热带海洋学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (1): 168-181.doi: 10.11978/2022043CSTR: 32234.14.2022043
南海北部水团及中尺度现象对营养盐时空分布的影响*
张金尚1,2,3( ), 邹定辉1, 马玉2,3(
), 邹定辉1, 马玉2,3( ), 李锐祥2,3, 刘愉强2,3, 孟强2,3, 刘同木2,3, 史华明2,3
), 李锐祥2,3, 刘愉强2,3, 孟强2,3, 刘同木2,3, 史华明2,3
- 1.华南理工大学环境与能源学院, 广东 广州 510006
2.国家海洋局南海调查技术中心, 广东 广州 510300
3.自然资源部海洋环境探测技术与应用重点实验室, 广东 广州 510300
-
收稿日期:2022-03-03修回日期:2022-05-04出版日期:2023-01-10发布日期:2022-05-05 -
通讯作者:马玉。email:362005949@qq.com -
作者简介:张金尚(1994—), 男, 河北省邢台市人, 硕士研究生, 从事海洋生物地球化学过程研究。email: zhangjinshang@smst.gz.cn*感谢航次观测期间“海测3301”船和“向阳红14”船全体科考队员和船员付出的辛苦努力; 感谢自然资源部杭州全球海洋Argo 系统野外科学观测研究站卢少磊工程师提供的Argo 浮标数据; 论文撰写得到了国家海洋局南海调查技术中心苏锡宝、王研等同事的答疑解惑, 一并谢忱! -
基金资助:自然资源部南海局科技发展基金(202205); 广东省海洋经济发展(海洋六大产业)专项资金项目(粤自然资合[2021]038 号); 广东省海洋经济发展(海洋六大产业)专项资金项目(自然资合[2020]025 号); 南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(珠海)项目(SML2021SP203); 广东省重点领域研发计划项目(2020B1111020003)
Effects of water mass and mesoscale phenomenon on the spatiotemporal distributions of nutrients in the northern South China Sea*
ZHANG Jinshang1,2,3( ), ZOU Dinghui1, MA Yu2,3(
), ZOU Dinghui1, MA Yu2,3( ), LI Ruixiang2,3, LIU Yuqiang2,3, MENG Qiang2,3, LIU Tongmu2,3, SHI Huaming2,3
), LI Ruixiang2,3, LIU Yuqiang2,3, MENG Qiang2,3, LIU Tongmu2,3, SHI Huaming2,3
- 1. School of Environment and Energy, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510006, China
2. South China Sea Marine Survey and Technology Center, State Oceanic Administration, Guangzhou 510300, China
3. Key Laboratory of Marine Environmental Survey Technology and Application, Ministry of Natural Resources, Guangzhou 510300, China
-
Received:2022-03-03Revised:2022-05-04Online:2023-01-10Published:2022-05-05 -
Contact:MA Yu. email:362005949@qq.com -
Supported by:The Sea Science&Technology Foundation of South China Sea Branch, Ministry of Natural Resources(202205); Special Fund for Marine Economic Development (Six Major Marine Industries) of Guangdong Province(GDNRC[2021]038); Special Fund for Marine Economic Development (Six Major Marine Industries) of Guangdong Province(GDNRC[2020]025); Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Zhuhai)(SML2021SP203); Key-Area Research and Development Project of Guangdong Province(2020B1111020003)
摘要:
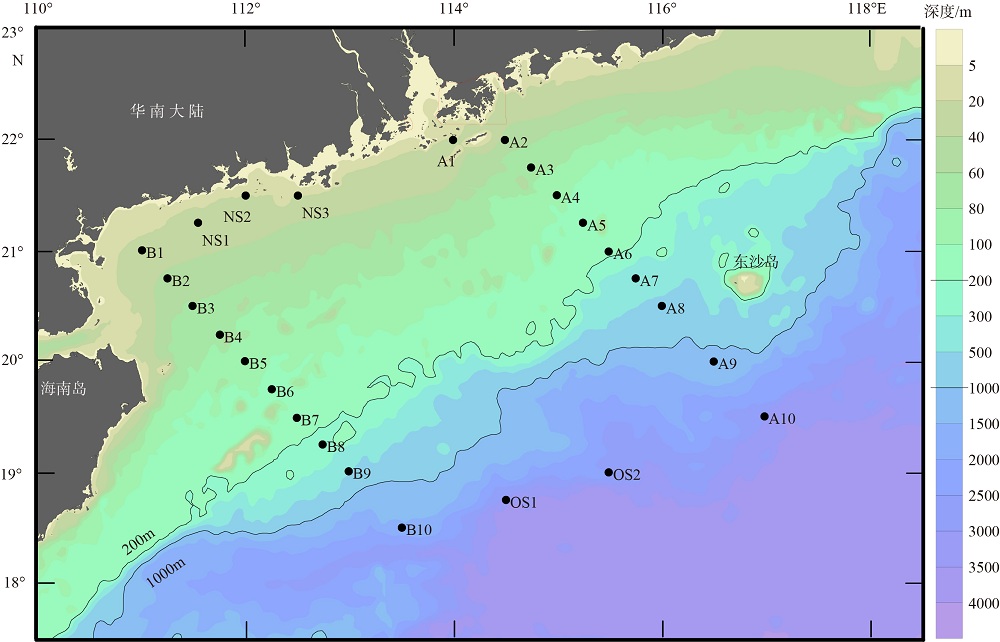
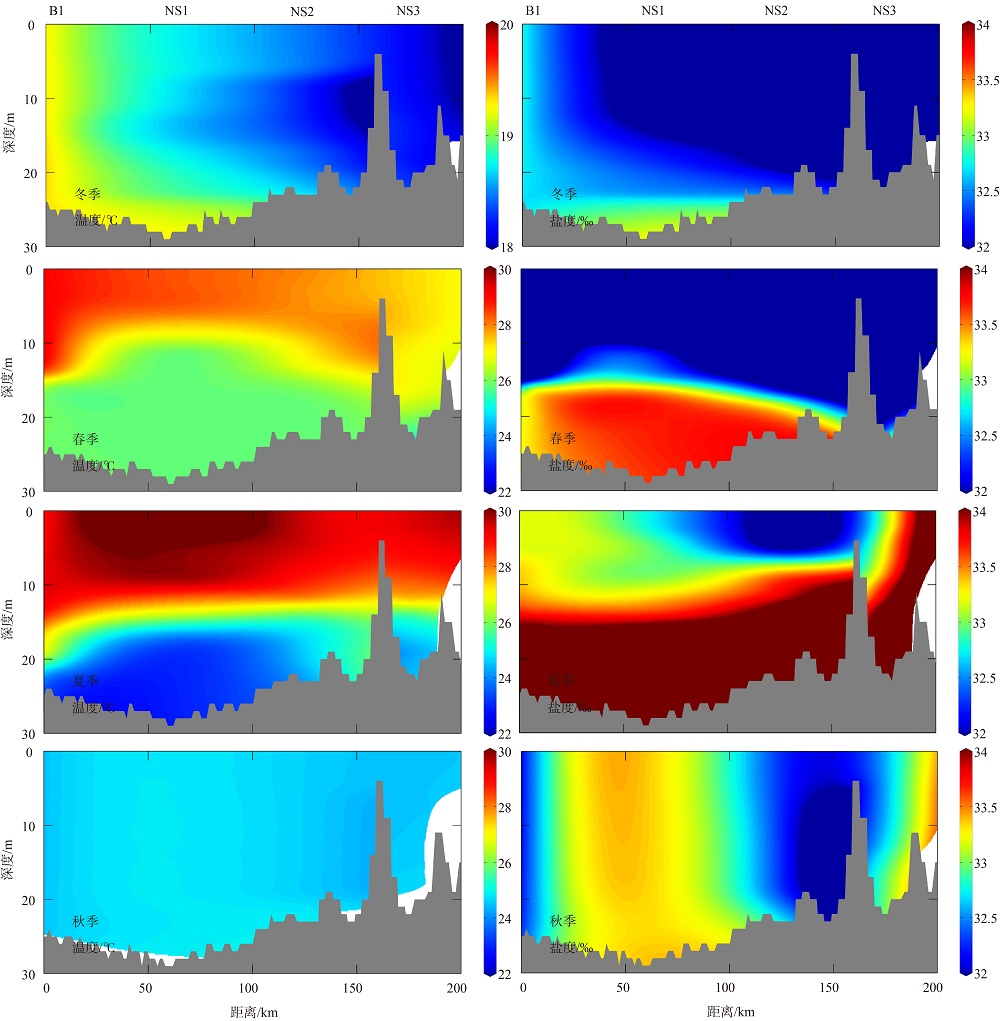
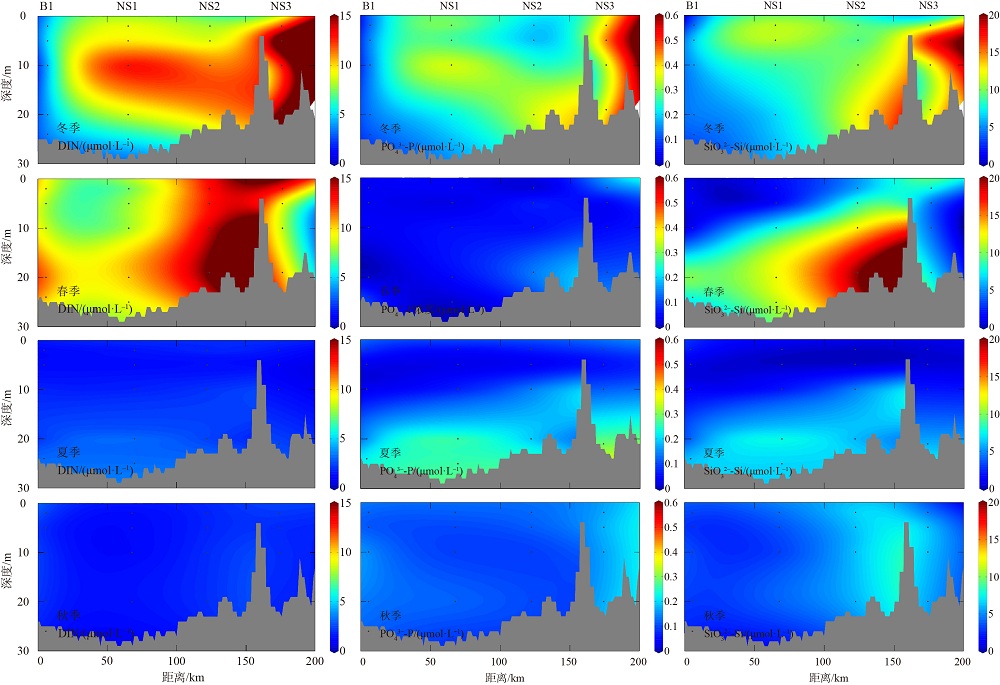
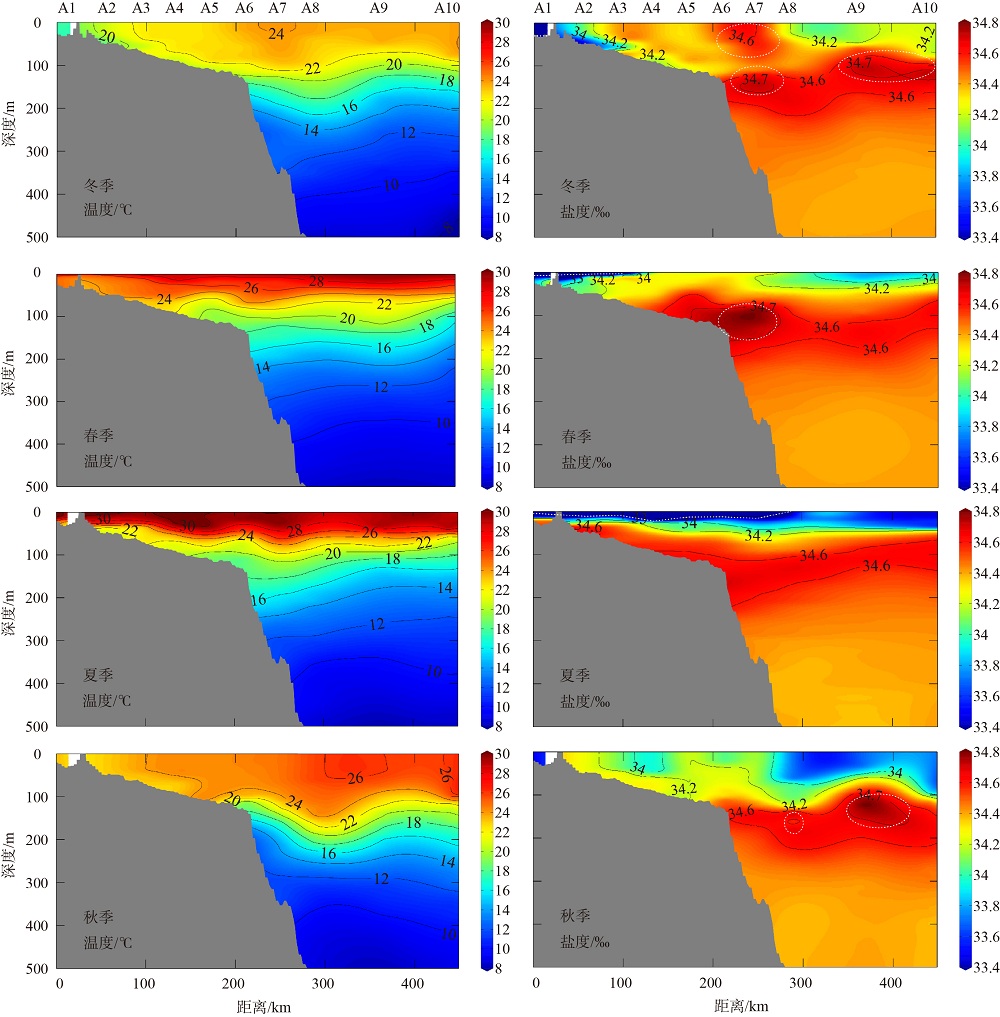
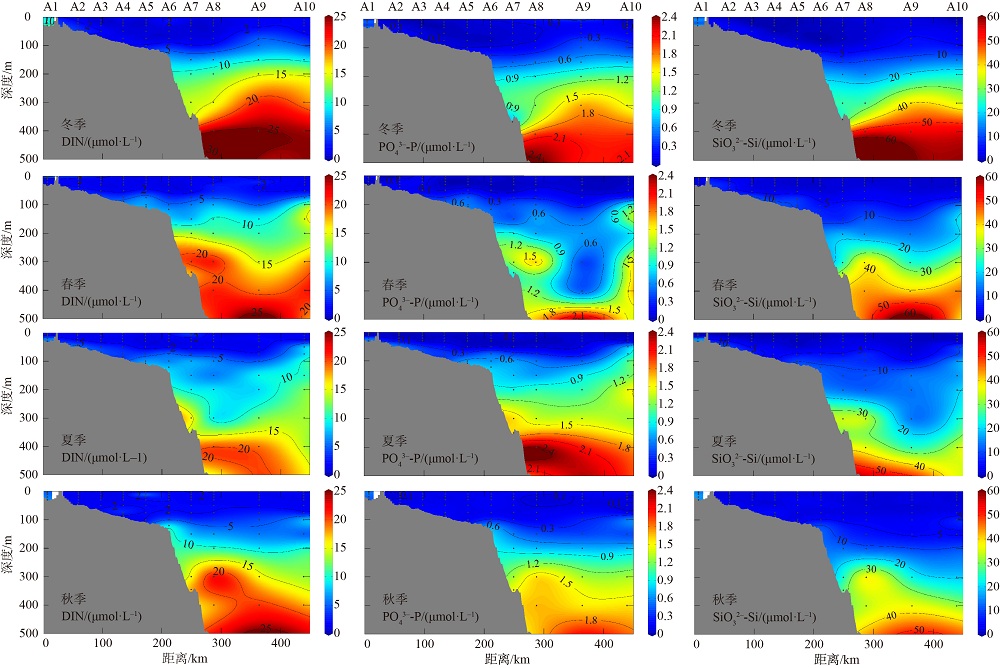
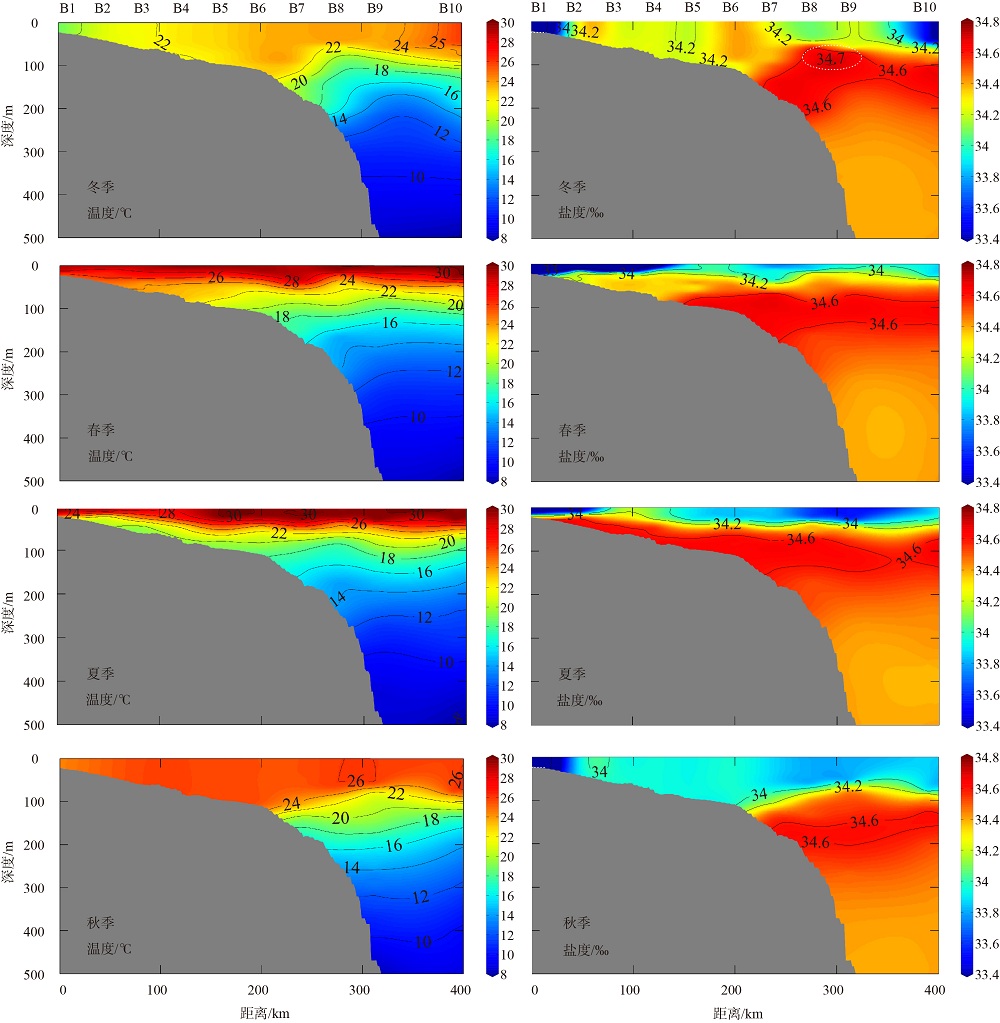
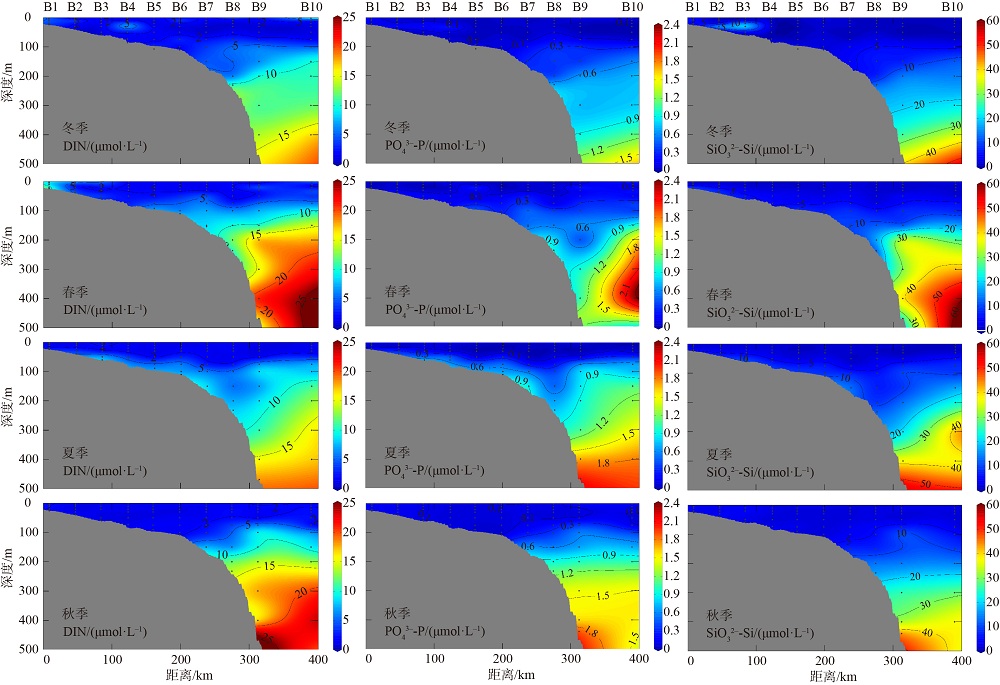
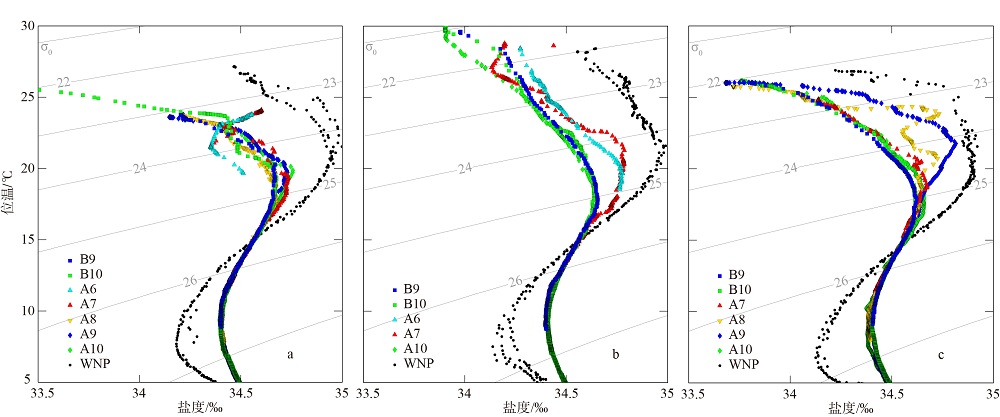
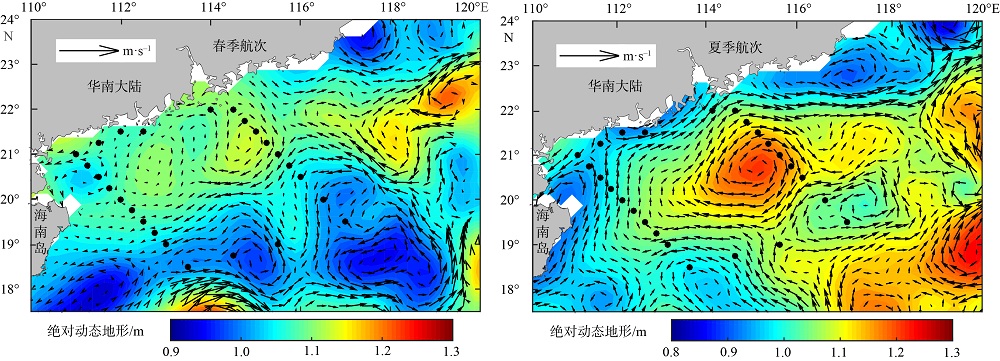
2019年在南海北部开展了4个季节的现场调查, 获取了调查海域海水温度、盐度和营养盐等环境要素的实测数据。珠江口西侧近岸海域营养盐表现出明显的季节性和区域特征, 除秋季为潜在的氮限制外, 冬、春、夏季均表现为磷限制, 且春季最为显著, 主要受冲淡水输入和陆架水入侵影响。受西南季风强弱和调查海域海底地形差异的影响, 春、夏季珠江口外跨陆架断面(A断面)上升流强度大于海南岛以东跨陆架断面(B断面), 且夏季营养盐浓度等值线的爬升高度和范围大于春季。黑潮水入侵稀释了陆架坡折处以外海域的营养盐浓度, 冬季75~150m深水体的营养盐浓度相比夏季降低了25%以上; El Niño期间黑潮水入侵增强, 春、秋季A断面的东沙群岛附近海域75~150m深水体的营养盐浓度比相邻站位均低20%以上。春季冷涡中心无机氮(dissolved inorganic nitrogen, DIN)、磷酸盐(PO43--P)和硅酸盐(SiO32--Si)相较于边缘区域分别升高了6.42μmol·L-1、0.71μmol·L-1和10.03μmol·L-1, 夏季上升流和中尺度涡共同作用造成了A断面营养盐的凹型结构。综上所述, 南海北部海域营养盐浓度主要受冲淡水、上升流、黑潮入侵、中尺度涡旋等因素的独立或耦合作用, 呈现复杂多变的时空分布。
引用本文
张金尚, 邹定辉, 马玉, 李锐祥, 刘愉强, 孟强, 刘同木, 史华明. 南海北部水团及中尺度现象对营养盐时空分布的影响*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(1): 168-181.
ZHANG Jinshang, ZOU Dinghui, MA Yu, LI Ruixiang, LIU Yuqiang, MENG Qiang, LIU Tongmu, SHI Huaming. Effects of water mass and mesoscale phenomenon on the spatiotemporal distributions of nutrients in the northern South China Sea*[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(1): 168-181.
表1
2019年近岸断面温度、盐度和营养盐浓度的变化范围及平均值"
| 参数 | 温度/℃ | 盐度/‰ | DIN浓度/(μmol·L-1) | PO43--P浓度/(μmol·L-1) | SiO32--Si浓度/(μmol·L-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冬季 | 变化范围 | 18.14~19.31 | 30.57~32.90 | 3.75~17.28 | 0.11~0.46 | 3.98~18.03 |
| 平均值±S.D. | 18.68±0.42 | 31.72±0.80 | 9.13±4.06 | 0.25±0.11 | 9.05±3.62 | |
| 春季 | 变化范围 | 25.78~29.0 | 28.13~33.70 | 7.12~15.65 | 0.01~0.14 | 1.02~20.09 |
| 平均值±S.D. | 27.16±1.08 | 30.94±1.72 | 10.44±2.49 | 0.06±0.04 | 7.04±5.11 | |
| 夏季 | 变化范围 | 23.04~30.67 | 31.74~34.54 | 0.98~3.85 | 0.03~0.34 | 0.24~9.79 |
| 平均值±S.D. | 27.35±2.46 | 33.61±0.77 | 1.97±0.82 | 0.12±0.10 | 2.94±2.94 | |
| 秋季 | 变化范围 | 24.53~24.89 | 32.27~33.37 | 1.20~2.45 | 0.09~0.18 | 2.43~6.75 |
| 平均值±S.D. | 24.67±0.12 | 32.75±0.40 | 1.81±0.38 | 0.13±0.03 | 4.51±1.55 | |
表2
2019年A断面温度、盐度和营养盐浓度的变化范围及平均值"
| 参数 | 温度/℃ | 盐度/‰ | DIN浓度/(μmol·L-1) | PO43--P浓度/(μmol·L-1) | SiO32--Si浓度/(μmol·L-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冬季 | 变化范围 | 7.71~24.09 | 31.75~34.76 | 0.42~31.45 | 0.02~2.49 | 0.05~76.16 |
| 平均值±S.D. | 16.58±5.49 | 34.41±0.33 | 5.61±7.40 | 0.41±0.59 | 9.66±16.41 | |
| 春季 | 变化范围 | 8.24~29.54 | 23.67~34.79 | 1.02~27.17 | 0.01~2.46 | 1.09~67.55 |
| 平均值±S.D. | 16.90±6.52 | 34.40±0.49 | 5.75±6.52 | 0.35±0.48 | 9.10±13.07 | |
| 夏季 | 变化范围 | 7.99~30.58 | 31.68~34.68 | 1.01~20.33 | 0.03~2.45 | 0.11~57.19 |
| 平均值±S.D. | 17.26±7.12 | 34.31±0.45 | 5.06±4.98 | 0.49±0.61 | 8.45±11.62 | |
| 秋季 | 变化范围 | 8.23~26.14 | 33.53~34.82 | 1.05~26.19 | 0.04~2.11 | 1.61~52.52 |
| 平均值±S.D. | 17.87±6.35 | 34.32±0.27 | 5.11±6.13 | 0.40±0.50 | 8.18±11.37 | |
表3
2019年B断面温度、盐度和营养盐浓度的变化范围及平均值"
| 参数 | 温度/℃ | 盐度/‰ | DIN浓度/(μmol·L-1) | PO43--P浓度/(μmol·L-1) | SiO32--Si浓度/(μmol·L-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冬季 | 变化范围 | 7.96~25.59 | 32.64~34.69 | 0.36~19.39 | 0.02~1.62 | 0.05~51.97 |
| 平均值±S.D. | 17.65±5.53 | 34.36±0.30 | 3.67±3.87 | 0.19±0.28 | 5.05±8.65 | |
| 春季 | 变化范围 | 8.04~30.06 | 30.09~34.68 | 1.34~26.72 | 0.01~2.31 | 0.82~63.03 |
| 平均值±S.D. | 18.12±6.79 | 34.33±0.51 | 6.05±5.83 | 0.30±0.43 | 7.72±12.03 | |
| 夏季 | 变化范围 | 7.90~30.07 | 33.14~34.65 | 1.00~19.8 | 0.01~2.05 | 0.52~51.44 |
| 平均值±S.D. | 17.96±7.02 | 34.38±0.28 | 4.43±4.43 | 0.38±0.49 | 7.11±10.75 | |
| 秋季 | 变化范围 | 8.87~26.01 | 32.54~34.62 | 0.83~24.00 | 0.05~1.92 | 1.59~44.39 |
| 平均值±S.D. | 19.57±6.15 | 34.23±0.35 | 4.21±5.67 | 0.31±0.44 | 6.13±8.97 | |
表4
2019年近岸海域N:P、Si:P和Si:N的变化范围及平均值"
| 季节 | N:P | Si:P | Si:N | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 变化范围 | 平均值±S.D. | 变化范围 | 平均值±S.D. | 变化范围 | 平均值±S.D. | |
| 冬季 | 29.3~47.9 | 36.1±5.4 | 24.1~49.7 | 35.8±6.0 | 0.7~1.3 | 1.0±0.2 |
| 春季 | 94.0~1324.6 | 348.3±374.4 | 30.0~1033.0 | 233.3±330.3 | 0.1~1.3 | 0.6±0.4 |
| 夏季 | 8.5~47.8 | 23.9±14.1 | 3.2~41.3 | 20.6±10.9 | 0.1~2.6 | 1.3±0.9 |
| 秋季 | 10.6~21.8 | 14.4±3.3 | 20.1~67.6 | 35.9±13.6 | 1.4~3.6 | 2.5±0.8 |
| [1] |
陈法锦, 陈淳青, 周凤霞, 等, 2017. 秋季珠江口外海海域的生态环境特征[J]. 海洋环境科学, 36(6): 844-852.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
冯士筰, 李凤岐, 李少菁, 1999. 海洋科学导论[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
高姗, 2011. 南海低营养级生态要素时空分布特征及模型研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
韩爱琴, 2012. 南海北部陆架营养盐生物地球化学循环及其与物理过程的耦合研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学. (in Chinese)
|
| [5] |
黄亚楠, 陈法锦, 赵辉, 等, 2015. 2012年冬季南海西北部营养盐浓度分布及结构特征[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 34(3): 310-316.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
柯志新, 黄良民, 谭烨辉, 等, 2013. 2008年夏末南海北部叶绿素a的空间分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 32(4): 51-57.
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2013.04.008 |
|
|
|
| [7] |
冷晓云, 杨阳, 孙军, 等, 2016. 夏季南海西部中尺度物理过程对营养盐和叶绿素a分布特征的影响[J]. 海洋学报, 38(4): 66-75.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
李伯志, 2018. 中国近海营养盐季节和年际变化特征分析[D]. 天津: 天津科技大学.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
李登辉, 2017. 南海北部陆坡区水团分析[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
廖秀丽, 戴明, 巩秀玉, 等, 2018. 南海南部次表层叶绿素a质量浓度最大值及其影响因子[J]. 热带海洋学报, 37(1): 45-56.
doi: 10.11978/2017020 |
|
|
|
| [11] |
林宏阳, 胡建宇, 郑全安, 2012. 吕宋海峡附近中尺度涡特征的统计分析[J]. 海洋学报, 34(1): 1-7.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
彭欣, 宁修仁, 孙军, 等, 2006. 南海北部浮游植物生长对营养盐的响应[J]. 生态学报, 26(12): 3959-3968.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
石晓勇, 李鸿妹, 韩秀荣, 等, 2014. 夏季南海北部典型中尺度物理过程对营养盐及溶解氧分布特征的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 34(3): 695-703.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
苏锡宝, 2019. 南海海盆溶解氧和碳酸盐系统的空间分布及主要调控机制[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
吴敏兰, 2014. 北部湾北部海域营养盐的分布特征及其对生态系统的影响研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
吴日升, 李立, 2003. 南海上升流研究概述[J]. 台湾海峡, 22(2): 269-277.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
许东禹, 刘锡清, 张训华, 等, 1997. 中国近海地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
许金电, 蔡尚湛, 宣莉莉, 等, 2013. 2006年夏季琼东、粤西沿岸上升流研究[J]. 海洋学报, 35(4): 11-18.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
徐文龙, 王桂芬, 周雯, 等, 2018. 南海东北部夏季叶绿素a浓度垂向变化特征及其对水动力过程的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 37(5): 62-73.
doi: 10.11978/2017121 |
|
|
|
| [20] |
许艳苹, 2009. 南海西部冷涡区域上层海洋营养盐的动力学[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
杨阳, 李锐祥, 朱鹏利, 等, 2014. 珠江冲淡水季节变化及动力成因[J]. 海洋通报, 33(1): 36-44.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
尹宜舟, 李多, 孙劭, 等, 2020. 2019年全球重大天气气候事件及其成因[J]. 气象, 46(4): 538-546.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
袁梁英, 2005. 南海北部营养盐结构特征[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
郑璟, 庞古乾, 杜尧东, 等, 2019. 2019年3—4月广东省天气气候特点及其影响评述[J]. 广东气象, 41(3): 封2, 封3 (in Chinese). (in Chinese)
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.1111/j.0022-3646.1985.00347.x |
| [26] |
pmid: 22457971 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1016/0278-4343(92)90065-R |
| [28] |
doi: 10.5194/bg-10-6419-2013 |
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
doi: 10.1002/rog.v54.3 |
| [32] |
doi: 10.1016/S0272-7714(05)80014-9 |
| [33] |
doi: 10.1007/s00376-011-0068-x |
| [34] |
doi: 10.1007/s10236-011-0426-3 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2014.05.012 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.3354/meps062283 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2004)017<3644:CLSTPA>2.0.CO;2 |
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ocemod.2011.01.002 |
| [40] |
doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9152-y |
| [41] |
doi: 10.1002/2013JC009172 |
| [42] |
doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2008.05.007 |
| [43] |
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2004.06.015 |
| [1] | 柳原, 柯志新, 李开枝, 谭烨辉, 梁竣策, 周伟华. 人类活动和沿岸流影响下的粤东近海浮游动物群落特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [2] | 江绿苗, 陈天然, 赵宽, 张婷, 许莉佳. 南海北部涠洲岛边缘珊瑚礁的生物侵蚀实验研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 155-165. |
| [3] | 许莉佳, 廖芝衡, 陈辉, 王永智, 黄柏强, 林巧云, 甘健锋, 杨静. 南海北部珊瑚群落结构特征及其对海洋热浪事件的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 58-71. |
| [4] | 赵明辉, 袁野, 张佳政, 张翠梅, 高金尉, 王强, 孙珍, 程锦辉. 南海北部被动陆缘洋陆转换带张裂-破裂研究新进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 173-183. |
| [5] | 杨一凯, 曾丽丽. 挟带黑潮高盐水的中尺度涡在南海北部的时空特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 75-85. |
| [6] | 周月月, 王友绍. 广东沿海红树林区水质变化特征与富营养状态评估[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(6): 1-11. |
| [7] | 吴伟志, 赵志霞, 杨升, 梁立成, 陈秋夏, 卢翔, 刘星, 张小伟. 浙江省红树林分布和造林成效分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(6): 67-74. |
| [8] | 曾毅港, 经志友, 黄小龙, 郑瑞玺. 夏季南海北部粤东陆架锋面的动力特征分析*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(4): 136-145. |
| [9] | 李傲, 冯洋, 王云涛, 薛惠洁. 基于OC-CCI数据的南海高叶绿素a浓度水域面积的时空变化研究*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(2): 77-89. |
| [10] | 马梦真, 李芊, 吴正超, 陈寅超, 俞建成. 南海北部最小含氧带水下滑翔机观测结果初步分析*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(1): 131-142. |
| [11] | 何子康, 王喜冬, 陈志强, 范开桂. 利用海洋温度剖面与海表盐度反演盐度剖面方法研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(6): 41-51. |
| [12] | 王仁政, 单正垛, 孟思雨, 宫响. 南海北部次表层叶绿素最大值年际变化特征分析*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(6): 63-75. |
| [13] | 王剑, 陈楚群, 周伟华, 李祥付, 吴颉, 叶海彬, 唐世林. 利用遥感技术估算南海北部表层异养细菌丰度*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(5): 53-62. |
| [14] | 苏晓康, 赵明辉, 李子正, 袁野, 王星月, 程锦辉, 张佳政. 南海北部陆缘OBS2018-H2测线地壳结构初步结果*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(5): 111-122. |
| [15] | 王丽芳, 黄韬, 杜川军, 郭香会. 不同海水营养盐现场连续观测系统的比较研究*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(3): 103-113. |
|
||