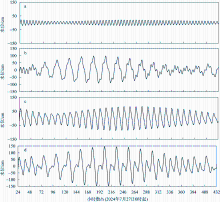
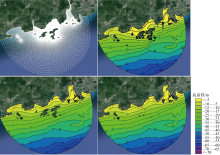
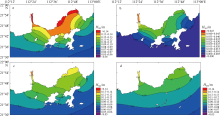
| [1] |
陈宜展, 曹永港, 罗士浩, 等, 2022. 粤西阳江海域春夏季沿岸激流现象及机理分析[J]. 海洋学报, 44(11): 1-11.
|
|
CHEN YIZHAN, CAO YONGGANG, LUO SHIHAO, et al, 2022. Mechanism analysis of alongshore shock current phenomenon in Yangjiang sea area along the coast of western Guangdong in spring and summer[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 44(11): 1-11 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
成印河, 梁广建, 朱凤芹, 等, 2017. 粤西沿岸海域潮汐特征[J]. 海洋科学, 41(6): 111-118.
|
|
CHENG YINHE, LIANG GUANGJIAN, ZHU FENGQIN, et al, 2017. Tidal characteristics along coast of Western Guangdong Province[J]. Marine Sciences, 41(6): 111-118 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
刁希梁, 丁扬, 鲍献文, 2017. 大亚湾海域潮位“双峰”现象生成机制研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 47(9): 1-10.
|
|
DIAO XILIANG, DING YANG, BAO XIANWEN, 2017. The generation mechanism of the double peak tidal elevation in Daya Bay[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 47(9): 1-10 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
国家海洋信息中心, 2023. 潮汐表(2024年, 第3册)[M]. 天津: 天津科学技术出版社: 1-445 (in Chinese).
|
| [5] |
李孟国, 郑敬云, 2007. 中国海域潮汐预报软件Chinatide的应用[J]. 水道港口, 28(1): 65-68.
|
|
LI MENGGUO, ZHENG JINGYUN, 2007. Introduction to Chinatide software for tide prediction in China seas[J]. Journal of Waterway and Harbor, 28(1): 65-68 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
李嵩, 管卫兵, 曹振轶, 等, 2020. 大亚湾和大鹏湾两个相邻海湾潮波浅水变形的异同分析[J]. 海洋学研究, 38(3): 31-47.
|
|
LI SONG, GUAN WEIBING, CAO ZHENYI, et al, 2020. Similarities and differences of shallow water deformation of tidal wave in two adjacent bays: Daya Bay and Dapeng Bay[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 38(3): 31-47 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
彭帅星, 朱佳, 陈照章, 等, 2021. 大亚湾双峰水位的形成条件及准调和分量应用的分析[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 60(5): 937-944.
|
|
PENG SHUAIXING, ZHU JIA, CHEN ZHAOZHANG, et al, 2021. Analyses of the formation conditions of bimodal phenomenon and the application of quasi-harmonic components in the Daya Bay[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 60(5): 937-944 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
王延强, 仉天宇, 朱学明, 2014. 基于18. 6年卫星高度计资料对南海潮汐的分析与研究[J]. 海洋预报, 31(2): 35-40.
|
|
WANG YANQIANG, ZHANG TIANYU, ZHU XUEMING, 2014. Tidal characteristics analysis in the South China Sea by 18. 6 years satellite altimetry data[J]. Marine Forecasts, 31(2): 35-40 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
武文, 严聿晗, 宋德海, 2017. 大亚湾的潮汐动力学研究——I. 潮波系统的观测分析与数值模拟[J]. 热带海洋学报, 36(3): 34-45.
doi: 10.11978/2016078
|
|
WU WEN, YAN YUHAN, SONG DEHAI, 2017. Study on the tidal dynamics in Daya Bay, China—Part I. Observation and numerical simulation of tidal dynamic system[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 36(3): 34-45 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
夏综万, 廖世智, 冯砚青, 2013. 粤东甲子海域潮波异常和南海北部潮波的传播[J]. 海洋学报, 35(1): 1-8.
|
|
XIA ZONGWAN, LIAO SHIZHI, FENG YANQING, 2013. Traveling of tidal wave in the north part of the South China Sea and the tidal energy divergence appearing in the area off Jiazi Station[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 35(1): 1-8 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
严聿晗, 武文, 宋德海, 等, 2017. 大亚湾的潮汐动力学研究——Ⅱ. 潮位和潮流双峰现象的产生机制[J]. 热带海洋学报, 36(3): 46-54.
doi: 10.11978/2016079
|
|
YAN YUHAN, WU WEN, SONG DEHAI, et al, 2017. Study on the tidal dynamics in Daya Bay, China—Part Ⅱ. The generation of double high waters and double-peak flood-current flows[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 36(3): 46-54 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
GODIN G, 1993. An investigation of the phenomenon of double high water or double low water at some harbours[J]. Deutsche Hydrografische Zeitschrift, 45(2): 87-106.
|
| [13] |
PAN HAIDONG, XU TENGFEI, WEI ZEXUN, 2023. A modified tidal harmonic analysis model for short-term water level observations[J]. Ocean Modelling, 186: 102251.
doi: 10.1016/j.ocemod.2023.102251
|
| [14] |
PAN HAIDONG, XU TENGFEI, WEI ZEXUN, 2024. Improved tidal estimates from short water level records via the modified harmonic analysis model[J]. Ocean Modelling, 189: 102372.
doi: 10.1016/j.ocemod.2024.102372
|