

Journal of Tropical Oceanography >
Influence on the biological community and environmental factors around Qi’ao Island caused by reclamation project
Received date: 2016-06-28
Request revised date: 2016-12-04
Online published: 2017-04-06
Supported by
Guangdong Provincial Oceanic Special Promotion (A201501D08)
Project Management of the Strategic Priority Research Program
Copyright
Land reclamation is an important way to use the ocean. But frequent human activities have a far-reaching influence on local marine ecosystem. Using the Qi’ao Island sea area as the study area, we surveyed the environmental factors and the changes of the biological community before and after reclamation. From the trend of the changes in the environment and the changes of phytoplankton, zooplankton, and the diversity and species of fish before and after reclamation, we investigated the influence on local marine ecosystems caused by the reclamation projects around the southern Qi’ao Island from 2010 to 2014. The results showed that the reclamation has had different degree of negative impact in terms of heavy metal pollution and eutrophication, and reduced the stability of local biological community. The community species has also decreased after the reclamation.
Key words: reclamation; Qi’ao Island; environmental factor; biological community
CUI Lei , LÜ Songhui , DONG Yuelei , GAO Xingchen , LI Li , LIU Fenghua , CEN Jingyi . Influence on the biological community and environmental factors around Qi’ao Island caused by reclamation project[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2017 , 36(2) : 96 -105 . DOI: 10.11978/2016065
Fig. 1 The reclamation project west of Qi’ao Island water area (from google map)图1 淇澳岛水域西侧围填海工程施工区域卫星图(图片来源: 谷歌地图) |
Fig. 2 The sampling stations of Qi’ao Island water area图2 淇澳岛附近水域采样站位示意图 |
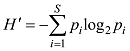
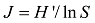
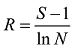
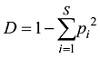
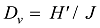
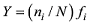
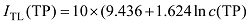
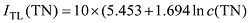
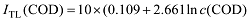

Fig. 3 Temporal distribution of heavy metal concentration at Station QO-2图3 QO-2站位重金属含量时间分布 |
Tab. 1 Results of evaluation of ITL and relationship with the alignment of the nutrition category and ITL表1 综合营养状态指数(ITL)结果及与营养类别的对应关系 |
| 调查时间 | ITL (TP) | ITL (TP) | ITL (COD) | ITL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QO-1 | 2011-11 | 58.40411 | 71.18249 | -1.93814 | 42.54949 |
| 2012-03 | 96.05474 | 59.79778 | 20.59628 | 58.81627 | |
| 2012-08 | 50.7794 | 54.10888 | 31.28259 | 45.39029 | |
| 2012-11 | 53.22108 | 64.71129 | -66.3137 | 17.20623 | |
| 2013-03 | 48.31405 | 72.40241 | — | 60.35823 | |
| 2013-08 | 50.38292 | 65.60242 | 12.75077 | 42.91204 | |
| 2013-11 | 49.28281 | 64.88265 | 16.68652 | 43.61733 | |
| 2015-11 | 44.32174 | 64.68554 | 2.890212 | 37.29916 | |
| 2016-03 | 52.9104 | 66.48724 | 10.12694 | 43.17486 | |
| 平均值 | 55.96347 | 64.87341 | 3.260187 | 43.48043 | |
| QO-2 | 2011-11 | 63.56276 | 67.60041 | 14.67732 | 48.6135 |
| 2012-03 | 97.25298 | 52.53767 | 24.16141 | 57.98402 | |
| 2012-08 | 53.1964 | 53.87984 | 14.91755 | 40.6646 | |
| 2012-11 | 47.1492 | 65.00202 | -76.2621 | 11.96303 | |
| 2013-03 | 45.89144 | 62.35763 | — | 54.12453 | |
| 2013-08 | 22.71624 | 65.643 | 21.08313 | 36.48079 | |
| 2013-11 | 45.28333 | 66.04099 | 14.38253 | 41.90229 | |
| 2015-11 | 57.20921 | 64.936 | 14.89369 | 45.67963 | |
| 2016-03 | 57.40511 | 64.24262 | 7.286138 | 42.97796 | |
| 平均值 | 54.40741 | 62.47113 | 4.392458 | 42.26559 | |
| QO-3 | 2011-11 | — | — | — | — |
| 2012-03 | — | — | — | — | |
| 2012-08 | 49.54345 | 57.75013 | 21.61822 | 42.9706 | |
| 2012-11 | — | — | — | — | |
| 2013-03 | 50.06911 | 73.70313 | — | 61.88612 | |
| 2013-08 | 53.7048 | 65.96416 | 15.51977 | 45.06291 | |
| 2013-11 | 47.08079 | 63.39568 | 6.861464 | 39.11264 | |
| 2015-11 | 47.3766 | 65.01571 | -5.8642 | 35.50937 | |
| 2016-03 | 46.02334 | 62.49294 | 8.921229 | 39.14584 | |
| 平均值 | 48.96635 | 64.72029 | 9.411296 | 43.94791 |
注: “—”表示该月份未采样。 |
Fig. 4 Changes of ITL at different sampling sites图4 各采样点综合营养状态指数(ITL)变化 |
Fig. 5 Results of PCA analysis图5 主成分分析结果 |
Tab. 2 Statistical characteristics of the first four axes of PCA analysis表2 主成分分析(PCA)前4轴的统计特征 |
| 轴1 | 轴2 | 轴3 | 轴4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 特征值 | 0.481 | 0.274 | 0.138 | 0.065 |
| 方差积累百分比/% | 48.1 | 75.5 | 89.3 | 95.8 |
Fig. 6 Temporal variation between diversity index of the positions of QQ-1(a), QQ-2(b) and QQ-3(c) and algae cells density图6 QQ-1站(a)、QQ-2站(b)及QQ-3站(c)的多样性指数与各站位细胞密度的时间变化(d) |
Tab. 3 Diversity index of zooplankton表3 浮游动物多样性指数 |
| 区域 | H | R | J | D | 种类数 | Dv | 总数/(个•L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QO-1 | 1.43 | 0.80 | 0.68 | 0.64 | 8 | 2.07 | 403 |
| QO-2 | 1.73 | 0.95 | 0.78 | 0.76 | 9 | 2.19 | 334 |
| QO-3 | 1.93 | 1.12 | 0.84 | 0.83 | 10 | 2.30 | 261 |
| 平均值 | 1.70 | 0.96 | 0.77 | 0.75 | 9 | 2.20 | 332.6 |
Tab. 4 Species composition of fish in Qi’ao Island表4 淇澳岛鱼类纲、目、科、属和种不同分类阶元组成 |
| 纲 | 目 | 数量(百分比/%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 科 | 属 | 种 | ||
| 软骨鱼纲 | 鳐形目 | 1(2.13) | 1(1.23) | 1(1.04) |
| 硬骨鱼纲 | 鲱形目 | 2(4.26) | 4(4.94) | 6(6.25) |
| 鲤形目 | 2(4.26) | 5(6.17) | 5(5.21) | |
| 鳗鲡目 | 2(4.26) | 3(3.70) | 3(3.13) | |
| 鲇形目 | 2(4.26) | 2(2.47) | 2(2.08) | |
| 颌针鱼目 | 2(4.26) | 2(2.47) | 2(2.08) | |
| 鲻形目 | 2(4.26) | 3(3.70) | 4(4.17) | |
| 鲈形目 | 25(53.19) | 45(55.56) | 57(59.38) | |
| 鲉形目 | 3(6.38) | 6(7.41) | 6(6.25) | |
| 鲀形目 | 2(4.26) | 4(4.94) | 4(4.17) | |
| 鲽形目 | 3(6.38) | 5(6.17) | 5(5.21) | |
| 合鳃鱼目 | 1(2.13) | 1(1.23) | 1(1.04) | |
| 总计 | 47 | 81 | 96 | |
Tab. 5 Diversity index of fish表5 鱼类多样性指数 |
| 区域 | Shannon-Wiener 指数 | Pielou 指数 | 种类丰富度指数 | 种类总数 | 个体总数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QO-1 | 3.6009 | 0.9143 | 8.8908 | 55 | 591 |
| QO-2 | 2.9817 | 0.8234 | 6.6373 | 32 | 248 |
| QO-3 | 2.9800 | 0.8848 | 5.7782 | 38 | 342 |
| 平均值 | 3.1875 | 0.8742 | 7.1021 | 96 | 1181 |
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
国家环境保护总局, 1997. GB 3097-1997 中华人民共和国海水水质标准[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社.
|
| 7 |
国家环境保护总局, 2002. GB 3838-2002 地表水环境质量标准[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社.
|
| 8 |
国家海洋局, 2008. GB 17378-2007 海洋监测规范[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社.
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
WEI, 2014. Fish community diversity in Haizhou Bay and its relationship with environmental factors[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 1-115 (in Chinese).
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
|
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |