热带海洋学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 86-96.doi: 10.11978/2025003CSTR: 32234.14.2025003
山东沿海三种海草根际真核生物群落结构及其影响因素
- 烟台大学海洋学院, 山东 烟台 264005
-
收稿日期:2025-01-02修回日期:2025-01-24出版日期:2025-09-10发布日期:2025-10-14 -
通讯作者:张燕英 -
作者简介:于蓁(1999—), 女, 硕士研究生, 从事海洋微生物研究。email: yuzhen1107726@163.com
-
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(41976147); 山东省自然科学基金项目(ZR2024MD008)
Community structure of rhizosphere eukaryotic microorganisms and its influencing factors of three seagrass species along the coast of Shandong Province
YU Zhen( ), GUO Xiangrui, LIU Xuerui, SUN Hao, ZHANG Yanying(
), GUO Xiangrui, LIU Xuerui, SUN Hao, ZHANG Yanying( )
)
- Ocean School, Yantai University, Yantai 264005, China
-
Received:2025-01-02Revised:2025-01-24Online:2025-09-10Published:2025-10-14 -
Contact:ZHANG Yanying -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(41976147); Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province(ZR2024MD008)
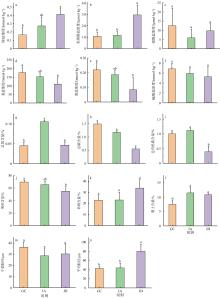
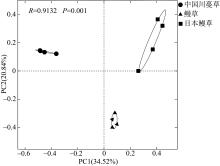
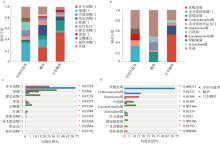
摘要: 海草床与红树林、珊瑚礁并称为地球上三大典型的近海海洋生态系统, 具有极高的生态服务功能, 被誉为“海洋之肺”。海草床具有较高的初级生产力水平, 在维持海洋生态系统的平衡与稳定方面发挥着核心作用。海草根际的真核生物对海草的生长发育至关重要, 在维持海草健康和生态系统碳、氮等营养元素循环过程中发挥重要作用。文章利用高通量测序技术分析了山东沿海地区中国川蔓草(Ruppia sinensis)、鳗草(Zostera marina)和日本鳗草(Zostera japonica)根际真核生物的多样性特征、群落结构及其与环境因子的关系。结果表明, 海草根际真核生物以藻类、后生动物和原生动物为主, 优势类群为绿藻门(Chlorophyta)和环节动物门(Annelida)。海草根际真核生物群落结构与根际沉积物的总碳含量、亚硝酸盐含量、铵盐含量和沉积物粒径大小显著相关。共现性网络分析揭示, 日本鳗草根际真核生物之间的互作关系更加复杂。
中图分类号:
- P735.121
引用本文
于蓁, 郭祥瑞, 刘雪睿, 孙浩, 张燕英. 山东沿海三种海草根际真核生物群落结构及其影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(5): 86-96.
YU Zhen, GUO Xiangrui, LIU Xuerui, SUN Hao, ZHANG Yanying. Community structure of rhizosphere eukaryotic microorganisms and its influencing factors of three seagrass species along the coast of Shandong Province[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(5): 86-96.
| [1] |
凌娟, 梁童茵, 岳维忠, 等, 2023. 热带海草泰来草沉积物真菌的群落结构、功能与分子生态网络研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 42(5): 64-75.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
刘鹏远, 2022. 黄渤海日本鳗草沉积物三域微生物的分布特征、生态功能及驱动因素[D]. 烟台: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院烟台海岸带研究所).
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
刘鹏远, 张海坤, 陈琳, 等, 2019. 黄渤海海草分布区日本鳗草根际微生物群落结构特征及其功能分析[J]. 微生物学报, 59(8): 1484-1499.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
宋增磊, 2023. 微生物在黄河三角洲互花米草与日本鳗草生态竞争中的作用及机制分析[D]. 烟台: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院烟台海岸带研究所).
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
孙延瑜, 2021. 威海泻湖海草床共附生微生物群落结构特征及硫入侵过程[D]. 烟台: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院烟台海岸带研究所).
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
孙延瑜, 宋增磊, 刘鹏远, 等, 2021. 威海天鹅湖大叶藻(Zostera marina)与日本鳗草(Zostera japonica)根际微生物群落结构及其驱动机制[J]. 微生物学报, 61(9): 2675-2692.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
王天雨, 2023. 山东东部沿海两种海草根际微生物群落结构及潜在功能[D]. 烟台: 烟台大学.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
徐少春, 2021. 黄渤海鳗草(Zostera marina)种群特征及生态修复研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院海洋研究所).
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
薛曌, 王兰, 孟华旦尚, 等, 2023. 色林错表层水体真核微生物多样性和群落分布格局[J]. 冰川冻土, 45(5): 1652-1666.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0240.2023.0126 |
|
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0240.2023.0126 |
|
| [10] |
于培, 2017. 鳗草对沉积物微生物群落的影响及其氮代谢的初步研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
张晓珂, 梁文举, 李琪, 2018. 我国土壤线虫生态学研究进展和展望[J]. 生物多样性, 26(10): 1060-1073.
doi: 10.17520/biods.2018082 |
|
doi: 10.17520/biods.2018082 |
|
| [12] |
周毅, 江志坚, 邱广龙, 等, 2023. 中国海草资源分布现状、退化原因与保护对策[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 54(5): 1248-1257.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1747 pmid: 17853906 |
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01312 pmid: 28751881 |
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00440 pmid: 27065991 |
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.1007/s00248-019-01457-w pmid: 31720759 |
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.12666 pmid: 25330396 |
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
doi: 10.1111/gcb.13384 pmid: 27272953 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.11.013 pmid: 26644196 |
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
doi: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-6-209 pmid: 23805896 |
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [1] | 冯战权, 苏冒亮, 杜媛媛, 钟友凌, 张俊彬. 基于MaxEnt模型分析全球气候变化对中国沿海带鱼潜在分布的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(5): 77-85. |
| [2] | 李达, 王云忠, 齐继光, 杨翠华. 水质变化对豆荚软珊瑚(Lobophytum sp.)共生藻(Symbiodiniaceae)、菌群落结构的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(4): 136-144. |
| [3] | 孙佳宁, 王玉清, 章守宇, 王凯. 绿华岛海域海藻场大型底栖生物群落结构及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(4): 119-135. |
| [4] | 何晨, 王佳宁, 周林滨, 柯志新, 刘炜炜, 刘甲星, 王军星, 谭烨辉, 陈志云. 海南新村港和黎安港海草床大型底栖生物的群落结构比较*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(4): 106-118. |
| [5] | 代丽, 潘铧康, 刘励阳, 何健, 赵科, 祁剑飞, 张真, 苏培, 冯丹青. 环境因子对污损生物沙筛贝(Mytilopsis sallei)幼体附着变态的影响研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(3): 121-129. |
| [6] | 周志希, 唐汇娟, 柯志新, 刘甲星, 周伟华. 基于形态学和高通量测序的春季南澳海域浮游植物群落特征及其与环境因子关系[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(1): 53-65. |
| [7] | 柳原, 柯志新, 李开枝, 谭烨辉, 梁竣策, 周伟华. 人类活动和沿岸流影响下的粤东近海浮游动物群落特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [8] | 刘玓玓, 张喜洋, 孙富林, 王明壮, 谭飞, 施祺, 王冠, 杨红强. 南海海滩岩微生物群落结构和特定菌株对其成因机制的启示*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 112-122. |
| [9] | 胡思敏, 周天成, 张琛, 刘胜, 李涛, 黄晖. 悬浮物对三亚珊瑚礁区浮游动物群落结构及其摄食的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 122-130. |
| [10] | 罗勇, 黄林韬, 杨剑辉, 练健生, 刘骋跃, 江雷, 梁宇娴, 陈伦举, 雷新明, 刘胜, 黄晖. 海南临高红牌—马袅沿岸海域造礁石珊瑚群落结构及其环境影响因子[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 72-86. |
| [11] | 耿婉璐, 邢永泽, 张秋丰, 管卫兵. 广西北海红树林宜林滩涂大型底栖动物群落结构特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(1): 107-115. |
| [12] | 孙婷婷, 郝雯瑾, 徐鹏臻, 叶丽靖, 董志军. 海水酸化对海月水母螅状体共附生微生物的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(6): 111-119. |
| [13] | 张兰兰, 程夏雯, 向荣, 邱卓雅, 常虎. 2019年春季孟加拉湾中部放射虫群落结构垂向变化*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(4): 166-175. |
| [14] | 宋星宇, 林雅君, 张良奎, 向晨晖, 黄亚东, 郑传阳. 粤港澳大湾区近海中小型浮游动物分布特征及影响因素*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 136-148. |
| [15] | 陈靖夫, 钟瑜, 王磊, 郭雨沛, 邱大俊. 环境DNA分析大亚湾夜光藻藻华对真核浮游生物群落的影响*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(5): 121-132. |
|
||