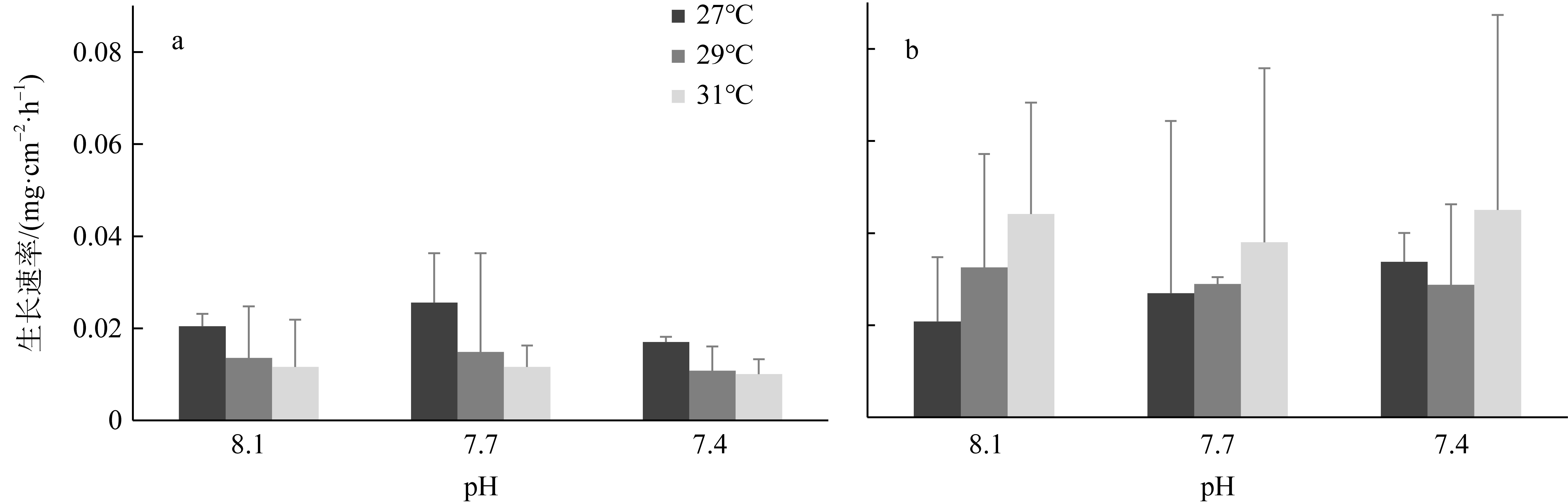
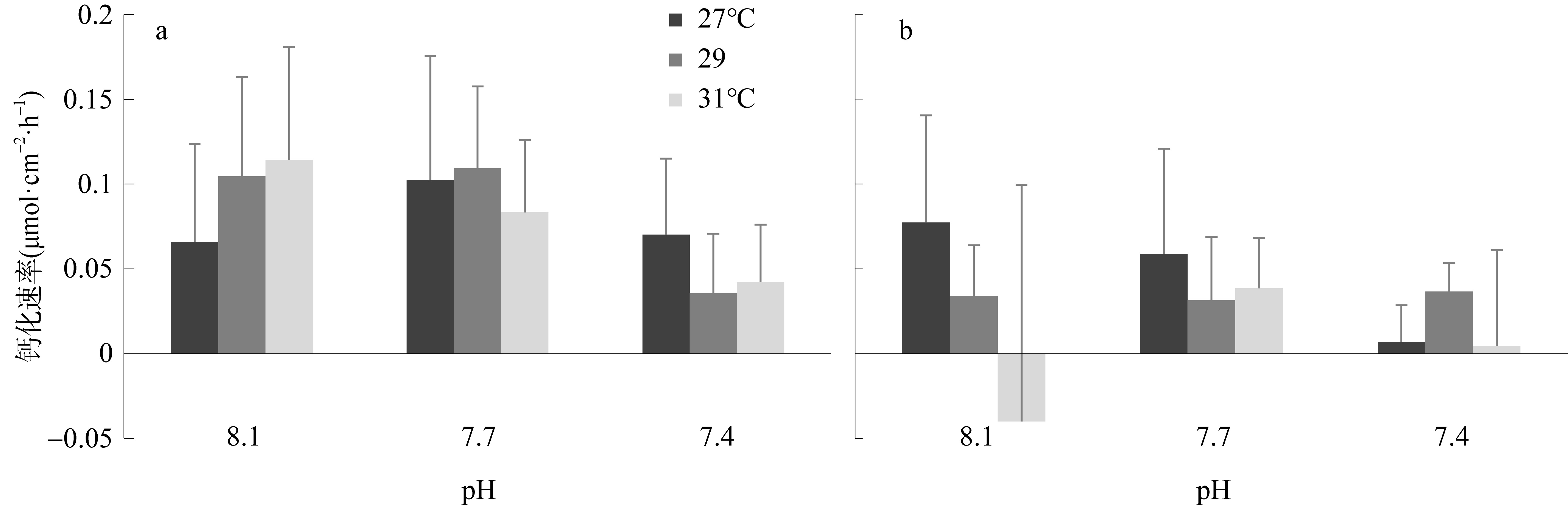
| [1] |
郭亚娟, 周伟华, 袁翔城, 等, 2018. 两种造礁石珊瑚对海水酸化和溶解有机碳加富的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 37(1): 57-63.
doi: 10.11978/2017018
|
|
GUO YAJUAN, ZHOU WEIHUA, YUAN XIANGCHENG, et al, 2018. Responses of two species of reef-building corals to acidification and dissolved organic carbon enrichment[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 37(1): 57-63 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
黄晖, 俞晓磊, 雷新明, 等, 2020. 环境变化对造礁石珊瑚营养方式的影响及其适应性[J]. 海洋科学进展, 38(2): 189-198.
|
|
HUANG HUI, YU XIAOLEI, LEI XINMING, et al, 2020. Research progress in the effects of environmental changes on the nutritional patterns and adaptability of the scleractinian corals[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 38(2): 189-198 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
江雷, 黄晖, 张浴阳, 等, 2016. 海水升温对壮实鹿角珊瑚幼虫存活和附着的影响[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 35(2): 217-222.
|
|
JIANG LEI, HUANG HUI, ZHANG YUYANG, et al, 2016. Effects of elevated temperature on larval survival and settlement of the broadcast spawning coral Acropora robusta[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 35(2): 217-222 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
李淑, 余克服, 施祺, 等, 2008. 海南岛鹿回头石珊瑚对高温响应行为的实验研究[J]. 热带地理, 28(6): 534-539.
|
|
LI SHU, YU KEFU, SHI QI, et al, 2008. Experimental study of stony coral response to the high temperature in Luhuitou of Hainan Island[J]. Tropical Geography, 28(6): 534-539 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
刘旭, 黄雯, 俞小鹏, 等, 2022. 适度热胁迫对造礁石珊瑚热耐受性影响的研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 44(1): 99-105.
|
|
LIU XU, HUANG WEN, YU XIAOPENG, et al, 2022. Studies on the effect of moderate heat stress on the heat tolerance of scleractinian coral[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 44(1): 99-105 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
骆雯雯, 梁甲元, 余克服, 等, 2019. 涠洲岛两种石珊瑚在高温胁迫下共生细菌群落结构变化特征[J]. 广西科学, 26(3): 299-307.
|
|
LUO WENWEN, LIANG JIAYUAN, YU KEFU, et al, 2019. Characteristics of symbiotic bacterial community structure changes in two species of stony corals in Weizhou Island under high temperature stress[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 26(3): 299-307 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
时翔, 谭烨辉, 黄良民, 等, 2008. 磷酸盐胁迫对造礁石珊瑚共生虫黄藻光合作用的影响[J]. 生态学报, 28(6): 2581-2586.
|
|
SHI XIANG, TAN YEHUI, HUANG LIANGMIN, et al, 2008. Effects of phosphate stress on the photosynthesis of symbiotic algae on the hermatypic corals[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28(6):2581-2586 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
孙有方, 江雷, 雷新明, 等, 2020. 海洋酸化、暖化对两种鹿角珊瑚幼虫附着及幼体存活的影响[J]. 海洋学报, 42(4): 96-103.
|
|
SUN YOUFANG, JIANG LEI, LEI XINMING, et al, 2020. Effects of ocean acidification and warming on the larvae settlement and post-settlement survival of two reef-building corals[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 42(4): 96-103 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
谭红建, 蔡榕硕, 颜秀花, 2018. 基于CMIP5预估21世纪中国近海海洋环境变化[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 37(2): 151-160.
|
|
TAN HONGJIAN, CAI RONGSHUO, YAN XIUHUA, 2018. Projecting changes of marine environment in coastal China Seas over 21st century based on CMIP5 Models[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 37(2): 151-160 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
张成龙, 黄晖, 黄良民, 等, 2012. 海洋酸化对珊瑚礁生态系统的影响研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 32(5): 1606-1615.
|
|
ZHANG CHENGLONG, HUANG HUI, HUANG LIANGMIN, et al, 2012. Research progress on the effects of ocean acidification on coral reef ecosystems[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32(5): 1606-1615 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
赵美霞, 余克服, 张乔民, 等, 2008. 三亚鹿回头石珊瑚物种多样性的空间分布[J]. 生态学报, 28(4): 1419-1428.
|
|
ZHAO MEIXIA, YU KEFU, ZHANG QIAOMIN, et al, 2008. Spatial pattern of coral diversity in Luhuitou fringing reef, Sanya[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28(4): 1419-1428 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
郑新庆, 郭富雯, 刘昕明, 等, 2015. 海洋酸化没有显著影响成体鹿角杯形珊瑚的钙化作用和光合能力[J]. 海洋学报, 37(10): 59-68.
|
|
ZHENG XINQING, GUO FUWEN, LIU XINMING, et al, 2015. Ocean acidification does not significantly affect the calcification and photosynthesis capacity of hermatypic coral Pocillopora damicornis[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 37(10): 59-68 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [13] |
ADZIS K A A, AMRI A Y, OLIVER J, et al, 2009. Effective and maximum quantum yield of the lace coral Pocillopora damicornis (Anthozoa: Scleractinia: Pocilloporidae) in Pulau Tioman, Malaysia[J]. Journal of Science and Technology in the Tropics, 5(1): 13-17.
|
| [14] |
ANDERSON K D, HERON S F, PRATCHETT M S, 2015. Species-specific declines in the linear extension of branching corals at a subtropical reef, Lord Howe Island[J]. Coral Reefs, 34(2): 479-490.
|
| [15] |
ANTHONY K R N, KLINE D I, DIAZ-PULIDO G, et al, 2008. Ocean acidification causes bleaching and productivity loss in coral reef builders[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(45): 17442-17446.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0804478105
pmid: 18988740
|
| [16] |
BAKER A C, STARGER C J, MCCLANAHAN T R, et al, 2004. Corals' adaptive response to climate change[J]. Nature, 430(7001): 741.
|
| [17] |
BUDDEMEIER R W, KINZIE R A, 1976. Coral growth[J]. Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual Review, 14: 183-225.
|
| [18] |
CHANCERELLE Y, 2000. Méthodes d'estimation des surfaces développées de coraux scléractiniaires à l'échelle d'une colonie ou d'un peuplement[J]. Oceanologica Acta, 23(2): 211-219.
|
| [19] |
COMEAU S, EDMUNDS P J, SPINDEL N B, et al, 2014. Fast coral reef calcifiers are more sensitive to ocean acidification in short-term laboratory incubations[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 59(3): 1081-1091.
|
| [20] |
COMEAU S, CARPENTER R C, LANTZ C A, et al, 2015. Ocean acidification accelerates dissolution of experimental coral reef communities[J]. Biogeosciences, 12(2): 365-372.
|
| [21] |
CRUZ-TRINIDAD A, ALIÑO P M, GERONIMO R C, et al, 2014. Linking food security with coral reefs and fisheries in the coral triangle[J]. Coastal Management, 42(2): 160-182.
|
| [22] |
DAVIES P S, 1989. Short-term growth measurements of corals using an accurate buoyant weighing technique[J]. Marine Biology, 101(3): 389-395.
|
| [23] |
EDMUNDS P J, 2005. The effect of sub-lethal increases in temperature on the growth and population trajectories of three scleractinian corals on the southern Great Barrier Reef[J]. Oecologia, 146(3): 350-364.
pmid: 16200400
|
| [24] |
IPCC, 2014. Climate change 2013: the physical science basis: working Group I contribution to the Fifth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press: 255-316.
|
| [25] |
JURY C P, TOONEN R J, 2019. Adaptive responses and local stressor mitigation drive coral resilience in warmer, more acidic oceans[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 286(1902): 20190614.
|
| [26] |
KORNDER N A, RIEGL B M, FIGUEIREDO J, 2018. Thresholds and drivers of coral calcification responses to climate change[J]. Global Change Biology, 24(11): 5084-5095.
doi: 10.1111/gcb.14431
pmid: 30152194
|
| [27] |
KWIATKOWSKI L, TORRES O, BOPP L, et al, 2020. Twenty-first century ocean warming, acidification, deoxygenation, and upper-ocean nutrient and primary production decline from CMIP6 model projections[J]. Biogeosciences, 17(13): 3439-3470.
|
| [28] |
MANULLANG C, MILLYANINGRUM I H, IGUCHI A, et al, 2020. Responses of branching reef corals Acropora digitifera and Montipora digitata to elevated temperature and pCO2[J]. PeerJ, 8: e10562.
|
| [29] |
MANZELLO D P, 2010. Coral growth with thermal stress and ocean acidification: lessons from the eastern tropical Pacific[J]. Coral Reefs, 29(3): 749-758.
|
| [30] |
MARSHALL A T, CLODE P, 2004. Calcification rate and the effect of temperature in a zooxanthellate and an azooxanthellate scleractinian reef coral[J]. Coral Reefs, 23(2): 218-224.
|
| [31] |
MUEHLLEHNER N, EDMUNDS P J, 2008. Effects of ocean acidification and increased temperature on skeletal growth of two scleractinian corals, Pocillopora meandrina and Porites rus[C]// Proceedings of the 11th international coral reef symposium. Ft. Lauderdale, Florida, USA: Nova Southeastern University National Coral Reef Institute, 3(2): 57-61.
|
| [32] |
RAVEN J, CALDEIRA K, ELDERFIELD H, et al, 2005. Ocean acidification due to increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide[M]. London: The Royal Society.
|
| [33] |
RAZAK T B, ROFF G, LOUGH J M, et al, 2020. Growth responses of branching versus massive corals to ocean warming on the Great Barrier Reef, Australia[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 705: 135908.
|
| [34] |
REYNAUD S, LECLERCQ N, ROMAINE-LIOUD S, et al, 2003. Interacting effects of CO2 partial pressure and temperature on photosynthesis and calcification in a scleractinian coral[J]. Global Change Biology, 9(11): 1660-1668.
|
| [35] |
SMITH S V, KINSEY D W, 1976. Calcium carbonate production, coral reef growth, and sea level change[J]. Science, 194(4268): 937-939.
pmid: 17748553
|
| [36] |
SMITH S V, 1978. Coral-reef area and the contributions of reefs to processes and resources of the world's oceans[J]. Nature, 273(5659): 225-226.
|
| [37] |
SPALDING M D, GRENFELL A M, 1997. New estimates of global and regional coral reef areas[J]. Coral Reefs, 16(4): 225-230.
|
| [38] |
STEINER Z, TURCHYN A V, HARPAZ E, et al, 2018. Water chemistry reveals a significant decline in coral calcification rates in the southern Red Sea[J]. Nature Communications, 9(1): 3615.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06030-6
pmid: 30190471
|
| [39] |
VAN DER ZANDE R M, ACHLATIS M, BENDER-CHAMP D, et al, 2020. Paradise lost: end-of-century warming and acidification under business-as-usual emissions have severe consequences for symbiotic corals[J]. Global Change Biology, 26(4): 2203-2219.
|
 ), 李颖心1,2,3,4, 郭亚娟5, 霍嘉欣1,2,3,4, 宋严1,2,3,4, 朱晴1,2,3,4, 袁翔城1,2,3(
), 李颖心1,2,3,4, 郭亚娟5, 霍嘉欣1,2,3,4, 宋严1,2,3,4, 朱晴1,2,3,4, 袁翔城1,2,3( ), 刘胜1,2,3, 黄晖1,2,3
), 刘胜1,2,3, 黄晖1,2,3
 ), LI Yingxin1,2,3,4, GUO Yajuan5, HUO Jiaxin1,2,3,4, SONG Yan1,2,3,4, ZHU Qing1,2,3,4, YUAN Xiangcheng1,2,3(
), LI Yingxin1,2,3,4, GUO Yajuan5, HUO Jiaxin1,2,3,4, SONG Yan1,2,3,4, ZHU Qing1,2,3,4, YUAN Xiangcheng1,2,3( ), LIU Sheng1,2,3, HUANG Hui1,2,3
), LIU Sheng1,2,3, HUANG Hui1,2,3