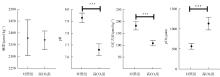
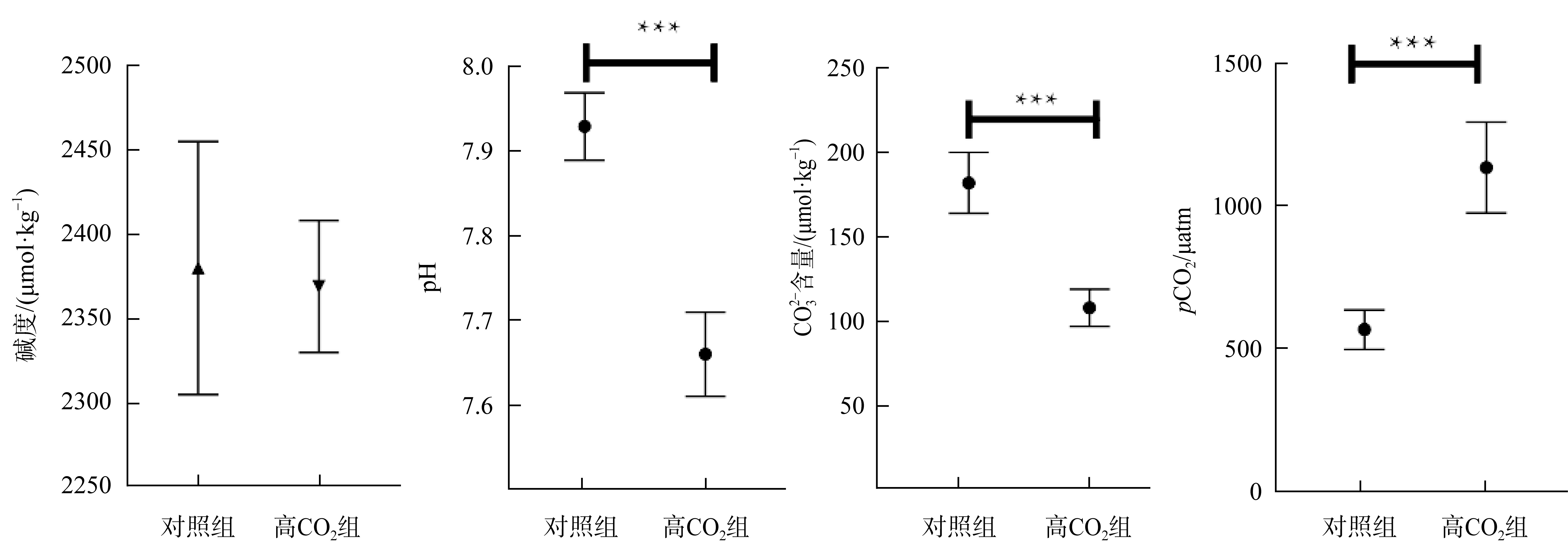
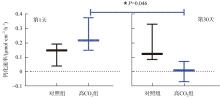
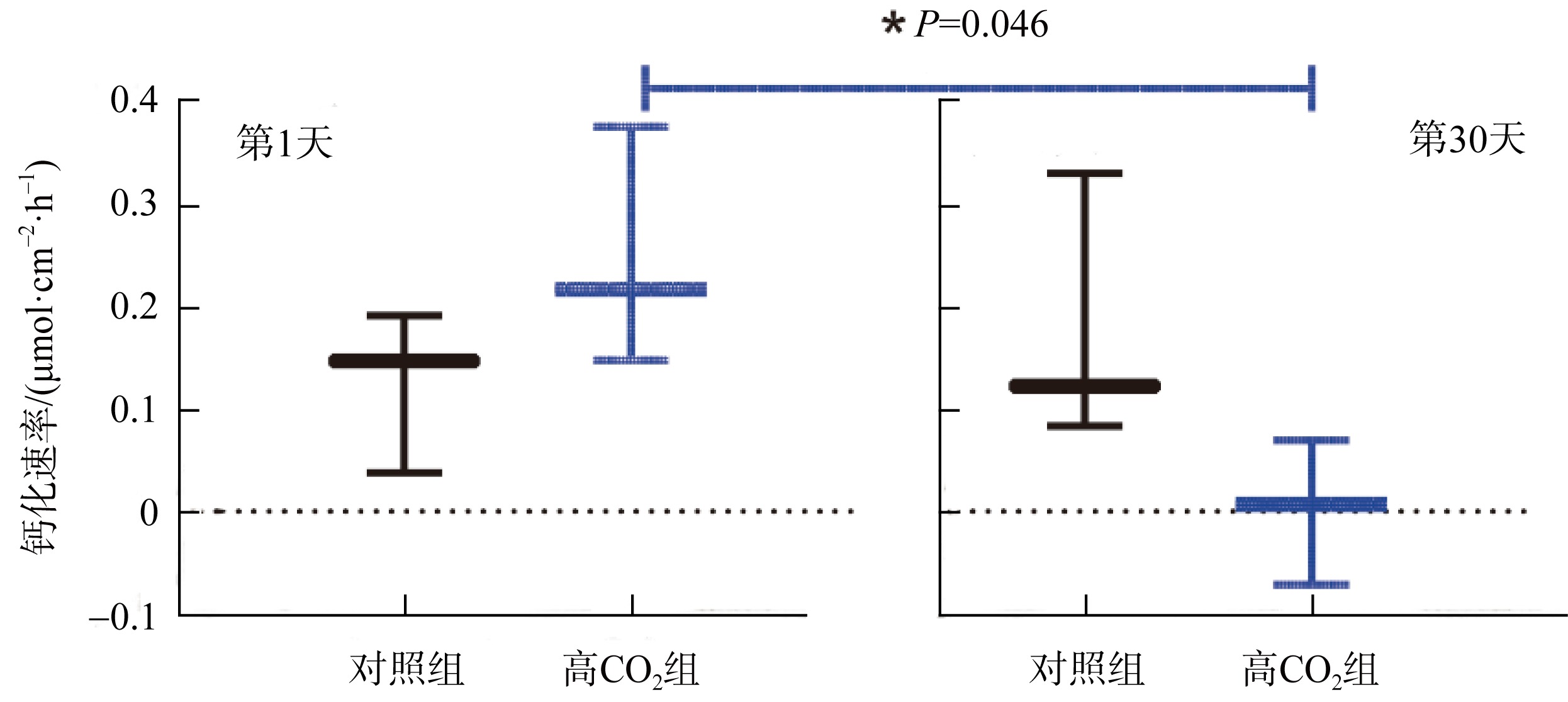
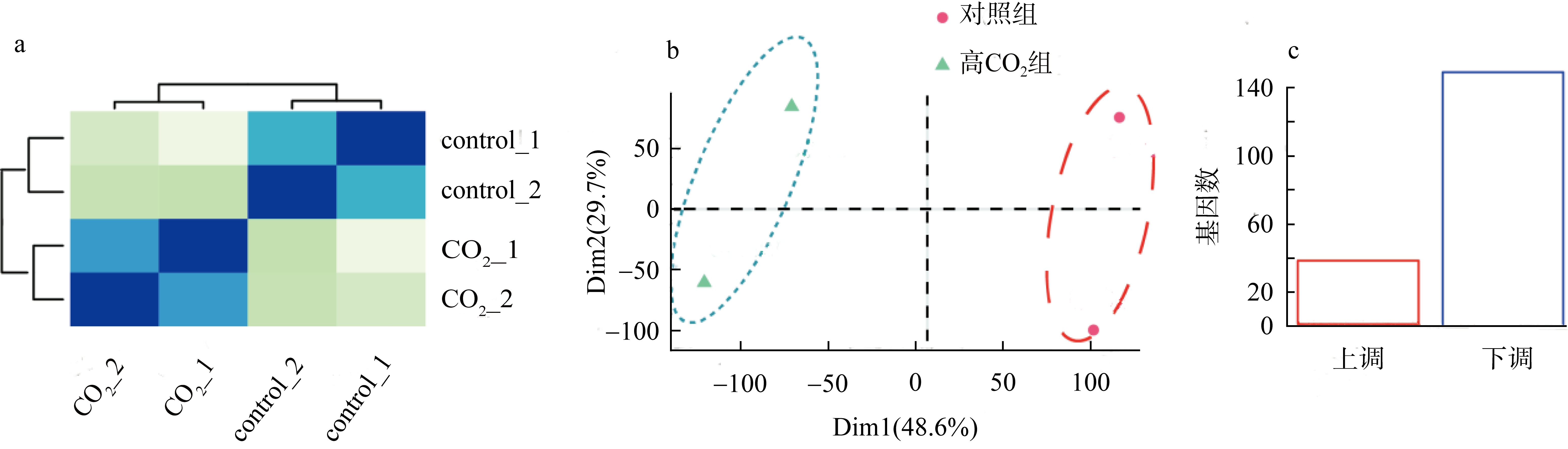
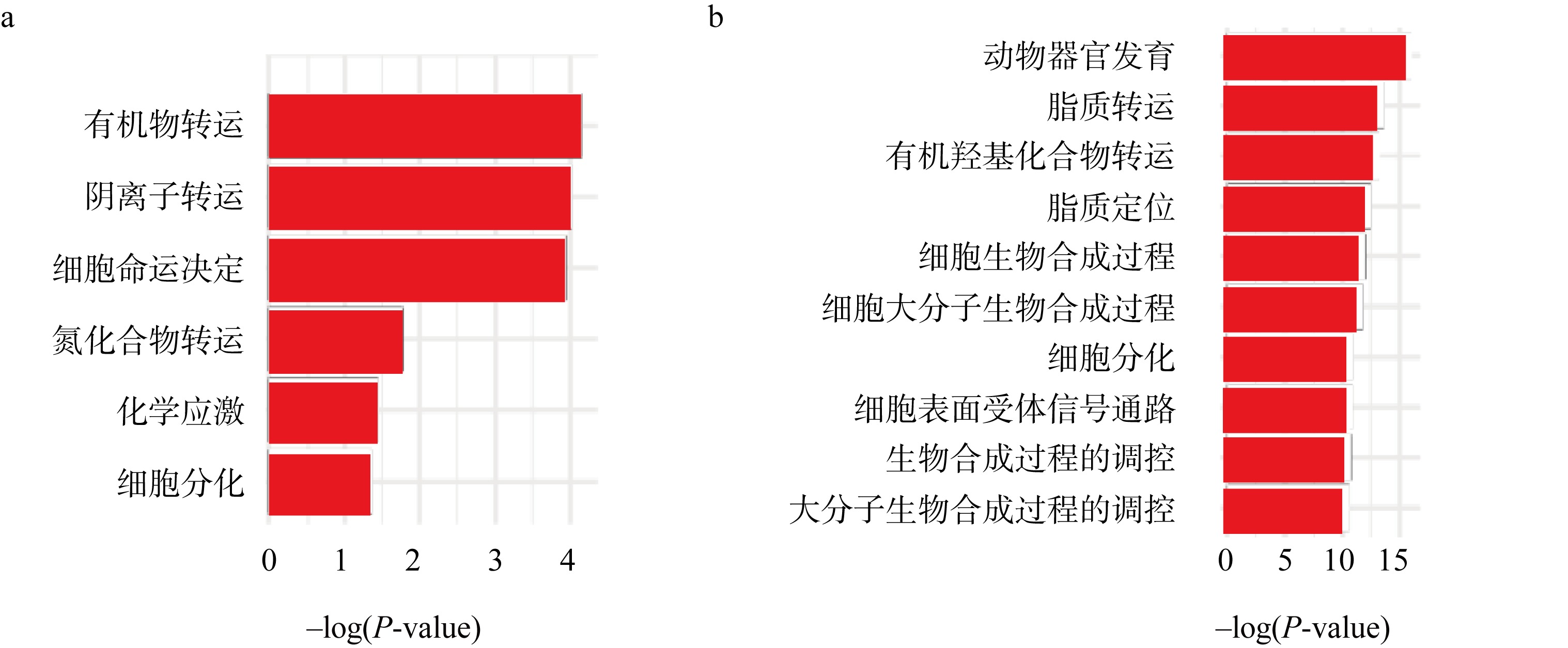
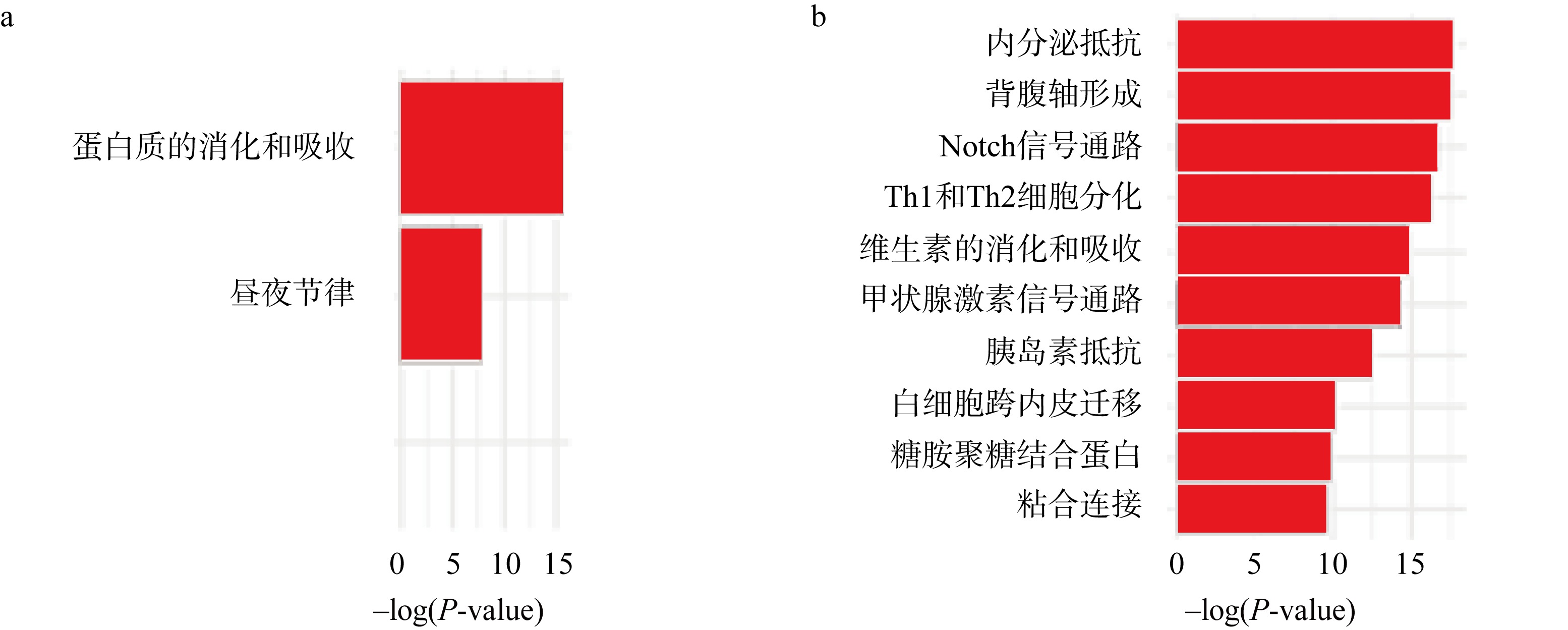
| [1] |
郭亚娟, 周伟华, 袁翔城, 等, 2018. 两种造礁石珊瑚对海水酸化和溶解有机碳加富的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 37(1): 57-63.
doi: 10.11978/2017018
|
|
GUO YAJUAN, ZHOU WEIHUA, YUAN XIANGCHENG, et al, 2018. Responses of two species of reef-building corals to acidification and dissolved organic carbon enrichment[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 37(1): 57-63 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
梁宇娴, 俞晓磊, 郭亚娟, 等, 2020. 3种传统方法对不同珊瑚表面积测量的适用性及其校准方法——以3D扫描技术为基准[J]. 热带海洋学报, 39(1): 85-93.
doi: 10.11978/2019039
|
|
LIANG YUXIAN, YU XIAOLEI, GUO YAJUAN, et al, 2020. Applicability and calibration methods of three traditional surface area measurement methods for different coral species — based on 3D scanning technology[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 39(1): 85-93 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.11978/2019039
|
| [3] |
朱亚兰, 姚伟, 乐超银, 等, 2006. 甲状旁腺激素促进骨形成的研究进展[J]. 山东医药, 46(7): 79-80. (in Chinese)
|
| [4] |
邹仁林, 2001. 中国动物志, 腔肠动物门, 珊瑚虫纲, 石珊瑚目, 造礁石珊瑚[M]. 北京: 科学出版社 (in Chinese).
|
| [5] |
ADAMIANO A, GOFFREDO S, DUBINSKY Z, et al, 2014. Analytical pyrolysis-based study on intra-skeletal organic matrices from Mediterranean corals[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 406(24): 6021-6033.
pmid: 25015043
|
| [6] |
AKIVA A, NEDER M, KAHIL K, et al, 2018. Minerals in the pre-settled coral Stylophora pistillata crystallize via protein and ion changes[J]. Nature Communications, 9(1): 1880.
|
| [7] |
BAROTT K L, PEREZ S O, LINSMAYER L B, et al, 2015. Differential localization of ion transporters suggests distinct cellular mechanisms for calcification and photosynthesis between two coral species[J]. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 309(3): R235-R246.
|
| [8] |
BISCÉRÉ T, ZAMPIGHI M, LORRAIN A, et al, 2019. High pCO2 promotes coral primary production[J]. Biology Letters, 15(7): 20180777.
|
| [9] |
CHEN SANG, GAGNON A C, ADKINS J F, 2018. Carbonic anhydrase, coral calcification and a new model of stable isotope vital effects[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 236: 179-197.
|
| [10] |
CLODE P L, STERN R A, MARSHALL A T, 2007. Subcellular imaging of isotopically labeled carbon compounds in a biological sample by ion microprobe (NanoSIMS)[J]. Microscopy Research and Technique, 70(3): 220-229.
pmid: 17279515
|
| [11] |
COMEAU S, TAMBUTTÉ E, CARPENTER R C, et al, 2017. Coral calcifying fluid pH is modulated by seawater carbonate chemistry not solely seawater pH[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 284(1847): 20161669.
|
| [12] |
CORNWALL C E, COMEAU S, KORNDER N A, et al, 2021. Global declines in coral reef calcium carbonate production under ocean acidification and warming[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 118(21): e2015265118.
|
| [13] |
DESALVO M K, VOOLSTRA C R, SUNAGAWA S, et al, 2008. Differential gene expression during thermal stress and bleaching in the Caribbean coral Montastraea faveolata[J]. Molecular Ecology, 17(17): 3952-3971.
|
| [14] |
DICKSON A G, SABINE C L, CHRISTIAN J R, 2007. Determination of total alkalinity in sea water using an open-cell titration: Guide to best practices for ocean CO2 measurements[R/OL]. (2007-07) [2022-08-23].https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/access/ocean-carbon-acidification-data-system/oceans/Handbook_2007/Guide_all_in_one.pdf
|
| [15] |
DRAKE J L, MASS T, STOLARSKI J, et al, 2020. How corals made rocks through the ages[J]. Global Change Biology, 26(1): 31-53.
doi: 10.1111/gcb.14912
pmid: 31696576
|
| [16] |
FANTAZZINI P, MENGOLI S, PASQUINI L, et al, 2015. Gains and losses of coral skeletal porosity changes with ocean acidification acclimation[J]. Nature Communications, 6: 7785.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms8785
pmid: 26183259
|
| [17] |
HOOK S E, GALLAGHER E P, BATLEY G E, 2014. The role of biomarkers in the assessment of aquatic ecosystem health[J]. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management, 10(3): 327-341.
doi: 10.1002/ieam.1530
pmid: 24574147
|
| [18] |
IPCC, 2022. Special report on the ocean and cryosphere in a changing climate[R]. New York: Cambridge University Press.
|
| [19] |
JOUBERT C, PIQUEMAL D, MARIE B, et al, 2010. Transcriptome and proteome analysis of Pinctada margaritifera calcifying mantle and shell: Focus on biomineralization[J]. BMC Genomics, 11(1): 613.
|
| [20] |
KENKEL C D, MOYA A, STRAHL J, et al, 2018. Functional genomic analysis of corals from natural CO2-seeps reveals core molecular responses involved in acclimatization to ocean acidification[J]. Global Change Biology, 24(1): 158-171.
|
| [21] |
KURIHARA H, TAKAHASHI A, REYES-BERMUDEZ A, et al, 2018. Intraspecific variation in the response of the scleractinian coral Acropora digitifera to ocean acidification[J]. Marine Biology, 165(2): 38.
|
| [22] |
LEWIS E R, WALLACE D W R, ALLISON L J, 1998. Program developed for CO2 system calculations[R]. Oak Ridge, Tennessee: Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, US Department of Energy.
|
| [23] |
LIONETTO M G, CARICATO R, ERROI E, et al, 2006. Potential application of carbonic anhydrase activity in bioassay and biomarker studies[J]. Chemistry and Ecology, 22(Sup1): S119-S125.
|
| [24] |
MARIN F, LUQUET G, MARIE B, et al, 2007. Molluscan shell proteins: primary structure, origin, and evolution[J]. Current Topics in Developmental Biology, 80: 209-276.
|
| [25] |
MASS T, DRAKE J L, HARAMATY L, et al, 2012. Aragonite precipitation by “proto-polyps” in coral cell cultures[J]. PLoS One, 7(4): e35049.
|
| [26] |
MCCONNAUGHEY T A, WHELAN J F, 1997. Calcification generates protons for nutrient and bicarbonate uptake[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 42(1-2): 95-117.
|
| [27] |
MONSERRAT J M, MARTÍNEZ P E, GERACITANO L A, et al, 2007. Pollution biomarkers in estuarine animals: Critical review and new perspectives[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology, 146(1-2): 221-234.
|
| [28] |
MOYA A, HUISMAN L, BALL E E, et al, 2012. Whole transcriptome analysis of the coral Acropora millepora reveals complex responses to CO2-driven Acidification during the initiation of calcification[J]. Molecular Ecology, 21(10): 2440-2454.
|
| [29] |
PARKER M D, BORON W F, 2013. The divergence, actions, roles, and relatives of sodium-coupled bicarbonate transporters[J]. Physiological Reviews, 93(2): 803-959.
doi: 10.1152/physrev.00023.2012
pmid: 23589833
|
| [30] |
REYES-BERMUDEZ A, DESALVO M K, VOOLSTRA C R, et al, 2009. Gene expression microarray analysis encompassing metamorphosis and the onset of calcification in the scleractinian coral Montastraea faveolata[J]. Marine Genomics, 2(3-4): 149-159.
|
| [31] |
RIEBESELL U, FABRY V J, HANSSON L, et al, 2010. Guide to best practices for ocean acidification research and data reporting[J]. Oceanography, 22(4): 260.
|
| [32] |
ROCKER M M, NOONAN S, HUMPHREY C, et al, 2015. Expression of calcification and metabolism-related genes in response to elevated pCO2and temperature in the reef-building coral Acropora millepora[J]. Marine Genomics, 24: 313-318.
|
| [33] |
SEVILGEN D S, VENN A A, HU M Y, et al, 2019. Full in vivo characterization of carbonate chemistry at the site of calcification in corals[J]. Science Advances, 5(1): eaau7447.
|
| [34] |
TOHSE H, MURAYAMA E, OHIRA T, et al, 2006. Localization and diurnal variations of carbonic anhydrase mRNA expression in the inner ear of the rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 145(3-4): 257-264.
|
| [35] |
VIDAL-DUPIOL J, ZOCCOLA D, TAMBUTTÉ E, et al, 2013. Genes related to ion-transport and energy production are upregulated in response to CO2-driven pH decrease in corals: New insights from transcriptome analysis[J]. PLos ONE, 8(3): e58652.
|
| [36] |
WEINER S, DOVE P M, 2003. An overview of biomineralization processes and the problem of the vital effect[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 54(1): 1-29.
|
| [37] |
YARDEN O, AINSWORTH T D, ROFF G, et al, 2007. Increased prevalence of ubiquitous ascomycetes in an acropoid coral (Acropora formosa) exhibiting symptoms of brown band syndrome and skeletal eroding band disease[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73(8): 2755-2757.
pmid: 17308192
|
| [38] |
ZOCCOLA D, GANOT P, BERTUCCI A, et al, 2015. Bicarbonate transporters in corals point towards a key step in the evolution of Cnidarian calcification[J]. Scientific Reports, 5(1): 9983.
|
| [39] |
ZOCCOLA D, TAMBUTTÉ E, KULHANEK E, et al, 2004. Molecular cloning and localization of a PMCA P-type calcium ATPase from the coral Stylophora pistillata[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1663(1-2): 117-126.
|
 ), 梁宇娴1,2,3,6, 宋严1,2,3,6, 俞晓磊1,2,3,6, 黄晖1,2,3,4,5, 周伟华1,2,3,4,5(
), 梁宇娴1,2,3,6, 宋严1,2,3,6, 俞晓磊1,2,3,6, 黄晖1,2,3,4,5, 周伟华1,2,3,4,5( )
)
 ), LIANG Yuxian1,2,3,6, SONG Yan1,2,3,6, YU Xiaolei1,2,3,6, HUANG Hui1,2,3,4,5, ZHOU Weihua1,2,3,4,5(
), LIANG Yuxian1,2,3,6, SONG Yan1,2,3,6, YU Xiaolei1,2,3,6, HUANG Hui1,2,3,4,5, ZHOU Weihua1,2,3,4,5( )
)