Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (6): 56-66.doi: 10.11978/2021127CSTR: 32234.14.2021127
• Special Column: Mangrove Forest • Previous Articles Next Articles
Morphological characteristics of hypocotyls with different fresh weights of Kandelia obovata and their effects on the seedling growth
LIU Shuangshuang1,2( ), YANG Sheng2, LIU Xing2, CHEN Qiuxia2(
), YANG Sheng2, LIU Xing2, CHEN Qiuxia2( ), WANG Jinwang2, GUO Jinmin1,2, WANG Jiayu2, WANG Wenqing3, WU Weizhi4,5, LIANG Licheng5, ZHANG Xiaowei4,5
), WANG Jinwang2, GUO Jinmin1,2, WANG Jiayu2, WANG Wenqing3, WU Weizhi4,5, LIANG Licheng5, ZHANG Xiaowei4,5
- 1. College of Forestry and Biotechnology, Zhejiang Agricultural and Forestry University, Hangzhou 311300, China
2. Zhejiang Institute of Subtropical Crops, Wenzhou 325005, China
3. College of the Environment and Ecology, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361102, China
4. Zhejiang Forest Resources Monitoring Center, Hangzhou 310020, China
5. Zhejiang Forestry Survey planning and Design Co., Ltd., Hangzhou 310020, China
-
Received:2021-09-19Revised:2021-12-22Online:2022-11-10Published:2021-12-27 -
Contact:CHEN Qiuxia E-mail:liushuangshuang202@163.com;yzscqx@163.com -
Supported by:Programs of Science and Technology on Basic Resources Survey for the Ministry of Science and Technology of China(2017FY100701);Zhejiang Science and Technology Major Program on Agricultural New Variety Breeding(2016C02056-9)
CLC Number:
- Q945
Cite this article
LIU Shuangshuang, YANG Sheng, LIU Xing, CHEN Qiuxia, WANG Jinwang, GUO Jinmin, WANG Jiayu, WANG Wenqing, WU Weizhi, LIANG Licheng, ZHANG Xiaowei. Morphological characteristics of hypocotyls with different fresh weights of Kandelia obovata and their effects on the seedling growth[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(6): 56-66.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 1
Morphological characteristics of different fresh weight grades of hypocotyls"
| 胚轴鲜重等级 | 鲜重/g | 长度/cm | 横径/mm | 顶径/mm | 干重/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.0~5.0g | 4.46±0.04a | 13.94±0.12a | 8.69±0.09a | 4.69±0.03a | 1.66±0.03a |
| 5.0~6.0g | 5.48±0.04b | 14.75±0.16b | 9.42±0.08b | 4.96±0.03b | 2.15±0.04b |
| 6.0~7.0g | 6.48±0.04c | 15.13±0.14b | 10.37±0.07c | 5.14±0.03c | 2.53±0.03c |
| 7.0~8.0g | 7.43±0.04d | 15.76±0.17c | 10.79±0.08d | 5.43±0.04d | 2.91±0.03d |
| 8.0~9.0g | 8.47±0.04e | 16.69±0.18d | 11.31±0.09e | 5.49±0.06d | 3.37±0.05e |
| 9.0~10.0g | 9.45±0.04f | 16.49±0.18d | 12.02±0.08f | 5.82±0.04e | 3.96±0.04f |
Tab. 2
Nutrient percentage content of different fresh weight grades of hypocotyls"
| 胚轴鲜重等级 | N含量/% | P含量/% | K含量/% | Na含量/(mg·g-1) | 有机碳含量/% | 淀粉含量/(mg·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.0~5.0g | 0.79±0.02c | 0.08±0.00d | 0.70±0.66c | 5.65±0.01d | 42.86±0.44ab | 332.51±11.99bc |
| 5.0~6.0g | 0.80±0.01c | 0.07±0.00bc | 0.66±0.64b | 5.93±0.02e | 47.53±0.77bc | 341.77±4.85c |
| 6.0~7.0g | 0.77±0.00bc | 0.06±0.00ab | 0.65±0.63ab | 5.97±0.04e | 43.84±0.20b | 314.97±2.31bc |
| 7.0~8.0g | 0.73±0.02ab | 0.05±0.00a | 0.62±0.59a | 5.51±0.07c | 51.58±3.69c | 310.23±5.71b |
| 8.0~9.0g | 0.71±0.18a | 0.06±0.00bc | 0.67±0.63b | 4.93±0.06a | 46.94±1.34bc | 254.83±6.64a |
| 9.0~10.0g | 0.77±0.01c | 0.07±0.01cd | 0.66±0.64b | 5.16±0.04b | 37.78±2.40a | 250.89±17.74a |
Tab. 3
Nutrient content of different fresh weight grades of hypocotyls"
| 胚轴鲜重等级 | N含量/mg | P含量/mg | K含量/mg | Na含量/mg | 有机碳含量/mg | 淀粉含量/mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.0~5.0g | 13.10±0.35a | 1.26±0.02a | 11.69±0.30a | 9.38±0.02a | 711.37±7.33a | 549.71±14.09a |
| 5.0~6.0g | 17.28±0.12b | 1.41±0.06a | 14.23±0.22b | 12.76±0.05b | 1021.81±16.47b | 730.87±8.60b |
| 6.0~7.0g | 19.47±0.09c | 1.42±0.03a | 16.42±0.16c | 15.10±0.11c | 1109.25±5.10b | 793.27±4.61b |
| 7.0~8.0g | 21.22±0.60d | 1.49±0.04a | 17.91±0.25d | 16.02±0.21d | 1500.85±107.42c | 900.89±10.69c |
| 8.0~9.0g | 24.04±0.60e | 2.15±0.11b | 22.48±0.52e | 16.61±0.20e | 1581.97±45.05c | 866.52±20.93c |
| 9.0~10.0g | 30.66±0.30f | 2.83±0.27c | 26.25±0.40f | 20.45±0.16f | 1495.92±94.85c | 1000.86±47.96d |
Tab. 4
The proportion of nutrient content of different fresh weight grades of hypocotyls"
| 胚轴鲜重等级 | C:N | N:P | C:P | K:Na |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.0~5.0g | 54.42±1.10ab | 10.36±0.12a | 562.98±6.24a | 1.25±0.03b |
| 5.0~6.0g | 59.13±0.90b | 12.40±0.59bc | 735.32±44.83b | 1.12±0.02a |
| 6.0~7.0g | 56.97±0.28b | 13.70±0.31cd | 780.43±18.54b | 1.09±0.01a |
| 7.0~8.0g | 70.30±3.17c | 14.35±0.76d | 1019.51±97.27c | 1.12±0.05a |
| 8.0~9.0g | 66.10±2.95c | 11.26±0.30ab | 746.91±48.64b | 1.36±0.01c |
| 9.0~10.0g | 48.78±3.02a | 11.31±1.00ab | 550.05±57.24a | 1.28±0.02b |
Tab. 5
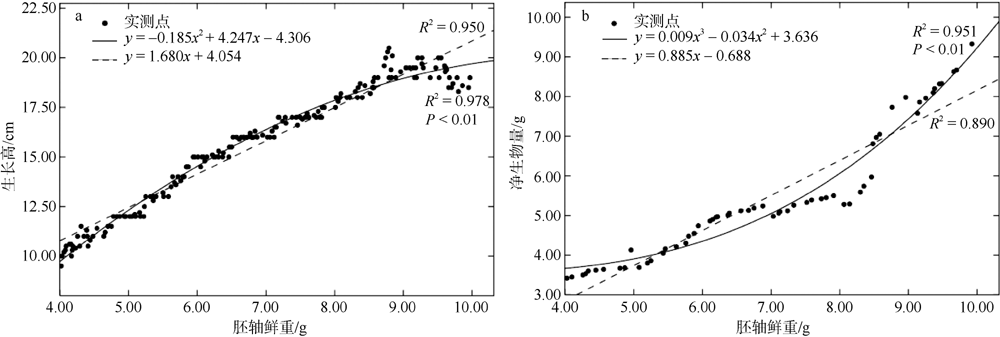
The seedling growth of Kandelia obovata of different fresh weight grades of hypocotyls"
| 胚轴鲜重 等级 | 生长高/cm | 基径/mm | 叶片数/ (片·株-1) | 根干重/g | 茎干重/g | 叶干重/g | 胚轴干重/g | 净生物量/g | 总生物量/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.0~5.0g | 11.08±0.29a | 5.88±0.13a | 7.23±0.19a | 0.87±0.11a | 0.86±0.13a | 1.41±0.16a | 1.84±0.08a | 3.14±0.36a | 4.98±0.42a |
| 5.0~6.0g | 14.53±0.33b | 6.52±0.12b | 8.10±0.23b | 1.37±0.12bc | 1.24±0.09b | 2.13±0.10b | 2.61±0.08b | 4.74±0.23b | 7.35±0.30b |
| 6.0~7.0g | 16.50±0.37c | 7.18±0.11c | 8.18±0.17b | 0.77±0.14a | 1.19±0.09ab | 2.09±0.21b | 2.53±0.09b | 4.05±0.41ab | 6.58±0.50b |
| 7.0~8.0g | 16.90±0.38c | 7.69±0.10d | 8.83±0.20b | 1.04±0.15ab | 1.27±0.15b | 2.19±0.14b | 2.98±0.06c | 4.50±0.37b | 7.48±0.42b |
| 8.0~9.0g | 17.23±0.32cd | 8.04±0.09e | 10.23±0.43c | 1.55±0.12cd | 1.83±0.12c | 3.06±0.15c | 3.58±0.10d | 6.44±0.31c | 10.02±0.37c |
| 9.0~10.0g | 18.18±0.42d | 8.51±0.11f | 12.28±0.42d | 1.85±0.18d | 2.23±0.14d | 3.57±0.20d | 4.18±0.13e | 7.64±0.41d | 11.82±0.44d |
Tab. 6
The correlation coefficient between hypocotyls and seedling growing traits of Kandelia obovata"
| 鲜重 | 长度 | 横径 | 顶径 | N | P | K | Na | 有机碳 | 淀粉 | C:N | N:P | C:P | K:Na | 生长高 | 基径 | 净生物量 | 总生物量 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 鲜重 | 1 | 0.972** | 0.994** | 0.990** | 0.976** | 0.890* | 0.985** | 0.970** | 0.928** | 0.947** | 0.039 | 0.066 | 0.062 | 0.443 | 0.913* | 0.994** | 0.908* | 0.935** |
| 长度 | 1 | 0.960** | 0.946** | 0.909* | 0.814* | 0.942** | 0.911* | 0.968** | 0.909* | 0.221 | 0.090 | 0.172 | 0.473 | 0.908* | 0.970** | 0.877* | 0.903* | |
| 横径 | 1 | 0.989** | 0.970** | 0.856* | 0.970** | 0.983** | 0.924** | 0.962** | 0.042 | 0.152 | 0.110 | 0.359 | 0.944** | 0.998** | 0.874* | 0.904* | ||
| 顶径 | 1 | 0.977** | 0.868* | 0.967** | 0.983** | 0.926** | 0.975** | 0.041 | 0.147 | 0.115 | 0.347 | 0.923** | 0.991** | 0.887* | 0.918** | |||
| N | 1 | 0.939** | 0.986** | 0.980** | 0.844* | 0.938** | -0.152 | 0.011 | -0.078 | 0.401 | 0.882* | 0.960** | 0.942** | 0.960** | ||||
| P | 1 | 0.953** | 0.855* | 0.687 | 0.767 | -0.347 | -0.331 | -0.382 | 0.632 | 0.683 | 0.837* | 0.965** | 0.961** | |||||
| K | 1 | 0.953** | 0.862* | 0.902* | -0.105 | -0.079 | -0.105 | 0.526 | 0.858* | 0.962** | 0.954** | 0.969** | ||||||
| Na | 1 | 0.878* | 0.980** | -0.052 | 0.203 | 0.085 | 0.245 | 0.951** | 0.977** | 0.877* | 0.906* | |||||||
| 有机碳 | 1 | 0.924** | 0.401 | 0.279 | 0.392 | 0.318 | 0.914* | 0.947** | 0.773 | 0.812* | ||||||||
| 淀粉 | 1 | 0.114 | 0.340 | 0.263 | 0.144 | 0.968** | 0.968** | 0.822* | 0.859* | |||||||||
| C:N | 1 | 0.529 | 0.877* | -0.142 | 0.182 | 0.102 | -0.187 | -0.145 | ||||||||||
| N:P | 1 | 0.867* | -0.792 | 0.421 | 0.177 | -0.223 | -0.164 | |||||||||||
| C:P | 1 | -0.527 | 0.331 | 0.160 | -0.237 | -0.177 | ||||||||||||
| K:Na | 1 | 0.086 | 0.353 | 0.569 | 0.540 | |||||||||||||
| 生长高 | 1 | 0.947** | 0.763 | 0.801 | ||||||||||||||
| 基径 | 1 | 0.866* | 0.899* | |||||||||||||||
| 净生物量 | 1 | 0.997** | ||||||||||||||||
| 总生物量 | 1 |
Tab. 7
Principal component loading matrix and variance contribution rate of Kandelia obovata hypocotyl characteristics"
| 指标类型 | 项目 | 性状 | 主成分1 | 主成分2 | 主成分3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 胚轴形态指标 | X1 | 长度 | 0.952 | 0.185 | 0.214 |
| X2 | 横径 | 0.972 | 0.176 | -0.038 | |
| X3 | 顶径 | 0.976 | 0.168 | -0.042 | |
| X4 | 干重 | 0.994 | 0.061 | -0.014 | |
| 胚轴营养成分指标 | X5 | N | 0.989 | -0.008 | -0.138 |
| X6 | P | 0.936 | -0.341 | -0.053 | |
| X7 | K | 0.994 | -0.057 | 0.001 | |
| X8 | Na | 0.963 | 0.174 | -0.196 | |
| X9 | 有机碳 | 0.888 | 0.392 | 0.239 | |
| X10 | 淀粉 | 0.930 | 0.333 | -0.140 | |
| X11 | C:N | -0.054 | 0.758 | 0.644 | |
| X12 | N:P | -0.021 | 0.951 | -0.306 | |
| X13 | C:P | -0.043 | 0.974 | 0.201 | |
| X14 | K:Na | 0.473 | -0.625 | 0.585 | |
| 幼苗生长指标 | X15 | 生长高 | 0.884 | 0.418 | -0.131 |
| X16 | 基径 | 0.968 | 0.215 | 0.005 | |
| X17 | 叶片数 | 0.975 | -0.192 | -0.065 | |
| X18 | 根干重 | 0.823 | -0.373 | 0.108 | |
| X19 | 茎干重 | 0.977 | -0.200 | -0.015 | |
| X20 | 叶干重 | 0.985 | -0.128 | -0.008 | |
| X21 | 胚轴干重 | 0.996 | -0.023 | 0.011 | |
| X22 | 净生物量 | 0.963 | -0.214 | 0.020 | |
| X23 | 总生物量 | 0.979 | -0.151 | 0.017 | |
| 初始特征值 | 17.592 | 3.852 | 1.110 | ||
| 方差贡献率/% | 76.485 | 16.746 | 4.827 | ||
| 累积方差贡献率/% | 76.485 | 93.231 | 98.059 | ||
Tab. 8
Main ingredient score and comprehensive score of Kandelia obovata hypocotyl characteristics"
| 胚轴鲜重等级 | F1 | 排序 | F2 | 排序 | F3 | 排序 | F | 排序 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.0~5.0g | -6.26 | 6 | 1.63 | 2 | -0.59 | 5 | -4.54 | 6 |
| 5.0~6.0g | -2.22 | 5 | -0.43 | 4 | -0.25 | 3 | -1.78 | 5 |
| 6.0~7.0g | -0.73 | 4 | -2.55 | 6 | -0.35 | 4 | -1.00 | 4 |
| 7.0~8.0g | 0.75 | 3 | -1.69 | 5 | 1.42 | 1 | 0.36 | 3 |
| 8.0~9.0g | 2.34 | 2 | 2.63 | 1 | 1.11 | 2 | 2.28 | 2 |
| 9.0~10.0g | 6.11 | 1 | 0.41 | 3 | -1.33 | 6 | 4.68 | 1 |
| [1] | 陈秋夏, 杨升, 王金旺, 等, 2019. 浙江红树林发展历程及探讨[J]. 浙江农业科学, 60(7): 1177-1181 |
| CHEN QIUXIA, YANG SHENG, WANG JINWANG, et al, 2019. Development history and discussion of mangrove forest in Zhejiang Province[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 60(7): 1177-1181. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 何琴飞, 彭玉华, 刘秀, 等, 2014. 秋茄胚轴育苗生境适应性试验[J]. 林业科技开发, 28(1): 108-110. |
| HE QINFEI, PENG YUHUA, LIU XIU, et al, 2014. Experiment on hypocotyle seedling growth of Kandelia candel in controlled habitats[J]. China Forestry Science and Technology, 28(1): 108-110. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 何文, 张秀芬, 郭素云, 等, 2021. 基于主成分分析和聚类分析对22份马铃薯种质的综合评价[J]. 种子, 40(3): 80-86. |
| HE WEN, ZHANG XIUFEN, GUO SUYUN, et al, 2021. Comprehensive evaluation of 22 potato germplasms based on principal component analysis and cluster analysis[J]. Seed, 40(3): 80-86. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 黄光文, 沈玉平, 李常健, 2010. 甘薯淀粉含量测定的新方法[J]. 湖南农业科学, (17): 109-111. |
| HUANG GUANGWEN, SHEN YUPING, LI CHANGJIAN, 2010. A new method for detecting starch content in sweet potato[J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, (17): 109-111. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 冷天凤, 陈兰, 孙建昌, 2020. 早实核桃优树种子品质及子代苗期生长比较[J]. 种子, 39(7): 86-90. |
| LENG TIANFENG, CHEN LAN, SUN JIANCHANG, 2020. Comparison of seed quality and growth of progeny seedlings of early fruiting walnut lines[J]. Seed, 39(7): 86-90. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 李泽伦, 丁红, 戴良香, 等, 2021. 种子大小与播种方式对花生生长发育、光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 种子, 40(2): 47-52. |
| LI ZELUN, DING HONG, DAI LIANGXIANG, et al, 2021. Effects of seed size and sowing pattern of peanut on growth and development, photosynthetic characteristics and yield[J]. Seed, 40(2): 47-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 刘博文, 黎桂阳, 常媛飞, 等, 2021. 野豌豆属种子形态多样性与种子分类鉴定方法的研究[J]. 草地学报, 29(7): 1375-1385. |
| LIU BOWEN, LI GUIYANG, CHANG YUANFEI, et al, 2021. Study on seed morphological diversity and seed classification and identification method of Vicia[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 29(7): 1375-1385. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 刘昌岭, 朱志刚, 贺行良, 等, 2007. 重铬酸钾氧化-硫酸亚铁滴定法快速测定海洋沉积物中有机碳[J]. 岩矿测试, 26(3): 205-208. |
| LIU CHANGLING, ZHU ZHIGANG, HE XINGLIANG, et al, 2007. Rapid determination of organic carbon in marine sediment samples by potassium dichromate oxidation-ferrous sulphate titrimetry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 26(3): 205-208. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 刘云霞, 温云杰, 黄金莉, 等, 2015. AA3型连续流动分析仪与钒钼黄比色法测定玉米植株全磷含量之比较[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 32(6): 577-582. |
| LIU YUNXIA, WEN YUNJIE, HUANG JINLI, et al, 2015. Determination total phosphour of maize plant samples by continuous flow analyzer in comparison with vanadium molybdate yellow colorimetric method[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 32(6): 577-582. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 吕航, 王秋彬, 崔佳慧, 等, 2021. 不同仪器测定玉米秸秆与籽粒全钾含量比较[J]. 现代农业科技, (1): 23-25. (in Chinese) |
| [11] | 史文辉, 2018. 种子养分和土壤肥力对栓皮栎苗木质量和造林效果的影响[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学. |
| SHI WENHUI, 2018. Effects of acorn nutrient and soil fertility on Quercus variabilis seedling quality and outplanting performance[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 王龙仁, 曾军, 刘双龙, 等, 2021. 白木香人工结香初期营养元素及叶片叶绿素含量的变化[J]. 热带生物学报, 12(3): 326-332. |
| WANG LONGREN, ZENG JUN, LIU SHUANGLONG, et al, 2021. The changes of nutrient and leaf chlorophyll contents of Aquilaria sinensis at the early agarwood inducing stage[J]. Journal of Tropical Biology, 12(3): 326-332. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 王素玉, 2020. 高寒草甸7种优势禾本科植物种子贮藏物质、萌发及幼苗对草地N、P添加的响应[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学. |
| WANG SUYU, 2020. Responses of seed storage substances, germination and seedlings of 7 dominant gramineous plants in alpine meadow to grassland N and P addition[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 王文卿, 王瑁, 2007. 中国红树林[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| WANG WENQING, WANG MAO, 2007. The mangroves of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 王鑫磊, 袁湘汝, 张潇潇, 等, 2020. 基于Kjeldahl与Dumas方法的农作物秸秆总氮含量分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 36(6): 206-214. |
| WANG XINLEI, YUAN XIANGRU, ZHANG XIAOXIAO, et al, 2020. Analysis of the total nitrogen content of crop residues determined by using Kjeldahl and Dumas methods[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 36(6): 206-214. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 武高林, 杜国祯, 2008. 植物种子大小与幼苗生长策略研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 19(1): 191-197. |
| WU GAOLIN, DU GUOZHEN, 2008. Relationships between seed size and seedling growth strategy of herbaceous plant: A review[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 19(1): 191-197. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 吴航, 王顺霞, 卜海燕, 等, 2014. 青藏高原53种菊科植物种子中碳、氮、磷含量与种子大小和海拔的关系[J]. 西北植物学报, 34(8): 1635-1641. |
| WU HANG, WANG SHUNXIA, BU HAIYAN, et al, 2014. Effect of seed size and altitude on the C, N, P contents of 53 compositae plant seeds on the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 34(8): 1635-1641. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 吴航, 2014. 种子大小和海拔对青藏高原东北缘常见植物种子中N、P含量的影响[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学. |
| WU HANG, 2014. The effect of seed size and altitude on the N、P content of seeds of common plants on the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 吴亚丽, 2016. 不同家系东京野茉莉种子营养成分和苗期生长差异研究[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学. |
| WU YALI, 2016. Differences of seed nutrient contents, seedling growth and cold tolerance in different families of Styrax tonkinensis[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Forestry University. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 杨慧仙, 2016. 种子大小和海拔对青藏高原东北缘常见植物种子主要营养成分含量的影响[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学. |
| YANG HUIXIAN, 2016. The effect of seed size and altitude on main seed reserves of common plants in an alpine meadow on the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 杨升, 刘星, 邓瑞娟, 等, 2020. 不同种源秋茄胚轴和幼苗生长性状的地理变异[J]. 生态学杂志, 39(6): 1769-1777. |
| YANG SHENG, LIU XING, DENG RUIJUAN, et al, 2020. Geographic variations of hypocotyl and seedling growth traits for Kandelia obovata with different provenances[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 39(6): 1769-1777. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] |
闫兴富, 邓晓娟, 王静, 等, 2020. 种子大小和干旱胁迫对辽东栎幼苗生长和生理特性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 31(10): 3331-3339.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202010.006 |
| YAN XINGFU, DENG XIAOJUAN, WANG JING, et al, 2020. Effects of seed size and drought stress on the growth and physiological characteristics of Quercus wutaishanica seedlings[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31(10): 3331-3339. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 袁珂, 薛月芹, 桂仁意, 等, 2010. 微波消解-原子吸收光谱法测定不同产地淡竹叶中微量元素的含量[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 30(3): 804-808. |
| YUAN KE, XUE YUEQIN, GUI RENYI, et al, 2010. Determination of trace elements in Lophatherum Gracile Brongn from different habitat by microwave digestion-atomic absorption spectroscopy[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 30(3): 804-808. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 张金峰, 程继铭, 闫兴富, 等, 2020. 种子特征和播种深度对辽东栎种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 广西植物, 40(2): 226-236. |
| ZHANG JINFENG, CHENG JIMING, YAN XINGFU, et al, 2020. Effects of seed characteristics and sowing depth on seed germination and seedling growth of Quercus wutaishanica[J]. Guihaia, 40(2): 226-236. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 赵燕昊, 张倩霞, 谢炜, 2019. 种子化学成分与种子活力相关性研究进展[J]. 现代农业科技, (15): 1-3. |
| ZHAO YANHAO, ZHANG QIANXIA, XIE WEI, 2019. Research progress on correlation between seed chemical composition and seed vigor[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, (15): 1-3. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] |
周晓旋, 蔡玲玲, 傅梅萍, 等, 2016. 红树植物胎生现象研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 40(12): 1328-1343.
doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2016.0087 |
|
ZHOU XIAOXUAN, CAI LINGLING, FU MEIPING, et al, 2016. Progress in the studies of vivipary in mangrove plants[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 40(12): 1328-1343. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2016.0087 |
|
| [27] | ABIFARIN T O, OTUNOLA G A, AFOLAYAN A J, 2021. Nutritional composition and antinutrient content of Heteromorpha arborescens (Spreng.) Cham. & Schltdl. leaves: An underutilized wild vegetable[J]. Food Science & Nutrition, 9(1): 172-179. |
| [28] |
CALISKAN S, MAKINECI E, 2014. Variations in carbon and nitrogen ratios and their effects on seed germination in Cupressus sempervirens populations[J]. Scandinavian Journal of Forest Research, 29(2): 162-169.
doi: 10.1080/02827581.2014.881544 |
| [29] |
GONZÁLEZ-RODRÍGUEZ V, VILLAR R, NAVARRO- CERRILLO R M, 2011. Maternal influences on seed mass effect and initial seedling growth in four Quercus species[J]. Acta Oecologica, 37(1): 1-9.
doi: 10.1016/j.actao.2010.10.006 |
| [30] | HAWKESFORD M, HORST W, KICHEY T, et al, 2012. Functions of macronutrients[M]// MARSCHNERP. Marschner's Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. 3rd ed. London: Academic Press: 135-189. |
| [31] |
HONG LIWEI, SU WENYUE, ZHANG YUANYE, et al, 2018. Transcriptome profiling during mangrove viviparity in response to abscisic acid[J]. Scientific Reports, 8: 770.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19236-x pmid: 29335506 |
| [32] |
HUXHAM M, KUMARA M P, JAYATISSA L P, et al, 2010. Intra- and interspecific facilitation in mangroves may increase resilience to climate change threats[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 365(1549): 2127-2135.
doi: 10.1098/rstb.2010.0094 |
| [33] |
JØRGENSEN M S, LABOURIAU R, OLESEN B, 2019. Seed size and burial depth influence Zostera marina L. (eelgrass) seed survival, seedling emergence and initial seedling biomass development[J]. PLoS One, 14(4): e0215157.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215157 |
| [34] |
LI JINBO, YANG ZHEHAN, SONG GUILONG, et al, 2021. Correlations of arsenic and nutrient elements in different tissues of Perennial ryegrass under arsenic stress[J]. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 21(2): 1542-1551.
doi: 10.1007/s42729-021-00460-w |
| [35] |
MA ZHEN, WILLIS C G, ZHANG CHUNHUI, et al, 2019. Direct and indirect effect of seed size on seedling survival along an experimental light availability gradient[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 281: 64-71.
doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2019.05.009 |
| [36] | MARSCHNER P, 2012. Marschner's mineral nutrition of higher plants[M]. London: Academic Press. |
| [37] |
MECHERGUI T, PARDOS M, JACOBS D F, 2021. Effect of acorn size on survival and growth of Quercus suber L. seedlings under water stress[J]. European Journal of Forest Research, 140(1): 175-186.
doi: 10.1007/s10342-020-01323-2 |
| [38] |
MOLES A T, WESTOBY M, 2004. Seedling survival and seed size: a synthesis of the literature[J]. Journal of Ecology, 92(3): 372-383.
doi: 10.1111/j.0022-0477.2004.00884.x |
| [39] |
MURRAY B R, BROWN A H D, GRACE J P, 2003. Geographic gradients in seed size among and within perennial Australian Glycine species[J]. Australian Journal of Botany, 51(1): 47-56.
doi: 10.1071/BT02069 |
| [40] | RAWAT K, BAKSHI M, 2011. Provenance variation in cone, seed and seedling characteristics in natural populations of Pinus wallichiana A.B. Jacks (Blue Pine) in India[J]. Annals of Forest Research, 54(1): 39-55. |
| [41] |
SOUSA W P, KENNEDY P G, MITCHELL B J, 2003. Propagule size and predispersal damage by insects affect establishment and early growth of mangrove seedlings[J]. Oecologia, 135(4): 564-575.
pmid: 12684857 |
| [42] |
TUMPA K, VIDAKOVIĆ A, DRVODELIĆ D, et al, 2021. The effect of seed size on germination and seedling growth in sweet chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.)[J]. Forests, 12(7): 858.
doi: 10.3390/f12070858 |
| [1] | WU Weizhi, ZHAO Zhixia, YANG Sheng, LIANG Licheng, Chen Qiuxia, LU Xiang, LIU Xing, ZHANG Xiaowei. The mangrove forest distribution and analysis of afforestation effect in Zhejiang Province [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(6): 67-74. |
|
||