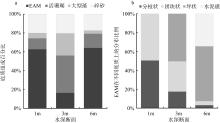
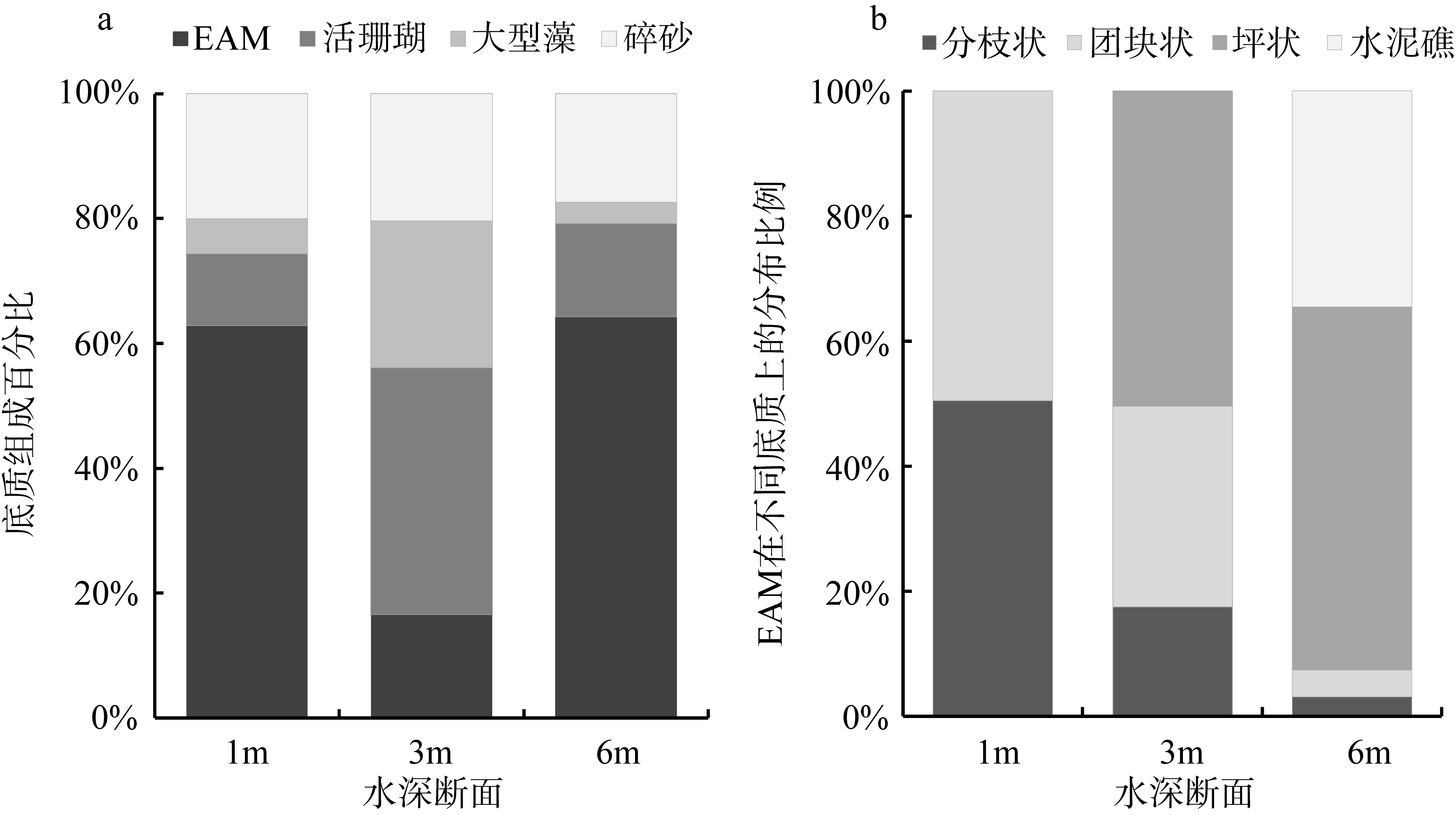
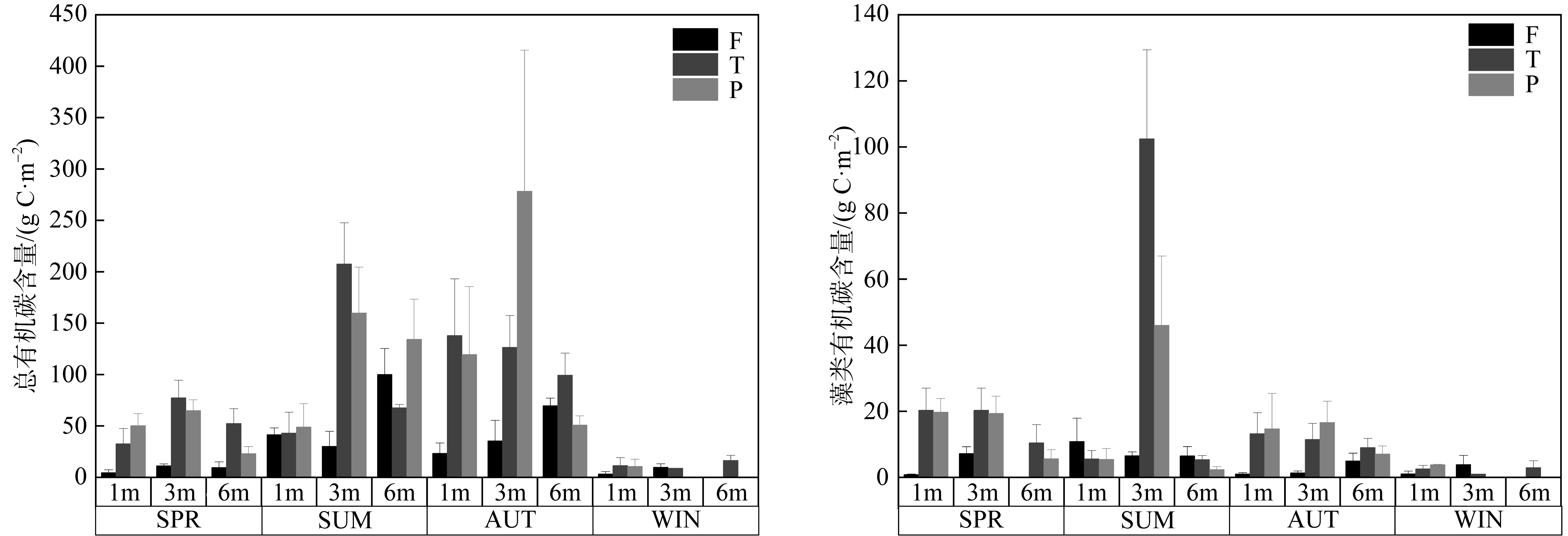
| [1] |
梁宇娴, 俞晓磊, 郭亚娟, 等, 2020. 3种传统方法对不同珊瑚表面积测量的适用性及其校准方法—以3D扫描技术为基准[J]. 热带海洋学报, 39(1): 85-93.
doi: 10.11978/2019039
|
|
LIANG YUXIAN, YU XIAOLEI, GUO YAJUAN, et al, 2020. Applicability and calibration methods of three traditional surface area measurement methods for different coral species—based on 3D scanning technology[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 39(1): 85-93 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
廖芝衡, 2021. 南海珊瑚群落和底栖海藻的空间分布特征及其生态影响[D]. 南宁: 广西大学.
|
|
LIAO ZHIHENG, 2021. Spatial distribution of coral community and benthic algae and their ecological impacts across the South China Sea[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
ARJUNWADKAR C V, TEBBETT S B, BELLWOOD D R, et al, 2022. Algal turf structure and composition vary with particulate loads on coral reefs[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 181: 113903.
|
| [4] |
BARROS G S F, CORDEIRO C A M M, FERREIRA C E L, 2024. Structuring patterns of the epilithic algal matrix cryptofauna in a tropical oceanic reef[J]. Regional Studies in Marine Science, 69: 103292.
|
| [5] |
BELLWOOD D R, FULTON C J, 2008. Sediment-mediated suppression of herbivory on coral reefs: Decreasing resilience to rising sea-levels and climate change?[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 53(6): 2695-2701.
|
| [6] |
BELLWOOD D R, TEBBETT S B, BELLWOOD O, et al, 2018. The role of the reef flat in coral reef trophodynamics: Past, present, and future[J]. Ecology and Evolution, 8(8): 4108-4119.
doi: 10.1002/ece3.3967
pmid: 29721284
|
| [7] |
BLANCHETTE A, ELY T, ZEKO A, et al, 2019. Damselfish Stegastes nigricans increase algal growth within their territories on shallow coral reefs via enhanced nutrient supplies[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 513: 21-26.
|
| [8] |
BROKOVICH E, AYALON I, EINBINDER S, et al, 2010. Grazing pressure on coral reefs decreases across a wide depth gradient in the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 399: 69-80.
|
| [9] |
CARPENTER R C, 1985. Relationships between primary production and iiradiance in coral reef algal communities[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 30(4): 784-793.
|
| [10] |
CARPENTER R C, 1986. Partitioning herbivory and its effects on coral reef algal communities[J]. Ecological Monographs, 56(4): 345-363.
|
| [11] |
CLAUSING R J, ANNUNZIATA C, BAKER G, et al, 2014. Effects of sediment depth on algal turf height are mediated by interactions with fish herbivory on a fringing reef[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 517: 121-129.
|
| [12] |
CONNELL S D, FOSTER M S, AIROLDI L, 2014. What are algal turfs? Towards a better description of turfs[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 495: 299-307.
doi: 10.3354/meps10513
|
| [13] |
COOPER A M, MACDONALD C, ROBERTS T E, et al, 2019. Variability in the functional composition of coral reef fish communities on submerged and emergent reefs in the central Great Barrier Reef, Australia[J]. PloS One, 14(5): e0216785.
|
| [14] |
COPERTINO M, CONNELL S D, CHESHIRE A, 2005. The prevalence and production of turf-forming algae on a temperate subtidal coast[J]. Phycologia, 44(3): 241-248.
|
| [15] |
DISHON G, DUBINSKY Z, FINE M, et al, 2012. Underwater light field patterns in subtropical coastal waters: A case study from the Gulf of Eilat (Aqaba)[J]. Israel Journal of Plant Sciences, 60(1-2): 265-275.
|
| [16] |
FANG J K H, SCHÖNBERG C H L, KLINE D I, et al, 2013. Methods to quantify components of the excavating sponge Cliona orientalis Thiele, 1900[J]. Marine Ecology, 34(2): 193-206.
|
| [17] |
FLOWER J, ORTIZ J C, CHOLLETT I, et al, 2017. Interpreting coral reef monitoring data: A guide for improved management decisions[J]. Ecological Indicators, 72: 848-869.
|
| [18] |
FONG C R, BITTICK S J, FONG P, 2018. Simultaneous synergist, antagonistic and additive interactions between multiple local stressors all degrade algal turf communities on coral reefs[J]. Journal of Ecology, 106(4): 1390-1400.
|
| [19] |
FRICKE A, TEICHBERG M, NUGUES M M, et al, 2014. Effects of depth and ultraviolet radiation on coral reef turf algae[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 461: 73-84.
|
| [20] |
GOATLEY C H R, BELLWOOD D R, 2011. The roles of dimensionality, canopies and complexity in ecosystem monitoring[J]. PloS One, 6(11): e27307.
|
| [21] |
GOATLEY C H R, BONALDO R M, FOX R J, et al, 2016. Sediments and herbivory as sensitive indicators of coral reef degradation[J]. Ecology and Society, 21(1): 29.
|
| [22] |
HACKNEY J M, SZE P, 1988. Photorespiration and productivity rates of a coral reef algal turf assemblage[J]. Marine Biology, 98(4): 483-492.
|
| [23] |
HARRIS J L, LEWIS L S, SMITH J E, 2015. Quantifying scales of spatial variability in algal turf assemblages on coral reefs[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 532: 41-57.
|
| [24] |
HUANG RONGYONG, YU KEFU, HUANG XUEYONG, et al, 2019. Combining Landsat images with historic records to estimate the live coral cover of Luhuitou fringing reef in Northern South China Sea[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 92: 103812.
|
| [25] |
HUANG LINTAO, JIANG LEI, YU XIAOLEI, et al, 2025. Conservation priorities for reef-building coral biodiversity across multiple dimensions in the South China Sea[J]. Coral Reefs, 44: 113-127.
|
| [26] |
KARCHER D B, ROTH F, CARVALHO S, et al, 2020. Nitrogen eutrophication particularly promotes turf algae in coral reefs of the central Red Sea[J]. PeerJ, 8: e8737.
|
| [27] |
KARIMI Z, DAIL LAUGHINGHOUSE H D 4TH, DAVIS V A, et al, 2021. Substrate properties as controlling parameters in attached algal cultivation[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 105(5): 1823-1835.
doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11127-y
pmid: 33564919
|
| [28] |
KENCH P S, BRANDER R W, 2006. Wave processes on coral reef flats: Implications for reef geomorphology using Australian case studies[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 22(1): 209-223.
|
| [29] |
KLUMPP D W, MCKINNON A D, 1989. Temporal and spatial patterns in primary production of a coral-reef epilithic algal community[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 131(1): 1-22.
|
| [30] |
KOHLER K E, GILL S M, 2006. Coral point count with excel extensions (CPCe): A visual basic program for the determination of coral and substrate coverage using random point count methodology[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 32(9): 1259-1269.
|
| [31] |
LI XIUBAO, TITLYANOV E A, ZHANG JING, et al, 2016. Macroalgal assemblage changes on coral reefs along a natural gradient from fish farms in southern Hainan Island[J]. Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management, 19(1): 74-82.
|
| [32] |
LIDDLE L B, 1975. The effect of intertidal stress on Padina sanctae-crueis (Phaeophyta)[J]. Journal of Phycology, 11(3): 327-330.
|
| [33] |
LITTLER M M, LITTLER D S, BROOKS B L, 2010. The effects of nitrogen and phosphorus enrichment on algal community development: Artificial mini-reefs on the Belize Barrier Reef sedimentary lagoon[J]. Harmful Algae, 9(3): 255-263.
|
| [34] |
LUO YONG, HUANG LINTAO, LEI XINMING, et al, 2022. Light availability regulated by particulate organic matter affects coral assemblages on a turbid fringing reef[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 177: 105613.
|
| [35] |
MAGALHÃES G M, AMADO-FILHO G M, ROSA M R, et al, 2015. Changes in benthic communities along a 0-60 m depth gradient in the remote St. Peter and St. Paul Archipelago (Mid-Atlantic Ridge, Brazil)[J]. Bulletin of Marine Science, 91(3): 377-396.
|
| [36] |
QUIMPO T J R, LIGSON C A, MANOGAN D P, et al, 2020. Fish farm effluents alter reef benthic assemblages and reduce coral settlement[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 153: 111025.
|
| [37] |
RAVEN J A, TAYLOR R, 2003. Macroalgal growth in nutrient-enriched estuaries: a biogeochemical and evolutionary perspective[J]. Water, Air and Soil Pollution: Focus, 3(1): 7-26.
|
| [38] |
ROTH F, KARCHER D B, RÄDECKER N, et al, 2020. High rates of carbon and dinitrogen fixation suggest a critical role of benthic pioneer communities in the energy and nutrient dynamics of coral reefs[J]. Functional Ecology, 34(9): 1991-2004.
|
| [39] |
SAMMARCO P W, 1983. Effects of fish grazing and damselfish territoriality on coral reef algae. I. Algal community structure[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 13(1): 1-14.
|
| [40] |
STENECK R S, MUMBY P J, MACDONALD C, et al, 2018. Attenuating effects of ecosystem management on coral reefs[J]. Science Advances, 4(5): eaao5493.
|
| [41] |
SURA S A, DELGADILLO A, FRANCO N, et al, 2019. Macroalgae and nutrients promote algal turf growth in the absence of herbivores[J]. Coral Reefs, 38(3): 425-429.
|
| [42] |
TEBBETT S B, BELLWOOD D R, 2021. Algal turf productivity on coral reefs: A meta-analysis[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 168: 105311.
|
| [43] |
TEBBETT S B, SGARLATTA M P, PESSARRODONA A, et al, 2022. How to quantify algal turf sediments and particulates on tropical and temperate reefs: An overview[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 179: 105673.
|
| [44] |
TEBBETT S B, BELLWOOD D R, 2020. Sediments ratchet-down coral reef algal turf productivity[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 713: 136709.
|
| [45] |
TEBBETT S B, BELLWOOD D R, 2019. Algal turf sediments on coral reefs: what’s known and what’s next[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 149: 110542.
|
| [46] |
TEBBETT S B, BELLWOOD D R, PURCELL S W, 2018. Sediment addition drives declines in algal turf yield to herbivorous coral reef fishes: implications for reefs and reef fisheries[J]. Coral Reefs, 37(3): 929-937.
|
| [47] |
TITLYANOV E A, TITLYANOVA T V, HUANG HUI, et al, 2019. Seasonal changes in the intertidal and subtidal algal communities of extremely and moderately polluted coastal regions of Sanya Bay (Hainan Island, China)[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 7(4): 93.
|
| [48] |
VERMEIJ M J A, VAN MOORSELAAR I, ENGELHARD S, et al, 2010. The effects of nutrient enrichment and herbivore abundance on the ability of turf algae to overgrow coral in the Caribbean[J]. PLoS One, 5(12): e14312.
|
| [49] |
WALDEN G, NOIROT C, NAGELKERKEN I, 2019. A future 1. 2 ℃ increase in ocean temperature alters the quality of mangrove habitats for marine plants and animals[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 690: 596-603.
|
| [50] |
WILSON S, BELLWOOD D R, 1997. Cryptic dietary components of territorial damselfishes (Pomacentridae, Labroidei)[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 153: 299-310.
|
| [51] |
WILSON S K, 2002. Nutritional value of detritus and algae in blenny territories on the Great Barrier Reef[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 271(2): 155-169.
|
| [52] |
WILSON S K, BELLWOOD D R, CHOAT J H, et al, 2003. Detritus in the epilithic algal matrix and its use by coral reef fishes[J]. Oceanography and Marine Biology, 41: 279-309.
|
| [53] |
ZHANG QIAOMIN, SHI QI, CHEN GANG, et al, 2006. Status monitoring and health assessment of Luhuitou fringing reef of Sanya, Hainan, China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 51(Suppl 2): 81-88.
|
 ), 周天成1,3, 张琛1,4, 贾男1,4, 刘胜1,2(
), 周天成1,3, 张琛1,4, 贾男1,4, 刘胜1,2( ), 李涛1,2,5, 黄晖1,2,5
), 李涛1,2,5, 黄晖1,2,5
 ), ZHOU Tiancheng1,3, ZHANG Chen1,4, JIA Nan1,4, LIU Sheng1,2(
), ZHOU Tiancheng1,3, ZHANG Chen1,4, JIA Nan1,4, LIU Sheng1,2( ), LI Tao1,2,5, HUANG Hui1,2,5
), LI Tao1,2,5, HUANG Hui1,2,5