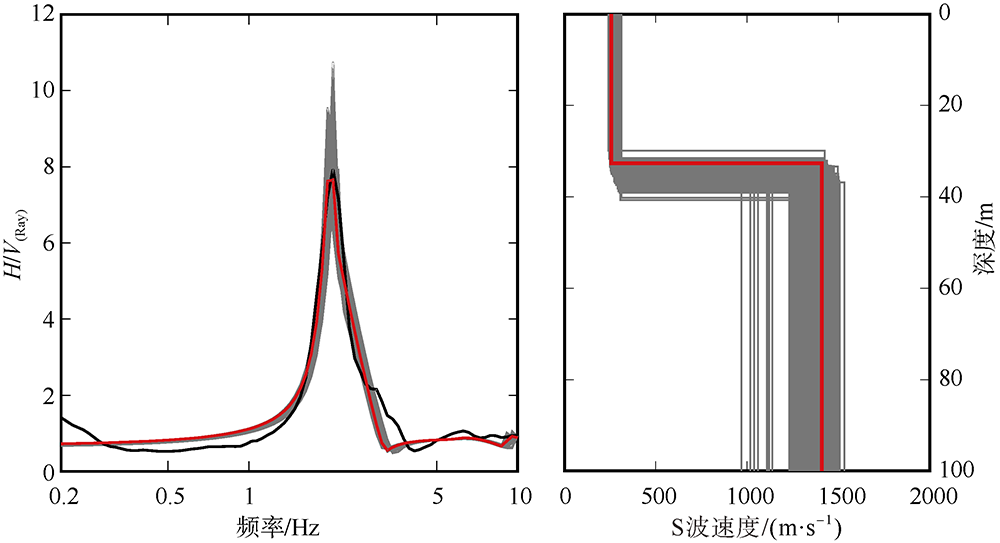
| [1] |
樊祺诚, 孙谦, 李霓, 等, 2004. 琼北火山活动分期与全新世岩浆演化[J]. 岩石学报, 20(3): 533-544.
|
|
FAN QICHENG, SUN QIAN, LI NI, et al, 2004. Periods of volcanic activity and magma evolution of Holocene in North Hainan island[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(3): 533-544. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [2] |
胡久常, 郭明瑞, 刘伟, 等, 2009. 海口地区火山活动初步研究[J]. 地震地质, 31(4): 647-654.
|
|
HU JIUCHANG, GUO MINGRUI, LIU WEI, et al, 2009. Primary research on the volcanic activity in Haikou area[J]. Seismology and Geology, 31(4): 647-654. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [3] |
孙谦, 2003. 琼北第四纪火山活动与岩浆演化[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所.
|
|
SUN QIAN, 2003. Quaternary volcanic activity and magma evolution in North Hainan island[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administrator. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [4] |
徐晓枫, 王惠琳, 陈小敏, 2014. 海南岛及邻区地震精确定位及断裂构造分析[J]. 地震研究, 37(2): 216-221.
|
|
XU XIAOFENG, WANG HUILIN, CHEN XIAOMIN, 2014. Analysis on accurate location of earthquakes and fault structure in Hainan island and its adjacent areas[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 37(2): 216-221. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [5] |
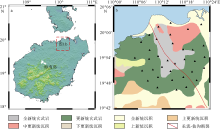
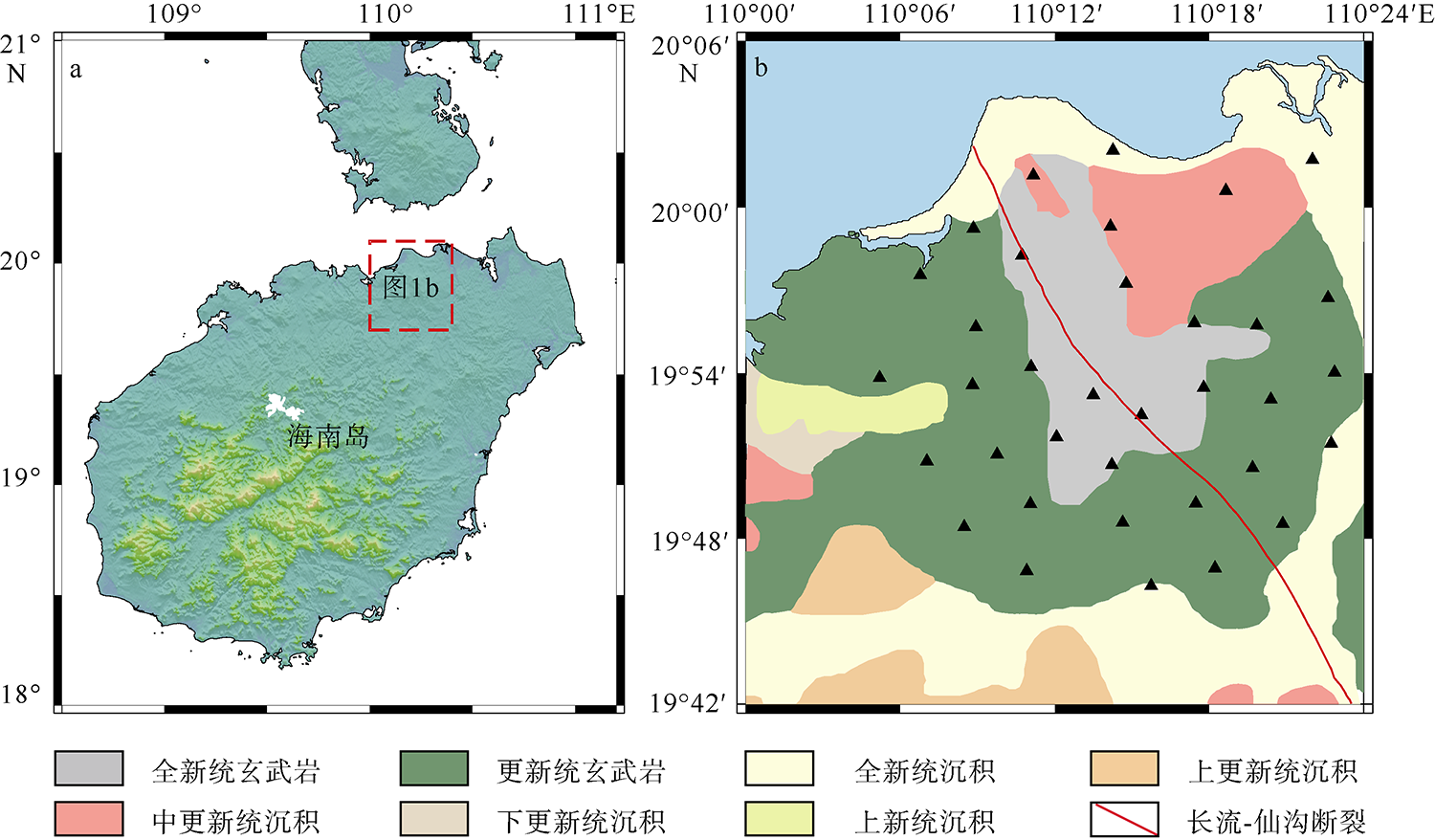
闫成国, 江娃利, 2007. 琼北地区北西方向长流-仙沟断裂带晚第四纪活动及与火山活动关系的讨论[J]. 震灾防御技术, 2(3): 230-242.
|
|
YAN CHENGGUO, JIANG WALI, 2007. Relationship between the activity of the Changliu-Xiangou fault zone in Late-Quaternary and volcanic activity in North Hainan island[J]. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 2(3): 230-242. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [6] |
詹文欢, 刘以宣, 1989. 琼州海峡的断裂构造与区域稳定性分析[J]. 热带海洋, 8(4): 70-77.
|
|
ZHAN WENHUAN, LIU YIXUAN, 1989. A study on faulting and regional stability in Qiongzhou strait[J]. Tropic Oceanology, 8(4): 70-77. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [7] |
张仲英, 刘瑞华, 韩中元, 1987. 海南岛沿海的第四纪地层[J]. 热带地理, 7(1): 54-64.
|
|
ZHANG ZHONGYING, LIU RUIHUA, HAN ZHONGYUAN, 1987. The quaternary stratigraphy along the coastal area of Hainan island[J]. Tropical Geography, 7(1): 54-64. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [8] |
邹和平, 黄玉昆, 1987. 琼北新生代坳陷构造特征及其演化[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 11(1): 33-46.
|
|
ZOU HEPING, HUANG YUKUN, 1987. The tectonic characteristics and evolution of the Qiongbei Cenozoic depression[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 11(1): 33-46. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [9] |
ACERRA C, AGUACIL G, ANASTASIADIS A, et al, 2004. Guidelines for the implementation of the H/V spectral ratio technique on ambient vibrations measurements, processing and interpretation[R]. European Commission.
|
| [10] |
ANDERSON J G, BODIN P, BRUNE J N, et al, 1986. Strong ground motion from the Michoacan, Mexico, Earthquake[J]. Science, 233(4768): 1043-1049.
doi: 10.1126/science.233.4768.1043
|
| [11] |
BAO FENG, LI ZHIWEI, YUEN D A, et al, 2018. Shallow structure of the Tangshan fault zone unveiled by dense seismic array and horizontal-to-vertical spectral ratio method[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 281: 46-54.
doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2018.05.004
|
| [12] |
BAO FENG, LI ZHIWEI, TIAN BAOFENG, et al, 2019. Sediment thickness variations of the Tangshan fault zone in North China from a dense seismic array and microtremor survey[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 185: 104045.
doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.104045
|
| [13] |
BONNEFOY-CLAUDET S, CÉCILE C, PIERRE-YVES B, et al, 2006. H/V ratio: a tool for site effects evaluation. Results from 1-D noise simulations[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 167(2): 827-837.
doi: 10.1111/gji.2006.167.issue-2
|
| [14] |
BONNEFOY-CLAUDET S, BAIZE S, BONILLA L F, et al, 2009. Site effect evaluation in the basin of Santiago de Chile using ambient noise measurements[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 176(3): 925-937.
doi: 10.1111/gji.2009.176.issue-3
|
| [15] |
CHEN QIFU, LIU LANBO, WANG WEIJUN, et al, 2009. Site effects on earthquake ground motion based on microtremor measurements for metropolitan Beijing[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54(2): 280-287.
|
| [16] |
DHAKAL Y P, AOI S, KUNUGI T, et al, 2017. Assessment of nonlinear site response at ocean bottom seismograph sites based on S-wave horizontal-to-vertical spectral ratios: a study at the Sagami Bay area K-NET sites in Japan[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 69(1): 29.
doi: 10.1186/s40623-017-0615-5
|
| [17] |
GARCÍA-JEREZ A, PIÑA-FLORES J, ÁNCHEZ-SESMA F J, et al, 2016. A computer code for forward calculation and inversion of the H/V spectral ratio under the diffuse field assumption[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 97: 67-78.
doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2016.06.016
|
| [18] |
GUILLIER B, CORNOU C, KRISTEK J, et al, 2006. Simulation of seismic ambient vibrations: does the H/V provide quantitative information in 2D-3D structure[C]// Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on the Effects of Surface Geology on Seismic Motion. Grenoble, France.
|
| [19] |
HOBIGER M, BARD P Y, CORNOU C, et al, 2009. Single station determination of Rayleigh wave ellipticity by using the random decrement technique (RayDec)[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 36(14): L14303.
doi: 10.1029/2009GL038863
|
| [20] |
HU YAXUAN, HAO MING, LI LINGYUN, et al, 2016. Three-dimensional crustal movement and the activities of earthquakes, volcanoes and faults in Hainan Island, China[J]. Geodesy and Geodynamics, 7(4): 284-294.
doi: 10.1016/j.geog.2016.05.008
|
| [21] |
HUANG JINLI, 2014. P- and S-wave tomography of the Hainan and surrounding regions: insight into the Hainan plume[J]. Tectonophysics, 633: 176-192.
doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2014.07.007
|
| [22] |
ISSAADI A, SEMMANE F, YELLES-CHAOUCHE A, et al, 2020. A shear-wave velocity model in the city of Oued-Fodda (northern Algeria) from Rayleigh wave ellipticity inversion[J]. Applied Sciences, 10(5): 1717.
doi: 10.3390/app10051717
|
| [23] |
KONNO K, OHMACHI T, 1998. Ground-motion characteristics estimated from spectral ratio between horizontal and vertical components of microtremor[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 88(1): 228-241.
doi: 10.1785/BSSA0880010228
|
| [24] |
LEI JIANSHE, ZHAO DAPENG, STEINBERGER B, et al, 2009. New seismic constraints on the upper mantle structure of the Hainan plume[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 173(1-2): 33-50.
doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2008.10.013
|
| [25] |
MUCCIARELLI M, GALLIPOLI M R, 2001. A critical review of 10 years of microtremor HVSR technique[J]. Bollettino di Geofisica Teorica ed Applicata, 42(3): 255-266.
|
| [26] |
NAKAMURA Y, 1989. A method for dynamic characteristics estimation of subsurface using microtremor on ground surface[J]. Quarterly Report of RTRI, 30(1): 25-33.
|
| [27] |
NAKAMURA Y, 2000. Clear identification of fundamental idea of Nakamura’s technique and its applications[C]// Proceedings of the 12th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering. New Zealand: Auckland: 25-30
|
| [28] |
SÁNCHEZ-SESMA F J, RODRÍGUEZ M, ITURRARÁN- VIVEROS U, et al, 2011. A theory for microtremor H/V spectral ratio: application for a layered medium[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 186(1): 221-225.
doi: 10.1111/gji.2011.186.issue-1
|
| [29] |
THEODOULIDIS N, CULTRERA G, CORNOU C, et al, 2018. Basin effects on ground motion: the case of a high-resolution experiment in Cephalonia (Greece)[J]. Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering, 16(2): 529-560.
doi: 10.1007/s10518-017-0225-4
|
| [30] |
XIA SHAOHONG, ZHAO DAPENG, SUN JINLONG, et al, 2016. Teleseismic imaging of the mantle beneath Southernmost China: new insights into the Hainan plume[J]. Gondwana Research, 36: 46-56.
doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2016.05.003
|
| [31] |
YAN PENG, LI ZHIWEI, LI FEI, et al, 2018. Antarctic ice sheet thickness estimation using the horizontal-to-vertical spectral ratio method with single-station seismic ambient noise[J]. The Cryosphere, 12(2): 795-810.
doi: 10.5194/tc-12-795-2018
|
| [32] |
ZHAO DAPENG, 2004. Global tomographic images of mantle plumes and subducting slabs: insight into deep Earth dynamics[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 146(1-2): 3-34.
doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2003.07.032
|
 ), GUO Zhen2, XIA Shaohong1,3,4(
), GUO Zhen2, XIA Shaohong1,3,4( ), ZHANG Changrong1,3,4, WU Xiaoyang2, REN Pengfei2
), ZHANG Changrong1,3,4, WU Xiaoyang2, REN Pengfei2