛三个典型的边缘珊瑚礁开展了近一年的原位侵蚀实验, 定量分析了珊瑚礁的生物侵蚀强度与侵蚀速率, 并结合卫星遥感监测的水体环境参数, 探究了珊瑚礁侵蚀与海水环境的关系。研究发现, 内部大型侵蚀生物的侵蚀速率相比侵蚀强度更能够指示海水富营养盐与高浊度环境, 而侵蚀强度能够体现侵蚀生物的群落演替阶段。此外, 将涠洲岛生物侵蚀速率数据与全球其他典型珊瑚礁区域进行对比, 发现涠洲岛生物侵蚀速率处于全球中等水平(以内部大型侵蚀生物为主导), 但在其所属的“人为边缘礁”类型中为较低水平。结合气候变化、城市化发展、礁体健康状况等趋势以及本研究结果, 推测涠洲岛的生物侵蚀可能会继续加强, 达到“人为边缘礁”的高侵蚀水平, 并进一步加剧珊瑚礁的退化。
引用本文
江绿苗, 陈天然, 赵宽, 张婷, 许莉佳. 南海北部涠洲岛边缘珊瑚礁的生物侵蚀实验研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 155-165.
JIANG Lyumiao, CHEN Tianran, ZHAO Kuan, ZHANG Ting, XU Lijia. Experimental study on bioerosion of marginal reefs in the Weizhou Island, northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 155-165.
表2
全球珊瑚礁的生物侵蚀原位实验的研究结果"
| 海域 | 地点 | 序号 | 暴露时间/月 | 生物侵蚀速率/(kg·m-2·yr-1) | 主要侵蚀生物 | 海水Chl a /(mg·m-3) | 海水Kd(490)/(m-1) | 区域特征 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 东热带太平洋 | 巴拿马 | ① | 24 | 1.36 | 双壳类、蠕虫 | 1.99 | 0.16 | 自然边缘礁 | Enochs et al, |
| 中太平洋 | 茂纳卢阿湾 (夏威夷欧胡岛) | ② | 12 | 0.04 | (未知) | 0.09 | 0.00 | 大洋珊瑚礁 | Lubarsky et al, |
| 卡内奥赫湾 (夏威夷欧胡岛) | ③ | 24 | 0.34 | (未知) | 0.20 | 0.00 | 大洋珊瑚礁 | Silbiger et al, | |
| 西热带太平洋 | 新加坡南部岛屿 | ④ | 12 | 1.08 | 海绵、蠕虫 | 2.85 | 0.25 | 人为边缘礁 | Januchowski-Hartley et al, |
| 中国香港 | ⑤ | 24 | 1.38 | 海胆、 蠕虫、双壳类 | 3.16 | 0.19 | 人为边缘礁 | Yeung et al, | |
| 中国涠洲岛 | ⑥ | 10 | 0.46 | 蠕虫 | 2.19 | 0.19 | 人为边缘礁 | ||
| 印度洋 | 泰国斯米兰群岛 (安达曼海) | ⑦ | 18 | 0.70 | 鹦嘴鱼 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 自然边缘礁 | Schmidt et al, |
| 红海 | 沙特阿拉伯 中部海湾 | ⑧ | 30 | 0.96 | 内部大型生物 | 0.76 | 0.05 | 自然边缘礁 | Roik et al, |
| [1] |
陈天然, 郑兆勇, 莫少华, 等, 2013. 涠洲岛滨珊瑚中的生物侵蚀及其环境指示意义[J]. 科学通报, 58(17): 1574-1582.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
何精科, 黄振鹏, 2019. 广西涠洲岛珊瑚分布状况研究[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 36(1): 57-62.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
黄晖, 马斌儒, 练健生, 等, 2009. 广西涠洲岛海域珊瑚礁现状及其保护策略研究[J]. 热带地理, 29(4): 307-312, 318.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
黄晓煦, 徐轶肖, 张腾, 等, 2021. 涠洲岛海域营养盐变化特征与评价[J]. 广西科学, 28(2): 130-135.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
金昱昕, 陈天然, 孟庆山, 等, 2017. 单轴抗压强度揭示南海珊瑚骨骼结构的差异[J]. 热带海洋学报, 36(2): 33-39.
doi: 10.11978/2016071 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2016071 |
|
| [6] |
梁文, 黎广钊, 张春华, 等, 2010. 20年来涠洲岛珊瑚礁物种多样性演变特征研究[J]. 海洋科学, 34(12): 78-87.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
梁文, 张春华, 叶祖超, 等, 2011. 广西涠洲岛造礁珊瑚种群结构的空间分布[J]. 生态学报, 31(1): 39-46.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
汤超莲, 周雄, 郑兆勇, 等, 2013. 未来海平面上升对涠洲岛珊瑚礁的可能影响[J]. 热带地理, 33(2): 119-123, 140.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
张文静, 郑兆勇, 张婷, 等, 2020. 1960-2017年北部湾珊瑚礁区海洋热浪增强原因分析[J]. 海洋学报, 42(5): 41-48.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
赵宽, 张婷, 陈天然, 2019. 南海北部滨珊瑚骨骼微生物侵蚀[J]. 热带海洋学报, 38(6): 74-79.
doi: 10.11978/2019006 |
|
|
|
| [11] |
周浩郎, 黎广钊, 2014. 涠洲岛珊瑚礁健康评估[J]. 广西科学院学报, 30(4): 238-247.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
pmid: 12065035 |
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
pmid: 17801530 |
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
pmid: 15757742 |
| [36] |
pmid: 11474098 |
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
doi: 10.1038/ncomms2409 pmid: 23360993 |
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
pmid: 17841404 |
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [1] | 柳原, 柯志新, 李开枝, 谭烨辉, 梁竣策, 周伟华. 人类活动和沿岸流影响下的粤东近海浮游动物群落特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [2] | 许莉佳, 廖芝衡, 陈辉, 王永智, 黄柏强, 林巧云, 甘健锋, 杨静. 南海北部珊瑚群落结构特征及其对海洋热浪事件的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 58-71. |
| [3] | 赵明辉, 袁野, 张佳政, 张翠梅, 高金尉, 王强, 孙珍, 程锦辉. 南海北部被动陆缘洋陆转换带张裂-破裂研究新进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 173-183. |
| [4] | 杨一凯, 曾丽丽. 挟带黑潮高盐水的中尺度涡在南海北部的时空特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 75-85. |
| [5] | 张金尚, 邹定辉, 马玉, 李锐祥, 刘愉强, 孟强, 刘同木, 史华明. 南海北部水团及中尺度现象对营养盐时空分布的影响*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(1): 168-181. |
| [6] | 曾毅港, 经志友, 黄小龙, 郑瑞玺. 夏季南海北部粤东陆架锋面的动力特征分析*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(4): 136-145. |
| [7] | 马梦真, 李芊, 吴正超, 陈寅超, 俞建成. 南海北部最小含氧带水下滑翔机观测结果初步分析*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(1): 131-142. |
| [8] | 王仁政, 单正垛, 孟思雨, 宫响. 南海北部次表层叶绿素最大值年际变化特征分析*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(6): 63-75. |
| [9] | 王剑, 陈楚群, 周伟华, 李祥付, 吴颉, 叶海彬, 唐世林. 利用遥感技术估算南海北部表层异养细菌丰度*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(5): 53-62. |
| [10] | 苏晓康, 赵明辉, 李子正, 袁野, 王星月, 程锦辉, 张佳政. 南海北部陆缘OBS2018-H2测线地壳结构初步结果*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(5): 111-122. |
| [11] | 舒婵, 耿兵绪, 房巍巍, 修鹏. 南海北部海洋生态模型的参数分析及遗传算法优化[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(2): 98-106. |
| [12] | 杨威, 董园, 俎婷婷, 刘长建, 修鹏. 南海北部夏季叶绿素a分布规律及影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(6): 9-20. |
| [13] | 赵宽, 张婷, 陈天然. 南海北部滨珊瑚骨骼微生物侵蚀[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(6): 74-79. |
| [14] | 王霞,方文东,陈荣裕. 南海北部海面高度的季节内变异及其传播特征 *[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(3): 1-12. |
| [15] | 黄妍丹, 许洁馨, 刘军亮, 陈植武, 蔡树群. 基于实测资料的南海北部台风“海鸥”致近惯性振荡研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(6): 16-25. |
|
||