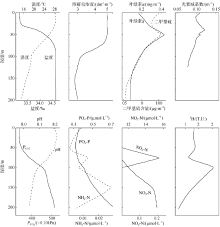
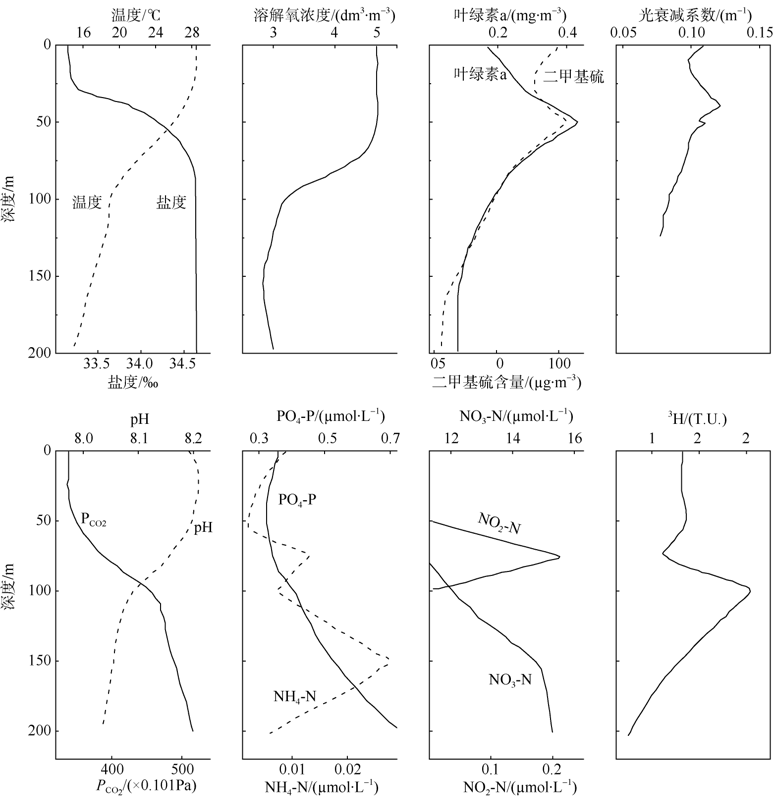
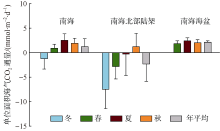
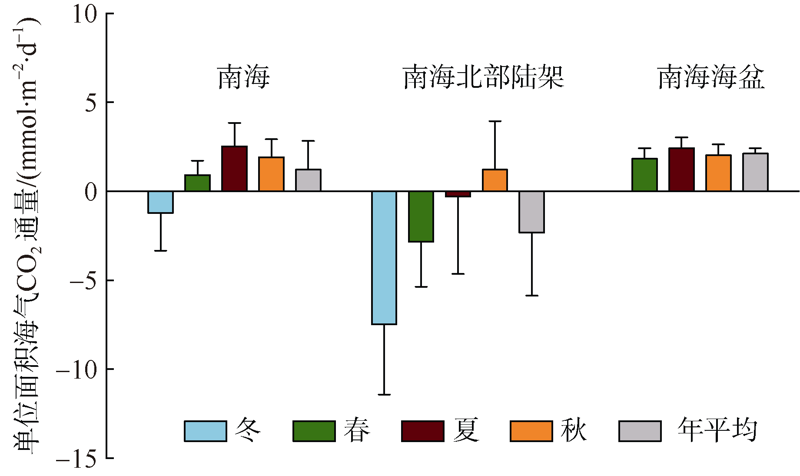
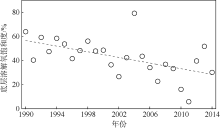
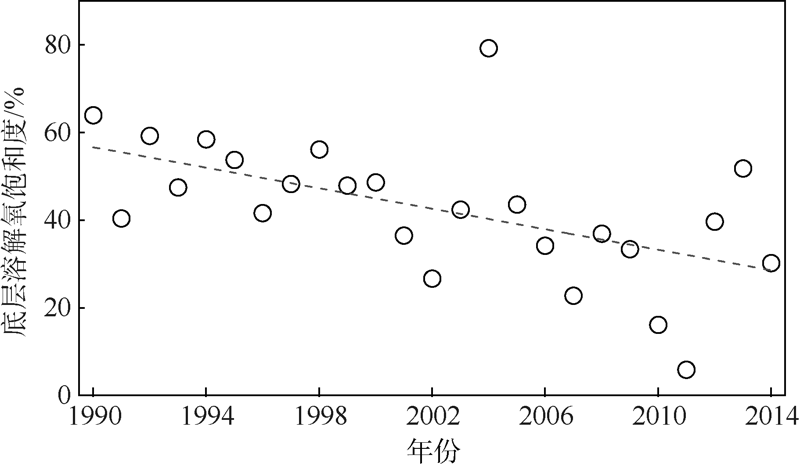
| [1] |
戴民汉, 孟菲菲, 2020. 南海碳循环: 通量、调控机理及其全球意义[J]. 科技导报, 38(18):30-34.
|
|
DAI MINHAN, MENG FEIFEI, 2020. Carbon cycle in the South China Sea: flux, controls and global implications[J]. Science & Technology Review, 38(18):30-34 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
房殿勇, 翦知湣, 汪品先, 1998. 南沙海区南部近30ka来的古生产力记录[J]. 科学通报, 43(18):2005-2008.
|
| [3] |
韩舞鹰, 王汉奎, 1991. 南海NO2-N薄层的研究[J]. 海洋学报, 13(2):200-206.
|
| [4] |
韩舞鹰, 王明彪, 王汉奎, 1994. 南沙海域上层海水碳垂直通量的初步研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 25(3):345-348.
|
|
HAN WUYING, WANG MINGBIAO, WANG HANKUI, 1994. The vertical carbon flux of epipelagic water in the Nansha area of the South China Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 25(3):345-348 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
韩舞鹰, 1998. 南海海洋化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 1-389.
|
| [6] |
翦知湣, 王律江, KIENAST M, 1999. 南海晚第四纪表层古生产力与东亚季风变迁[J]. 第四纪研究, (1):32-40.
|
|
JIAN ZHIMIN, WANG LÜJIANG, KIENAST M, 1999. Late quaternary surface paleoproductivity and variations of the east Asian monsoon in the South China Sea[J]. Quaternary Sciences, (1):32-40 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
焦念志, 梁彦韬, 张永雨, 等, 2018. 中国海及邻近区域碳库与通量综合分析[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 48(11):1393-1421.
|
|
JIAO NAINZHI, LIANG YANTAO, ZHANG YONGYU, et al, 2018. Carbon pools and fluxes in the China Seas and adjacent oceans[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 61(11):1535-1563.
|
| [8] |
李建如, 王汝建, 李保华, 2002. 南海南部12 Ma以来的蛋白石堆积速率与古生产力变化[J]. 科学通报, 47(3):235-237.
|
| [9] |
李团结, 2017. 伶仃洋地形地貌阶段性演变过程及趋势分析[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学: 1-112.
|
|
LI TUANJIE, 2017. Analysis of Lingding Bay landform stage evolution and trends[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences: 1-112 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
李秀芹, 卢楚谦, 蔡伟叙, 等, 2014. 珠江口上游海域春季水体缺氧特征及相关因素[J]. 海洋环境科学, 33(6):854-859.
|
|
LI XIUQIN, LU CHUQIAN, CAI WEIXU, et al, 2014. The character of hypoxia and the correlating factors in the upper reach of the Pearl River Estuary during spring[J]. Marine Environmental Sciences, 33(6):854-859 (in Chinese with English Abstract).
|
| [11] |
林洪瑛, 韩舞鹰, 1989. 我国低纬度海水中O2最大值的初步研究[J]. 海洋学报, 11(2):162-169.
|
| [12] |
林洪瑛, 韩舞鹰, 2001. 南沙群岛海域理化参数垂向分布特征及跃层生态系的提法[J]. 海洋学报, 23(1):43-51.
|
|
LIN HONGYING, HAN WUYING, 2001. Vertical characteristics for the physical and chemical parameters, and a viewpoint of the thermocline ecosystem in the Nansha Islands[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 23(1):43-51 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [13] |
林洪瑛, 程赛伟, 韩舞鹰, 等, 2003. 南沙群岛海域次表层溶解氧垂直分布最大值的强度特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 22(3):9-15.
|
|
LIN HONGYING, CHENG SAIWEI, HAN WUYING, et al, 2003. Intensity of vertically distributed maximum DO in Nansha Islands Sea Area[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 22(3):9-15 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [14] |
刘茜, 郭香会, 尹志强, 等, 2018. 中国邻近边缘海碳通量研究现状与展望[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 48(11):1422-1443.
|
|
LIU QIAN, GUO XIANGHUI, YIN ZHIQIANG, et al, 2018. Carbon fluxes in the China Seas: an overview and perspective[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 61(11):1564-1582.
|
| [15] |
龙爱民, 陈绍勇, 周伟华, 等, 2006. 南海北部秋季营养盐、溶解氧、pH值和叶绿素a分布特征及相互关系[J]. 海洋通报, 25(5):9-16.
|
|
LONG AIMIN, CHEN SHAOYONG, ZHOU WEIHUA, et al, 2006. Distribution of macro-nutrients, dissolved oxygen, pH and Chl a and their relationships in northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 25(5):9-16 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [16] |
宋金明, 1997. 中国近海沉积物-海水界面化学[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社: 1-222.
|
|
SONG JINMING, 1997. Chemistry of sediment-seawater interface of the China Seas[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press: 1-222(in Chinese).
|
| [17] |
宋金明, 1999a. 维持南沙珊瑚礁生态系统高生产力的新观点──拟流网理论[J]. 海洋科学集刊, (41):79-85.
|
|
SONG JINMING, 1999a. The new viewpoint of the high productivity supporting Nansha coral reef ecosystem-simulated drift-net theory[J]. Studia Marina Sinica, (41):79-85 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [18] |
宋金明, 1999b. 南沙珊瑚礁生态系中元素的垂直转移途径[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 30(1):1-5.
|
|
SONG JINMING, 1999b. Paths of element vertical transport in the Nansha coral reef ecosystem, South China Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 30(1):1-5 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [19] |
宋金明, 2004. 中国近海生物地球化学[M]. 济南: 山东科学技术出版社: 1-591.
|
| [20] |
宋金明, 徐永福, 胡维平, 等, 2008. 中国近海与湖泊碳的生物地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 1-533.
|
|
SONG JINMING, XU YONGFU, HU WEIPING, et al, 2008. Biogeochemistry of carbon in China seas and lakes[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 1-533(in Chinese).
|
| [21] |
宋金明, 曲宝晓, 李学刚, 等, 2018. 黄东海的碳源汇: 大气交换、水体溶存与沉积物埋藏[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 48(11):1444-1455.
|
| [22] |
宋金明, 段丽琴, 王启栋, 2020. 直面健康海洋之问题2—海水低氧及其生态环境效应[M]//李乃胜. 经略海洋(2020). 北京: 海洋出版社: 21-46.
|
| [23] |
叶丰, 黄小平, 刘庆霞, 2012. 2010年夏季珠江口海域溶解氧的分布特征和海气交换通量[J]. 海洋环境科学, 31(3):346-351.
|
|
YE FENG, HUANG XIAOPING, LIU QINGXIA, 2012. Characteristics of dissolved oxygen and O2 flux across the water-air interface of the Pearl River Estuary during summer 2010[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 31(3):346-351 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [24] |
叶丰, 贾国东, 韦刚健, 2019. 稳定碳氮同位素对珠江口溶解氧亏损的共同限定[C]// 中国矿物岩石地球化学学会第17届学术年会论文摘要集. 杭州: 中国矿物岩石地球化学学会: 634.
|
| [25] |
赵卫东, 宋金明, 李鹏程, 等, 2001. 珊瑚礁生态系的协同营养模式[J]. 中国科学基金, 15(1):32-35.
|
|
ZHAO WEIDONG, SONG JINMING, LI PENGCHENG, et al, 2001. Cooperation model of nutrition processes in coral reef ecosystem[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 15(1):32-35 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [26] |
郑国侠, 宋金明, 孙云明, 等, 2006. 南海深海盆表层沉积物氮的地球化学特征与生态学功能[J]. 海洋学报, 28(6):44-52.
|
|
ZHENG GUOXIA, SONG JINMING, SUN YUNMING, et al, 2006. Geochemical characteristics and ecological functions of nitrogen in the abyssal basin surface sediments, South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 28(6):44-52 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [27] |
NING X, LIN CHUN, HAO QIANG, et al, 2009. Long term changes in the ecosystem in the northern South China Sea during 1976-2004[J]. Biogeosciences, 6(10):2227-2243.
doi: 10.5194/bg-6-2227-2009
|
| [28] |
QIAN WEI, GAN JIANPING, LIU JINWEN, et al, 2018. Current status of emerging hypoxia in a eutrophic estuary: the lower reach of the Pearl River Estuary, China[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 205:58-67.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2018.03.004
|
| [29] |
SONG JINMING, 2010. Biogeochemical processes of biogenic elements in China marginal seas[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer: 1-662.
|
| [30] |
SONG JINMING, QU BAOXIAO, LI XUEGANG, et al, 2018. Carbon sinks/sources in the Yellow and East China Seas—Air-sea interface exchange, dissolution in seawater, and burial in sediments[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 61(11):1583-1593.
doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9213-6
|
| [31] |
SONG JINMING, WANG QIDONG, 2020. A new mechanism of atmospheric CO2 absorption promoted by iron-nitrogen coupling in low-latitude oceans during ice age[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 63(1):167-168.
doi: 10.1007/s11430-019-9558-8
|
 ), WANG Qidong1,2,3,4
), WANG Qidong1,2,3,4