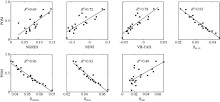
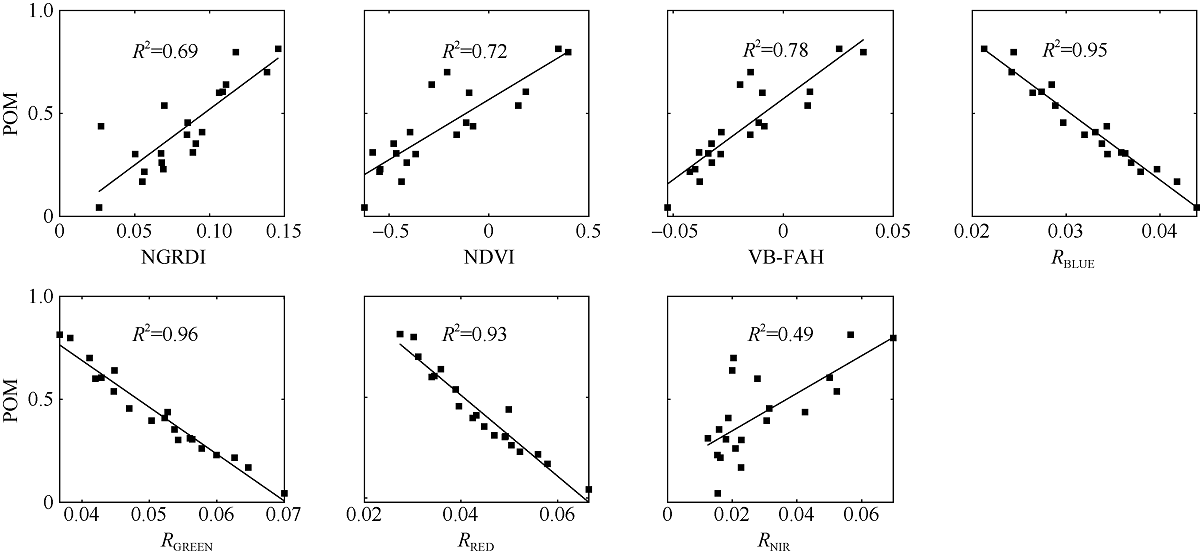
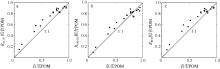
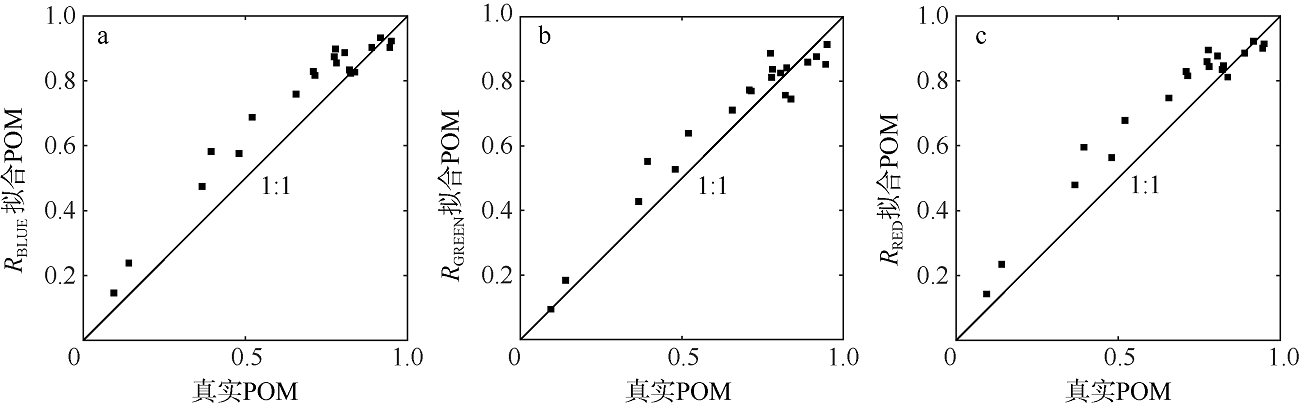
| [1] |
安德玉, 邢前国, 魏振宁, 等, 2018. 黄海典型漂浮大型藻类光谱特征分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 49(5): 1054-1060.
|
|
AN DEYU, XING QIANGUO, WEI ZHENNING, et al, 2018. Spectral features and analysis of typical floating macroalgae in the yellow sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 49(5): 1054-1060. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [2] |
丁一, 黄娟, 崔廷伟, 等, 2015. 基于NDVI与丰度关系的MODIS影像浒苔混合像元分解方法[J]. 海洋学报, 37(7): 123-131.
doi: 10.1007/s13131-018-1255-8
|
|
DING YI, HUANG JUAN, CUI TINGWEI, et al, 2015. The decomposition method of MODIS images Enteromorpha mixed pixels based on the relation of NDVI to abundance[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 37(7): 123-131. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi: 10.1007/s13131-018-1255-8
|
| [3] |
樊彦国, 白羽, 陈潘潘, 等, 2015. 青岛近海浒苔光谱特征研究[J]. 海洋科学, 39(4): 87-91.
|
|
FAN YANGUO, BAI YU, CHEN PANPAN, et al, 2015. Research of spectrum characteristics of enteromorpha in Qingdao offshore[J]. Marine Sciences, 39(4): 87-91. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [4] |
蒋兴伟, 刘建强, 邹斌, 等, 2009. 浒苔灾害卫星遥感应急监视监测系统及其应用[J]. 海洋学报, 31(1): 52-64.
|
|
JIANG XINGWEI, LIU JIANQIANG, ZOU BIN, et al, 2009. The satellite remote sensing system used in emergency response monitoring for Entermorpha prolifera disaster and its application[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 31(1): 52-64. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [5] |
刘岩, 刘涛, 于丹, 等, 2010. 常见石莼科绿藻的生物学特征及分子系统学分析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 40(12): 71-80.
|
|
LIU YAN, LIU TAO, YU DAN, et al, 2010. Biological characteristics and molecular systematics studies on common green algae of Ulvaceae[J]. Periodical Of Ocean University Of China, 40(12): 71-80. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [6] |
邢前国, 郑向阳, 施平, 等, 2011. 基于多源、多时相遥感影像的黄、东海绿潮影响区检测[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 31(6): 1644-1647.
|
|
XING QIANGUO, ZHENG XIANGYANG, SHI PING, et al, 2011. Monitoring “green tide” in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea using multi-temporal and multi-source remote sensing images[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 31(6): 1644-1647. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [7] |
CUI TINGWEI, ZHANG JIE, SUN LIE, et al, 2012. Satellite monitoring of massive green macroalgae bloom (GMB): imaging ability comparison of multi-source data and drifting velocity estimation[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 33(17): 5513-5527.
doi: 10.1080/01431161.2012.663112
|
| [8] |
GOWER J, KING S, 2019. Seaweed, seaweed everywhere[J]. Science, 365(6448): 27.
doi: 10.1126/science.aay0989
|
| [9] |
HAN HONGBIN, SONG WEI, WANG ZONGLING, et al, 2019. Distribution of green algae micro-propagules and their function in the formation of the green tides in the coast of Qinhuangdao, the Bohai Sea, China[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 38(8): 72-77.
|
| [10] |
HU CHUANMIN, 2009. A novel ocean color index to detect floating algae in the global oceans[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 113(10): 2118-2129.
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2009.05.012
|
| [11] |
LI LIN, XING QIANGUO, LI XUERONG, et al, 2018a. Assessment of the impacts from the world's largest floating macroalgae blooms on the water clarity at the West Yellow Sea using MODIS data (2002-2016)[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 11(5): 1397-1402.
doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2806626
|
| [12] |
LI LIN, ZHENG XIANGYANG, WEI ZHENNING, et al, 2018b. A spectral-mixing model for estimating sub-pixel coverage of sea-surface floating macroalgae[J]. Atmosphere-Ocean, 56(4): 296-302.
doi: 10.1080/07055900.2018.1509834
|
| [13] |
LIU DONGYAN, KEESING J K, XING QIANGUO, et al, 2009. World's largest macroalgal bloom caused by expansion of seaweed aquaculture in China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 58(6): 888-895.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2009.01.013
|
| [14] |
MORAND P, MERCERON M, 2005. Macroalgal population and sustainability[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 21(5): 1009-1020.
|
| [15] |
QI LIN, HU CHUANMIN, XING QIANGUO, et al, 2016. Long-term trend of Ulva prolifera blooms in the western Yellow Sea[J]. Harmful Algae, 58: 35-44.
doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2016.07.004
|
| [16] |
QI LIN, HU CHUANMIN, WANG MENGQIU, et al, 2017. Floating algae blooms in the East China Sea[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 44(22): 11501-11509.
doi: 10.1002/2017GL075525
|
| [17] |
SCHREYERS L, VAN EMMERIK T, BIERMANN L, et al, 2021. Spotting green tides over Brittany from space: three decades of monitoring with Landsat imagery[J]. Remote Sensing, 13(8): 1408.
doi: 10.3390/rs13081408
|
| [18] |
SHEN HUI, PERRIE W, LIU QINGRONG, et al, 2014. Detection of macroalgae blooms by complex SAR imagery[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 78(1-2): 190-195.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.10.044
|
| [19] |
SMETACEK V, ZINGONE A, 2013. Green and golden seaweed tides on the rise[J]. Nature, 504(7478): 84-88.
doi: 10.1038/nature12860
|
| [20] |
VALIELA I, MCCLELLAND J, HAUXWELL J, et al, 1997. Macroalgal blooms in shallow estuaries: controls and ecophysiological and ecosystem consequences[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 42(5): 1105-1118.
doi: 10.4319/lo.1997.42.5_part_2.1105
|
| [21] |
WANG MENGQIU, HU CHUANMIN, 2016. Mapping and quantifying Sargassum distribution and coverage in the Central West Atlantic using MODIS observations[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 183: 350-367.
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2016.04.019
|
| [22] |
WANG MENGQIU, HU CHUANMIN, BARNES B B, et al, 2019. The great Atlantic Sargassum belt[J]. Science, 365(6448): 83-87.
doi: 10.1126/science.aaw7912
|
| [23] |
XING QIANGUO, TOSI L G, BRAGA F, et al, 2015. Interpreting the progressive eutrophication behind the world's largest macroalgal blooms with water quality and ocean color data[J]. Natural Hazards, 78(1): 7-21.
doi: 10.1007/s11069-015-1694-x
|
| [24] |
XING QIANGUO, HU CHUANMIN, 2016a. Mapping macroalgal blooms in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea using HJ-1 and Landsat data: application of a virtual baseline reflectance height technique[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 178: 113-126.
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2016.02.065
|
| [25] |
XING QIANGUO, BRAGA F, TOSI L, et al, 2016b. Detection of low salinity groundwater seeping into the eastern Laizhou Bay (China) with the aid of Landsat thermal data[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 74(S1): 149-156.
doi: 10.2112/SI74-014.1
|
| [26] |
XING QIANGUO, GUO RUIHONG, WU LINGLING, et al, 2017. High-resolution satellite observations of a new hazard of golden tides caused by floating sargassum in winter in the Yellow Sea[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 14(10): 1815-1819.
doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2737079
|
| [27] |
XING QIANGUO, WU LINGLING, TIAN LIQIAO, et al, 2018. Remote sensing of early-stage green tide in the Yellow Sea for floating-macroalgae collecting campaign[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 133: 150-156.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.05.035
|
| [28] |
XING QIANGUO, AN DEYU, ZHENG XIANGYANG, et al, 2019. Monitoring seaweed aquaculture in the Yellow Sea with multiple sensors for managing the disaster of macroalgal blooms[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 231: 111279.
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2019.111279
|
| [29] |
YE NAIHAO, ZHANG XIAOWEN, MAO YUZE, et al, 2011. ‘Green tides' are overwhelming the coastline of our blue planet: taking the world's largest example[J]. Ecological Research, 26(3): 477-485.
doi: 10.1007/s11284-011-0821-8
|
 ), ZHENG Xiangyang1,2,3, XING Qianguo1,2,3(
), ZHENG Xiangyang1,2,3, XING Qianguo1,2,3( ), LIU Hailong1,2,3
), LIU Hailong1,2,3