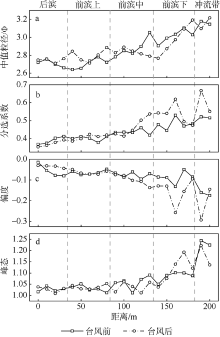
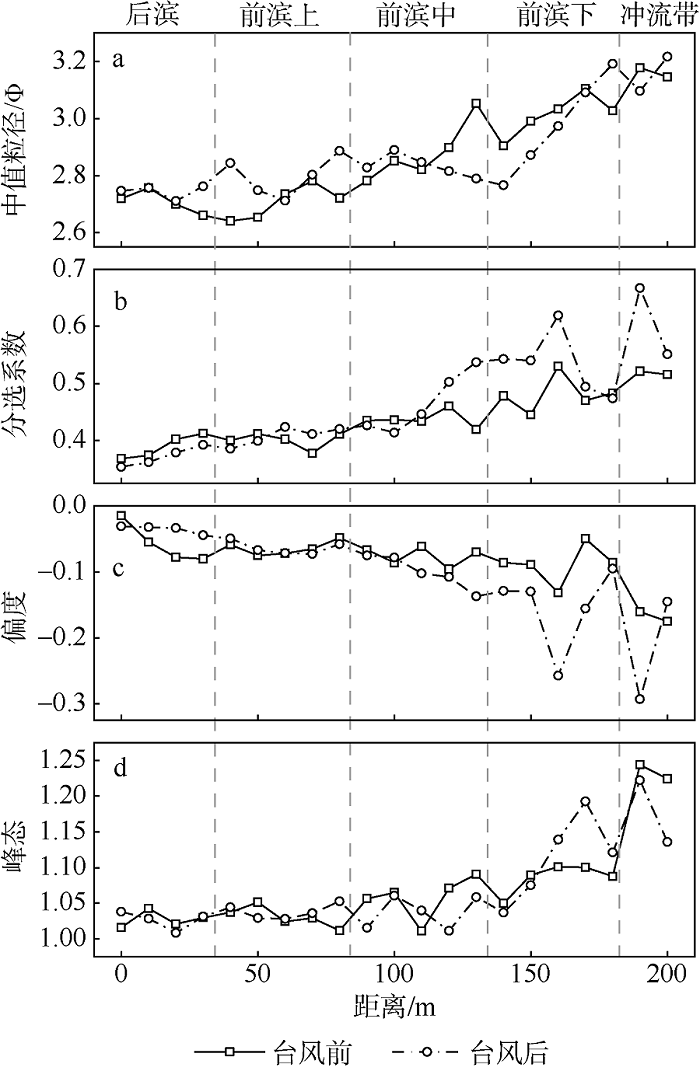
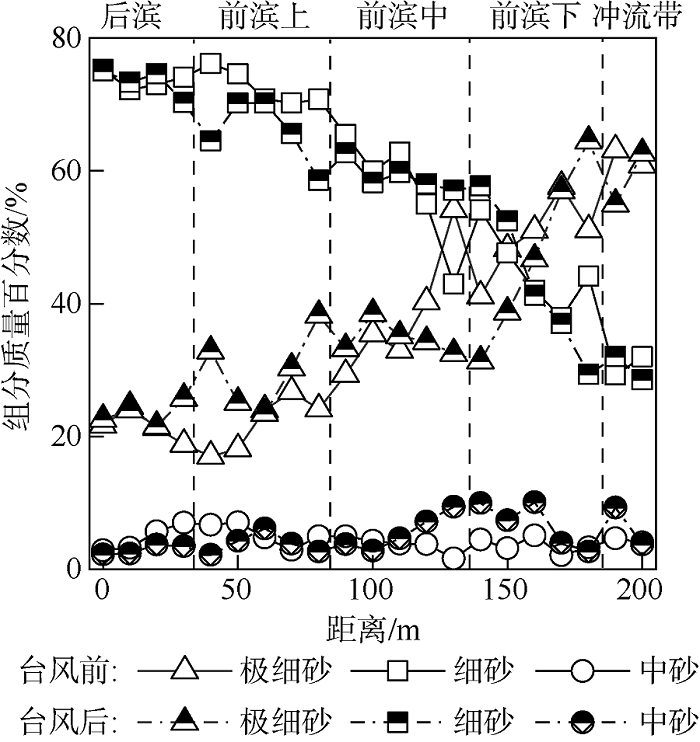
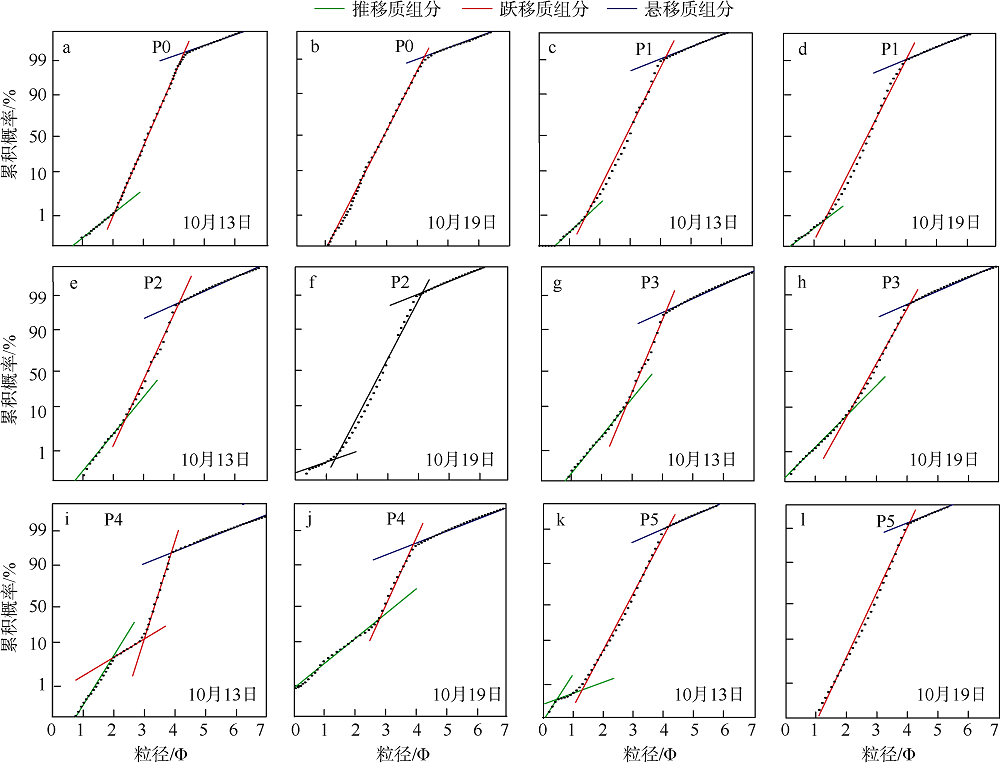
| [1] |
蔡锋, 苏贤泽, 夏东兴, 2004. 热带气旋前进方向两侧海滩风暴效应差异研究——以海滩对0307号台风“伊布都”的响应为例[J]. 海洋科学进展, 22(4): 436-445.
|
|
CAI FENG, SU XIANZE, XIA DONGXING, 2004. Study on the difference between storm effects of beaches on two sides of the tropical cyclone track--Taking the responses of beaches to No. 0307 Typhoon Imbudo as an example[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 22(4): 436-445. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [2] |
陈波, 董德信, 陈宪云, 等, 2017. 南海北部台风引起的广西近岸增减水研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, (2): 1-11.
|
|
CHEN BO, DONG DEXIN, CHEN XIANYUN, et al, 2017. A research on fluctuations of water level in Guangxi coast caused by typhoons in the northern South China Sea[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, (2): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [3] |
陈宪云, 刘晖, 董德信, 等, 2013. 广西主要海洋灾害风险分析[J]. 广西科学, 20(3): 248-253.
|
|
CHEN XIANYUN, LIU HUI, DONG DEXIN, et al, 2013. Analysis of Guangxi marine disaster risk[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 20(3): 248-253. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [4] |
陈子燊, 1995. 弧形海岸海滩地貌对台风大浪的响应特征[J]. 科学通报, 40(23): 2168-2170. (in Chinese)
|
| [5] |
戴志军, 李春初, 2008. 华南弧形海岸动力地貌过程[M]. 上海: 华东师范大学出版社. (in Chinese)
|
| [6] |
龚昊, 陈沈良, 钟小菁, 等, 2017. 海南岛东北部海滩侵蚀与恢复对连续台风的复杂响应[J]. 海洋学报, 39(5): 68-77.
|
|
GONG HAO, CHEN SHENLIANG, ZHONG XIAOQING, et al, 2017. Complicated responses of beach erosion and restoration to consecutive typhoons along northeastern Hainan Island, China[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 39(5): 68-77. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [7] |
黄鹄, 戴志军, 施伟勇, 等, 2011. 强潮环境下的海滩剖面沉积特征----以春季广西北海银滩为例[J]. 热带海洋学报, 30(4): 71-76.
|
|
HUANG HU, DAI ZHIJUN, SHI WEIYONG, et al, 2011. Deposition characteristics of beach profile in strong-tidal environment—A case study of Yintan, Guangxi during spring[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 30(4): 71-76. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [8] |
黄祖明, 戴志军, 黎树式, 等, 2021. 中强潮海滩剖面冲淤过程研究——以北海银滩为例[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 41(4): 36-47.
|
|
HUANG ZUMING, DAI ZHIJUN, LI SHUSHI, et al, 2021. Erosion and accretion of a meso-macro-tidal beach profile—A case from the Yintan Beach of Beihai[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 41(4): 36-47. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [9] |
吉学宽, 林振良, 闫有喜, 等, 2019. 海岸侵蚀、防护与修复研究综述[J]. 广西科学, 26(6): 604-613.
|
|
JI XUEKUAN, LIN ZHENLIANG, YAN YOUXI, et al, 2019. Review on the research of coastal erosion, protection and restoration[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 26(6): 604-613. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [10] |
雷刚, 蔡锋, 2005. 福建江田下沙沙滩沉积地貌组合对台风的响应模式[J]. 台湾海峡, 24(3): 395-403.
|
|
LEI GANG, CAI FENG, 2005. Typhoon response model of sedimentary and geomorphological associations on Xiasha beach, Jiangtian, Fujian[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 24(3): 395-403. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [11] |
黎树式, 戴志军, 葛振鹏, 等, 2017. 强潮海滩响应威马逊台风作用动力沉积过程研究——以北海银滩为例[J]. 海洋工程, 35(3): 89-98.
|
|
LI SHUSHI, DAI ZHIJUN, GE ZHENPENG, et al, 2017. Sediment dynamic processes of macro-tidal beach in response to Typhoon Rammasun action—A case study of Yintan, Beihai[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 35(3): 89-98. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [12] |
刘涛, 王增军, 张建兵, 2020. 广西北海银滩侵蚀动力研究[J]. 海洋学报, 42(7): 147-154.
|
|
LIU TAO, WANG ZENGJUN, ZHANG JIANBIN, 2020. The dynamic of the Yintan Beach erosion in the Beihai, Guangxi[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 42(7): 147-154. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [13] |
ATHANASIOU P, VAN DONGEREN A, GIARDINO A, et al, 2020. Uncertainties in projections of sandy beach erosion due to sea level rise: an analysis at the European scale[J]. Scientific Reports, 10(1): 11895.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68576-0
|
| [14] |
CAI FENG, SU XUANZE, LIU JIANHUI, et al, 2009. Coastal erosion in China under the condition of global climate change and measures for its prevention[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 19(4): 415-426.
doi: 10.1016/j.pnsc.2008.05.034
|
| [15] |
COCO G, SENECHAL N, REJAS A, et al, 2014. Beach response to a sequence of extreme storms[J]. Geomorphology, 204: 493-501.
doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2013.08.028
|
| [16] |
FOLK R L, WARD W C, 1957. Brazos River bar: a study in the significance of grain size parameters[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 27(1): 3-26.
doi: 10.1306/74D70646-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
|
| [17] |
GE ZHENPENG, DAI ZHIJUN, PANG WENHONG, et al, 2017. LIDAR-based detection of the post-typhoon recovery of a meso-macro-tidal beach in the Beibu Gulf, China[J]. Marine Geology, 391: 127-143.
doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2017.08.008
|
| [18] |
GERVAIS M, BALOUIN Y, BELON R, 2012. Morphological response and coastal dynamics associated with major storm events along the Gulf of Lions Coastline, France[J]. Geomorphology, 143-144: 69-80.
doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2011.07.035
|
| [19] |
HARLEY M D, TURNER I L, KINSELA M A, et al, 2017. Extreme coastal erosion enhanced by anomalous extratropical storm wave direction[J]. Scientific Reports, 7(1): 6033.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05792-1
|
| [20] |
MA BINBIN, DAI ZHIJUN, PAN WENHONG, et al, 2019. Dramatic typhoon-induced variability in the grain size characteristics of sediments at a meso-macrotidal beach[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 191: 104006.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2019.104006
|
| [21] |
MEEHL G A, WASHINGTON W M, COLLINS W D, et al, 2005. How much more global warming and sea level rise?[J]. Science, 307(5716): 1769-1772.
doi: 10.1126/science.1106663
|
| [22] |
NICHOLLS R J, CAZENAVE A, 2010. Sea-level rise and its impact on coastal zones[J]. Science, 328(5985): 1517-1520.
doi: 10.1126/science.1185782
|
| [23] |
SHIMOZONO T, TAJIMA Y, KUMAGAI K, et al, 2020. Coastal impacts of super typhoon Hagibis on Greater Tokyo and Shizuoka areas, Japan[J]. Coastal Engineering Journal, 62(2): 129-145.
doi: 10.1080/21664250.2020.1744212
|
| [24] |
SHORT A D, 1991. Macro-meso tidal beach morphodynamics: an overview[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 7(2): 417-436.
|
| [25] |
SHORT A D, 1996. The role of wave height, period, slope, tide range and embaymentisation in beach classifications: a review[J]. Revista Chilena de Historia Natural, 69: 589-604.
|
| [26] |
STOCKDON H F, SALLENGER A H JR, HOLMAN R A, et al, 2007. A simple model for the spatially-variable coastal response to hurricanes[J]. Marine Geology, 238(1-4): 1-20.
doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2006.11.004
|
| [27] |
VALENTÍN J M P, MÜLLER M F, 2020. Impact of Hurricane Maria on beach erosion in Puerto Rico: Remote sensing and causal inference[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 47(6): e2020GL087306.
|
| [28] |
VOUSDOUKAS M I, RANASINGHE R, MENTASCHI L, et al, 2020. Sandy coastlines under threat of erosion[J]. Nature Climate Change, 10(3): 260-263.
doi: 10.1038/s41558-020-0697-0
|
| [29] |
WANG P, KIRBY J H, HABER J D, et al, 2006. Morphological and sedimentological impacts of Hurricane Ivan and immediate poststorm beach recovery along the northwestern Florida barrier-island coasts[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2006(226): 1382-1402.
|
 ), WANG Riming2, FENG Bingbin3, CHEN Bo1(
), WANG Riming2, FENG Bingbin3, CHEN Bo1( )
)