热带海洋学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (1): 53-65.doi: 10.11978/2024046CSTR: 32234.14.2024046
基于形态学和高通量测序的春季南澳海域浮游植物群落特征及其与环境因子关系
周志希1( ), 唐汇娟1(
), 唐汇娟1( ), 柯志新2,3, 刘甲星2, 周伟华2
), 柯志新2,3, 刘甲星2, 周伟华2
- 1.华南农业大学, 广东 广州 510640
2.中国科学院热带海洋生物资源与生态重点实验室, 中国科学院南海海洋研究所, 广东 广州 510301
3.粤东上升流区海洋生态系统综合观测研究站, 广东 汕头 515041
-
收稿日期:2024-02-28修回日期:2024-03-25出版日期:2025-01-10发布日期:2025-02-10 -
通讯作者:唐汇娟 -
作者简介:周志希(1999—), 男, 湖北省荆州市人, 硕士研究生, 主要从事海洋浮游植物生态学研究。email: 20223140078@stu.scau.edu.cn
-
基金资助:广东省科技计划项目(2021B1212050023); 广东省基础与应用研究金(2022A1515010656); 广州市重点研发计划(2023B03J1328)
Phytoplankton community structure and its relationship with environmental factors in the spring coastal region of Nan’ao based on morphology and high-throughput sequencing
ZHOU Zhixi1( ), TANG Huijuan1(
), TANG Huijuan1( ), KE Zhixin2,3, LIU Jiaxing2, ZHOU Weihua2
), KE Zhixin2,3, LIU Jiaxing2, ZHOU Weihua2
- 1. South China Agricultural University, Guangzhou 510640, China
2. Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
3. Comprehensive Observatory of Marine Ecosystems in the Upwelling Regions of Eastern Guangdong, Shantou 515041, China
-
Received:2024-02-28Revised:2024-03-25Online:2025-01-10Published:2025-02-10 -
Contact:TANG Huijuan -
Supported by:Special Fund for Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province of China(2021B1212050023); Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation(2022A1515010656); Guangzhou Municipal Key Science and Technology Project(2023B03J1328)
摘要:
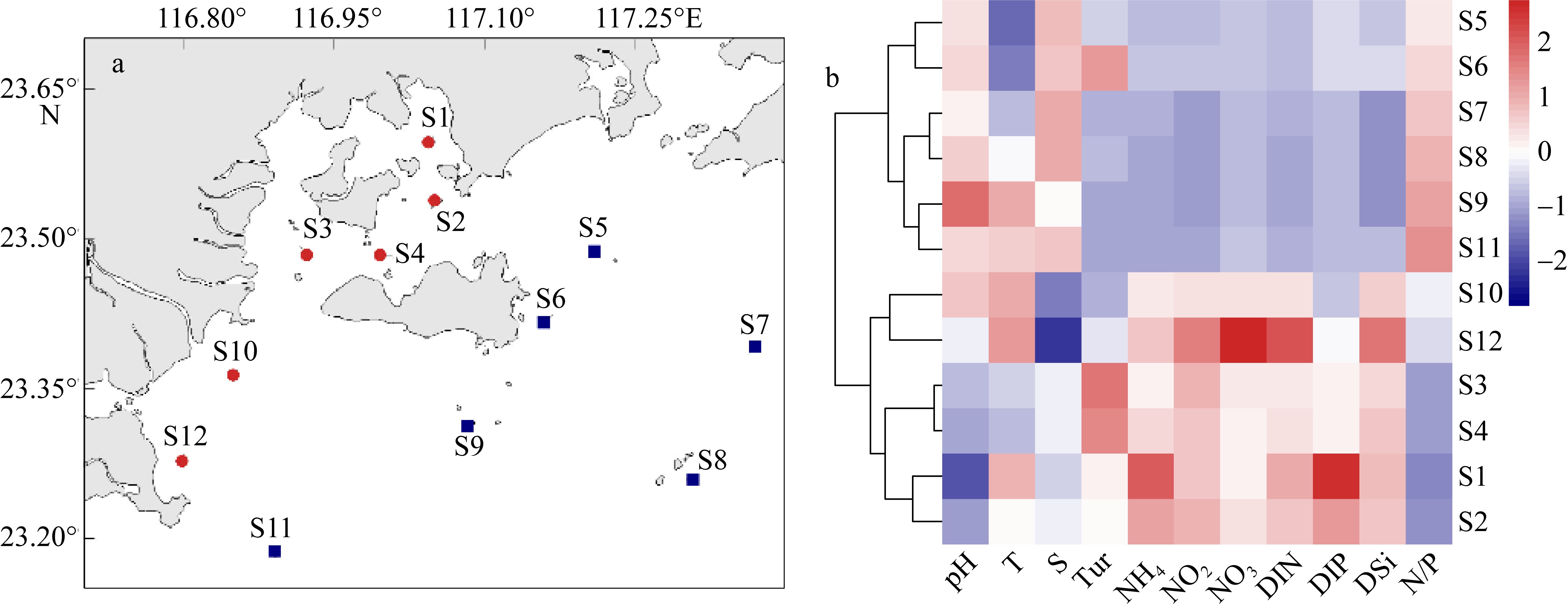
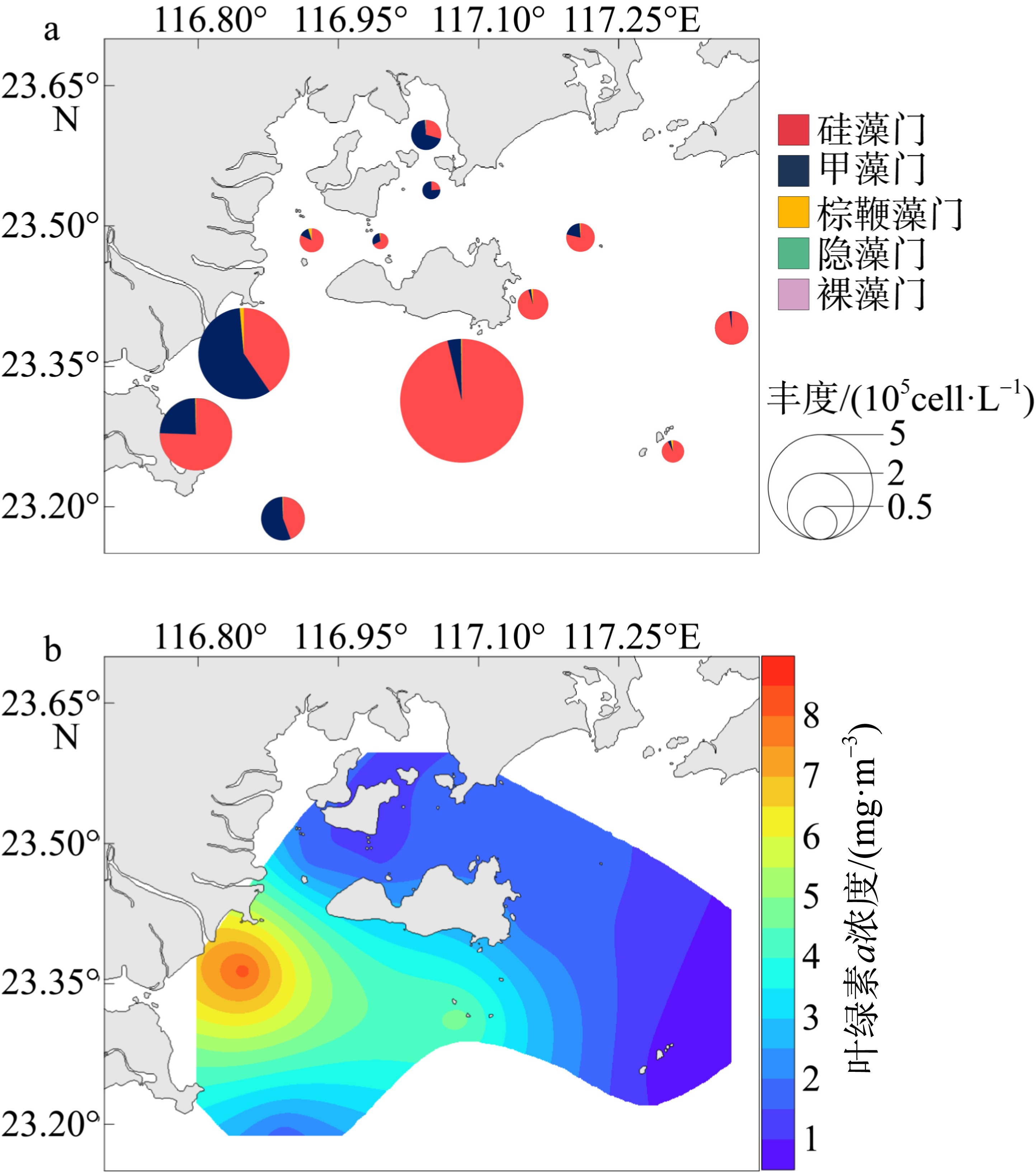
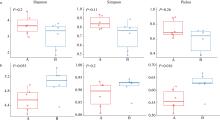
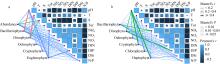
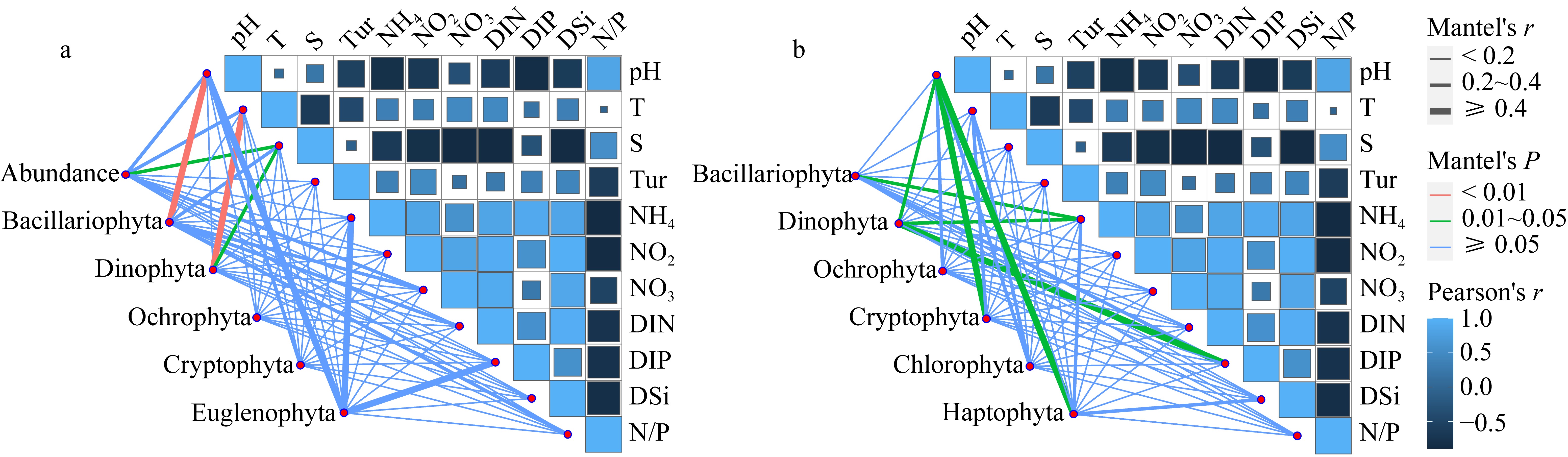
利用形态学鉴定和高通量测序技术, 对2022年5月南澳海域浮游植物群落结构进行了研究, 探讨其空间分布与环境因子的关系, 并对两种不同方法得出的结果进行了比较和讨论。根据环境因子聚类分析, 调查海域可分为近岸区域和远岸区域。通过形态学方法鉴定浮游植物5门8纲27目39科52属105种, 高通量测序鉴定出6门32纲97目155科272属 543种, 其中硅藻门(Bacillariophyta)和甲藻门(Dinophyta)为优势类群, 分别平均占形态学鉴定结果的74.54%和24.78%以及高通量测序结果的 17.52%和67.84%。形态学鉴定结果显示浮游植物丰度变化范围为0.11×105~6.85×105cells·L-1, 与叶绿素a浓度分布显著相关, 浮游植物多样性指数低于高通量测序方法。两种方法得到优势种均为7种, 其中形态学鉴定结果中绝对优势种为扁面角毛藻(Chaetoceros compressus), 高通量测序鉴定结果中绝对优势种为球形异帽藻(Heterocapsa rotundata)。相关性分析结果表明, 春季影响南澳浮游植物群落结构的主要环境因子是pH、盐度和溶解态无机磷。利用形态学鉴定与高通量测序技术相结合的方法, 可以更全面、更准确地描述浮游植物群落结构及多样性。
中图分类号:
- P735
引用本文
周志希, 唐汇娟, 柯志新, 刘甲星, 周伟华. 基于形态学和高通量测序的春季南澳海域浮游植物群落特征及其与环境因子关系[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(1): 53-65.
ZHOU Zhixi, TANG Huijuan, KE Zhixin, LIU Jiaxing, ZHOU Weihua. Phytoplankton community structure and its relationship with environmental factors in the spring coastal region of Nan’ao based on morphology and high-throughput sequencing[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(1): 53-65.
表1
2022年5月南澳近海不同海域环境因子差异及检验显著性"
| 因子 | 温度/℃ | 盐度/‰ | pH | 浊度/NTU | DIN/(μmol·L-1) | DIP/(μmol·L-1) | DSi/(μmol·L-1) | 氮磷比 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 近岸 | 23.55±0.39 | 28.04±1.85 | 8.03±0.09 | 4.17±2.63 | 12.31±4.39 | 0.77±0.59 | 24.56±4.55 | 26.13±21.53 |
| 远岸 | 23.22±0.50 | 31.37±0.78 | 8.16±0.06 | 1.93±2.22 | 2.06±0.64 | 0.16±0.09 | 7.20±3.61 | 105.08±18.47 |
| t-test | t=1.528, P=0.187 | t=5.126, P<0.01 | t=5.665, P<0.01 | t=1.53, P=0.187 | t=5.81, P<0.05 | t=2.95, P<0.05 | t=8.93, P<0.01 | t=17.45, P<0.01 |
表2
2022年5月南澳海域浮游植物优势种"
| 分类水平 | 优势度 | 出现频率% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 门 | 种 | 形态学鉴定 | 高通量测序 | |
| 硅藻门Bacillariophyta | 扁面角毛藻Chaetoceros compressus | 0.33 | - | 83.33 |
| 微眼藻Minutocellus sp. | - | 0.05 | 100 | |
| 多形微眼藻Minutocellus polymorphus | - | 0.03 | 100 | |
| 艾氏角毛藻Chaetoceros eibenii | 0.02 | - | 58.33 | |
| 洛氏菱形藻Nitzschia lorenziana | 0.02 | - | 83.33 | |
| 尖刺拟菱形藻Pseudo-nitzschia pungens | 0.02 | - | 100 | |
| 中肋骨条藻Skeletonema costatum | 0.02 | - | 41.67 | |
| 甲藻门 Dinophyta | 球形异帽藻Heterocapsa rotundata | - | 0.22 | 100 |
| 海洋原甲藻Prorocentrum micans | 0.13 | - | 100 | |
| 剧毒卡洛藻Karlodinium veneficum | - | 0.09 | 100 | |
| 单眼藻Warnowia sp. | - | 0.09 | 100 | |
| 单眼藻Warnowia spp. | 0.07 | 100 | ||
| 锥状斯氏藻Scrippsiella trochoidea | 0.02 | - | 83.33 | |
| 绿藻门Chlorophyta | 共球藻目Picochlorum sp. | - | 0.03 | 100 |
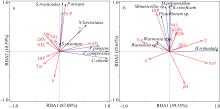
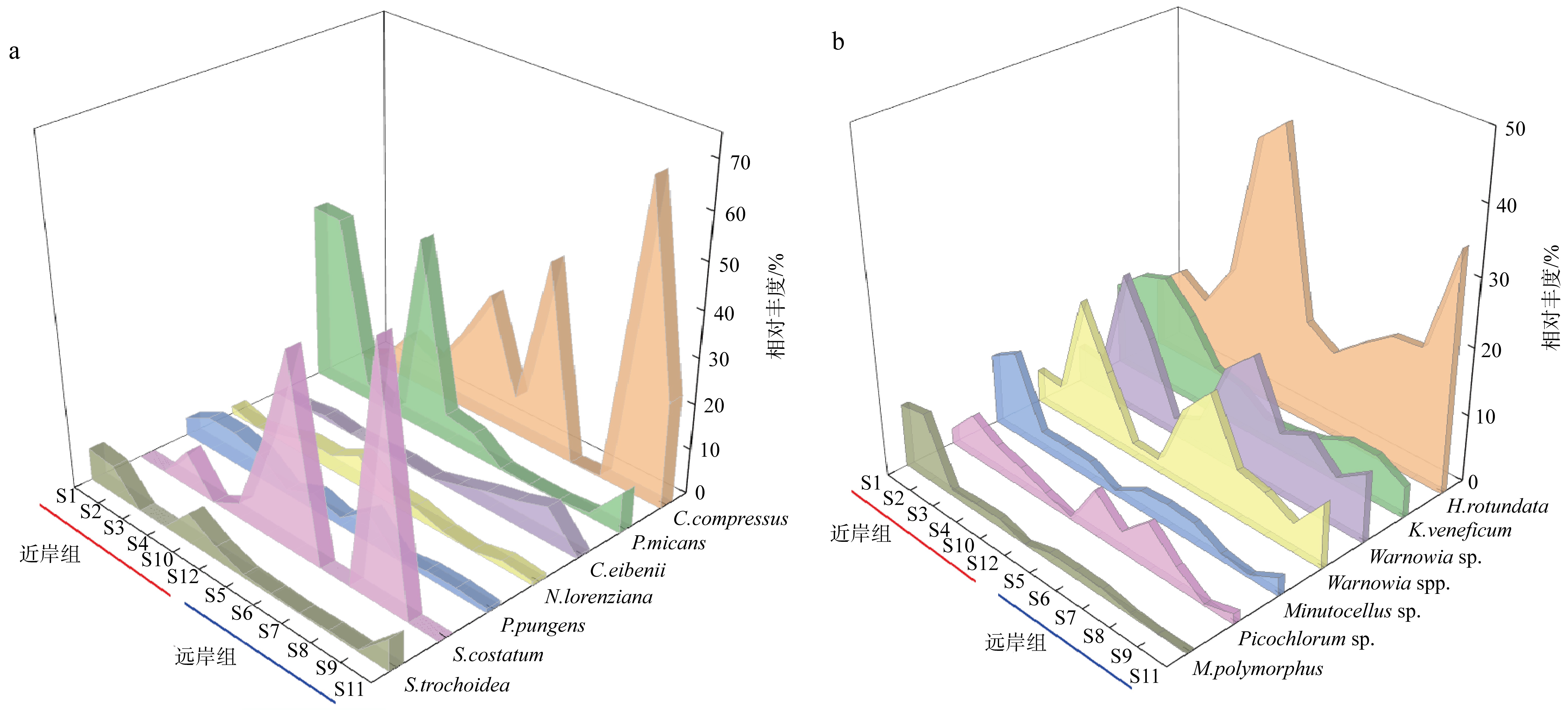
图6
形态学鉴定(a)和高通量测序(b)的浮游植物优势种相对丰度及分布情况 C. compressus为扁面角毛藻, C. eibenii为艾氏角毛藻, N. lorenziana为洛氏菱形藻, P. pungens为尖刺拟菱形藻, S. costatum为中肋骨条藻, P. micans为海洋原甲藻, S. trochoidea锥状斯氏藻, H. rotundata为球形异帽藻, K. veneficum为剧毒卡洛藻, Warnowia sp.和Warnowia spp.为单眼藻, Minutocellus sp. 为微眼藻, Picochlorum sp. 属于共球藻目, M. polymorphus为多形微眼藻"
| [1] |
蔡德华, 陈振明, 唐书怿, 2020. 南澳岛周边海域海水质量近10年变化趋势浅析[J]. 环境影响评价, 42(2): 63-66.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈丹婷, 柯志新, 谭烨辉, 等, 2020. 汕头南澳-东山海域营养盐季节分布特征及其对浮游植物生长的潜在性限制[J]. 生态科学, 39(4): 41-50.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
陈菊芳, 齐雨藻, 徐宁, 等, 2005. 大亚湾拟菱形藻水华及其在生物群落中的生态地位[J]. 海洋学报, 27(1): 114-119.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
陈炜婷, 姜广甲, 邓伟, 等, 2023. 基于GIS的2001-2020年广东近岸海域赤潮时空分布[J]. 环境工程, 41(S2): 49-53.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
杜虹, 王亮根, 曹会彬, 等, 2011. 汕头港浮游植物组成特征及其与环境的关系[J]. 生态学杂志, 30(8): 1757-1765.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
郭玉洁, 2003. 中国海藻志[M]. 北京: 科学出版社 (in Chinese).
|
| [7] |
黄长江, 董巧香, 郑磊, 1999. 1997年底中国东南沿海大规模赤潮原因生物的形态分类与生态学特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 30(6): 581-590.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
黄圆, 岑竞仪, 梁芊艳, 等, 2024. 基于高通量测序技术的深圳湾真核浮游植物群落结构研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 43(2): 21-33.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
暨卫东, 黄尚高, 1990. 台湾海峡西部营养盐变化特征-Ⅲ. 水系混合及浮游植物摄取转移对磷酸盐含量变化影响的统计分析[J]. 海洋学报, 12(4): 447-454 (in Chinese).
|
| [10] |
雷光英, 杨宇峰, 李宵, 2010. 龙须菜对赤潮异弯藻和海洋原甲藻的生长抑制效应[J]. 海洋环境科学, 29(1): 27-31.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
李冀刚, 杨振雄, 葛颂, 等, 2023. 汕头韩江榕江河口近岸海域浮游植物群落结构与环境因子的关系[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 45(2): 133-141.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
黎素菊, 洪捷娴, 陈树鹏, 2022. 柘林湾养殖区氮、磷季节分布特征及富营养化评价[J]. 江西水产科技, (4): 45-47, 51 (in Chinese).
|
| [13] |
李欣, 孙军, 田伟, 等, 2012. 2009年夏季南海北部的浮游植物群落[J]. 海洋科学, 36(10): 33-39.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
林更铭, 杨清良, 2021. 西太平洋浮游植物物种多样性[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
刘陈, 魏南, 王庆, 等, 2019. 广东汕头南澳岛近岸海域浮游植物群落结构与环境特征[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 25(5): 1091-1098.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
刘卫东, 宋伦, 吴景, 2017. 环境样本中微型和微微型浮游植物高通量测序的引物优化[J]. 生态学报, 37(12): 4208-4216.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
刘旭平, 单忠才, 李媛芳, 等, 2023. 滤食性贝类选择性摄食行为研究现状[J]. 特种经济动植物, 26(5): 89-92, 107 (in Chinese).
|
| [18] |
马华栋, 王平, 温玉波, 等, 2021. 基于生态足迹分析的南澳岛旅游业可持续发展评估[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 38(8): 61-66.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
彭璇, 马胜伟, 陈海刚, 等, 2014. 夏季柘林湾-南澳岛海洋牧场营养盐的空间分布及其评价[J]. 南方水产科学, 10(6): 27-35.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
宋荪阳, 黄金臣, 岳强, 等, 2023. 唐山市海水养殖尾水监测及分析[J]. 河北渔业, (7): 23-29.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
苏纪兰, 王卫, 1990. 南海域台湾暖流源地问题[J]. 东海海洋, 8(3): 1-9.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
孙军, 刘东艳, 2004. 多样性指数在海洋浮游植物研究中的应用[J]. 海洋学报, 26(1): 62-75.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
孙军, 2007. 今生颗石藻的有机碳泵和碳酸盐反向泵[J]. 地球科学进展, 22(12): 1231-1239.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
谭香, 夏小玲, 程晓莉, 等, 2011. 丹江口水库浮游植物群落时空动态及其多样性指数[J]. 环境科学, 32(10): 2875-2882.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
唐涛, 蔡庆华, 刘建康, 2002. 河流生态系统健康及其评价[J]. 应用生态学报, 13(9): 1191-1194.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
王艳, 聂瑞, 李扬, 等, 2010. 广东沿海角毛藻(Chaetoceros)的种类多样性及其地理分布[J]. 海洋科学进展, 28(3): 342-352.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
王雨, 林茂, 林更铭, 等, 2011. 闽粤近岸夏季上升流区浮游植物群落组成及其影响因素[J]. 应用生态学报, 22(2): 503-512.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
吴转璋, 朱超, 唐萍, 等, 2023. 巢湖湖区浮游植物群落与水质因子相关性分析[J]. 生物学杂志, 40(1): 79-84.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员, 2007. GB/T12763. 6-2007海洋调查规范第6部分:海洋生物调查 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 6-37.
|
|
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China, 2007. GB/T12763. 6-2007 Specifications for oceanographic survey—Part 6: Marine biological survey[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China: 6-37 (in Chinese).
|
|
| [30] |
中华人民共和国生态环境部,2020. 近岸海域环境监测规范(HJ 442. 3-2020)第三部分近岸海域水质监测[S]. 北京: 中国环境出版集团出版.
|
|
Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, 2020. Technical specification for offshore environmental monitoring Part 3 offshore seawater quality monitoring[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press.
|
|
| [31] |
周凯, 黄长江, 姜胜, 等, 2002. 2000-2001年柘林湾浮游植物群落结构及数量变动的周年调查[J]. 生态学报, 22(5): 688-698.
|
|
|
|
| [32] |
朱小山, 吴玲玲, 杨瑶, 等, 2005. 粤东柘林湾增养殖区氮磷的分布特征及其富营养化状态评价[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, (3): 16-22.
|
|
|
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [1] | 柳原, 柯志新, 李开枝, 谭烨辉, 梁竣策, 周伟华. 人类活动和沿岸流影响下的粤东近海浮游动物群落特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [2] | 刘玓玓, 张喜洋, 孙富林, 王明壮, 谭飞, 施祺, 王冠, 杨红强. 南海海滩岩微生物群落结构和特定菌株对其成因机制的启示*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 112-122. |
| [3] | 胡思敏, 周天成, 张琛, 刘胜, 李涛, 黄晖. 悬浮物对三亚珊瑚礁区浮游动物群落结构及其摄食的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 122-130. |
| [4] | 贾男, 周天成, 胡思敏, 张琛, 黄晖, 刘胜. 南沙群岛海域珊瑚礁区三种寄居蟹的摄食差异比较[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 109-121. |
| [5] | 罗勇, 黄林韬, 杨剑辉, 练健生, 刘骋跃, 江雷, 梁宇娴, 陈伦举, 雷新明, 刘胜, 黄晖. 海南临高红牌—马袅沿岸海域造礁石珊瑚群落结构及其环境影响因子[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 72-86. |
| [6] | 林先智, 周岩岩, 林皓晔, 胡思敏, 黄晖, 张黎, 刘胜. 南沙群岛珊瑚礁区黑斑鹦嘴鱼(Scarus globiceps)食性分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 100-108. |
| [7] | 黄圆, 岑竞仪, 梁芊艳, 吕颂辉, 王建艳. 基于高通量测序技术的深圳湾真核浮游植物群落结构研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 21-33. |
| [8] | 耿婉璐, 邢永泽, 张秋丰, 管卫兵. 广西北海红树林宜林滩涂大型底栖动物群落结构特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(1): 107-115. |
| [9] | 孙婷婷, 郝雯瑾, 徐鹏臻, 叶丽靖, 董志军. 海水酸化对海月水母螅状体共附生微生物的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(6): 111-119. |
| [10] | 张兰兰, 程夏雯, 向荣, 邱卓雅, 常虎. 2019年春季孟加拉湾中部放射虫群落结构垂向变化*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(4): 166-175. |
| [11] | 宋星宇, 林雅君, 张良奎, 向晨晖, 黄亚东, 郑传阳. 粤港澳大湾区近海中小型浮游动物分布特征及影响因素*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 136-148. |
| [12] | 赵红五一, 周雯, 曾凯, 邓霖, 廖健祖, 曹文熙. 基于浮游植物吸收系数和光合有效辐射的南海区域性分粒级初级生产力算法初探[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(1): 43-55. |
| [13] | 陈靖夫, 钟瑜, 王磊, 郭雨沛, 邱大俊. 环境DNA分析大亚湾夜光藻藻华对真核浮游生物群落的影响*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(5): 121-132. |
| [14] | 周雯, 魏盼盼, 李彩, 王桂芬, 郑文迪, 邓霖, 赵红五一, 余凌晖, 曹文熙. 琼东水体后向散射系数与浮游植物生物量的关系模型*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(3): 29-37. |
| [15] | 马文刚, 夏景全, 魏一凡, 尹洪洋, 覃乐政, 刘相波, 胡雪晴, 许强, 李秀保, 王爱民. 三亚蜈支洲岛海洋牧场近岛区底表大型底栖动物群落结构及评价[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(3): 135-146. |
|
||