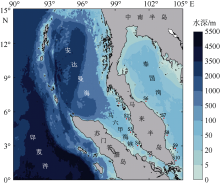
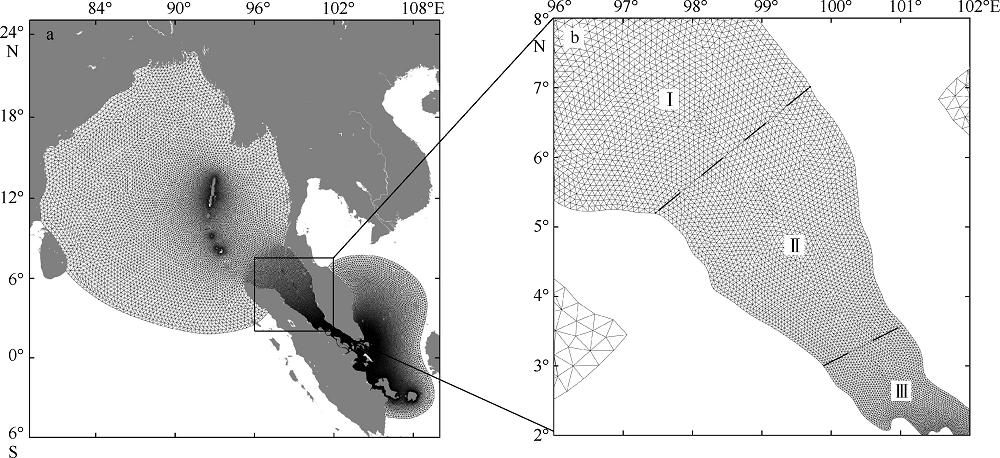
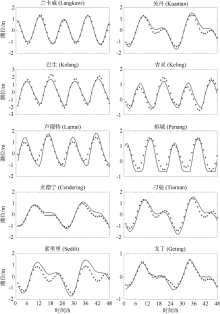
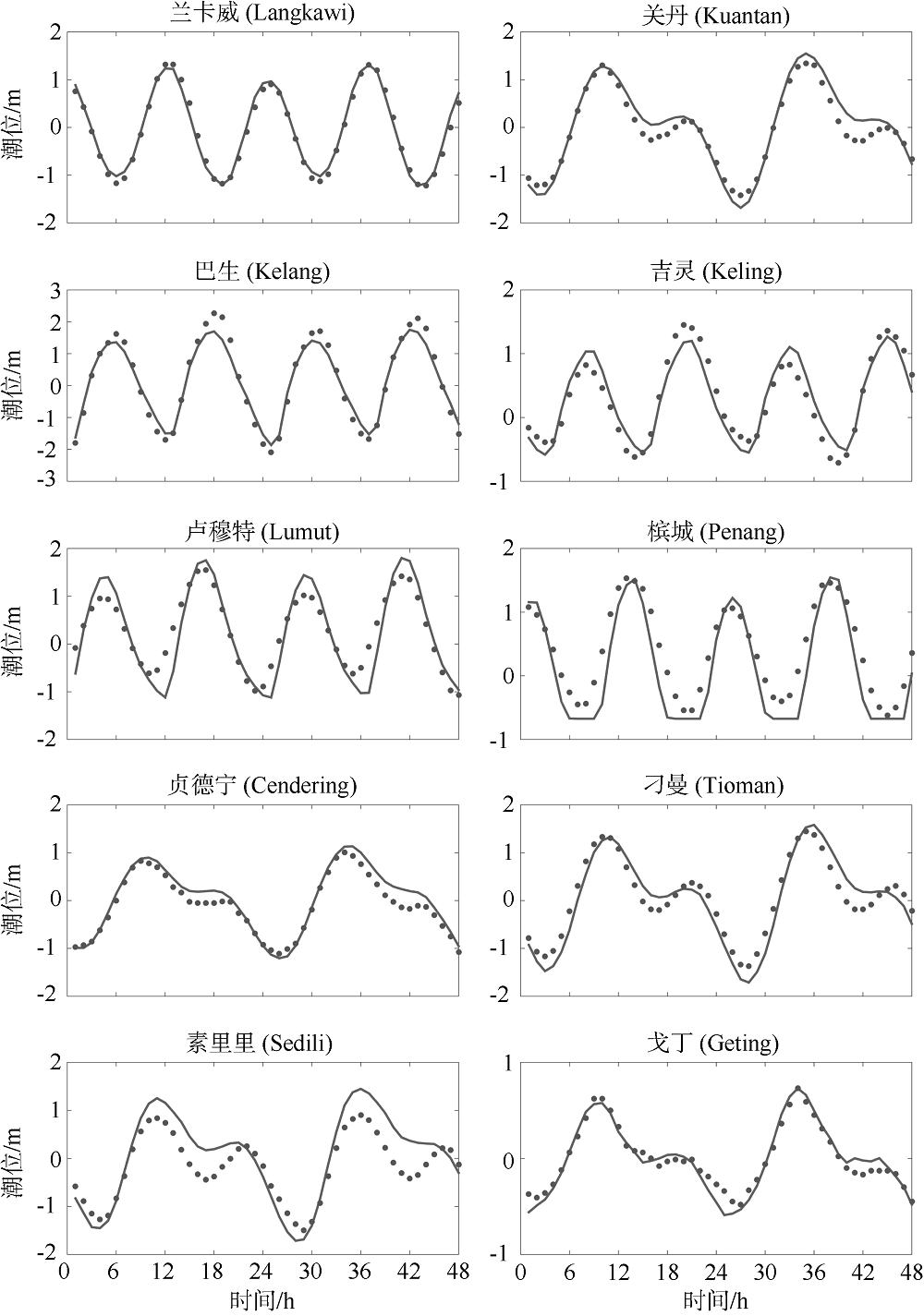
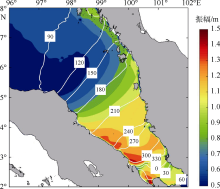
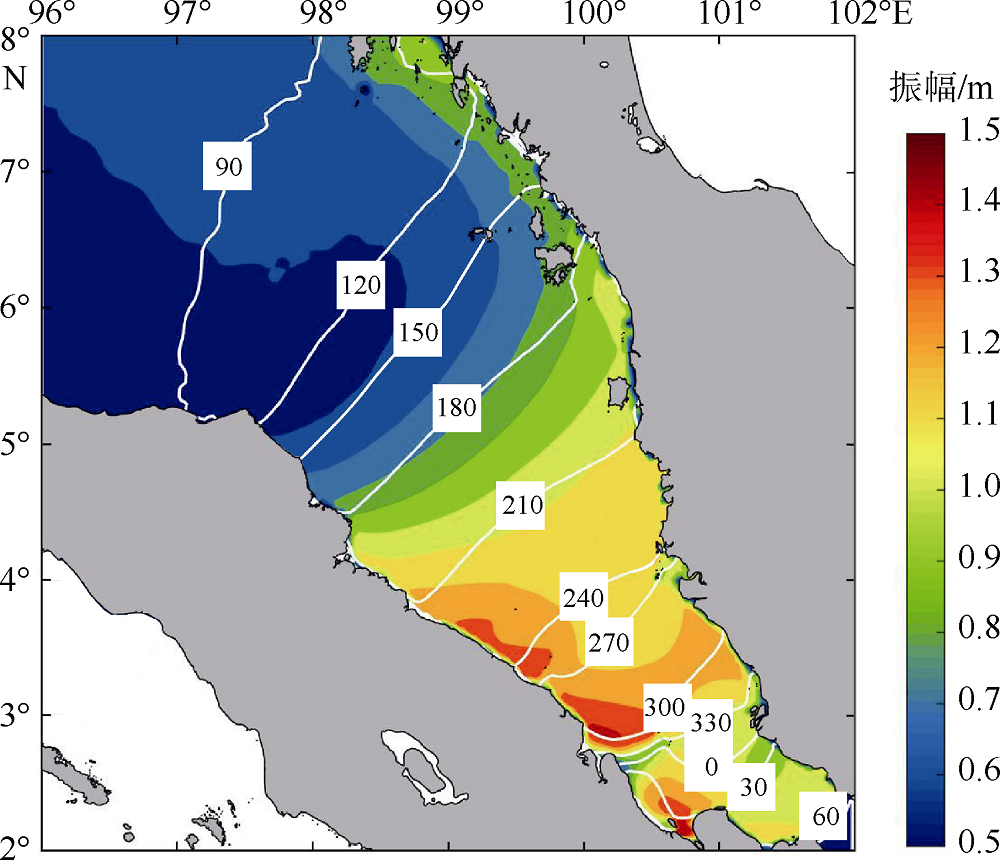
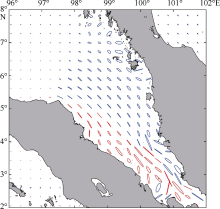
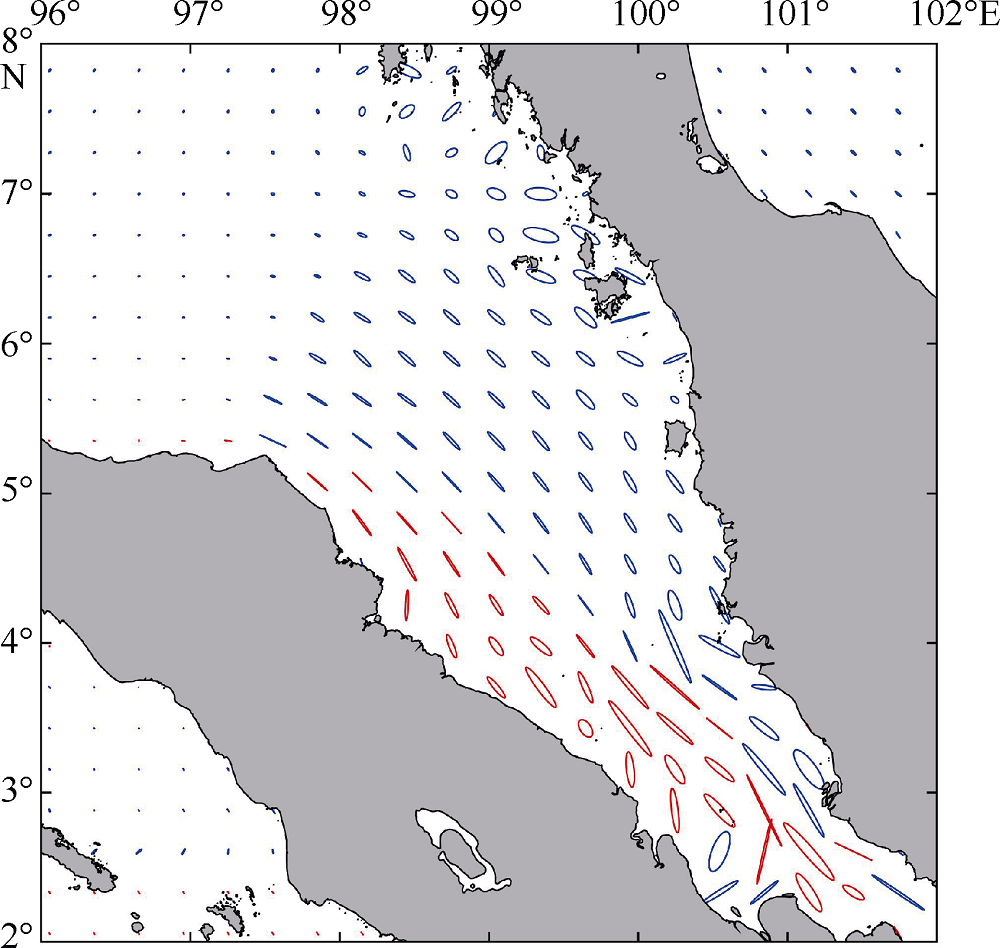
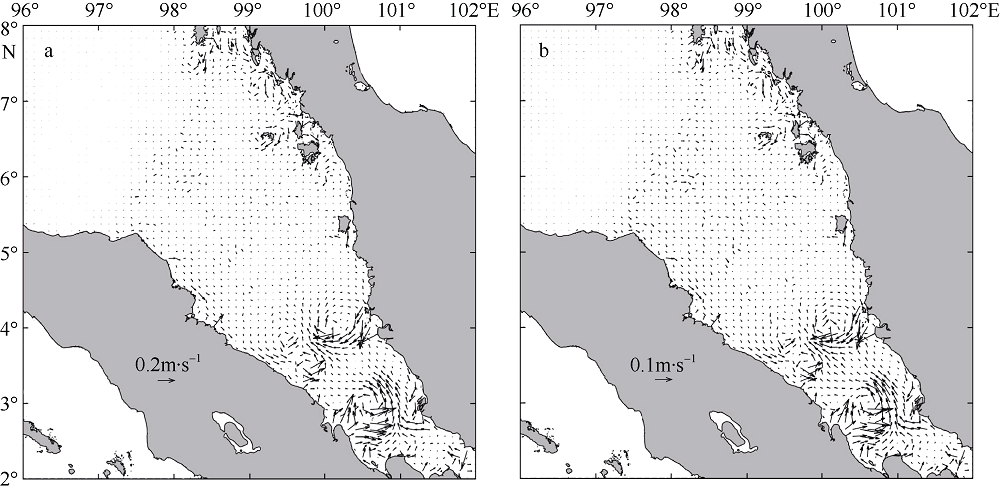
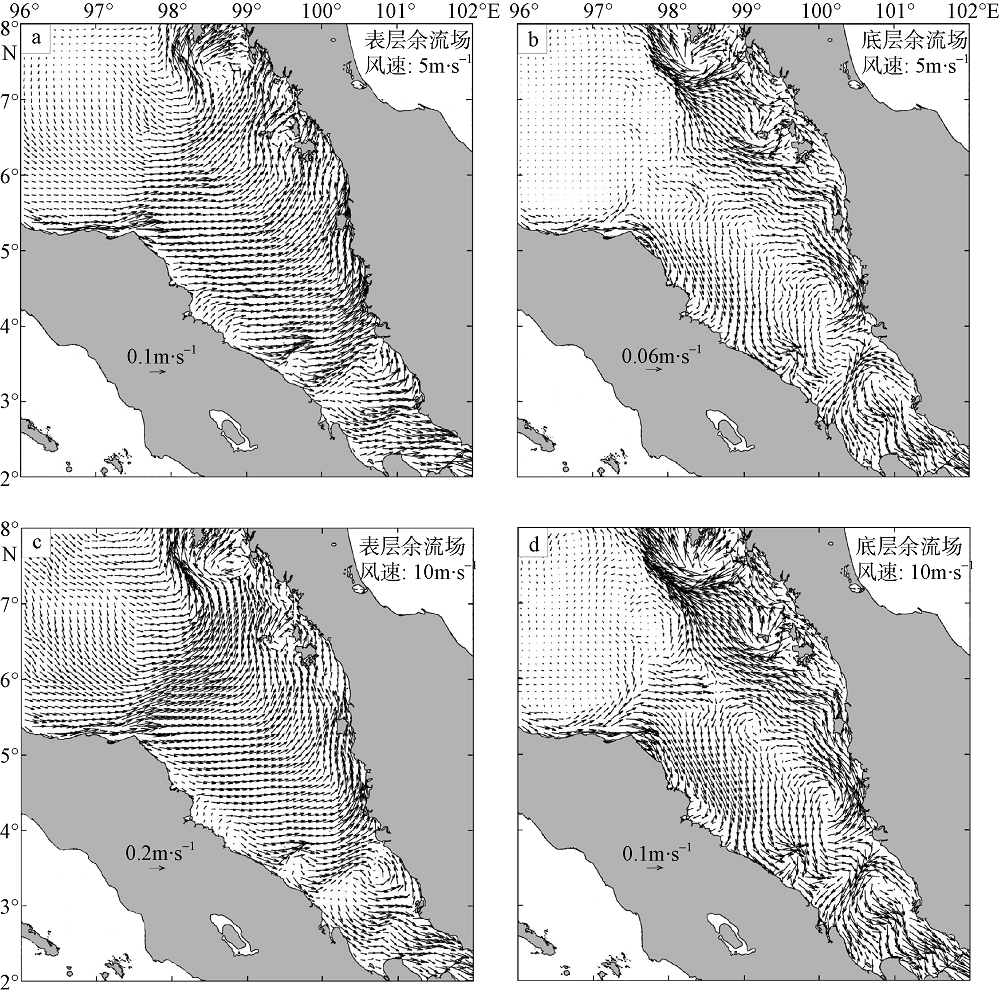
| [1] |
陈沈良, 2000. 崎岖列岛海区的水文泥沙及其峡道效应[J]. 海洋学报(中文版), 22(3):123-131.
|
|
CHEN SHENLIANG, 2003. Hydrodynamics, sediments and strait-channel effects for the Qiqu Archipelago[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 22(3):123-131(in Chinese).
|
| [2] |
李身铎, 孙卫阳, 1995. 杭州湾潮致余流数值研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 26(3):254-261.
|
|
LI SHENDUO, SUN WEIYANG. 1995. Numerical modeling of residual currents in Hangzhou bay[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 26(3):254-261 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
李玉中, 陈沈良, 2003. 洋山港海域余流分离和会聚现象研究[J]. 水利学报, (5):24-29,34
|
|
LI YUZHONG, CHEN SHENLIANG. 2003. Separation and convergence of residual flows in Yangshan Harbor area[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, (5):24-29,34(in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
刘洋, 杨晓丹, 毛新燕, 2013. 马六甲海峡的潮汐特征分析[J]. 海洋预报, 30(3):18-25.
|
|
LIU YANG, YANG XIAODAN, MAO XINYAN. 2013. Analysis of the tide in the Strait of Malacca[J]. Marine Forecasts, 30(3):18-25 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
俞慕耕, 1986. 马六甲海峡的水文气象要素统计[J]. 海洋预报, 3(1):46-48 (in Chinese).
|
| [6] |
俞慕耕, 1987. 略论马六甲海峡的水文特点[J]. 海洋湖沼通报,, (2):6-16
|
|
YU MUGENG. 1987. Hydrographic in the strait of Malacca[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, (2):6-16 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
CHEN CHANGSHENG, BEARDSLEY R C, COWLES G, 2006. An unstructured, grid, finite-volume coastal ocean model (FVCOM) system[J]. Oceanography, 19(1):78-89.
doi: 10.5670/oceanog
|
| [8] |
CHEN CHANGSHENG, LIU HEDONG, BEARDSLEY R C, 2003. An unstructured grid, finite-volume, three-dimensional, primitive equations ocean model: application to coastal ocean and estuaries[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 20(1):159-186.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0426(2003)020<0159:AUGFVT>2.0.CO;2
|
| [9] |
CHEN HAOLIANG, MALANOTTE-RIZZOLI P, KOH T Y, et al, 2014. The relative importance of the wind-driven and tidal circulations in Malacca Strait[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 88:92-102.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.07.012
|
| [10] |
DING YANG, BAO XIANWEN, YU HUAMING, et al, 2012. A numerical study of the barotropic tides and tidal energy distribution in the Indonesian seas with the assimilated finite volume coastal ocean model[J]. Ocean Dynamics, 62(4):515-532.
doi: 10.1007/s10236-011-0518-0
|
| [11] |
MASSERAN N, RAZALI A M, 2016. Modeling the wind direction behaviors during the monsoon seasons in Peninsular Malaysia[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 56:1419-1430.
doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.11.040
|
| [12] |
PAWLOWICZ R, BEARDSLEY B, LENTZ S, 2002. Classical tidal harmonic analysis including error estimates in MATLAB using T_TIDE[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 28(8):929-937.
|
| [13] |
RIZAL S, DAMM P, WAHID M A, et al, 2012. General circulation in the Malacca strait and Andaman sea: a numerical model study[J]. American Journal of Environmental Sciences, 8(5):479-488.
doi: 10.3844/ajessp.2012.479.488
|
| [14] |
RIZAL S, SÜNDERMANN J, 1994. On the M2-tide of the Malacca Strait: A numerical investigation[J]. Deutsche Hydrografische Zeitschrift, 46(1):61-80.
|
| [15] |
RIZAL S, 2000. The role of non-linear terms in the shallow water equation with the application in three-dimensional tidal model of the Malacca Strait and Taylor's Problem in low geographical latitude[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 20(15):1965-1991.
doi: 10.1016/S0278-4343(00)00059-5
|
| [16] |
RIZAL S, SETIAWAN I, ISKANDAR T, et al, 2010. Currents simulation in the Malacca straits by using three-dimensional numerical model[J]. Sains Malaysiana, 39(4):519-524.
|
| [17] |
THIA-ENG C, GORRE I R L, ROSS S A, et al, 2000. The Malacca Straits[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 41(1-6):160-178.
doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(00)00108-9
|
| [18] |
WYRIKI K, 1961. Physical oceanography of the Southeast Asian waters[D]. California: Scripps Institution of Oceanography,The University of California, 1-195.
|
 ), Song HU1,2,3(
), Song HU1,2,3( )
)