Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 97-107.doi: 10.11978/2025006CSTR: 32234.14.2025006
• Marine Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Microzooplankton grazing rates and viral lysis rates on prokaryotes in summer Sanya Bay*
LI Chunshan1,2( ), ZHANG Jiandong3(
), ZHANG Jiandong3( ), LONG Chao3, LONG Lijuan1, HUANG Sijun1(
), LONG Chao3, LONG Lijuan1, HUANG Sijun1( )
)
- 1. Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Acedemy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3. Marine Environmental Engineering Center, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
-
Received:2025-01-07Revised:2025-03-05Online:2025-09-10Published:2025-10-14 -
Contact:HUANG Sijun -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(42176116); National Natural Science Foundation of China(42306134); National Natural Science Foundation of China(41576126); Science & Technology Fundamental Resources Investigation Program(2023FY100803); Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province(2017A030306020); Rising Star Foundation of the South China Sea Institute of Oceanology(NHXX2019ST0101)
CLC Number:
- P735.122
Cite this article
LI Chunshan, ZHANG Jiandong, LONG Chao, LONG Lijuan, HUANG Sijun. Microzooplankton grazing rates and viral lysis rates on prokaryotes in summer Sanya Bay*[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(5): 97-107.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 1
Statistics of environmental and biological parameters in Sanya Bay over the one-month sampling period"
| 参数 | 范围 | 平均值(X±SD) | 参数 | 范围 | 平均值(X±SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 温度/℃ | 26.10~29.40 | 28.33±1.16 | Syn/(×104cells·L-1) | 0.33~7.38 | 2.98±2.47 |
| 盐度/‰ | 31.97~33.73 | 32.99±0.43 | PC_Syn/(×102cells·L-1) | 1.0~15.00 | 6.38±4.39 |
| DO/(mg·L-1) | 4.26~6.30 | 5.63±0.50 | PE_Syn/(×104cells·L-1) | 0.31~7.33 | 2.92±2.46 |
| Chl a/(μg·L-1) | 4.26~6.30 | 0.39±0.17 | Vir/(×107VLPs·mL-1) | 0.11~2.82 | 1.00±0.78 |
| | 0.96~3.88 | 1.83±0.82 | μ /d-1 | 1.61~3.87 | 2.69±0.66 |
| | 0.09~0.26 | 0.15±0.04 | v/d-1 | 0.31~1.21 | 0.77±0.34 |
| | 1.51~4.23 | 2.84±0.70 | g/d-1 | 0.12~1.88 | 0.83±0.58 |
| | 0.05~0.30 | 0.12±0.06 | Pv/% | 6.18~70.31 | 50.86±18.04 |
| | 2.55~7.00 | 3.88±1.33 | Pg/% | 0.29~84.70 | 49.69±26.53 |
| Prok/(×105cells·L-1)) | 2.33~14.00 | 5.79±4.07 | Cv/(×106fg·mL-1) | 0.18~7.75 | 2.66±2.11 |
| PicoEuk/(×103cells·L-1) | 0.01~4.20 | 1.82±1.46 | Cg/(×106fg·mL-1) | 0.01~9.51 | 2.81±2.61 |
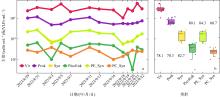
Fig. 2
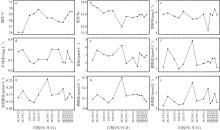
Fluctuations of picoplankton abundances in Sanya Bay over the one-month sampling period. (a) Diurnal variation in the abundances of picoplankton and viruses; (b) abundance distribution and variation across picoplankton and virus groups. Vir: virioplankton; Prok: prokaryotes; Syn: Synechococcus; PicoEuk: picoeukaryotes; PC_Syn: phycocyanin-rich Synechococcus; PE_Syn: phycoerythrin-rich Synechococcus; The numerical values in panel b represent the coefficient of variation, used to assess the variability in the abundance of each group"

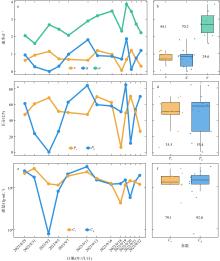
Fig. 3
Diurnal variations in prokaryotic growth rates, viral lysis, and microzooplankton grazing in Sanya Bay over the one-month sampling period. (a) Line graph showing the diurnal variation in viral lysis rate, microzooplankton grazing rate, and prokaryotic growth rate; (b) boxplot showing the diurnal variation in viral lysis rate, microzooplankton grazing rate, and prokaryotic growth rate; (c) line graph showing the diurnal variation in the percentage of cells lysed by viruses and grazed by microzooplankton; (d) boxplot showing the diurnal variation in the percentage of cells lysed by viruses and grazed by microzooplankton; (e) line graph showing the diurnal variation in carbon flux caused by viral lysis and microzooplankton grazing; (f) boxplot showing the diurnal variation in carbon flux caused by viral lysis and microzooplankton grazing. μ: prokaryotic growth rate; v: viral lysis rate; g: microzooplankton grazing rate; Pv: percentage of cells lysed by viruses; Pg: percentage of cells grazed by microzooplankton; Cv: carbon flux caused by viral lysis; Cg: carbon flux caused by microzooplankton grazing. The values shown in panels b, d, and f indicate the coefficient of variation, used to reflect the extent of variability in each parameter"

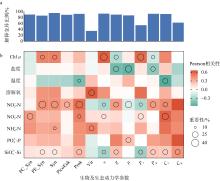
Fig. 4
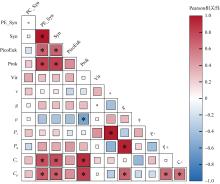
Contributions of environmental factors to the differences in planktonic community, prokaryotic growth rates, viral lysis, and microzooplankton grazing. (a) Proportion of variance in each response variable explained by environmental factors; (b) Pearson correlations (color gradient) and variable importance (circle size) between environmental factors and response variables"

| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50635-z pmid: 39138161 |
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
pmid: 17798278 |
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [40] |
doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.14634 pmid: 31001886 |
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02197.x pmid: 20406288 |
| [49] |
|
| [31] |
pmid: 15953930 |
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-121916-063627 pmid: 29996063 |
| [35] |
pmid: 17289995 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-76590-5 pmid: 33188261 |
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
doi: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2015.24 pmid: 27572161 |
| [52] |
doi: 10.1128/MMBR.64.1.69-114.2000 pmid: 10704475 |
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
doi: 10.1038/s41579-019-0270-x pmid: 31690825 |
| [1] | LI Jieli, ZOU Ligong, YANG Yufeng, WANG Qing. Zooplankton community structure and fecal carbon flux in the seaweed Sargassum beds of Weizhou Island, Guangxi, based on morphological and environmental DNA metabarcoding [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(3): 104-120. |
| [2] | YANG Ding-tian, LIU Su-min, SHAN Xiu-juan. Progress in detecting seagrass carbon flux over optically shallow water using satellite remote sensing [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(6): 108-114. |
| [3] | ZHOU Lin-bin, TAN Ye-hui, HUANG Liang-min. Negative phytoplankton growth rates in dilution experiments and the possible causes [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(1): 48-54. |
| [4] | ZUO Yun-long,XIANG Wen-zhou,LIU Ji-hua,SU Jiao-jiao,HE Hui,ZHANG. Isolation, culture, and identification of a picophytoplankton [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2011, 30(1): 86-90. |
|
||