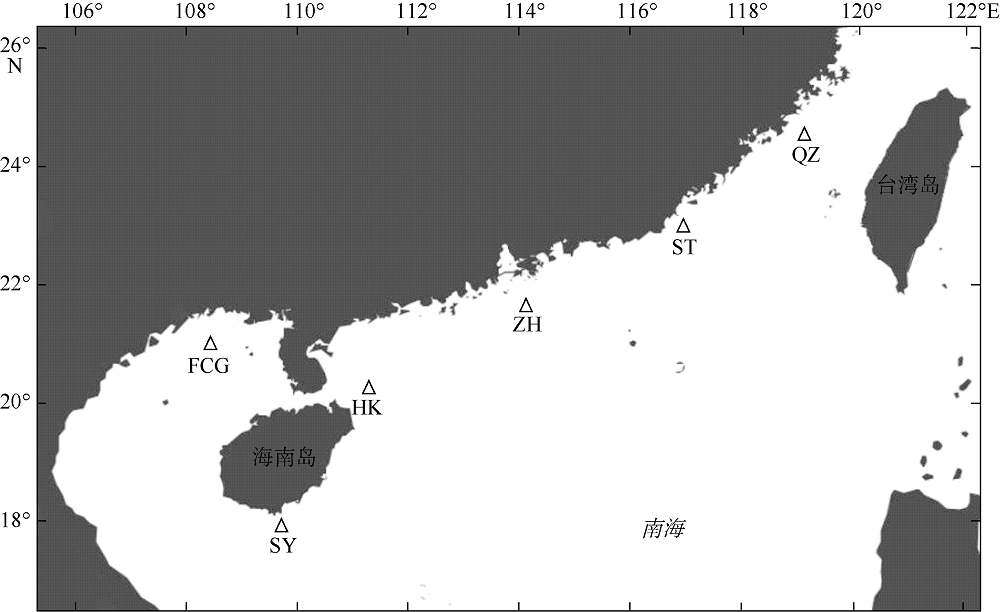
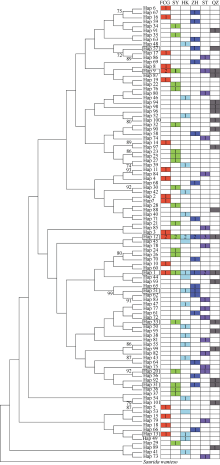
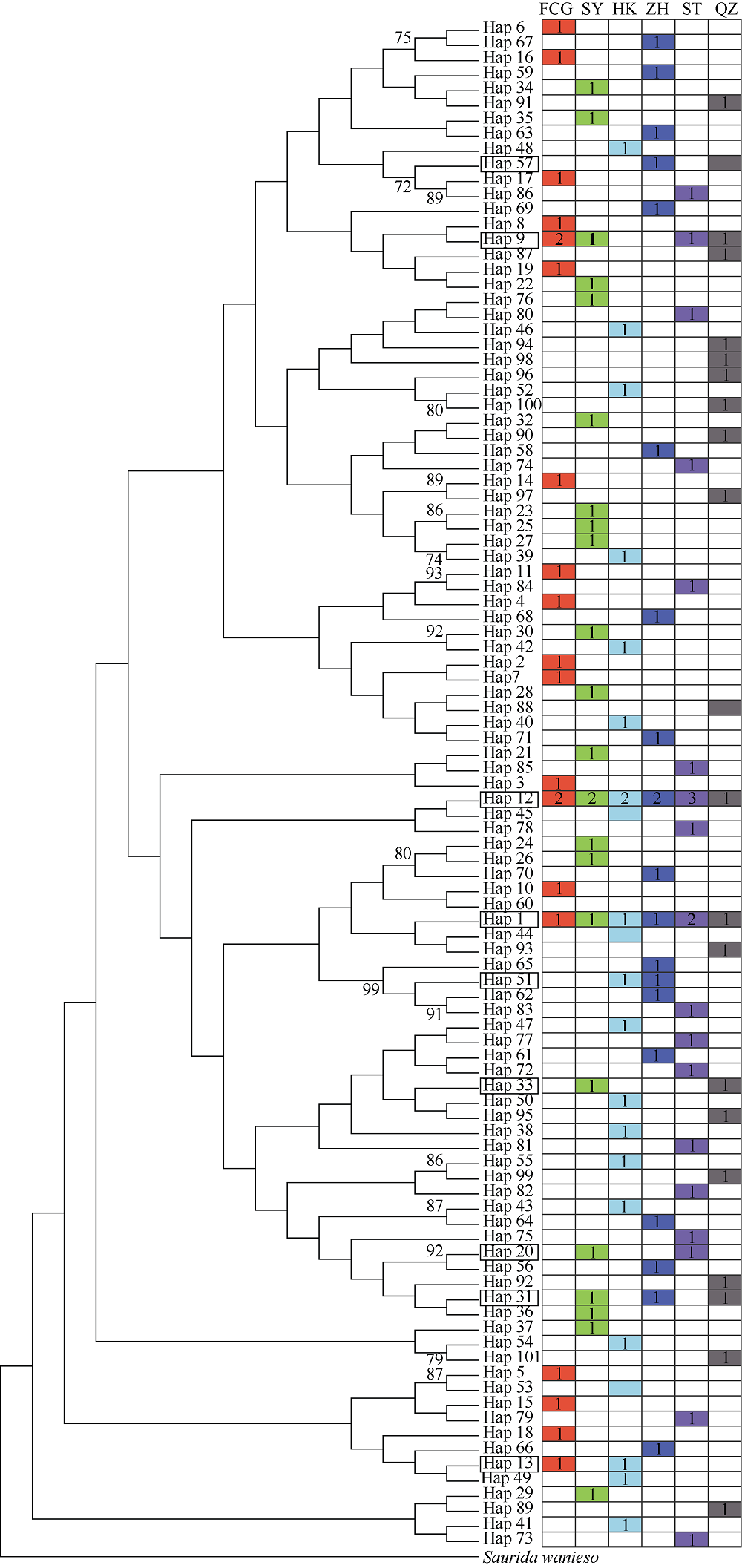
| [1] |
蔡研聪, 徐姗楠, 陈作志, 等, 2018. 南海北部近海渔业资源群落结构及其多样性现状[J]. 南方水产科学, 14(2):10-18.
|
|
CAI YANCONG, XU SHANNAN, CHEN ZUOZHI, et al, 2018. Current status of community structure and diversity of fishery resources in offshore northern South China Sea[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 14(2):10-18 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
陈再超, 刘继兴, 1982. 南海经济鱼类[M]. 广州: 广东科学与技术出版社: 184-188(in Chinese).
|
| [3] |
陈作志, 邱永松, 徐姗楠, 等, 2012. 北部湾花斑蛇鲻生物学特征的演化[J]. 中国水产科学, 19(2):321-328.
|
|
CHEN ZUOZHI, QIU YONGSONG, XU SHANNAN, et al, 2012. Evolution of biological characteristics of Saurida undosquamis (Richardson) in the Beibu Gulf, South China Sea[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 19(2):321-328 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
郜星晨, 章群, 薛丹, 等, 2016. 基于线粒体控制区部分序列的南海大斑石鲈遗传多样性分析[J]. 海洋科学, 40(7):41-45.
|
|
GAO XINGCHEN, ZHANG QUN, XUE DAN, et al, 2016. Genetic diversity of Pomadasys maculatus in coastal waters of South China Sea via mtDNA control region partial sequences[J]. Marine Sciences, 40(7):41-45 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
黄小林, 李文俊, 林黑着, 等, 2018. 基于线粒体DNA D-loop序列的黄斑篮子鱼群体遗传多样性分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 37(4):45-51.
|
|
HUANG XIAOLIN, LI WENJUN, LIN HEIZHAO, et al, 2018. Genetic variations among Siganus oramin populations in coastal waters of southeast China based on mtDNA control region sequences[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 37(4):45-51 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
黄梓荣, 2002. 休渔对南海北部多齿蛇鲻资源的影响[J]. 湛江海洋大学学报, 22(6):26-31.
|
|
HUANG ZIRONG, 2002. Effect of Close Season on Bloch et Schneider (S. tumbil) Stock in the North of South China Sea[J]. Journal of Zhanjiang Ocean University, 22(6):26-31 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
江艳娥, 许友伟, 范江涛, 等, 2019. 南海北部陆架水域多齿蛇鲻与花斑蛇鲻的年龄与生长[J]. 中国水产科学, 26(1):82-90.
|
|
JIANG YAN’E, XU YOUWEI, FAN JIANGTAO, et al, 2019. Age and growth of Saurida tumbil and Saurida undosquamis in the continental shelf of the northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 26(1):82-90 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
梁述章, 宋炜, 马春艳, 等, 2019. 基于线粒体控制区的中国近海棘头梅童鱼群体遗传结构研究[J]. 海洋渔业, 41(2):138-148.
|
|
LIANG SHUZHANG, SONG WEI, MA CHUNYAN, et al, 2019. Genetic structure of Collichthys lucidus populations from China coastal waters based on mt DNA control region[J]. Marine Fisheries, 41(2):138-148 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
吕金磊, 章群, 杨喜书, 等, 2017. 基于线粒体控制区的中国南海海域卵形鲳鲹遗传多样性[J]. 海洋渔业, 39(3):241-248.
|
|
LV JINLEI, ZHANG QUN, YANG XISHU, et al, 2017. Genetic diversity of Trachinotus ovatus in the South China Sea inferred from Mitochondrial DNA control region sequences[J]. Marine Fisheries, 39(3):241-248 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
舒黎明, 邱永松, 2004a. 南海北部花斑蛇鲻生长死亡参数估计及开捕规格[J]. 湛江海洋大学学报, 24(3):29-35.
|
|
SHU LIMING, QIU YONGSONG, 2004a. Estimate for growth, mortality parameters and first capture specification suggestion of Saurida undosquamis (Richardson) in Northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Zhanjiang Ocean University, 24(3):29-35 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
舒黎明, 邱永松, 2004b. 南海北部多齿蛇鲻生物学分析[J]. 中国水产科学, 11(2):154-158.
|
|
SHU LIMING, QIU YONGSONG, 2004b. Biology analysis of Saurida tumbil in northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 11(2):154-158 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
苏纪兰, 袁业立, 2005. 中国近海水文[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社: 1-367(in Chinese).
|
| [13] |
孙冬芳, 董丽娜, 李永振, 等, 2010. 南海北部海域多齿蛇鲻的种群分析[J]. 水产学报, 34(9):1387-1394.
|
|
SUN DONGFANG DONG LI’NA LI YONGZHEN, et al, 2010. Population analysis of Saurida tumbil in the Northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2010,34(9):1387-1394 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [14] |
孙典荣, 林昭进, 2004. 北部湾主要经济鱼类资源变动分析及保护对策探讨[J]. 热带海洋学报, 23(2):62-68.
|
|
SUN DIANRONG, LIN ZHAOJIN, 2004. Variations of major commercial fish stocks and strategies for fishery management in beibu gulf[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 23(2):62-68 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [15] |
熊丹, 李敏, 陈作志, 等, 2015. 南海短尾大眼鲷的种群遗传结构分析[J]. 南方水产科学, 11(2):27-34.
|
|
XIONG DAN, LI MIN, CHEN ZUOZHI, et al, 2015. Genetic structure of Priacanthus macracanthus population from the South China Sea[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 11(2):27-34 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [16] |
许友伟, 陈作志, 范江涛, 等, 2015. 南沙西南陆架海域底拖网渔获物组成及生物多样性[J]. 南方水产科学, 11(5):76-81.
|
|
XU YOUWEI, CHEN ZUOZHI, FAN JIANGTAO, et al, 2015. Composition and biodiversity of catches by bottom trawl fishery in southwestern continent shelf of Nansha area[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2015,11(5):76-81 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [17] |
杨炳忠, 杨吝, 谭永光, 等, 2017. 南海区2种桁杆虾拖网渔获组成调查与分析[J]. 南方水产科学, 13(6):115-122.
|
|
YANG BINGZHONG, YANG LIN, TAN YONGGUANG, et al, 2017. Analysis of catch composition of two shrimp beam trawls in South China Sea[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 13(6):115-122 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [18] |
杨喜书, 章群, 薛丹, 等, 2018. 中国近海细鳞鯻线粒体控制区的遗传多样性[J]. 生态学报, 38(5):1852-1859.
|
|
YANG XISHU, ZHANG QUN, XUE DAN, et al, 2018. Genetic analysis of Terapon jarbua in coastal waters of China by using mitochondrial DNA control region sequencing[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(5):1852-1859 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [19] |
张俊, 陈国宝, 陈作志, 等, 2015. 南沙南部陆架海域渔业资源声学评估[J]. 南方水产科学, 11(5):1-10.
|
|
ZHANG JUN, CHEN GUOBAO, CHEN ZUOZHI, et al, 2015. Acoustic estimation of fishery resources in southern continental shelf of Nansha area[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 11(5):1-10 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [20] |
ALZOHAIRY A M, 2011. BioEdit: an important software for molecular biology[J]. GERF Bulletin of Biosciences, 2(1):60-61.
|
| [21] |
CADRIN S X, KERR LA, MARIAN S, 2014. Chapter One-Stock identification methods: an overview[M]//CADRIN S X, KERR LA, MARIAN S. Stock Identification Methods. 2nd ed. San Diego: Elsevier Inc.: 1-5.
|
| [22] |
CHHANDAPRAJNADARSINI E M, ROUL S K, SWAIN S, et al, 2018. Biometric analysis of brushtooth lizard fish Saurida undosquamis (Richardson, 1848) from Mumbai waters[J]. Journal of Entomology and Zoology Studies, 6(2):1165-1171.
|
| [23] |
COATES D J, BYRNE M, MORITZ C, 2018. Genetic diversity and conservation units: dealing with the species-population continuum in the age of genomics[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 6:165.
|
| [24] |
EXCOFFIER L, LISCHER H E L, 2010. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: a new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows[J]. Molecular Ecology Resources, 10(3):564-567.
pmid: 21565059
|
| [25] |
FRANKHAM R, BALLOU J D, BRISCOE D A, 2002. Introduction to conservation genetics[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press: 78-104.
|
| [26] |
FROESE R, PAULY D, (20190801)[20190925] FishBase [DB/OL]. https://www.fishbase.in/summary/Saurida-undosquamis.html
|
| [27] |
GRANT W S, BOWEN B W, 1998. Shallow population histories in deep evolutionary lineages of marine fishes: insights from sardines and anchovies and lessons for conservation[J]. Journal of Heredity, 89(5):415-426.
|
| [28] |
HEWITT G M, 2000. The genetic legacy of the Quaternary ice ages[J]. Nature, 405(6789):907-913.
doi: 10.1038/35016000
pmid: 10879524
|
| [29] |
KUMAR S, STECHER G, TAMURA K, 2016. MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 33(7):1870-1874.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw054
pmid: 27004904
|
| [30] |
LAIKRE L, PALM S, RYMAN N, 2005. Genetic population structure of fishes: Implications for coastal zone management[J]. Ambio, 34(2):111-119.
pmid: 15865307
|
| [31] |
MALI K S, KUMAR M V, FAREJIYA M K, et al, 2017. Reproductive biology of Saurida tumbil (Bloch 1795) and Saurida undosquamis (Richardson 1848) inhabiting Northwest coast of India[J]. International Journal of Pure & Applied Bioscience, 5(6):957-964.
|
| [32] |
NAJMUDEEN T M, SEETHA P K, ZACHARIA P U, 2019. Stock dynamics of the brushtooth lizardfish Saurida undosquamis (Richardson, 1848) from a tropical multispecies fishery in the southeastern Arabian Sea[J]. Aquatic Living Resources, 32(5):9.
|
| [33] |
PALSBØLL P J, BÉRUBÉ M, ALLENDORF F W, 2007. Identification of management units using population genetic data[J]. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 22(1):11-16.
pmid: 16982114
|
| [34] |
PALUMBI S R, 1994. Genetic divergence, reproductive isolation, and marine speciation[J]. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 25:547-572.
|
| [35] |
PINSKY M L, PALUMBI S R, 2014. Meta-analysis reveals lower genetic diversity in overfished populations[J]. Molecular Ecology, 23(1):29-39.
doi: 10.1111/mec.12509
pmid: 24372754
|
| [36] |
REISS H, HOARAU G, DICKEY-COLLAS M, et al, 2009. Genetic population structure of marine fish: mismatch between biological and fisheries management units[J]. Fish and Fisheries, 10(4):361-395.
|
| [37] |
ROZAS J, FERRER-MATA A, SÁNCHEZ-DELBARRIO J C, et al, 2017. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 34(12):3299-3302.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msx248
pmid: 29029172
|
 ), 孔啸兰1, 许友伟1, 陈作志1,2,3(
), 孔啸兰1, 许友伟1, 陈作志1,2,3( )
)
 ), Xiaolan KONG1, Youwei XU1, Zuozhi CHEN1,2,3(
), Xiaolan KONG1, Youwei XU1, Zuozhi CHEN1,2,3( )
)