热带海洋学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 106-118.doi: 10.11978/2024170
海南新村港和黎安港海草床大型底栖生物的群落结构比较*
何晨1,2( ), 王佳宁1,2, 周林滨1, 柯志新1, 刘炜炜1, 刘甲星1, 王军星3, 谭烨辉1,2(
), 王佳宁1,2, 周林滨1, 柯志新1, 刘炜炜1, 刘甲星1, 王军星3, 谭烨辉1,2( ), 陈志云1(
), 陈志云1( )
)
- 1.中国科学院南海海洋研究所, 南海海洋生物标本馆, 广东省应用海洋生物学重点实验室, 广东 广州 510301
2.中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
3.惠州市自然资源局, 惠州市海洋技术中心, 广东 惠州 516003
-
收稿日期:2024-09-06修回日期:2024-10-13出版日期:2025-07-10发布日期:2025-07-31 -
通讯作者:谭烨辉, 陈志云 -
作者简介:何晨(1999−), 男, 广东省佛山市人, 硕士研究生, 研究方向: 海洋贝类分类学。email: tingsaki@outlook.com
*感谢中国科学院南海海洋研究所黄小平研究员、江志坚研究员、李开枝研究员和厦门大学蔡立哲教授团队在样品采集和鉴定工作以及论文写作中给予的帮助
-
基金资助:国家科技基础资源调查专项(2015FY110600); 广东省科技计划项目(2023B1212060047); 广东省科技计划项目(2024B1212040008); 中国科学院分类学科学家岗位项目(CAS-TAX-24-043); 国家动物标本资源库
Comparison of macrobenthic community structure between seagrass beds in Xincungang and Li’angang, Hainan
HE Chen1,2( ), WANG Jianing1,2, ZHOU Linbin1, KE Zhixin1, LIU Weiwei1, LIU Jiaxing1, WANG Junxing3, TAN Yehui1,2(
), WANG Jianing1,2, ZHOU Linbin1, KE Zhixin1, LIU Weiwei1, LIU Jiaxing1, WANG Junxing3, TAN Yehui1,2( ), CHEN Zhiyun1(
), CHEN Zhiyun1( )
)
- 1. Marine Biodiversity Collection of South China Sea, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Applied Marine Biology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3. Ocean Technology Center of Huizhou, Department of National Resources of Huizhou Bureau, Huizhou 516003, China
-
Received:2024-09-06Revised:2024-10-13Online:2025-07-10Published:2025-07-31 -
Contact:TAN Yehui, CHEN Zhiyun -
Supported by:National Investigation of Technological Basic Resources Project(2015FY110600); Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province(2023B1212060047); Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province(2024B1212040008); Taxonomist Project, Chinese Academy of Sciences(CAS-TAX-24-043); National Animal Collection Resource Center, China
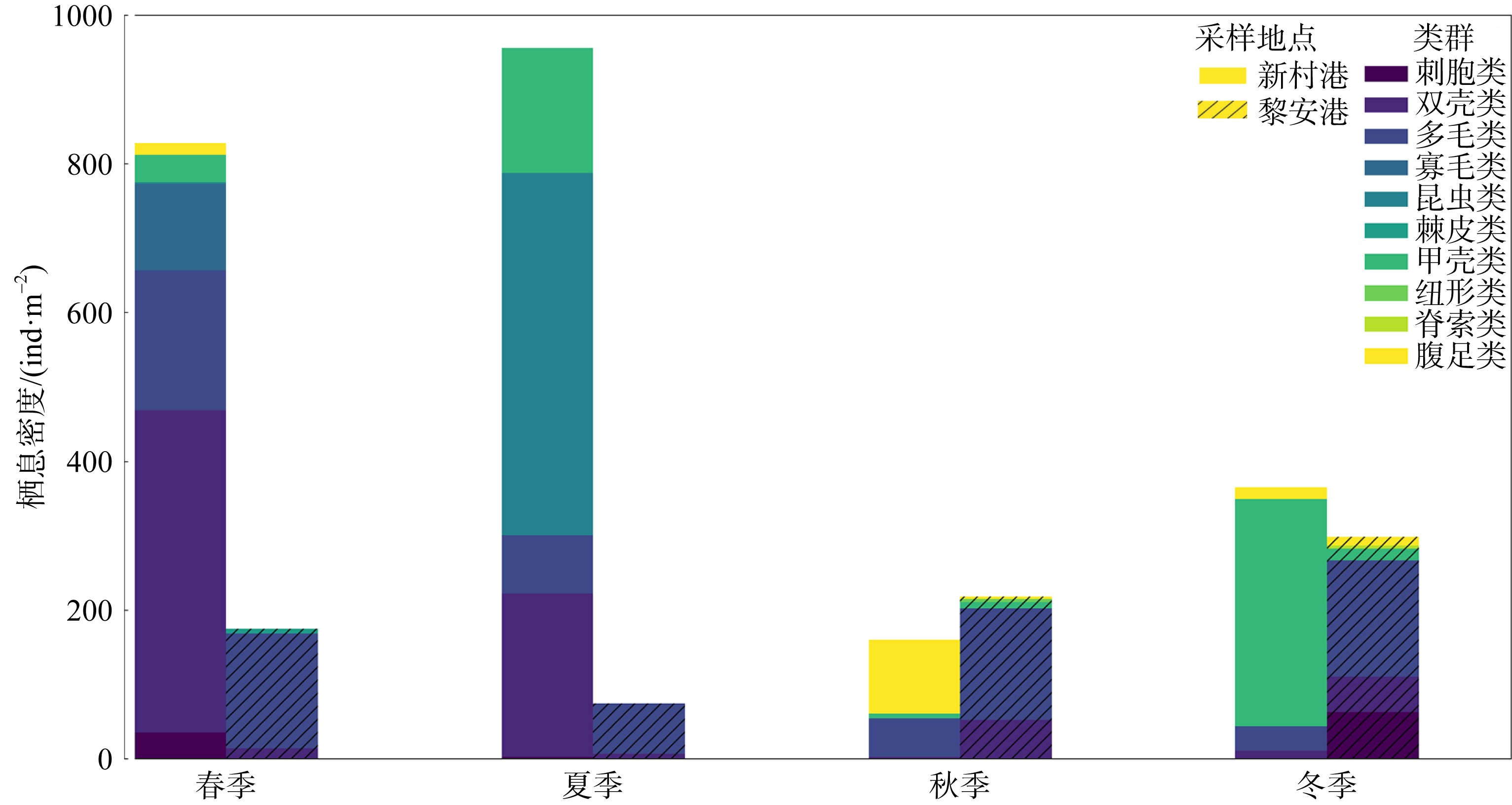
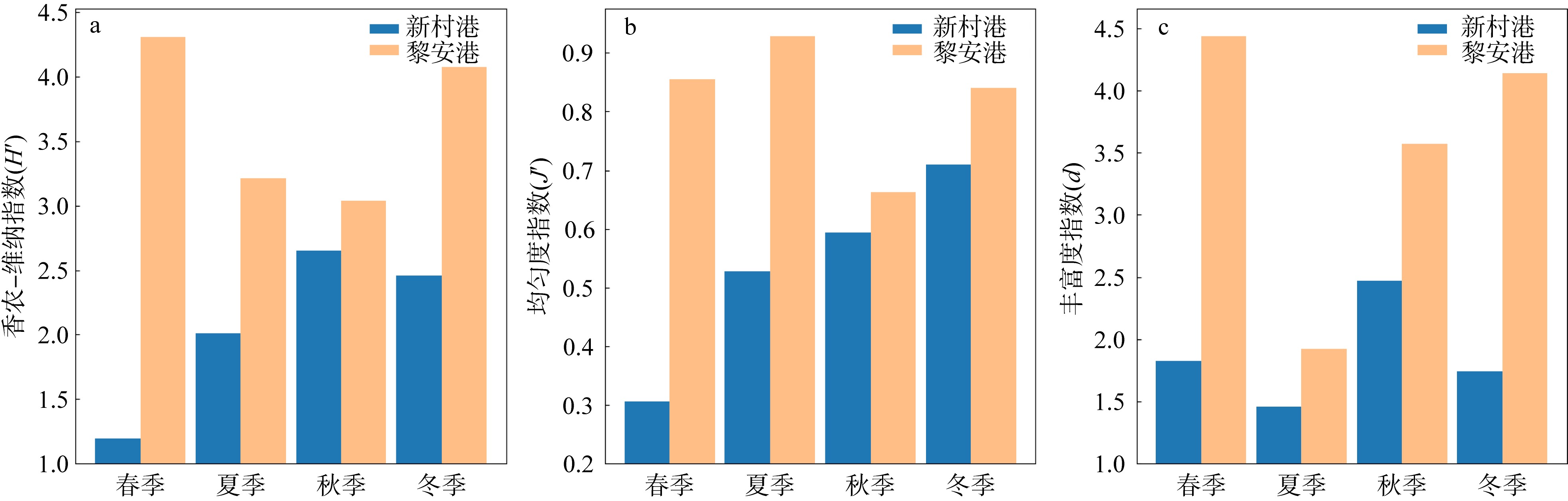
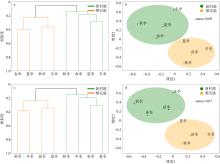
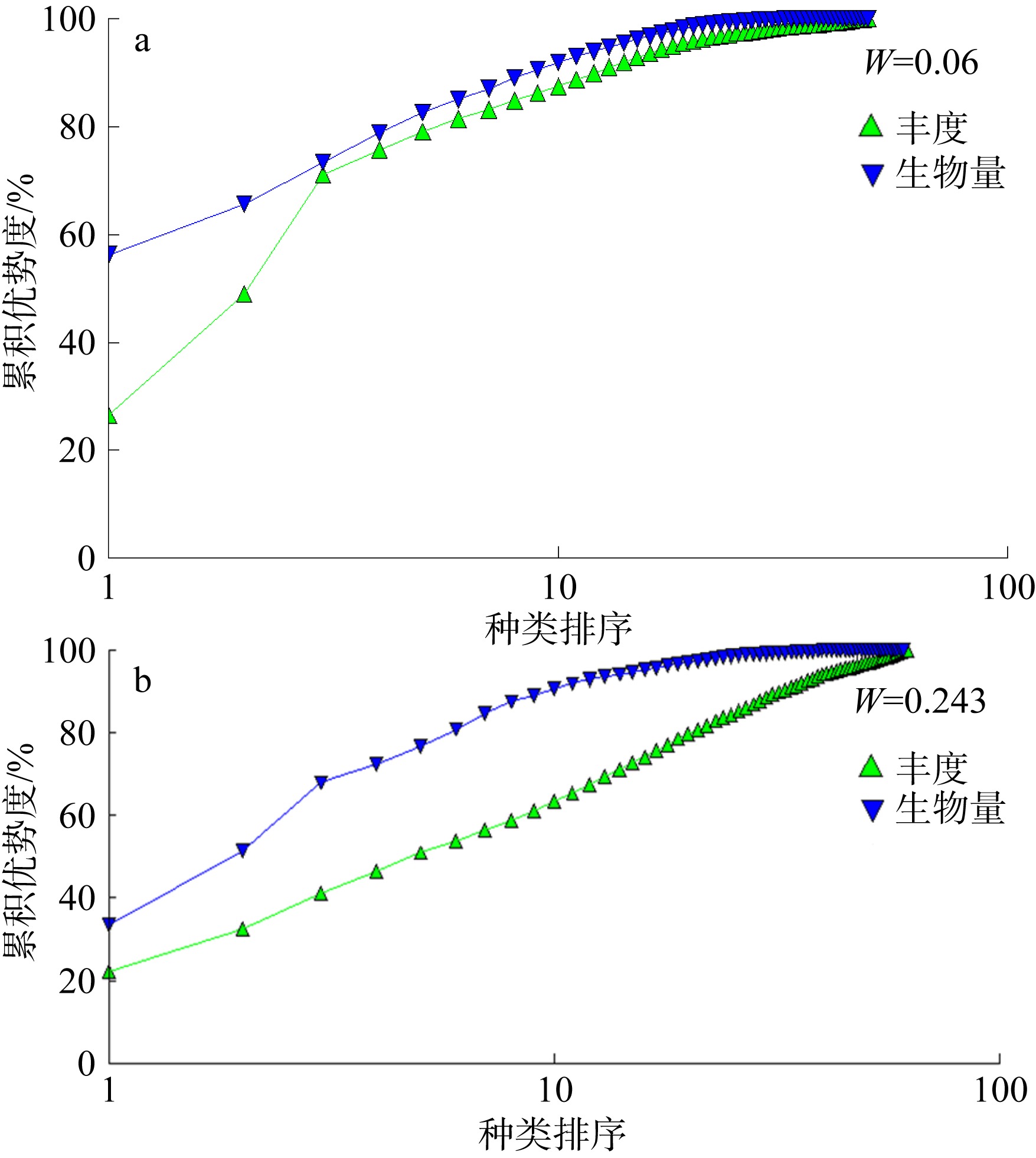
摘要: 基于2015—2016海南新村港和2017—2018年黎安港两地海草床四季大型底栖生物生态调查数据, 对其群落结构进行比较。结果表明: (1)共记录两个区域海草床大型底栖生物96种, 其中新村港和黎安港各50种和62种, 环节动物是两地海草床的主要类群; 厚鳃蚕(Dasybranchus caducus)是其共有的优势种; 除秋季外, 新村港的大型底栖生物平均栖息密度均高于黎安港; 除夏季外, 黎安港的生物量皆高于新村港; (2)黎安港的Shannon-Wiener多样性指数(H′)、Pielou均匀度指数(J′)和Margalef丰富度指数(d)均高于新村港; 黎安港的丰度/生物量曲线W值远大于新村港, 后者海草床大型底栖生物群落结构比前者受到干扰更小; (3)基于群落栖息密度和生物量聚类结果都显示, 约15%的相似性水平上可将两地群落分为两组, 两地海草床大型底栖生物群落结构差别较大。结合上述研究和历史研究结果, 两地群落差异可能是由两地的水文特征差异和渔业养殖带来的污染差异引起的。与历史数据对比显示, 两地海草床保护区的大型底栖生物群落已有所恢复, 持续的保护和修复工作是有效且必要的。
中图分类号:
- P735
引用本文
何晨, 王佳宁, 周林滨, 柯志新, 刘炜炜, 刘甲星, 王军星, 谭烨辉, 陈志云. 海南新村港和黎安港海草床大型底栖生物的群落结构比较*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(4): 106-118.
HE Chen, WANG Jianing, ZHOU Linbin, KE Zhixin, LIU Weiwei, LIU Jiaxing, WANG Junxing, TAN Yehui, CHEN Zhiyun. Comparison of macrobenthic community structure between seagrass beds in Xincungang and Li’angang, Hainan[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(4): 106-118.
表1
新村港和黎安港各季节大型底栖生物主要类群种类数量"
| 分类阶元 | 春季种类 | 夏季种类 | 秋季种类 | 冬季种类 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 新村港 | 黎安港 | 新村港 | 黎安港 | 新村港 | 黎安港 | 新村港 | 黎安港 | |
| 环节动物门Annelida | 15 | 18 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 13 | 9 | 15 |
| 节肢动物门Arthropoda | 4 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| 软体动物门Mollusca | 2 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 11 | 4 | 8 |
| 刺胞动物门Cnidaria | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 纽形动物门Nemertea | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 脊索动物门Chordata | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 棘皮动物门Arthropoda | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
表2
新村港和黎安港大型底栖生物不同季节的优势种及其优势度指数(Y)"
| 优势种 | 春季Y | 夏季Y | 秋季Y | 冬季Y | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 新村港 | 黎安港 | 新村港 | 黎安港 | 新村港 | 黎安港 | 新村港 | 黎安港 | |
| 小头虫 Capitella capitata | 0.086 | |||||||
| 岩虫 Marphysa sanguinea | 0.025 | |||||||
| 多色天螺 Diala varia | 0.404 | |||||||
| 珠带拟蟹守螺 Cerithidea cingulata | 0.037 | |||||||
| 厚鳃蚕 Dasybranchus caducus | 0.021 | 0.092 | 0.054 | 0.119 | 0.061 | |||
| 沼蚓 Limnodriloides sp. | 0.04 | |||||||
| 南海毛满月蛤 Pillacina cietnamica | 0.45 | 0.114 | ||||||
| 蜾蠃蜚 Corophium sp. | 0.022 | |||||||
| 强壮藻钩虾 Ampithoe valida | 0.06 | 0.626 | ||||||
| 摇蚊科 Chironomidae | 0.191 | |||||||
| 软须阿曼吉虫 Arandia leptocirris | 0.042 | |||||||
| 奋镜蛤 Dosinia exasperata | 0.051 | |||||||
| 海葵 Haliplanella sp. | 0.028 | |||||||
| 背蚓虫 Notomastus sp. | 0.024 | |||||||
| 锥稚虫 Aonicles oxycephala | 0.023 | 0.03 | ||||||
| 莫桑比克岩虫 Marphysa mossabicca | 0.03 | |||||||
表3
新村港和黎安港海草床大型底栖动物主要群落参数历史数据对比"
| 调查结果 | 调查区域 | 物种数量 | 栖息密度均值/(ind·m-2) | 生物量均值/(g·m-2) | 多样性指数(H′) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2002年(黄小平 等, | 新村港 | 10 | 1152.68 | 286.77 | 0.67 |
| 黎安港 | 24 | 2317.6 | 856.59 | 2.13 | |
| 2009—2013年(涂志刚 等, | 新村港和黎安港 | 95 | 137.53 | 167. 57 | 1.9 |
| 2013年(李洋, | 新村港 | 42 | 518.38 | 201.9 | 2.83 |
| 2015—2016年(本研究) | 新村港 | 50 | 576.75 | 17.27 | 2.08 |
| 2017—2018年(本研究) | 黎安港 | 62 | 191 | 222.59 | 3.66 |
| 2020年(郭治明 等, | 新村港 | 15 | 292.6 | 81.82 | 0.81 |
| 黎安港 | 17 | 133.4 | 102.22 | 0.95 |
附表1
新村港和黎安港海草床大型底栖生物名录"
| 中文名 | 拉丁名 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 冬季 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 新村港 | 黎安港 | 新村港 | 黎安港 | 新村港 | 黎安港 | 新村港 | 黎安港 | ||
| 海葵目 | Actiniaria | √ | |||||||
| 柱形阿里螺 | Aliculastrum cylindricum | √ | |||||||
| 西方似蛰虫 | Amaeana occidentalis | √ | |||||||
| 似蛰虫 | Amaeana trilobata | √ | √ | ||||||
| 藻钩虾 | Ampithoe sp. | √ | |||||||
| 强壮藻钩虾 | Ampithoe valida | √ | √ | ||||||
| 无齿蛤 | Anodontia edentula | √ | √ | ||||||
| 鳞杓拿蛤 | Anomalodiscus squamosus | √ | |||||||
| 锥稚虫 | Aonides oxycephala | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| 大角玻璃钩虾 | Apohyale grandicornis | √ | |||||||
| 矮小稚齿虫 | Apoprionospio pygmaea | √ | |||||||
| 飞白枫海星 | Archaster typicus | √ | |||||||
| 凸壳肌蛤 | Arcuatula senhousia | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| 软须阿曼吉虫 | Armandia leptocirris | √ | √ | ||||||
| 中阿曼吉虫 | Armandia intermedia | √ | |||||||
| 海鞘 | Ascidia sp. | √ | |||||||
| 网纹藤壶 | Balanus inprovisus | √ | √ | ||||||
| 黑斑鳍缨虫 | Branchiomma nigromaculatum | √ | √ | ||||||
| 斑鳍缨虫 | Branchiomma sp. | √ | |||||||
| 小头虫 | Capitella capitata | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| 角沙蚕 | Ceratonereis mirabilis | √ | √ | ||||||
| 刚鳃虫 | Chaetozone setosa | √ | |||||||
| 摇蚊 | Chironomus sp. | √ | √ | ||||||
| 美女蛤 | circe scripta | √ | |||||||
| 须鳃虫 | Cirriformia tentaculata | √ | |||||||
| 奥莱彩螺 | Clithon oualaniensis | √ | |||||||
| 蜾蠃蜚 | Corophium sp. | √ | |||||||
| 厚鳃蚕 | Dasybranchus caducus | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||
| 多色天螺 | Diala varia | √ | |||||||
| 奋镜蛤 | Dosinia exasperata | √ | √ | ||||||
| 矶沙蚕 | Eunice sp. | √ | |||||||
| 真裂虫 | Eusyllis sp. | √ | |||||||
| 艾裂虫亚科 | Exogoninae | √ | |||||||
| 凸加夫蛤 | Gafrarium tumidum | √ | |||||||
| 加夫蛤 | Gafrarium pectinatum | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| 钩虾 | Gammarus sp. | √ | √ | ||||||
| 皱文蛤 | Gomphina undulosa | √ | |||||||
| 海葵 | Haliplanella sp. | √ | |||||||
| 纵条矶海葵 | Haliplanella luciae | √ | √ | ||||||
| 丝异须虫 | Heteromastus sp. | √ | |||||||
| 彩虹明樱蛤 | Iridona iridescens | √ | |||||||
| 红明樱蛤 | Jitlada culter | √ | |||||||
| 后指虫 | Laonice cirrata | √ | |||||||
| 简锥虫属 | Leitoscoloplis sp. | √ | √ | ||||||
| 长锥虫属 | Leodamas sp. | √ | |||||||
| 沼蚓 | Limnodriloides sp. | √ | |||||||
| 精巧扁蛰虫 | Loimia ingens | √ | |||||||
| 索沙蚕 | Lumbrineris sp. | √ | √ | ||||||
| 似帚毛虫 | Lygdamis indicus | √ | |||||||
| 大眼蟹属 | Macrophthalmus sp. | √ | |||||||
| 印度锥稚虫 | Malacoceros indicus | √ | √ | ||||||
| 岩虫 | Marphysa sanguinea | √ | √ | ||||||
| 莫桑比克岩虫 | Marphysa mossambica | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||
| 扁平岩虫 | Marphysa depressa | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| 尼科巴立蛤蛤 | Meropesta nicobarica | √ | |||||||
| 小健足虫 | Micropodarke dubia | √ | |||||||
| 多微稚齿虫 | Microspio multidentata | √ | |||||||
| 麦氏偏顶蛤 | Modiolus metcaifei | √ | |||||||
| 寻氏肌蛤 | Musculus senhousei | √ | |||||||
| 方斑玉螺 | Naticarius onca | √ | |||||||
| 尾刺沙蚕 | Neanthes acuminata | √ | |||||||
| 纽虫门 | Nemertea sp. | √ | |||||||
| 沙蚕属 | Nereis sp. | √ | |||||||
| 沙蚕属 | Nereis sp. | √ | |||||||
| 虹光亮樱蛤 | Nitidotellina valtonis | √ | |||||||
| 小亮樱蛤 | Nitidotellina lischkei | √ | |||||||
| 亮樱蛤 | Nitidotellina nitidula | √ | |||||||
| 背蚓虫 | Notomastus latericeus | √ | |||||||
| 背蚓虫 | Notomastus sp. | √ | |||||||
| 无背毛蛇潜虫 | Oxydromus berrisfordi | √ | |||||||
| 玛叶须虫 | Phyllodoce malmgreni | √ | |||||||
| 叶须虫 | Phyllodoce aminosa | √ | |||||||
| 珠带拟蟹守螺 | Pirenella cingulata | √ | |||||||
| 褐片阔沙蚕 | Plattynereis dumerilii | √ | |||||||
| 杜氏阔沙蚕 | Platynereis dumerilii | √ | √ | ||||||
| 蛇杂毛虫 | Poecilochaetus serpens | √ | |||||||
| 才女虫 | Polydora sp. | √ | |||||||
| 多眼虫 | Polyophthalmus cf pictus | √ | |||||||
| 梭子蟹 | Portunus sp. | √ | |||||||
| 稚齿虫 | Prionospio sp. | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||
| 膜质伪才女虫 | Pseudopolydora kempi | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| 克氏锉棒螺 | Rhinoclavis kochi | √ | |||||||
| 南海毛满月蛤 | Rugalucina vietnamica | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||
| 缨鳃虫科 | Sabellidae | √ | |||||||
| 鳞腹沟虫 | Scolelepis squamata | √ | |||||||
| 红刺尖锥虫 | Scoloplos cf rubra | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| 蟳 | Scylla sp. | √ | |||||||
| 双带蛤 | Semele sp. | √ | |||||||
| 拟箱美丽蛤 | Serratina capsoides | √ | |||||||
| 红角沙蚕 | Simplisetia erythraeensis | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| 裂虫科 | Syllidae | √ | |||||||
| 海裂虫 | Syllidia armata | √ | |||||||
| 钝缀锦蛤 | Tapes dorsatus | √ | |||||||
| 缀锦蛤 | Tapes literatus | √ | √ | ||||||
| 丽缀锦蛤 | Tapes literatus aspeersa | √ | |||||||
| 梳鳃虫 | Terebellidea stroemii | √ | |||||||
| 短桨蟹 | Thalamita sp. | √ | |||||||
| 钝齿短桨蟹 | Thalamita crenata | √ | |||||||
| 覆瓦小蛇螺蛇螺 | Thylacodes adamsii | √ | |||||||
| 鳃毛虫属 | Timarete sp. | √ | |||||||
| 火腿樱蛤 | Tonganaella perna | √ | |||||||
| 模裂虫 | Typosyllis sp. | √ | |||||||
| 欧文虫 | Owenia fusiformis | √ | |||||||
| [1] |
毕耜瑶, 许永久, 俞存根, 等, 2018. 南麂列岛海洋自然保护区岩相潮间带软体动物种类组成与数量分布[J]. 水产学报, 42(6): 902-911.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
蔡立哲, 马丽, 高阳, 等, 2002. 海洋底栖动物多样性指数污染程度评价标准的分析[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 41(5): 641-646.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
蔡泽富, 陈石泉, 吴钟解, 等, 2017. 海南岛海湾与潟湖中海草的分布差异及影响分析[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, (3): 74-84.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
陈娴, 李洋, 2020. 陵水黎安港水质环境分析及评价[J]. 广东化工, 47(7): 76-78, 87.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
郭治明, 杨熙, 余威, 等, 2023. 华南沿海海草床分布区大型底栖动物群落特征初探[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 42(3): 469-478.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
韩秋影, 施平, 2008. 海草生态学研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 28(11): 5561-5570.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
胡桂坤, 秦璐璐, 李郁郁, 等, 2019. 基于ABC曲线的天津潮间带生物群落受扰动的分析[J]. 天津科技大学学报, 34(5): 57-62.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
黄小平, 黄良民, 2007. 中国南海海草研究[M]. 广州: 广东经济出版社 (in Chinese).
|
| [9] |
黄小平, 江志坚, 张景平, 等, 2018. 全球海草的中文命名[J]. 海洋学报, 40(4): 127-133.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
黄宗国, 林茂, 2012. 中国海洋生物图集-第四册, 2-动物界[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社 (in Chinese).
|
| [11] |
李北兴, 黎傲雪, 董建宇, 等, 2023. 湛江湾潮间带大型底栖动物的群落结构及其受干扰程度[J]. 南方水产科学, 19(2): 12-20.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
李洋, 2015. 海南岛东海岸海草场大型底栖生物研究[D]. 海口: 海南大学.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
林显程, 凌娟, 张燕英, 等, 2019. 海草生长的影响因素及组学技术研究进展[J]. 生物技术, 29(5): 507-511.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
刘瑞玉, 2008. 中国海洋生物名录[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
刘颖, 李进京, 陈晨, 等, 2021. 浙江象山港岛屿春、夏季潮间带大型底栖生物的群落结构特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 52(3): 685-696.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
庞巧珠, 骆丽珍, 曾广锐, 等, 2021. 黎安港海水和沉积物中叶绿素a含量及与环境因子的关系分析[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 43(1): 133-141.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
涂志刚, 韩涛生, 陈晓慧, 等, 2016. 海南陵水新村港与黎安港海草特别保护区大型底栖动物群落结构与多样性[J]. 海洋环境科学, 35(1): 41-48.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
吴钟解, 陈石泉, 王道儒, 等, 2014. 海南岛东海岸海草床生态系统健康评价[J]. 海洋科学, 38(8): 67-74.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
徐凤山, 张素萍, 2008. 中国海产双壳类图志[M]. 北京: 科学出版社 (in Chinese).
|
| [20] |
杨宗岱, 1982. 中国海草的生态学研究[J]. 海洋科学, (2): 34-37.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
郑凤英, 邱广龙, 范航清, 等, 2013. 中国海草的多样性、分布及保护[J]. 生物多样性, 21(5): 517-526.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.10038 |
|
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.10038 |
|
| [22] |
中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 2007a. 海洋调查规范第6部分: 海洋生物调查 (GB/T 12763. 6—2007)[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社.
|
|
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China, 2007b. Specification for oceanographic survey-Part 6: Marine biological survey (GB/T 12763.6—2007)[S]. Beijing: Standards press of China (in Chinese).
|
|
| [23] |
中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 2007b. 海洋监测规范第3部分:样品采集、贮存与运输 (GB 17378. 3—2007)[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社.
|
|
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China, 2007a. The specification for marine monitoring Part 3: Sample collection, storage and transportation (GB 17378. 3—2007)[S]. Beijing: Standards press of China (in Chinese).
|
|
| [24] |
周立柱, 杨顶田, 尹小青, 2018. 海南新村港和黎安港非点源污染负荷估算[J]. 生态科学, 37(3): 11-20.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
周毅, 江志坚, 邱广龙, 等, 2023. 中国海草资源分布现状、退化原因与保护对策[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 54(5): 1248-1257.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
doi: S0025-326X(14)00475-5 pmid: 25103900 |
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12354-y pmid: 28928433 |
| [39] |
|
| [1] | 于蓁, 郭祥瑞, 刘雪睿, 孙浩, 张燕英. 山东沿海三种海草根际真核生物群落结构及其影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(5): 86-96. |
| [2] | 李达, 王云忠, 齐继光, 杨翠华. 水质变化对豆荚软珊瑚(Lobophytum sp.)共生藻(Symbiodiniaceae)、菌群落结构的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(4): 136-144. |
| [3] | 李若安, 李旭清, 陈天然. 南海南部珊瑚骨骼δ18O和Sr/Ca对ENSO的分级响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(4): 45-55. |
| [4] | 孙佳宁, 王玉清, 章守宇, 王凯. 绿华岛海域海藻场大型底栖生物群落结构及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(4): 119-135. |
| [5] | 王炎炎, 宋丹瑛, 陈治. 旅游干扰对西沙全富岛、银屿潮间带大型底栖动物群落的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(4): 77-94. |
| [6] | 黄红伟, 张志新, 仲嘉, 林强, 郭宝英, 严小军. 印太交汇区八种鱼类群体遗传结构和连通性分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(1): 9-23. |
| [7] | 周志希, 唐汇娟, 柯志新, 刘甲星, 周伟华. 基于形态学和高通量测序的春季南澳海域浮游植物群落特征及其与环境因子关系[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(1): 53-65. |
| [8] | 王庆, 任辉, 柯志新. 广东南澳海水养殖区中小型浮游动物群落结构特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(6): 92-103. |
| [9] | 黄良民, 林强, 谭烨辉, 黄小平, 周林滨, 黄晖. 热带海洋特色生态系统恢复重构与保护思考*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(6): 1-12. |
| [10] | 饶义勇, 赵美榕, 旷泽行, 黄洪辉, 谭萼辉. 浮筏式牡蛎养殖对大型底栖动物群落功能结构的影响——以大鹏澳为例*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 69-83. |
| [11] | 赵中伟, 吴凌云, 高伟健, 李伟. 海南岛峨蔓五彩湾内海蚀平台对海蚀崖侵蚀的影响研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 106-115. |
| [12] | 柳原, 柯志新, 李开枝, 谭烨辉, 梁竣策, 周伟华. 人类活动和沿岸流影响下的粤东近海浮游动物群落特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [13] | 刘玓玓, 张喜洋, 孙富林, 王明壮, 谭飞, 施祺, 王冠, 杨红强. 南海海滩岩微生物群落结构和特定菌株对其成因机制的启示*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 112-122. |
| [14] | 胡思敏, 周天成, 张琛, 刘胜, 李涛, 黄晖. 悬浮物对三亚珊瑚礁区浮游动物群落结构及其摄食的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 122-130. |
| [15] | 罗勇, 黄林韬, 杨剑辉, 练健生, 刘骋跃, 江雷, 梁宇娴, 陈伦举, 雷新明, 刘胜, 黄晖. 海南临高红牌—马袅沿岸海域造礁石珊瑚群落结构及其环境影响因子[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 72-86. |
|
||