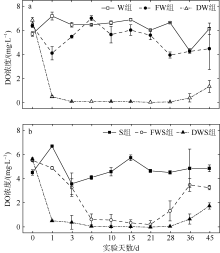
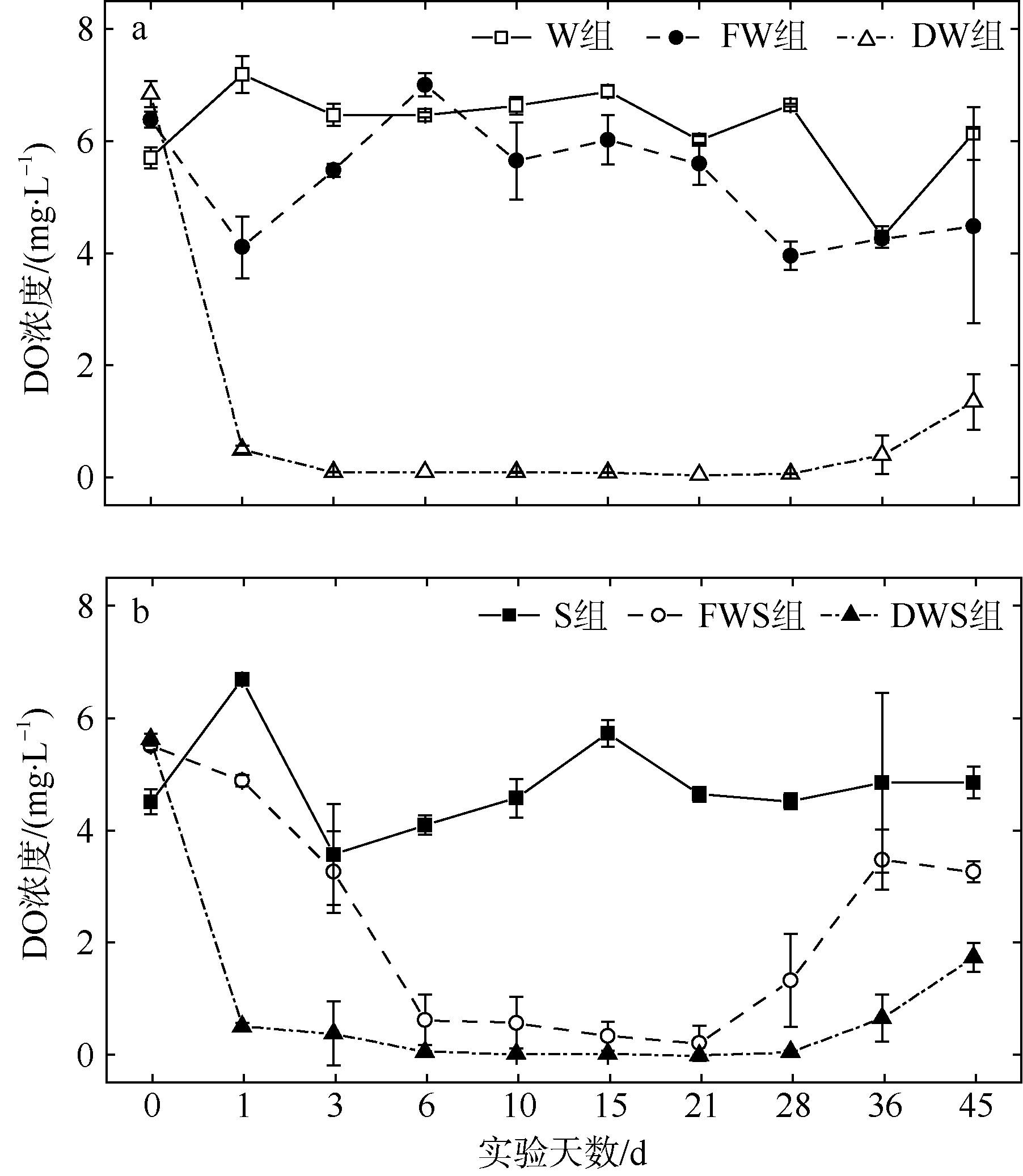
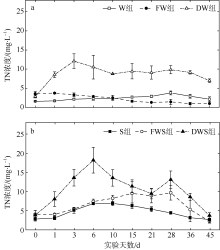
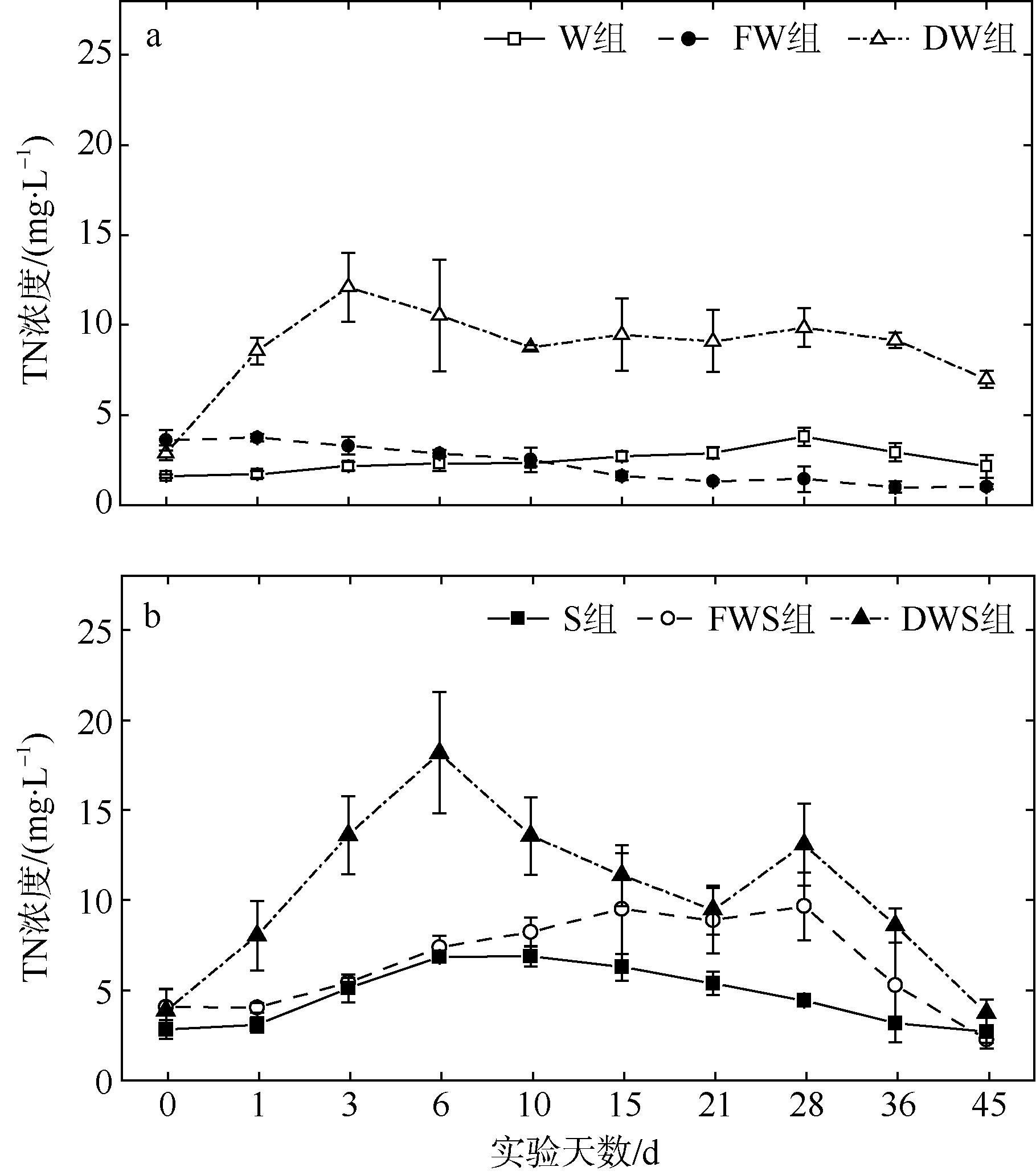
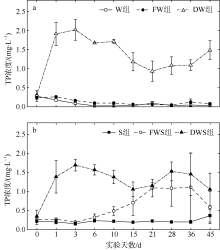
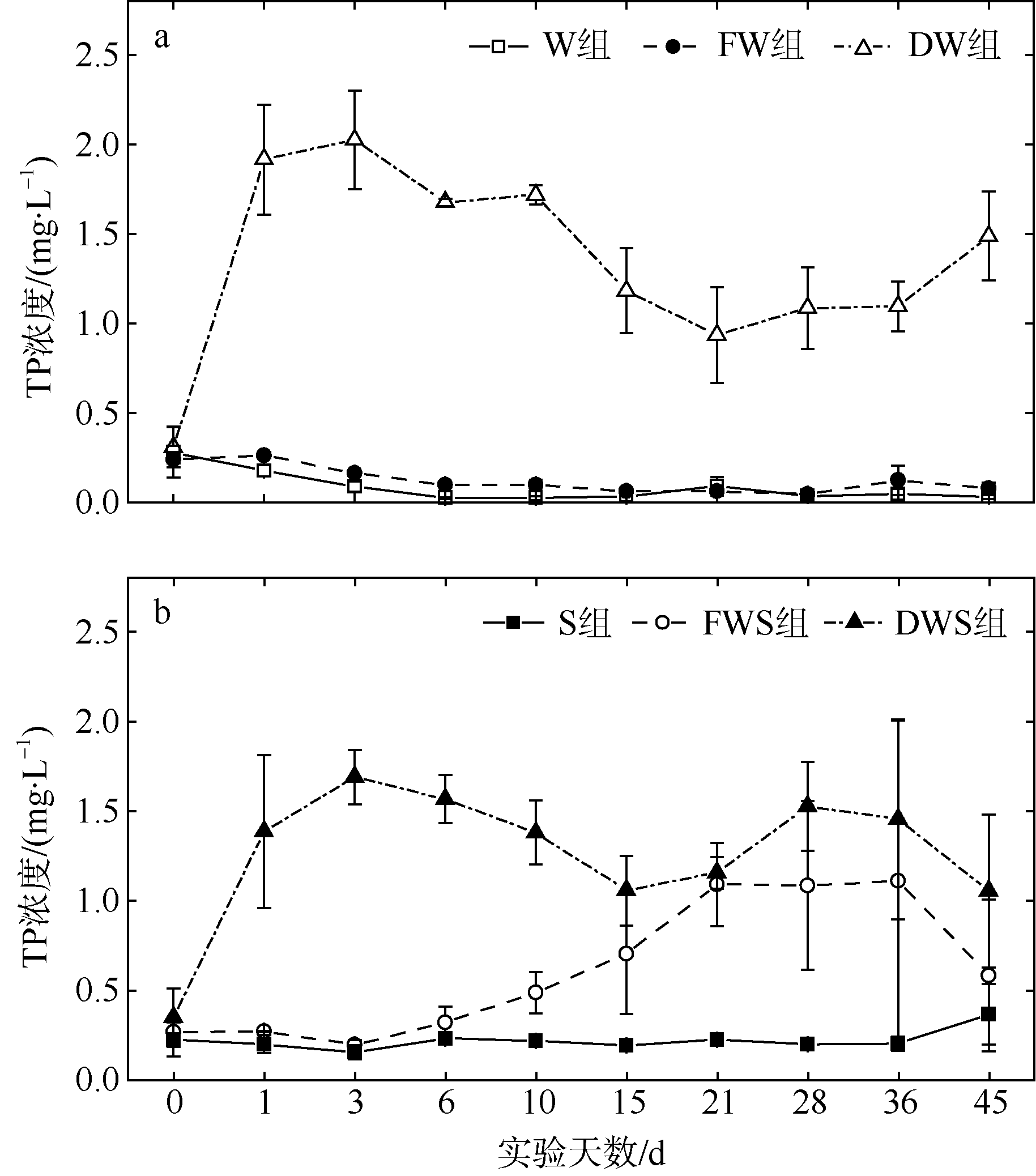
| [1] |
曹勋, 韩睿明, 章婷曦, 等, 2015. 冬季水生植物分解过程及其对水质的影响研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 34(2):361-369.
|
|
CAO XUN, HAN RUIMING, ZHANG TINGXI, et al, 2015. Decomposition of aquatic plants during winter and its influence on water quality[J]. Journal of Agro- Environment Science, 34(2):361-369 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
陈洪森, 叶春, 李春华, 等, 2020. 入湖河口区水生植物群落衰亡分解释放营养盐过程模拟研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 10(2):220-228.
|
|
CHEN HONGSEN, YE CHUN, LI CHUNHUA, et al, 2020. Simulation study on decomposition and release of nutrients from aquatic macrophyte communities in confluence area between lake and river[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 10(2):220-228 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
杜立刚, 2013. 三峡库区消落带植被淹水碳氮磷释放及消落带氮磷交换通量研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学.
|
|
DU LIGANG, 2013. Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus release from the vegetation and flux of nitrogen, phosphorus of WLFZ in the Three Gorges Reservoir[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
刘湘庆, 王宗灵, 辛明, 等, 2016. 浒苔衰亡过程中营养盐的释放过程及规律[J]. 海洋环境科学, 35(6):801-805, 813.
|
|
LIU XIANGQING, WANG ZONGLING, XIN MING, et al, 2016. Study on process of nutrient release during the decay of Ulva Prolifera[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 35(6):801-805, 813 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
刘之威, 罗洪添, 武宇辉, 等, 2019. 汕头南澳龙须菜规模栽培对水质和浮游植物的影响[J]. 中国水产科学, 26(1):99-107.
|
|
LIU ZHIWEI, LUO HONGTIAN, WU YUHUI, et al, 2019. Large-scale cultivation of Gracilaria lemaneiformis in Nan’ao Island of Shantou and its effects on the aquatic environment and phytoplankton[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 26(1):99-107 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
孟祥森, 邵雪琳, 高丽, 等, 2016. 绿潮硬毛藻衰亡分解过程中营养盐的释放规律[J]. 海洋环境科学, 35(4):495-500.
|
|
MENG XIANGSEN, SHAO XUELIN, GAO LI, et al, 2016. The research on nutrients release during the decomposition of Chaetomorpha sp.[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 35(4):495-500 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
农业农村部渔业渔政管理局, 2019. 中国渔业年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社.
|
|
Fisheries and Fisheries Administration Bureau of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Areas, 2019. China fisheries yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press (in Chinese).
|
| [8] |
童雄, 罗沛, 刘锋, 等, 2019. 绿狐尾藻分解及其氮磷释放特征[J]. 环境科学, 40(7):3118-3125.
|
|
TONG XIONG, LUO PEI, LIU FENG, et al, 2019. Decomposition of Myriophyllum aquaticum and the associated release of nitrogen and phosphorus[J]. Environmental Science, 40(7):3118-3125 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
王博, 叶春, 杨劭, 等, 2009. 腐解黑藻生物量对高硝态氮水体氮素的影响[J]. 环境科学研究, 22(10):1198-1203.
|
|
WANG BO, YE CHUN, YANG SHAO, et al, 2009. Effect of Hydrilla verticillata decomposition biomass on nitrogen content in water containing high concentration of nitrate[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 22(10):1198-1203 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
王立志, 王国祥, 2013. 衰亡期沉水植物对水和沉积物磷迁移的影响[J]. 生态学报, 33(17):5426-5437.
doi: 10.5846/stxb201206070821
|
|
WANG LIZHI, WANG GUOXIANG, 2013. Influence of submerged macrophytes on phosphorus transference between sediment and overlying water in decomposition period[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(17):5426-5437 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.5846/stxb201206070821
|
| [11] |
王立志, 宋红丽, 董彬, 等, 2020. 黑藻与金鱼藻自然衰亡过程中营养盐释放规律研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 33(1):138-146.
|
|
WANG LIZHI, SONG HONGLI, DONG BIN, et al, 2020. Nutrition release during natural decomposition of submerged macrophyte Hydrilla verticillata and Ceratophyllum demersum[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 33(1):138-146 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
王云祥, 李正, 秦传新, 等, 2016. 不同季节江蓠脱落物对大型海藻场上覆水的影响[J]. 南方水产科学, 12(2):13-20.
|
|
WANG YUNXIANG, LI ZHENG, QIN CHUANXIN, et al, 2016. Effect of Gracilaria confervoides after falling off on overlying water of seaweed field in different seasons[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 12(2):13-20 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [13] |
叶春, 王博, 李春华, 等, 2014. 沉水植物黑藻腐解过程中营养盐释放过程[J]. 中国环境科学, 34(10):2653-2659.
|
|
YE CHUN, WANG BO, LI CHUNHUA, et al, 2014. Nutrient release process during decomposition of submerged macrophytes (Hydrilla verticillata Royle)[J]. China Environmental Science, 34(10):2653-2659 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [14] |
中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 2008. GB/T 12763.4-2007 海洋调查规范第4部分: 海水化学要素调查[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社.
|
|
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration , 2008. GB/T 12763.4-2007 Specifications for oceanographic survey-Part 4: Survey of chemical parameters in sea water[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China (in Chinese).
|
| [15] |
BASTVIKEN S K, ERIKSSON P G, PREMROV A, et al, 2005. Potential denitrification in wetland sediments with different plant species detritus[J]. Ecological Engineering, 25(2):183-190.
|
| [16] |
BATTLE J M, MIHUC T B, 2000. Decomposition dynamics of aquatic macrophytes in the lower Atchafalaya, a large floodplain river[J]. Hydrobiologia, 418(1):123-136.
|
| [17] |
BRAECKMAN U, PASOTTI F, VÁZQUEZ S, et al, 2019. Degradation of macroalgal detritus in shallow coastal Antarctic sediments[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 64(4):1423-1441.
doi: 10.1002/lno.11125
pmid: 31598006
|
| [18] |
BROCK T C M, HUIJBREGTS C A M, VAN DE STEEG- HUBERTS M J H A, et al, 1982. In situ studies on the breakdown of Nymphoides peltata (Gmel.) O. Kuntze (Menyanthaceae); Some methodological aspects of the litter bag technique[J]. Hydrobiological Bulletin, 16(1):35-49.
|
| [19] |
BROUWER P E M, 1996. Decomposition in situ of the sublittoral Antarctic macroalga Desmarestia anceps Montagne[J]. Polar Biology, 16(2):129-137.
|
| [20] |
DETHIER M N, BROWN A S, BURGESS S, et al, 2014. Degrading detritus: changes in food quality of aging kelp tissue varies with species[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 460:72-79.
|
| [21] |
FILBEE-DEXTER K, PEDERSEN M F, FREDRIKSEN S, et al, 2020. Carbon export is facilitated by sea urchins transforming kelp detritus[J]. Oecologia, 192(1):213-225.
doi: 10.1007/s00442-019-04571-1
pmid: 31828530
|
| [22] |
GARCÍA-ROBLEDO E, CORZO A, DE LOMAS J G, et al, 2008. Biogeochemical effects of macroalgal decomposition on intertidal microbenthos: a microcosm experiment[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 356:139-151.
|
| [23] |
GARCÍA-ROBLEDO E, REVSBECH N P, RISGAARD- PETERSEN N, et al, 2013. Changes in N cycling induced by Ulva detritus enrichment of sediments[J]. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 69(2):113-122.
doi: 10.3354/ame01626
|
| [24] |
GESSNER M O, 1991. Differences in processing dynamics of fresh and dried leaf litter in a stream ecosystem[J]. Freshwater Biology, 26(3):387-398.
|
| [25] |
GOECKE F, THIEL V, WIESE J, et al, 2013. Algae as an important environment for bacteria-phylogenetic relationships among new bacterial species isolated from algae[J]. Phycologia, 52(1):14-24.
|
| [26] |
LI CHUNHUA, WANG BO, YE CHUN, et al, 2014. The release of nitrogen and phosphorus during the decomposition process of submerged macrophyte (Hydrilla verticillata Royle) with different biomass levels[J]. Ecological Engineering, 70:268-274.
|
| [27] |
MAWI S, KRISHNAN S, DIN M F, et al, 2020. Bioremediation potential of macroalgae Gracilaria edulis and Gracilaria changii co-cultured with shrimp wastewater in an outdoor water recirculation system[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 17:100571.
|
| [28] |
OLSON J S, 1963. Energy storage and the balance of producers and decomposers in ecological systems[J]. Ecology, 44(2):322-331.
|
| [29] |
OZALP M, CONNER W H, LOCKABY B G, 2007. Above-ground productivity and litter decomposition in a tidal freshwater forested wetland on Bull Island, SC, USA[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 245(1-3):31-43.
|
| [30] |
PAALME T, KUKK H, KOTTA J, et al, 2002. ‘In vitro’ and ‘in situ’ decomposition of nuisance macroalgae Cladophora glomerata and Pilayella littoralis[C]// Proceedings of the 31st Symposium of the Estuarine and Coastal Sciences Association. Bilbao, Spain: Springer:469-476.
|
| [31] |
PEDERSEN M F, JOHNSEN K L, 2017. Nutrient (N and P) dynamics of the invasive macroalga Gracilaria vermiculophylla: nutrient uptake kinetics and nutrient release through decomposition[J]. Marine Biology, 164(8):172.
|
| [32] |
SHILLA D, ASAEDA T, FUJINO T, et al, 2006. Decomposition of dominant submerged macrophytes: implications for nutrient release in Myall Lake, NSW, Australia[J]. Wetlands Ecology and Management, 14(5):427-433.
|
| [33] |
WANG LIZHI, LIU QIANJIN, HU CHANGWEI, et al, 2018. Phosphorus release during decomposition of the submerged macrophyte Potamogeton crispus[J]. Limnology, 19(3):355-366.
|
| [34] |
WU SUQING, HE SHENGBING, ZHOU WEILI, et al, 2017. Decomposition characteristics of three different kinds of aquatic macrophytes and their potential application as carbon resource in constructed wetland[J]. Environmental Pollution, 231:1122-1133.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.07.049
pmid: 28818519
|
| [35] |
YANG YUFENG, CHAI ZHAOYANG, WANG QING, et al, 2015. Cultivation of seaweed Gracilaria in Chinese coastal waters and its contribution to environmental improvements[J]. Algal Research, 9:236-244.
|
| [36] |
ZHOU XIAOHONG, HE ZHENLI, DING FENGHUA, et al, 2018. Biomass decaying and elemental release of aquatic macrophyte detritus in waterways of the Indian River Lagoon basin, South Florida, USA[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 635:878-891.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.047
|
 ), 胡韧1, 罗洪添1,2, 王庆1,2, 胡晓娟1,3, 白敏冬4, 杨宇峰1,2(
), 胡韧1, 罗洪添1,2, 王庆1,2, 胡晓娟1,3, 白敏冬4, 杨宇峰1,2( )
)
 ), HU Ren1, LUO Hongtian1,2, WANG Qing1,2, HU Xiaojuan1,3, BAI Mindong4, YANG Yufeng1,2(
), HU Ren1, LUO Hongtian1,2, WANG Qing1,2, HU Xiaojuan1,3, BAI Mindong4, YANG Yufeng1,2( )
)