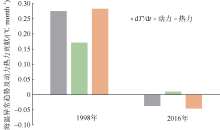
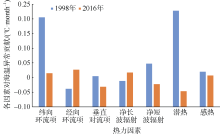
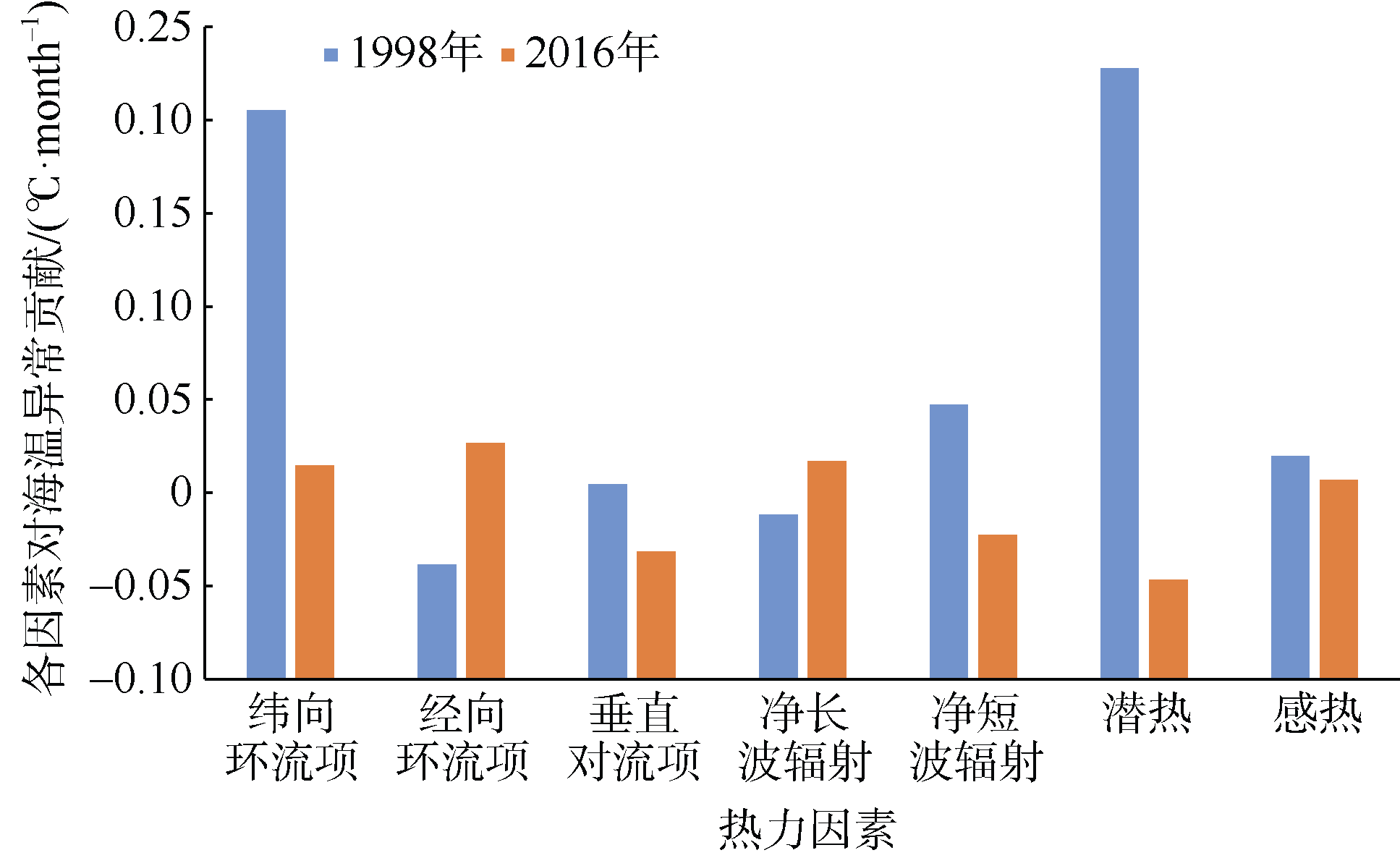
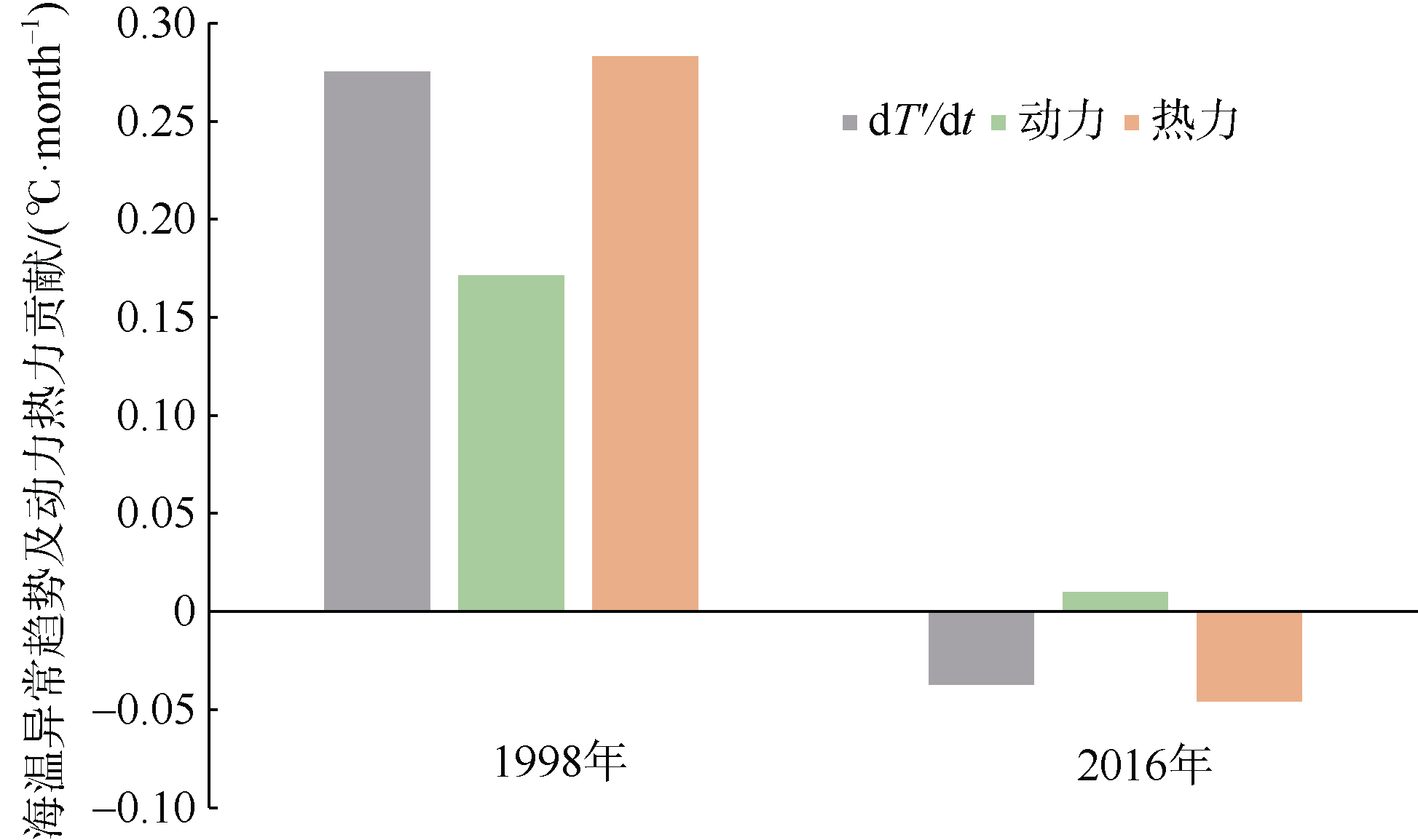Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2020, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (3): 19-30.doi: 10.11978/2019085CSTR: 32234.14.2019085
• Marine Hydrology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Differences of sea surface temperature anomalies in the North Atlantic in springs of 1998 and 2016 and their causes
Wenjing XUE, Jinhua YU( ), Lin CHEN
), Lin CHEN
- Key Laboratory of Meteorological Disasters, Ministry of Education, Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology/ Collaborative Innovation Center for Forecast and Evaluation of Meteorological Disasters, Nanjing 210044, China
-
Received:2019-09-09Revised:2019-11-13Online:2020-05-10Published:2020-05-19 -
Contact:Jinhua YU E-mail:jhyu@nuist.edu.cn -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(41575083);National Natural Science Foundation of China(41730961)
Cite this article
Wenjing XUE, Jinhua YU, Lin CHEN. Differences of sea surface temperature anomalies in the North Atlantic in springs of 1998 and 2016 and their causes[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(3): 19-30.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Fig. 1
Anomalous Ni?o 3.4 (170°-120°W, 5°S-5°N) index (dotted line, left axis), anomalous North Atlantic tripole mode index (solid line, right axis) evolution during El Ni?o events of 1997-1998 (a) and 2015-2016 (b). The number 0 represents a developing year, and 1 represents a decaying year"
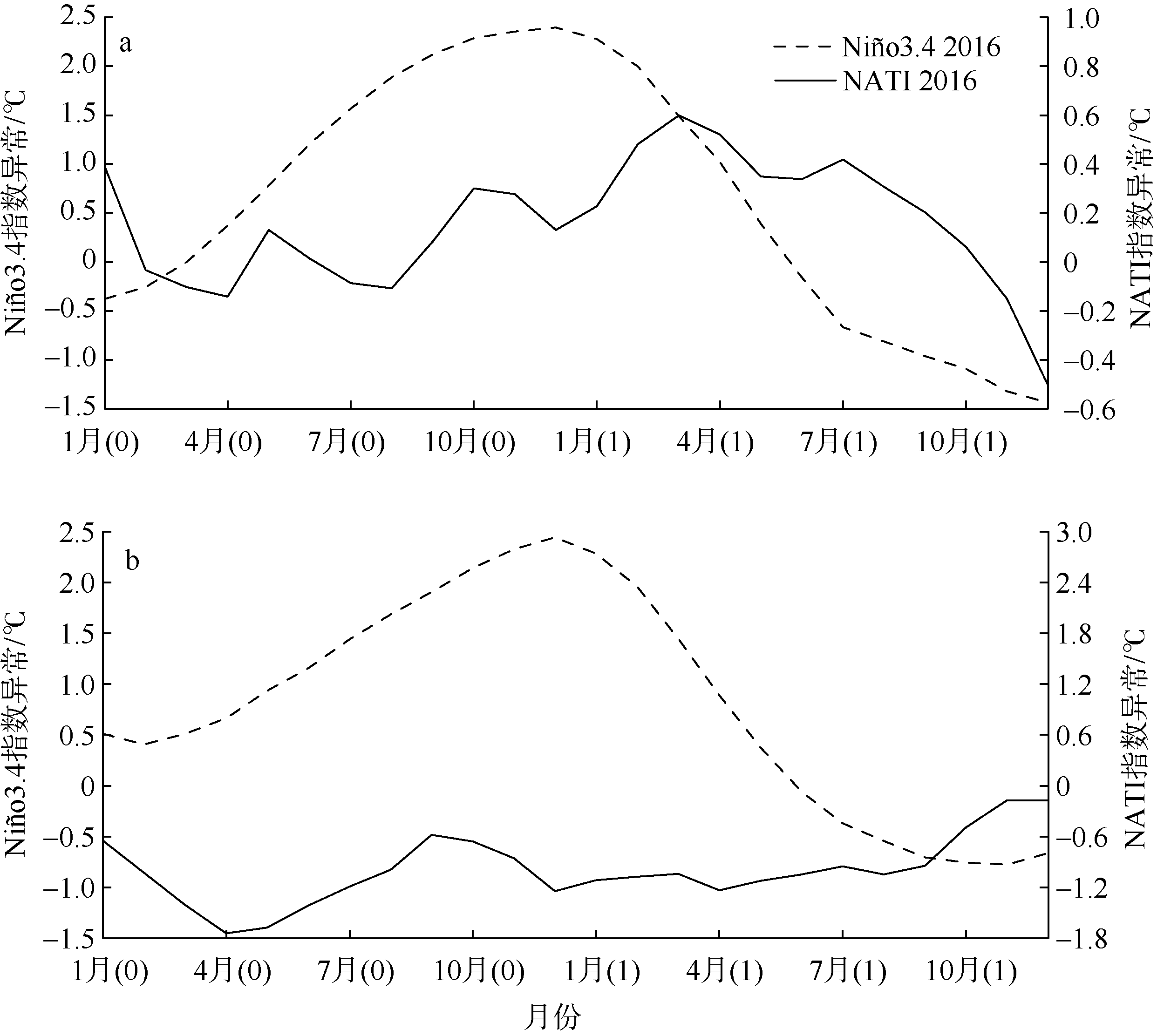
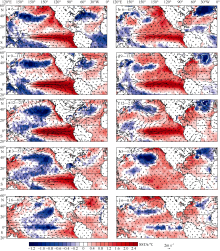
Fig. 2
SSTA (shading) and anomalous wind vector at 850 hPa (arrow) during the developing phase in June-August (a, b) and September-November (c, d), the peak phase in December-February (e, f), and the El Ni?o decaying phase in March-May (g, h) and June-August (i, j) for 1997-1998 (left panels) and 2015-2016 ( right panels)"

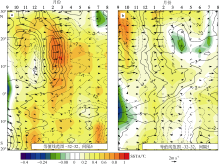
Fig. 5
Meridional time section structure of the tropical North Atlantic surface wind anomaly (arrow; units: m·s-1), latent heat flux anomaly (contour; units: W·M-2, downward is positive), SSTA (shading; units: ℃) from September in El Ni?o developing phase to August in El Ni?o decaying phase. All data are regionally-averaged in the tropical North Atlantic (50°-15°W). The solid line is positive and the dashed line is negative. a) 1997-1998; b) 2015-2016"

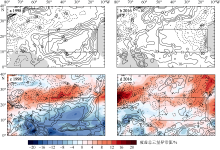
Fig. 6
Spatial distributions of tropical North Atlantic surface latent heat flux anomaly (a, b; units: W·M-2), net surface shortwave radiation anomaly (c, d; units: W·M-2) in February and the anomalous total cloud cover (c, d; shading, units: % ) in January-March in El Ni?o developing years. The solid line is positive and the dashed line is negative, Contour lines range from -60 to 60 with an interval of 10 (a, b) and range from -16 to 16 with an interval of 4 (c, d); Boxes are tropical diagnostic area. (a, c) are for 1998, and (b, d) are for 2016"
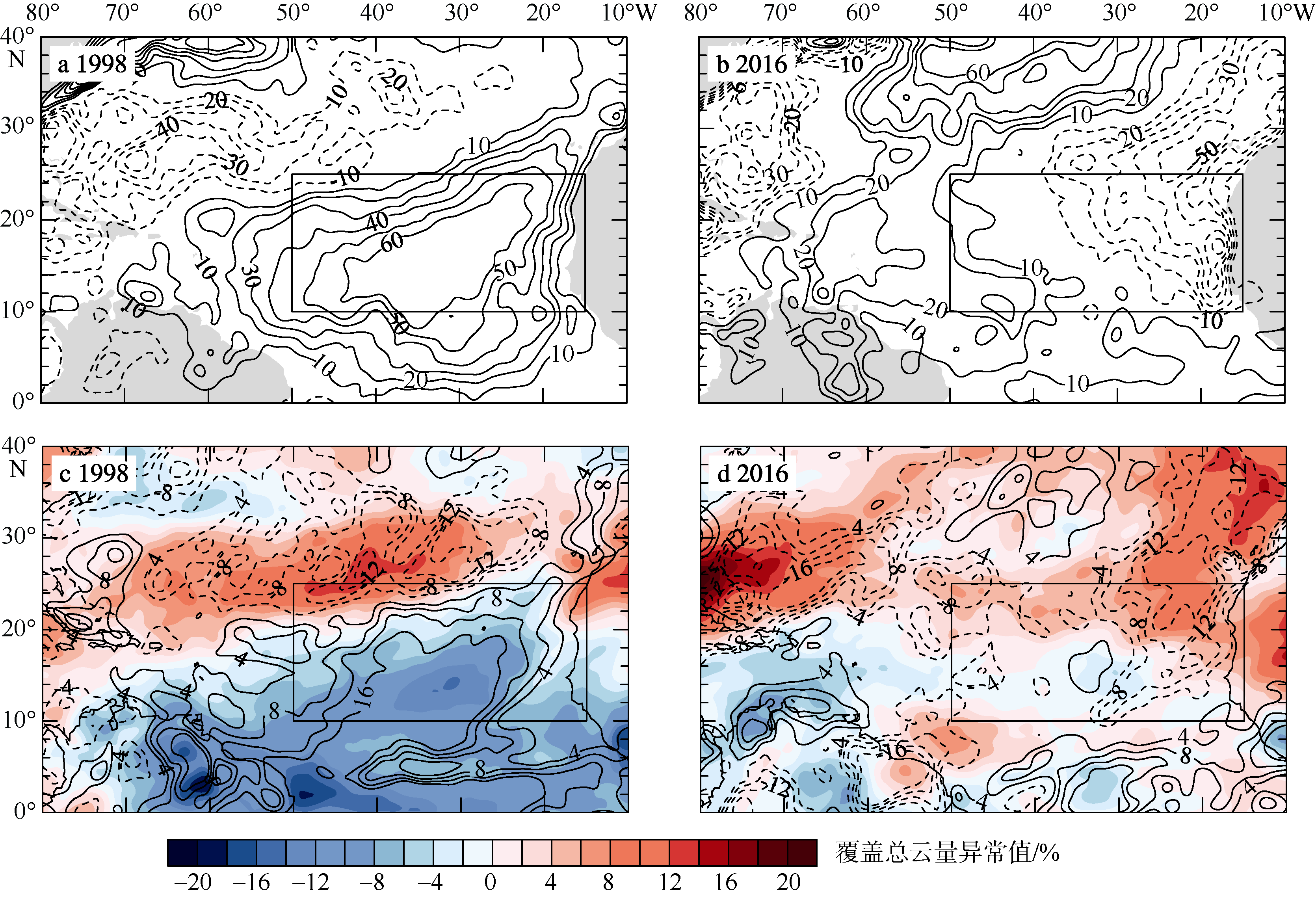
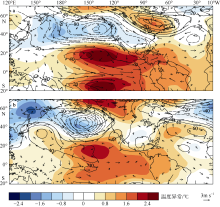
Fig. 7
Spatial distributions of Pacific and Atlantic anomalous geopotential height at 500 hPa (contour; units: gpm), anomalous tropospheric temperature (shading; units: ℃) and anomalous wind vector at 850 hPa (arrow; unit:s m·s-1) in Jannuary-March in El Ni?o developing years. The solid line is positive and the dashed line is negative. a) 1998; b) 2016"
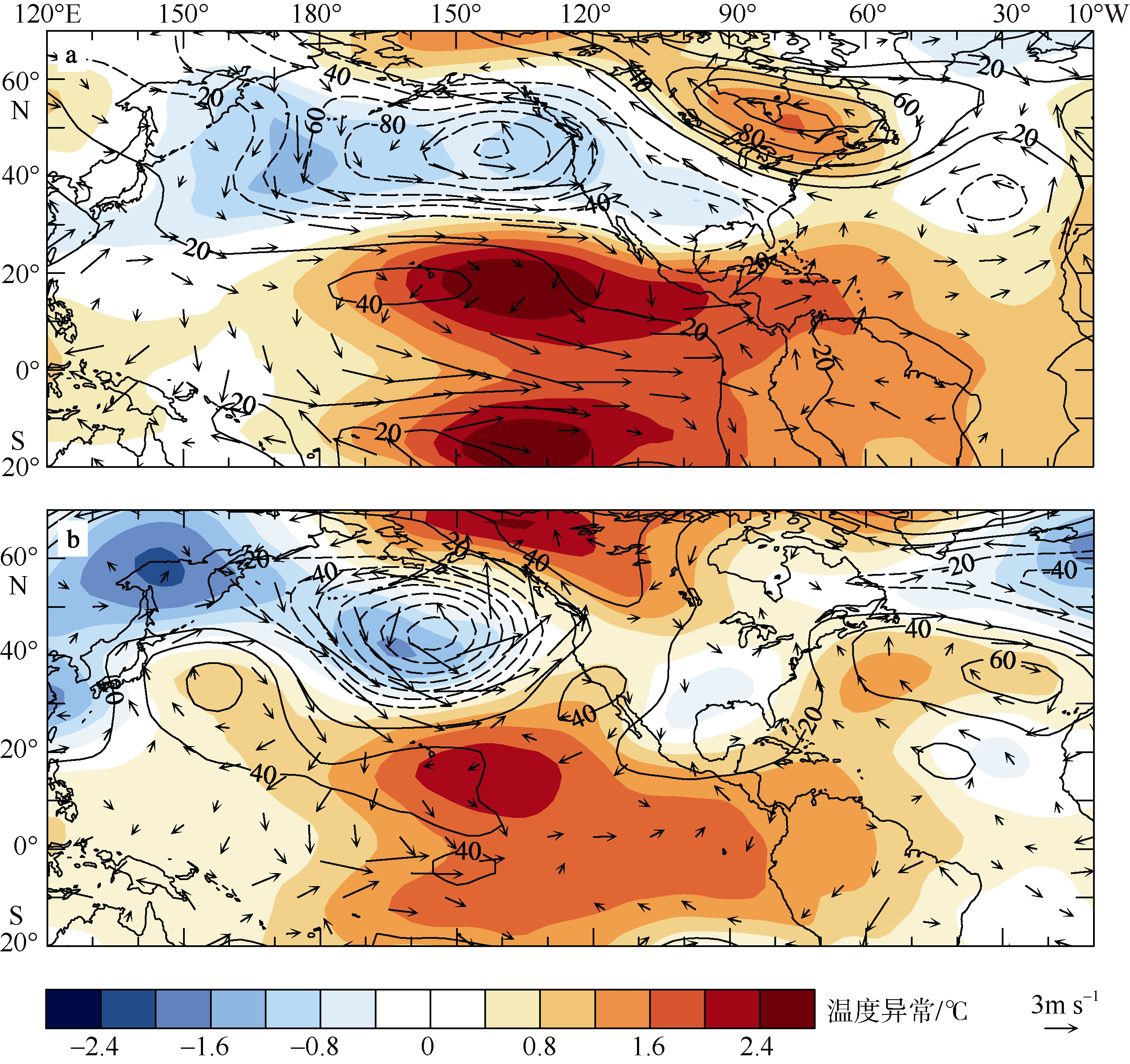
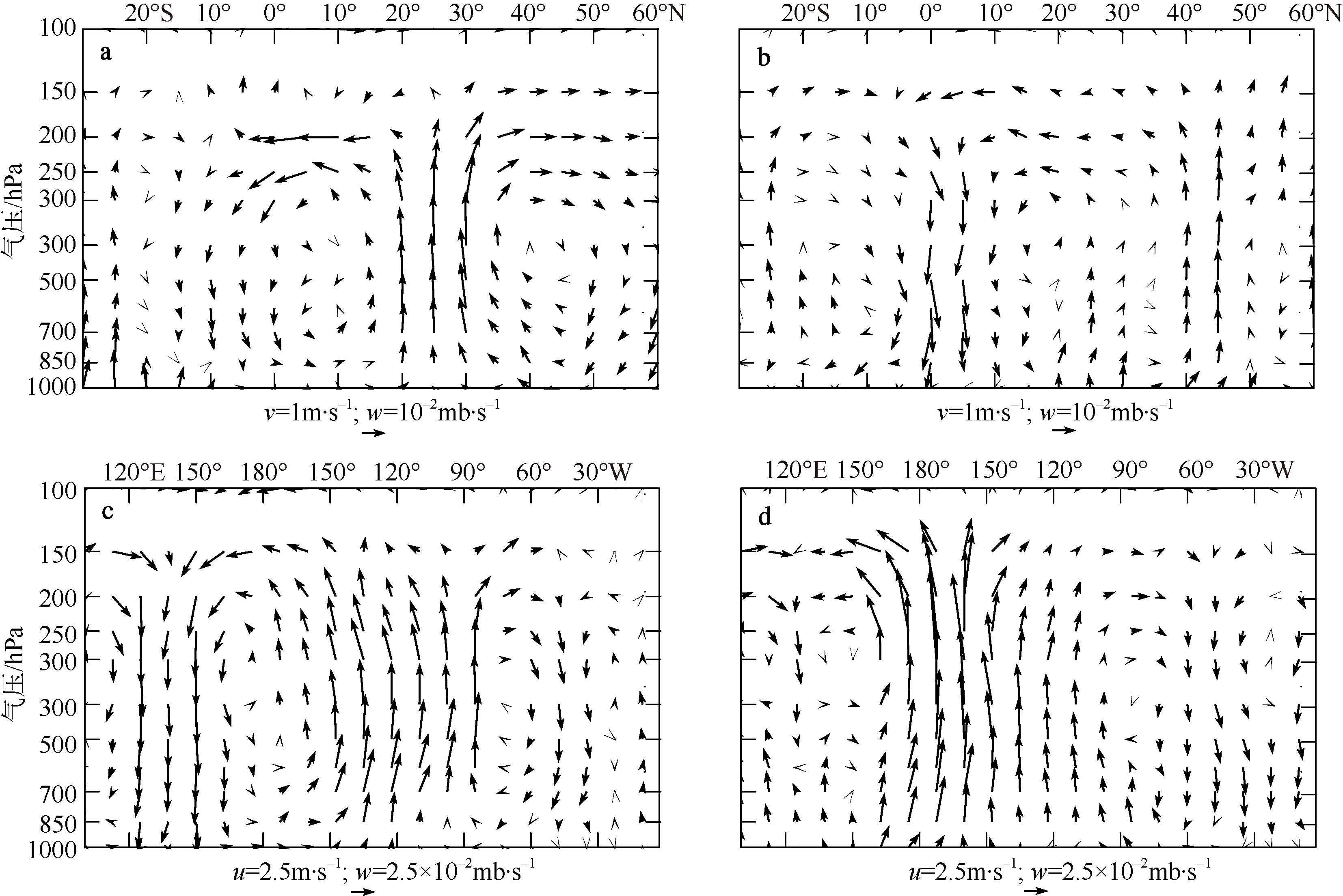
Fig. 9
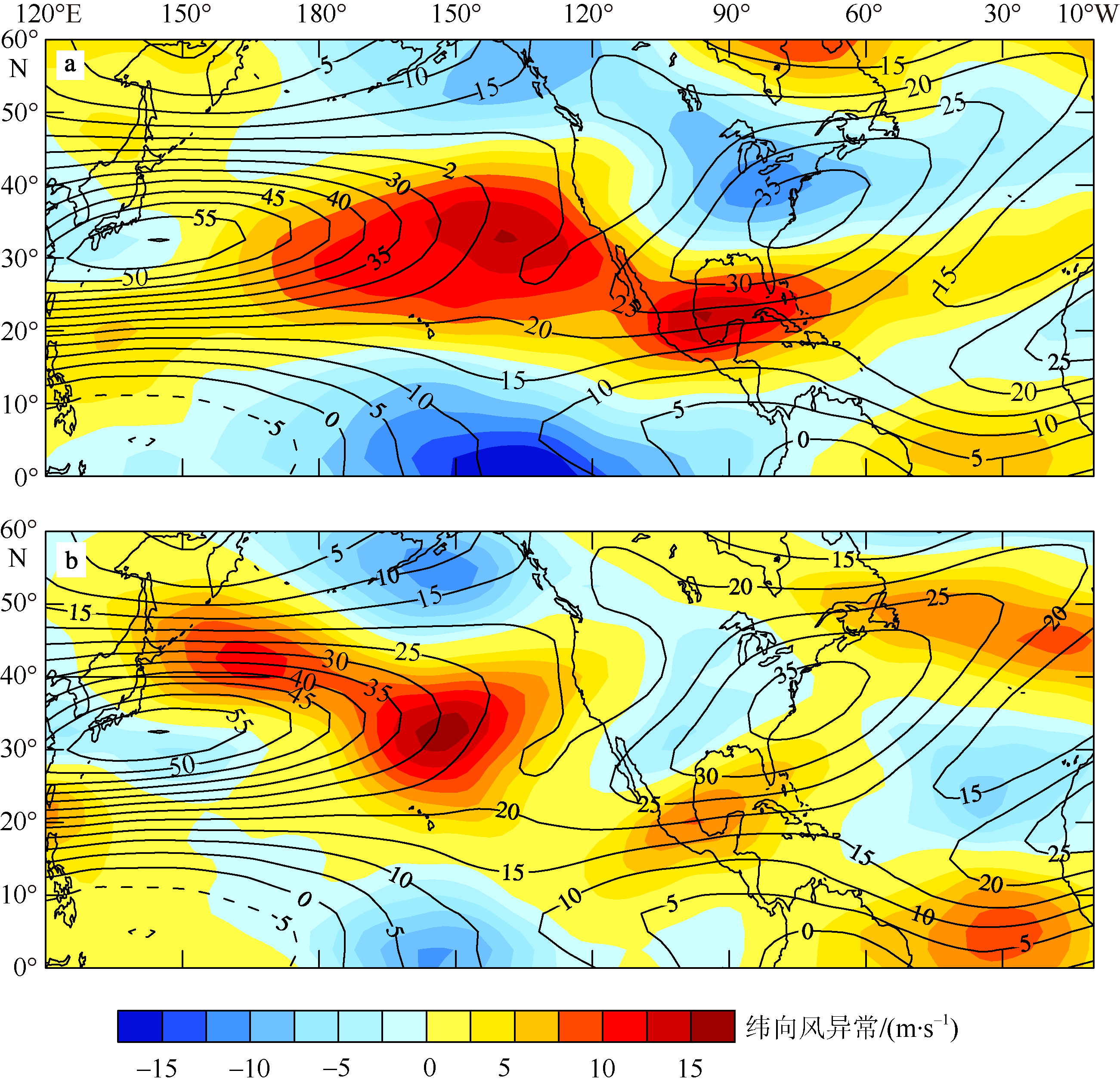
Meridional vertical section structure of Hadley circulation anomalies in the Atlantic (between 80°W and 0°) by averaging anomalous longitudinal divergent wind (a, b; units: m·s-1) and anomalous vertical velocity, zonal vertical section structure of Walker circulation anomalies (between 5°S and 5°N) by averaging anomalous latitudinal divergent wind (units: m·s-1) and anomalous vertical velocity (c, d; units: 10-2 mb·s-1) during El Ni?o developing phase in January-March. (a, c) 1998; (b, d) 2016"
| 1 |
杜美芳, 徐海明, 周超 , 2015. 基于CMIP5资料的热带大洋非均匀增暖及其成因的分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 34(3):1-12
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2015.03.001 |
|
DU MEIFANG, XU HAIMIN, ZHOU CHAO, . 2015. Analysis of non-uniform sea surface temperature warming over the tropical oceans and its causes based on CMIP5 data[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 34(3):1-12 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2015.03.001 |
|
| 2 |
李刚, 李崇银, 江晓华 , 等, 2015. 1900~2009年全球海表温度异常的时空变化特征分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 34(4): 12-22.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2015.04.002 |
|
LI GANG, LI CHONGYIN, JIANG XIAOHUA, et al. 2015. Analysis of spatiotemporal variability of global sea surface temperature anomalies during 1900~2009[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 34(4):12-22 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2015.04.002 |
|
| 3 |
李晓燕, 翟盘茂 , 2000. ENSO事件指数与指标研究[J]. 气象学报, 58(1): 102-109.
doi: 10.11676/qxxb2000.010 |
|
LI XIAOYAN, ZHAI PANMAO . 2000. On indices and indicators of ENSO episodes[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 58(1):102-109 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.11676/qxxb2000.010 |
|
| 4 | 刘珊, 王辉, 姜华 , 等, 2013. 北太平洋海表温度及各贡献因子的变化[J]. 海洋学报, 35(1): 63-75. |
| LIU SHAN, WANG HUI, JIANG HUA, et al, 2013. Variation of sea surface temperature and its influence factors in the North Pacific[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 35(1):63-75 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 5 | 任宏昌, 左金清, 李维京 , 2018. 1998年和2016年北大西洋海温异常对中国夏季降水影响的数值模拟研究[J]. 气象学报, 75(6):877-893. |
| REN HONGCHANG, ZUO JINQING, LI WEIJING. 2017. Role of the North Atlantic SST anomalies in the 1998 and 2016 summer floods in China[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 75(6):877-893 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 6 |
薛峰, 段欣妤, 苏同华 , 2018. 强El Niño衰减年东亚夏季风的季节内变化: 1998年和2016年的对比分析[J]. 大气科学,42(6):1407-1420.
doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1711.17205 |
|
XU FENG, DUAN XINYU, SU TONGHUA, 2018. Intraseasonal variation of East Asian summer monsoon during strong El Niño decaying summer: comparison between 1998 and 2016[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 42(6):1407-1420 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1711.17205 |
|
| 7 | 郑依玲, 陈泽生, 王海 , 等, 2019. 2015/2016年超强厄尔尼诺事件基本特征及生成和消亡机制[J]. 热带海洋学报, 38(4):10-19. |
| ZHENG YILING, CHEN ZESHENG, WANG HAI, et al. 2019. Features of 2015/2016 extreme El Niño event and its evolution mechanisms[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 38(4):10-19 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 8 | AMAYA D J, FOLTZ G R , 2014. Impacts of canonical and modoki El Niño on tropical Atlantic SST[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 119(2):777-789. |
| 9 | BJERKNES J , 1964. Atlantic air-sea interaction[J]. Advances in Geophysics, 10:1-82. |
| 10 | BJERKNES J , 1969. Atmospheric teleconnections from the equatorial Pacific[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 97(3):163-172. |
| 11 | BRÖNNIMANN S , 2007. Impact of El Niño-southern Oscillation on European climate[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 45(3): RG3003. |
| 12 | CARTON J A, CAO XIANHE , 1996. Decadal and interannual SST variability in the tropical Atlantic Ocean[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 26(7):1165-1175. |
| 13 | CAYAN D R , 1992. Latent and sensible heat flux anomalies over the northern oceans: driving the sea surface temperature[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 22(8):859-881. |
| 14 | CHIANG J C H, SOBEL A H , 2002. Tropical tropospheric temperature variations caused by ENSO and their influence on the remote tropical climate[J]. Journal of Climate, 15(18):2616-2631. |
| 15 | CURTIS S, HASTENRATH S , 1995. Forcing of anomalous sea surface temperature evolution in the tropical Atlantic during Pacific warm events[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 100(C8):15835-15847. |
| 16 | CZAJA A, MARSHALL J , 2001. Observations of atmosphere- ocean coupling in the North Atlantic[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 127(576):1893-1916. |
| 17 |
DELWORTH T L , 1996. North Atlantic interannual variability in a coupled ocean-atmosphere model[J]. Journal of Climate, 9(10):2356-2375.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1996)009<2356:NAIVIA>2.0.CO;2 |
| 18 | DELWORTH T L, GREATBATCH R J , 2000. Multidecadal thermohaline circulation variability driven by atmospheric surface flux forcing[J]. Journal of Climate, 13(9):1481-1495. |
| 19 | ENFIELD D B, MAYER D A , 1997. Tropical Atlantic sea surface temperature variability and its relation to El Niño-southern Oscillation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 102(C1):929-945. |
| 20 | GARCÍA-SERRANO J, CASSOU C, DOUVILLE H , et al, 2017. Revisiting the ENSO teleconnection to the tropical North Atlantic[J]. Journal of Climate, 30(17):6945-6957. |
| 21 |
GILL A E , 1980. Some simple solutions for heat-induced tropical circulation[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 106(449):447-462.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1477-870X |
| 22 | GOUIRAND I, MORON V , 2003. Variability of the impact of El Niño-southern Oscillation on sea-level pressure anomalies over the North Atlantic in January to March (1874-1996)[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 23(13):1549-1566. |
| 23 | GRAF H F, ZANCHETTIN D , 2012. Central Pacific El Niño, the “subtropical bridge,” and Eurasian climate[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 117(D1):D01102. |
| 24 | HALLIWELL G R JR , 1998. Simulation of North Atlantic decadal/multidecadal winter SST anomalies driven by basin-scale atmospheric circulation anomalies[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 28(1):5-21. |
| 25 | HOREL J D, WALLACE J M , 1981. Planetary-scale atmospheric phenomena associated with the southern oscillation[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 109(4):813-829. |
| 26 | KLEIN S A, SODEN B J, LAU N C , 1999. Remote sea surface temperature variations during ENSO: evidence for a tropical atmospheric bridge[J]. Journal of Climate, 12(4):917-932. |
| 27 | KUSHNIR Y , 1994. Interdecadal variations in North Atlantic sea surface temperature and associated atmospheric conditions[J]. Journal of Climate, 7(1):141-157. |
| 28 | LEE S K, WANG CHUNZAI, MAPES B E , 2009. A simple atmospheric model of the local and teleconnection responses to tropical heating anomalies[J]. Journal of Climate, 22(2):272-284. |
| 29 | LI T, ZHANG YONGSHENG, LU ER , et al, 2002. Relative role of dynamic and thermodynamic processes in the development of the Indian Ocean dipole: an OGCM diagnosis[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 29(23):2110. |
| 30 |
ROPELEWSKI C F, HALPERT M S , 1987. Global and regional scale precipitation patterns associated with the El Niño/southern Oscillation[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 115(8):1606-1626.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1987)115<1606:GARSPP>2.0.CO;2 |
| 31 | SARAVANAN R, CHANG PING , 2000. Interaction between tropical Atlantic variability and El Niño-southern Oscillation[J]. Journal of Climate, 13(13):2177-2194. |
| 32 | SU JINGZHI, ZHANG RENHE, LI T , et al, 2010. Causes of the El Niño and La Niña amplitude asymmetry in the equatorial eastern Pacific[J]. Journal of Climate, 23(3):605-617. |
| 33 | SUTTON R T, ALLEN M R , 1997. Decadal predictability of North Atlantic sea surface temperature and climate[J]. Nature, 388(6642):563-567. |
| 34 | TALLEY L D , 1984. Meridional heat transport in the Pacific Ocean[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 14(2):231-241. |
| 35 |
TRENBERTH K E, CARON J M , 2000. The southern Oscillation revisited: sea level pressures, surface temperatures, and precipitation[J]. Journal of Climate, 13(24):4358-4365.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2000)013<4358:TSORSL>2.0.CO;2 |
| 36 | WANG CHUNZAI , 2004. ENSO, Atlantic climate variability, and the Walker and Hadley circulations[M] //DIAZ H F, BRADLEY R S. The Hadley circulation: Present, past and future. Dordrecht: Springer:173-202. |
| 37 |
WU RENGUANG, YANG SONG, LIU SHI , et al, 2010. Changes in the relationship between northeast China summer temperature and ENSO[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 115(D21):D21107.
doi: 10.1029/2010JD014422 |
| 38 |
YU JINHUA, CHEN CHENG, LI T , et al, 2016. Contribution of major SSTA modes to the climate variability of tropical cyclone genesis frequency over the western North Pacific[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 142(695):1171-1181.
doi: 10.1002/qj.2016.142.issue-695 |
| 39 |
ZHANG WENJUN, WANG ZIQI, STUECKER M F , et al, 2019. Impact of ENSO longitudinal position on teleconnections to the NAO[J]. Climate Dynamics, 52(1-2):257-274.
doi: 10.1007/s00382-018-4135-1 |
| No related articles found! |
|
||