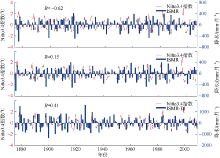
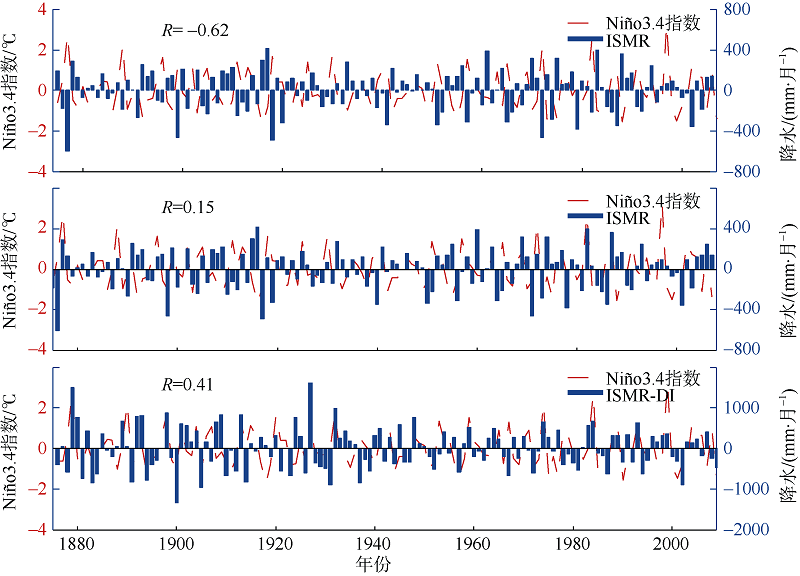
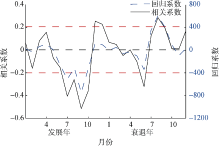
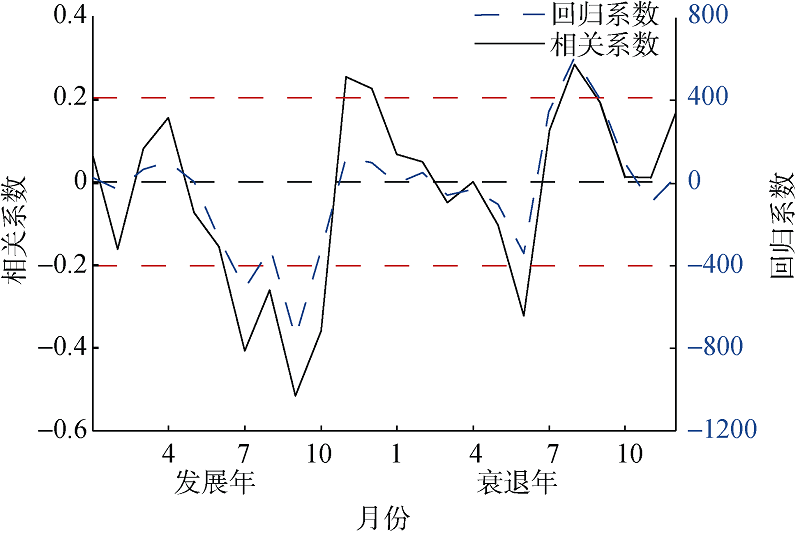
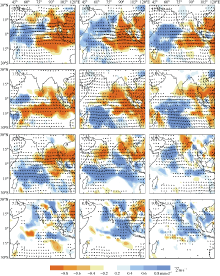
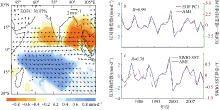
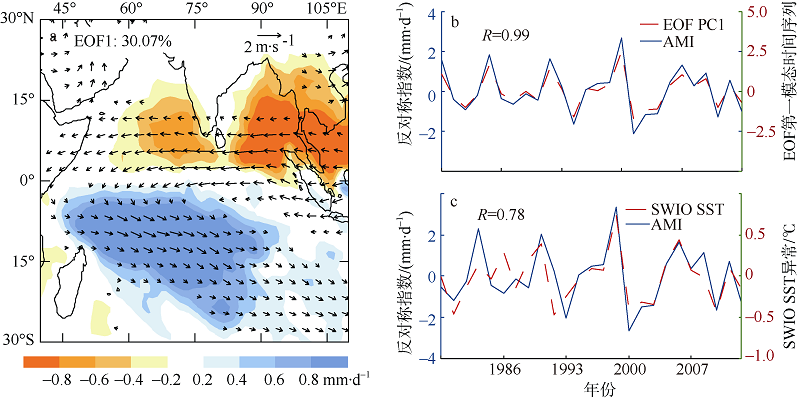
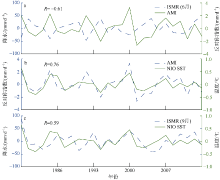
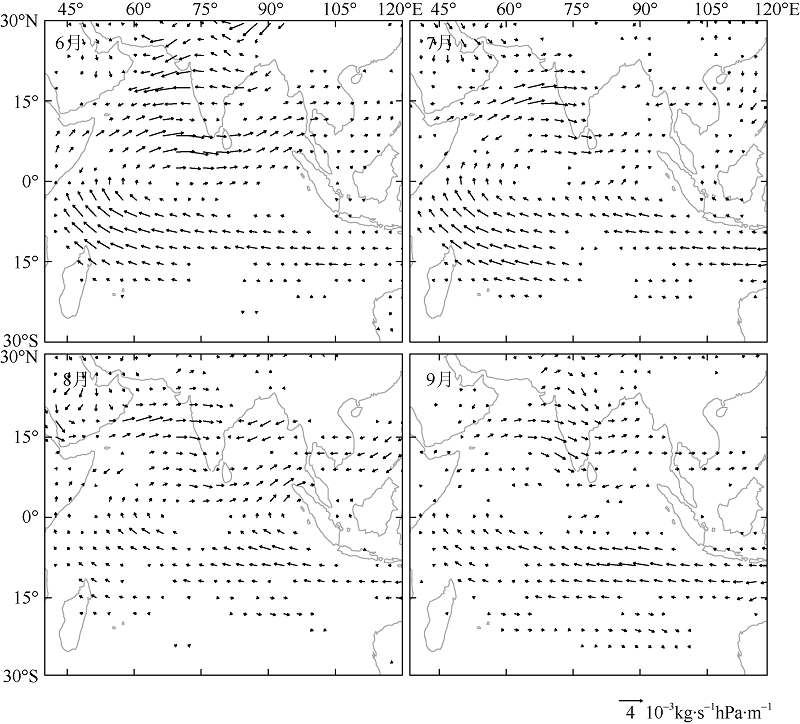
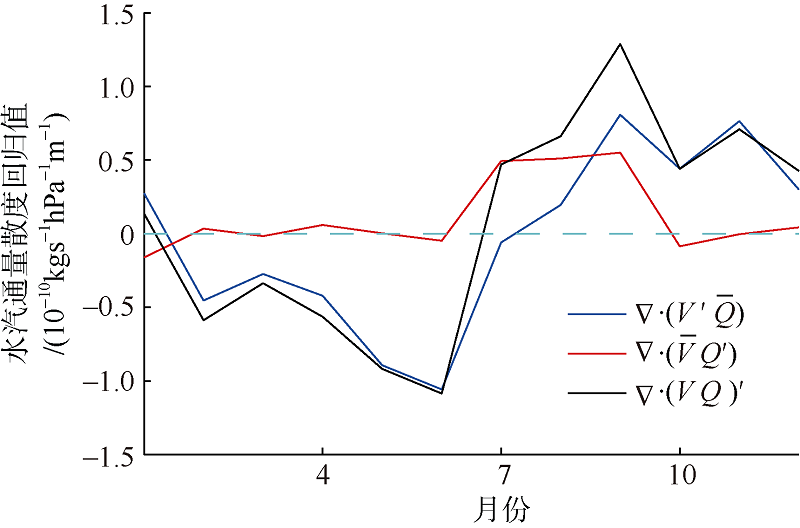
| 1 |
AILIKUN B, YASUNARI T, 2001. ENSO and Asian summer monsoon: persistence and transitivity in the seasonal March[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, 79(1): 145-159.
|
| 2 |
ALEXANDER M A, BLADÉ I, NEWMAN M, et al, 2002. The atmospheric bridge: The influence of ENSO teleconnections on air-sea interaction over the global oceans[J]. Journal of Climate, 15(16): 2205-2231.
|
| 3 |
ANNAMALAI H, LIU PING, XIE SHANGPING, 2005. Southwest Indian Ocean SST variability: Its local effect and remote influence on Asian monsoons[J]. Journal of Climate, 18(20): 4150-4167.
|
| 4 |
BOSCHAT G, TERRAY P, MASSON S, 2011. Interannual relationships between Indian Summer Monsoon and Indo-Pacific coupled modes of variability during recent decades[J]. Climate Dynamics, 37(5): 1019-1043.
|
| 5 |
CHIANG J C H, SOBEL A H, 2002. Tropical tropospheric temperature variations caused by ENSO and their influence on the remote tropical climate[J]. Journal of Climate, 15(18): 2616-2631.
|
| 6 |
DU YAN, XIE SHANGPING, HUANG GANG, et al, 2009. Role of air-sea interaction in the long persistence of El Niño-induced North Indian Ocean warming[J]. Journal of Climate, 22(8): 2023-2038.
|
| 7 |
HE HAIYAN, SUI CHUNG-HSIUNG, JIAN MAOQIU, et al, 2003. The evolution of tropospheric temperature field and its relationship with the onset of Asian summer monsoon[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, 81(5): 1201-1223.
|
| 8 |
HUANG BOHUA, KINTER J L III, 2002. Interannual variability in the tropical Indian Ocean[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 107(C11): 20-1-20-26.
|
| 9 |
IHARA C, KUSHNIR Y, CANE M A, et al, 2007. Indian summer monsoon rainfall and its link with ENSO and Indian Ocean climate indices[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 27(2): 179-187.
|
| 10 |
IZUMO T, MONTÉGUT C B, LUO JINGJIA, et al, 2008. The role of the Western Arabian Sea upwelling in Indian monsoon rainfall variability[J]. Journal of Climate, 21(21): 5603-5623.
|
| 11 |
KAWAMURA R, MATSUURA T, IIZUKA S, 2001. Role of equatorially asymmetric sea surface temperature anomalies in the Indian Ocean in the Asian summer monsoon and El Niño-Southern Oscillation coupling[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 106(D5): 4681-4693.
|
| 12 |
KINTER J L, MIYAKODA K, YANG S, 2002. Recent change in the connection from the Asian monsoon to ENSO[J]. Journal of Climate, 15(10): 1203-1225.
|
| 13 |
KLEIN S A, BRIAN J S, LAU N C, 1999. Remote sea surface temperature variations during ENSO: Evidence for a tropical atmospheric bridge[J]. Journal of Climate, 12(4): 917-932.
|
| 14 |
KOTHAVALE D R, KULKARNI J R, 2015. Performance of August-September Indian monsoon rainfall when June-July rainfall is reported as being in deficit/excess[J]. Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics, 127(2): 147-161.
|
| 15 |
KRISHNAN R, MUJUMDAR M, VAIDYA V, et al, 2003. The abnormal Indian summer monsoon of 2000[J]. Journal of Climate, 16: 1177-1194.
|
| 16 |
KUMAR K K, RAJAGOPALAN B, CANE M A, 1999. On the weakening relationship between the Indian monsoon and ENSO[J]. Science, 284(5423): 2156-2159.
|
| 17 |
LAU N C, NATH M J, 2000. Impact of ENSO on the variability of the Asian-Australian Monsoons as simulated in GCM experiments[J]. Journal of Climate, 13(24): 4287-4309.
|
| 18 |
PARK H S, CHIANG J C H, LINTNER B R, et al, 2010. The delayed effect of major El Niño events on Indian monsoon rainfall[J]. Journal of Climate, 23(4): 932-946.
|
| 19 |
PARTHASARATHY B, MUNOT A A, KOTHAWALE D R, 1994. All-India monthly and seasonal rainfall series: 1871-1993[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 49(4): 217-224.
|
| 20 |
RASMUSSON E M, CARPENTER T H, 1983. The relationship between eastern equatorial Pacific sea surface temperatures and rainfall over India and Sri Lanka[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 111(3): 517-528.
|
| 21 |
SHUKLA J, 2007. Monsoon mysteries[J]. Science, 318(5848): 204-205.
|
| 22 |
SIKKA D R, GADGIAL S, 1980. On the maximum cloud zone and the ITCZ over Indian, longitudes during the southwest monsoon[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 108(11): 1840-1853.
|
| 23 |
SREEJITH O P, PANICKAL S, PAI S, et al, 2015. An Indian Ocean precursor for Indian summer monsoon rainfall variability[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 42(21): 9345-9354.
|
| 24 |
SRIVASTAVA A K, SRIJITH O P, KSHIRSAGAR S R, et al, 2015. Has modulation of Indian summer monsoon rainfall by sea surface temperature of the equatorial Pacific Ocean, weakened in recent years[J]? Climate Dynamics, 45(7/8): 2237-2254.
|
| 25 |
TERRAY P, DELECLUSE P, LABATTU S, et al, 2003. Sea surface temperature associations with the late Indian summer monsoon[J]. Climate Dynamics, 21(7/8): 593-618.
|
| 26 |
VENZKE S, LATIF M, VILLWOCK A, 2000. The coupled GCM ECHO-2. Part Ⅱ: Indian Ocean response to ENSO[J]. Journal of Climate, 13(8): 1371-1383.
|
| 27 |
WANG BIN, WU RENGUANG, LI TIM, 2003. Atmosphere-warm Ocean interaction and its impacts on Asian-Australian monsoon variation[J]. Journal of Climate, 16(8): 1195-1211.
|
| 28 |
WEBSTER P J, YANG SONG, 1992. Monsoon and ENSO: selectively interactive systems[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 118(507): 877-926.
|
| 29 |
WU RENGUANG, BEN P K, KRISHNAMURTHY V, 2008. An asymmetric mode of tropical Indian Ocean rainfall variability in boreal spring[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 113: D05104, doi: 10.1029/2007JD009316.
|
| 30 |
XIE SHANGPING, PHILANDER S G H, 1994. A coupled ocean-atmosphere model of relevance to the ITCZ in the eastern Pacific[J]. Tellus A, 46(4): 340-350.
|
| 31 |
XIE SHANGPING, ANNAMALAI H, SCHOTT F A, et al, 2002. Structure and mechanisms of South Indian Ocean climate variability[J]. Journal of Climate, 15(8): 864-878.
|
| 32 |
XIE SHANGPING, HU KAIMING, HAFNER J, et al, 2009. Indian Ocean capacitor effect on Indo-western Pacific climate during the summer following El Niño[J]. Journal of Climate, 22(3): 730-747.
|
| 33 |
YANG JIANLING, LIU QINYU, XIE SHANGPING, et al, 2007. Impact of the Indian Ocean SST basin mode on the Asian summer monsoon[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 34: L02708.
|
| 34 |
YANG YALI, DU YAN, WU YANLING, et al, 2012. The Interannual Variations of Summer Precipitation in the Northern Indian Ocean Associated with ENSO[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 5(4): 301-305.
|
 ), Xiaotong ZHENG
), Xiaotong ZHENG