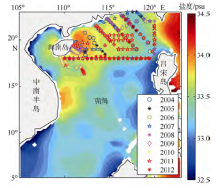
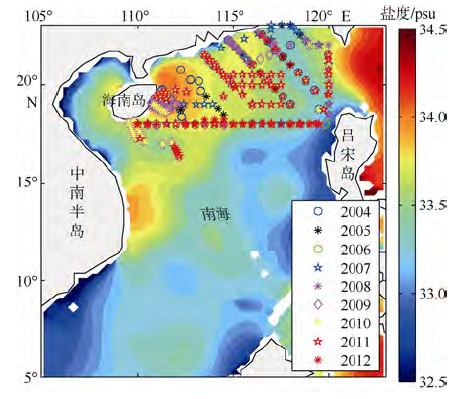
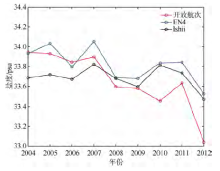
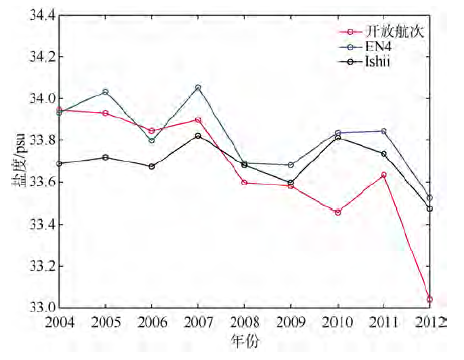
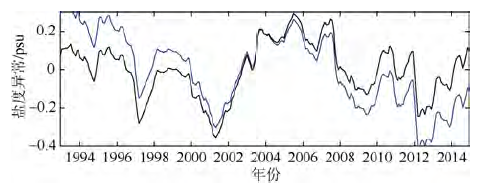
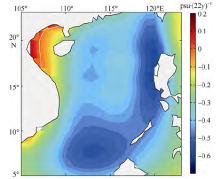
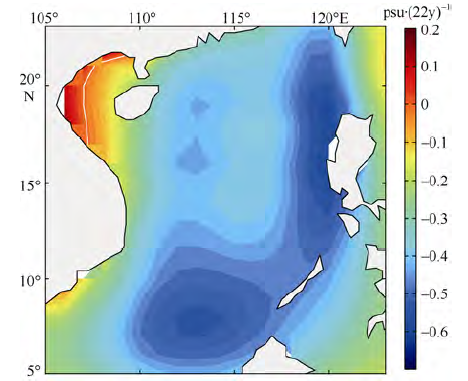
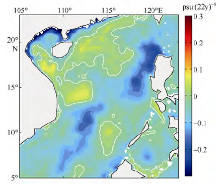
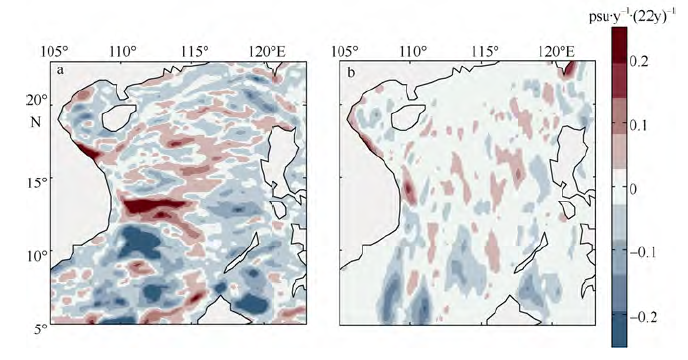
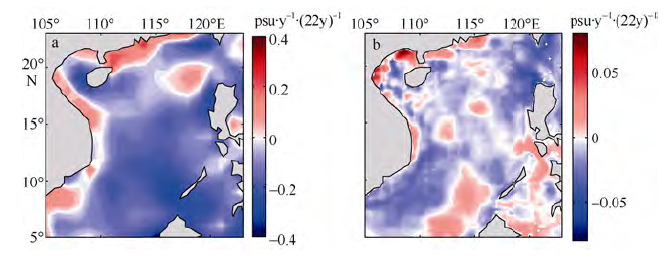
| [1] |
郭敬, 陈显尧, 张远凌, 2013. 影响南海混合层盐度季节变化的因素分析[J]. 海洋科学进展, 31(2): 180-187.
|
|
GUO JING, CHEN XIANYAO, ZHANG YUANLING, 2013. Factors influencing the seasonal variations of mixed layer salinity in the South China Sea[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 31(2): 180-187 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
王静, 赵飞达, 齐义泉, 2015. 夏末秋初南海18°N断面混合层结构特征分析[J]. 海洋通报, 34(1): 52-58.
|
|
WANG JING, ZHAO FEIDA, QI YIQUAN, 2015. Characteristics of mixed layer cross section 18°N in the South China Sea during late summer and early autumn[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 34(1): 52-58 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
李磊, 李凤岐, 苏洁, 许建平, 2002. 1998年南海夏冬季南海水团分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 33(4): 393-401.
|
|
LI LEI, LI FENGQI, SU JIE, XU JIANPING, 2002. Analysis on water masses in the South China Sea in summer and winter of 1998[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 33(4): 393-401(in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
DELCROIX T, HÉNIN C, 1991. Seasonal and interannual variations of sea surface salinity in the tropical Pacific Ocean[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 96(C12): 22135-22150.
|
| [5] |
DU YAN, ZHANG YUHONG, FENG MING, et al, 2015. Decadal trends of the upper ocean salinity in the tropical Indo-Pacific since mid-1990s[J]. Scientific Reports, 5: 16050.
|
| [6] |
GOOD S A, MARTIN M J, RAYNER N A, 2013. EN4: quality controlled ocean temperature and salinity profiles and monthly objective analyses with uncertainty estimates[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 118(12): 6704-6716.
|
| [7] |
HELD I M, SODEN B J, 2006. Robust responses of the hydrological cycle to global warming[J]. Journal of Climate, 19(12): 5686-5699.
|
| [8] |
IPCC, 2007. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis[M]. Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA: Cambridge University Press: 1-996.
|
| [9] |
ISHII M, KIMOTO M, SAKAMOTO K, et al, 2006. Steric sea level changes estimated from historical ocean subsurface temperature and salinity analyses[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 62(2): 155-170.
|
| [10] |
KATSURA S, OKA E, QIU BO, et al, 2013. Formation and subduction of North Pacific tropical water and their interannual variability[J]. Journal Physical Oceanography, 43(11): 2400-2415.
|
| [11] |
KHALED H H, 2008. Trend detection in hydrologic data: The Mann-Kendall trend test under the scaling hypothesis[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 349(3-4): 350-363.
|
| [12] |
LAGERLOEF G S E, 2002. Introduction to the special section: The role of surface salinity on upper ocean dynamics, air-sea interaction and climate[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 107(C12): 8000.
|
| [13] |
NAN FENG, XUE HUIJIE, CHAI FEI, et al, 2013. Weakening of the Kuroshio Intrusion into the South China Sea over the past two decades[J]. Journal of Climate, 26(20): 8097-8110.
|
| [14] |
QU TANGDONG, DU YAN, SASAKI H, 2006. South China Sea throughflow: A heat and freshwater conveyor[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 33(23): L23617.
|
| [15] |
REN LI, RISER S C, 2009. Seasonal salt budget in the northeast Pacific Ocean[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 114(12): C12004.
|
| [16] |
REN LI, RISER S C, 2010. Observations of decadal time scale salinity changes in the subtropical thermocline of the North Pacific Ocean[J]. Deep Sea Research, Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 57(13-14): 1161-1170.
|
| [17] |
WILLIAMS P D, GUILYARDI E, SUTTON R, et al, 2007. A new feedback on climate change from the hydrological cycle[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 34(8): L08706.
|
| [18] |
XU HAIMING, XIE SHANG-PING, WANG YUQING, et al, 2008. Orographic effects on South China Sea summer climate[J]. Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics, 100(1-4): 275-289.
|
| [19] |
YANG JIAYAN, LIN XIAOPEI, WU DEXING, 2012. On the dynamics of the seasonal variation in the South China Sea throughflow transport[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Ocean, 118: 6854-6866.
|
| [20] |
YAN YUNWEI, WANG GUIHUA, WANG CHUNZAI, et al, 2015. Low-salinity water off West Luzon Island in summer[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Ocean, 120(4): 3011-3021.
|
| [21] |
ZENG LILI, LIU T W, XUE HUIJIE, et al, 2014. Freshening in the South China Sea during 2012 revealed by Aquarius and in situ data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 119(12): 8296-8314.
|
 ), 程旭华1(
), 程旭华1( ), 张玉红1, 严幼芳1, 杜岩1
), 张玉红1, 严幼芳1, 杜岩1
 ), Xuhua CHENG1(
), Xuhua CHENG1( ), Yuhong ZHANG1, Youfang YAN1, Yan DU1
), Yuhong ZHANG1, Youfang YAN1, Yan DU1