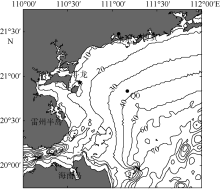
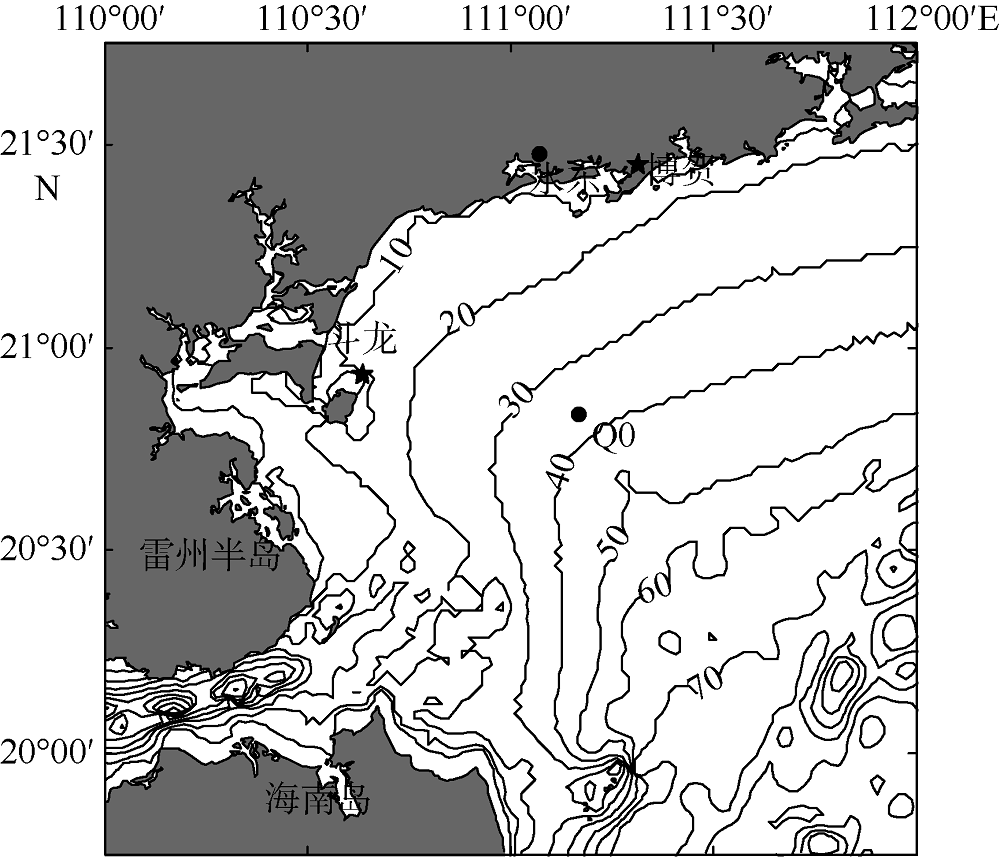
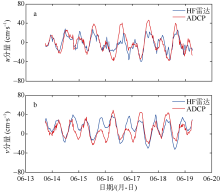
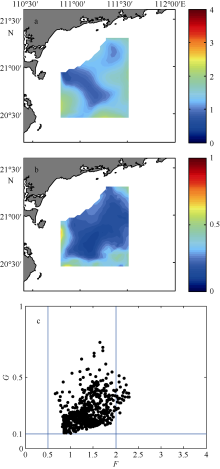
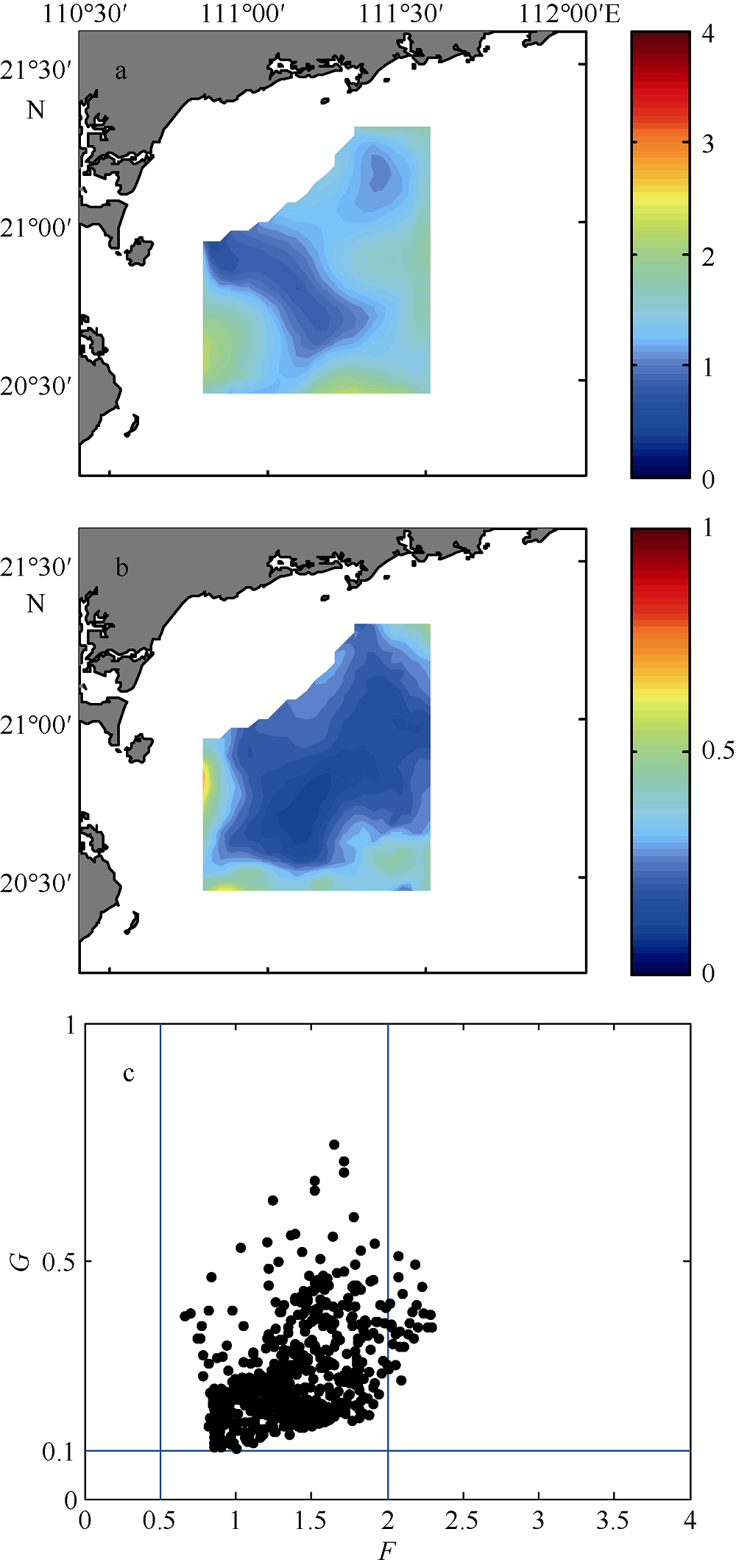
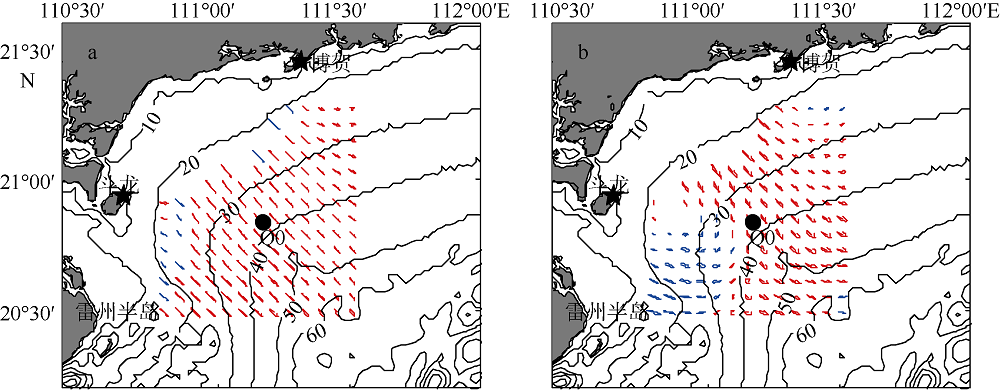
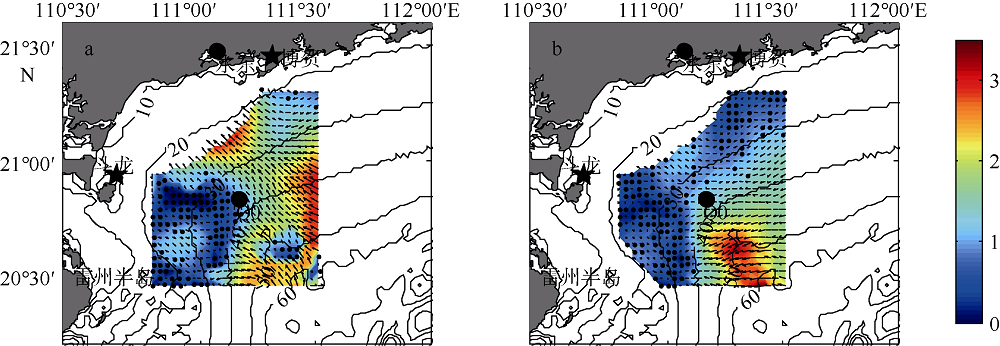
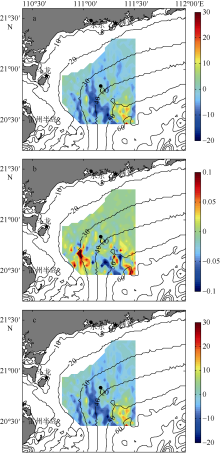
| [1] |
丁文兰, 1986. 南海潮汐和潮流的分布特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 17(6): 468-480.
|
|
DING WENLAN, 1986. Distribution of tides and tidal currents in the South China Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 17(6): 468-480 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
方国洪, 曹德明, 黄企洲, 1994. 南海潮汐潮流的数值模拟[J]. 海洋学报, 16(4): 1-12.
|
|
FANG GUOHONG, CAO DEMING, HUANG QIZHOU, 1994. Numerical simulation of tidal currents in South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 16(4): 1-12 (in Chinese).
|
| [3] |
何洪钜, 1987. 华南沿海潮汐基本特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 6(2): 37-45.
|
|
HE HONGJU, 1987. Tidal characteristics along South China Sea coast[J]. Tropic Oceanography, 6(2): 37-45 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
侯杰昌, 吴世才, 杨子杰, 等, 1997. 海洋表面流的高频雷达遥感[J]. 地球物理学报, 40(1): 18-26.
|
|
HOU JIECHANG, WU SHICAI, YANG ZIJIE, et al, 1997. Remote sensing of ocean surface currents by HF Radar[J]. Acta Geophysica Sinica, 40(1): 18-26 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
李立, 许金电, 靖春生, 等, 2002. 南海海面高度、动力地形和环流的周年变化——TOPEX/Poseidon卫星测高应用研究[J]. 中国科学, 32(12): 978-986.
|
|
LI LI, XU JINDIAN, JING CHUNSHENG, et al, 2003. Annual variation of sea surface height, dynamic topography and circulation in the South China Sea[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 46(2): 127-138.
|
| [6] |
沈育疆, 胡定明, 梅丽明, 等, 1985. 南海潮汐数值计算[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 1985(1): 1-11.
|
|
SHEN YUJIANG, HU DINGMING, MEI LIMING, et al, 1985. Numerical computation of the tides in the South China Sea[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 1985(1): 1-11 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
伍伯瑜, 1990. 珠江口以西陆架海域环流研究Ⅲ[J]. 台湾海峡, 9(2): 118-126.
|
|
WU BOYU, 1990. A Study on the circulation in shelf waters west to Zhujiang River mouth Ⅲ. Shelf circulation model[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 9(2): 118-126 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
吴雄斌, 杨绍麟, 程丰, 等, 2003. 高频地波雷达东海海洋表面矢量流探测试验[J]. 地球物理学报, 46(3): 340-346.
|
|
WU XIONGBIN, YANG SHAOLIN, CHENG FENG, et al, 2003. Ocean surface currents detection at the eastern China Sea by HF surface wave radar[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 46(3): 340-346 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
严金辉, 陈达森, 2005. 粤西水东单点系泊海域潮流和低频流特征[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2005(3): 8-15.
|
|
YAN JINHUI, CHEN DASEN, 2005. The characteristics of low frequency currents in the area of Shuidong anchored floating whelf in the west of Guangdong coastal waters[J]. Transaction of Oceanology and Limnology, 2005(3): 8-15 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
杨士瑛, 鲍献文, 陈长胜, 等, 2003. 夏季粤西沿岸流特征及其产生机制[J]. 海洋学报, 25(6): 1-8.
|
|
YANG SHIYING, BAO XIANWEN, CHEN CHANGSHENG, et al, 2003. Analysis on characteristics and mechanism of current system in west coast of Guangdong Province in the summer[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 25(6): 1-8 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
俞慕耕, 1984. 南海潮汐特征的初步探讨[J]. 海洋学报, 6(3): 15-22.
|
|
YU, MUGENG, 1984. A preliminary study of tidal characteristics in the South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 6(3): 293-300 (in Chinese).
|
| [12] |
章卫胜, 宋志尧, 张金善, 等. 中国近海潮波运动特征分析[C]//第十二届中国海岸工程学术研讨会论文集. 北京: 中国海洋工程学会, 2005.
|
| [13] |
郑有任, 张娟, 吴日升, 2012. 南海北部沿岸海域潮汐的调和分析[J]. 台湾海峡, 31(4): 549-556.
|
|
ZHENG YOUREN, ZHANG JUAN, WU RISHENG, 2012. Tidal analysis along the coast of the northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 31(4): 549-556 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [14] |
中华人民共和国交通部, 1988. 港口工程技术规范(1987) 上卷[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社: 393-399.
|
| [15] |
周浩, 文必洋, 2002. 高频地波雷达生成海洋表面矢量流图[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 33(1): 1-7.
|
|
ZHOU HAO, WEN BIYANG, 2002. Mapping ocean surface vector currents by dual HF ground wave radars[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 33(1): 1-7 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [16] |
朱大勇, 邵浩, 李炎, 等, 2007. OSMAR高频地波雷达福建示范系统径向流数据质量分析[J]. 台湾海峡, 26(1): 7-16.
|
|
ZHU DAYONG, SHAO HAO, LI YAN, et al, 2007. Quality analyses of radial currents measured by a demonstration system of OSMAR HF radar in Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 26(1): 7-16 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [17] |
BARRICK D E, EVANS M W, WEBER B L, 1977. Ocean surface currents mapped by radar[J]. Science, 198(4313): 138-144.
|
| [18] |
CROMBIE D D, 1955. Doppler spectrum of sea echo at 13.56 Mc./s.[J]. Nature, 175(4459): 681-682.
|
| [19] |
FANG GUOHONG, 1986. Tide and tidal current charts for the marginal seas adjacent to China[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 4(1): 1-16.
|
| [20] |
FANG GUOHONG, KWOK Y K, YU KEJUN, et al, 1999. Numerical simulation of principal tidal constituents in the South China Sea, Gulf of Tonkin and Gulf of Thailand[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 19(7): 845-869.
|
| [21] |
LIPA B, BARRICK D, 1983. Least-squares methods for the extraction of surface currents from CODAR crossed-loop data: Application at ARSLOE[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 8(4): 226-253.
|
| [22] |
PAWLOWICZ R, BEARDSLEY B, LENTZ S, 2002. Classical tidal harmonic analysis including error estimates in MATLAB using T_TIDE[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 28(8): 929-937.
|
| [23] |
STEWART R H, JOY J W, 1974. HF radio measurements of surface currents[J]. Deep Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 21(12): 1039-1049.
|
| [24] |
ZU TINGTING, GAN JIANPING, EROFEEVA S Y, 2008. Numerical study of the tide and tidal dynamics in the South China Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 55(2): 137-154.
|
 ), Tingting ZU1(
), Tingting ZU1( ), Jian LI1, Yeqiang SHU1, Ju CHEN1, Dongxiao WANG1
), Jian LI1, Yeqiang SHU1, Ju CHEN1, Dongxiao WANG1