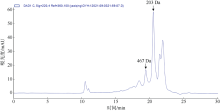
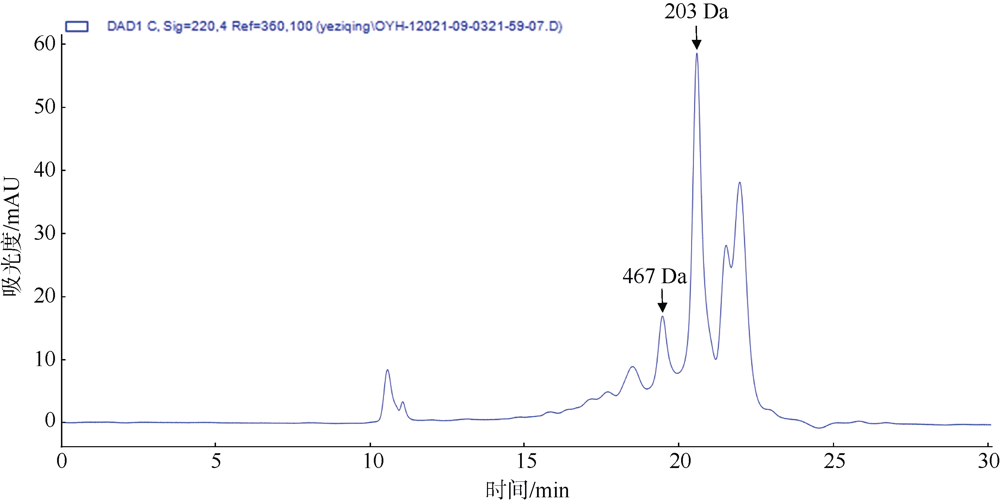
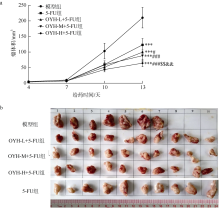
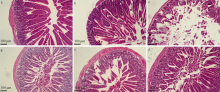
Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (5): 105-116.doi: 10.11978/2021155CSTR: 32234.14.2021155
• Exploitation of Marine Resources • Previous Articles Next Articles
Oyster hydrolysates alleviate 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucosal injury on S180 tumor-bearing mice*
YE Ziqing1,2,4( ), ZHAO Xiangdan1,2,4, CAI Bingna1,3,4, WAN Peng1,3,4, CHEN Hua1,3,4, PAN Jianyu1,3,4(
), ZHAO Xiangdan1,2,4, CAI Bingna1,3,4, WAN Peng1,3,4, CHEN Hua1,3,4, PAN Jianyu1,3,4( )
)
- 1. CAS Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou 511458, China
4. Institution of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
-
Received:2021-11-10Revised:2021-12-21Online:2022-09-10Published:2021-12-22 -
Contact:PAN Jianyu E-mail:yeziqing19@mails.ucas.ac.cn;jypan@scsio.ac.cn -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Program of China(2018YFC0311202);Marine Economy Development Special Project of Guangdong Province(GDNRC[2020]038);Marine Economy Development Special Project of Guangdong Province(GDNRC[2020]036);National Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong, China(2018A030313088);Key Special Project for Introduced Talents Team of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou)(GML2019ZD0406);Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province(2020B1111030004);Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences(ISEE2021PY05)
CLC Number:
- P735.4
Cite this article
YE Ziqing, ZHAO Xiangdan, CAI Bingna, WAN Peng, CHEN Hua, PAN Jianyu. Oyster hydrolysates alleviate 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucosal injury on S180 tumor-bearing mice*[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(5): 105-116.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 1
Different experimental groups and treatments of animals"
| 组名 | 是否移植肉瘤细胞株 | 腹腔注射5-氟尿嘧啶剂量/(mg·kg-1) | 每日灌胃牡蛎酶解物剂量/(mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 正常组 | 否 | — | — |
| 模型组 | 是 | — | — |
| 5-氟尿嘧啶组(5-FU组) | 是 | 30 | — |
| 低剂量牡蛎胰蛋白酶水解物联合5-氟尿嘧啶组(OYH-L+5-FU组) | 是 | 30 | 200 |
| 中剂量牡蛎胰蛋白酶水解物联合5-氟尿嘧啶组(OYH-M+5-FU组) | 是 | 30 | 400 |
| 高剂量牡蛎胰蛋白酶水解物联合5-氟尿嘧啶组(OYH-H+5-FU组) | 是 | 30 | 800 |
Tab. 3
Analysis of amino acid composition of OYH"
| 氨基酸种类 | 氨基酸含量/% | 氨基酸种类 | 氨基酸含量/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 天冬氨酸 Asp | 3.76 | 亮氨酸 Leu* | 2.39 |
| 苏氨酸 Thr* | 1.65 | 酪氨酸 Tyr | 1.60 |
| 丝氨酸 Ser | 1.44 | 苯丙氨酸 Phe* | 1.27 |
| 谷氨酸 Glu | 5.80 | 赖氨酸 Lys* | 2.58 |
| 脯氨酸 Pro | 1.99 | 组氨酸 His* | 0.88 |
| 甘氨酸 Gly | 3.08 | 精氨酸 Arg | 2.30 |
| 丙氨酸 Ala | 2.46 | 色氨酸Trp* | 0.23 |
| 缬氨酸 Val* | 1.69 | 氨基酸总量TAA | 35.29 |
| 蛋氨酸 Met* | 0.60 | 必需氨基酸含量EAA | 12.86 |
| 异亮氨酸 Ile* | 1.57 | EAA/TAA | 36.44 |
Tab. 4
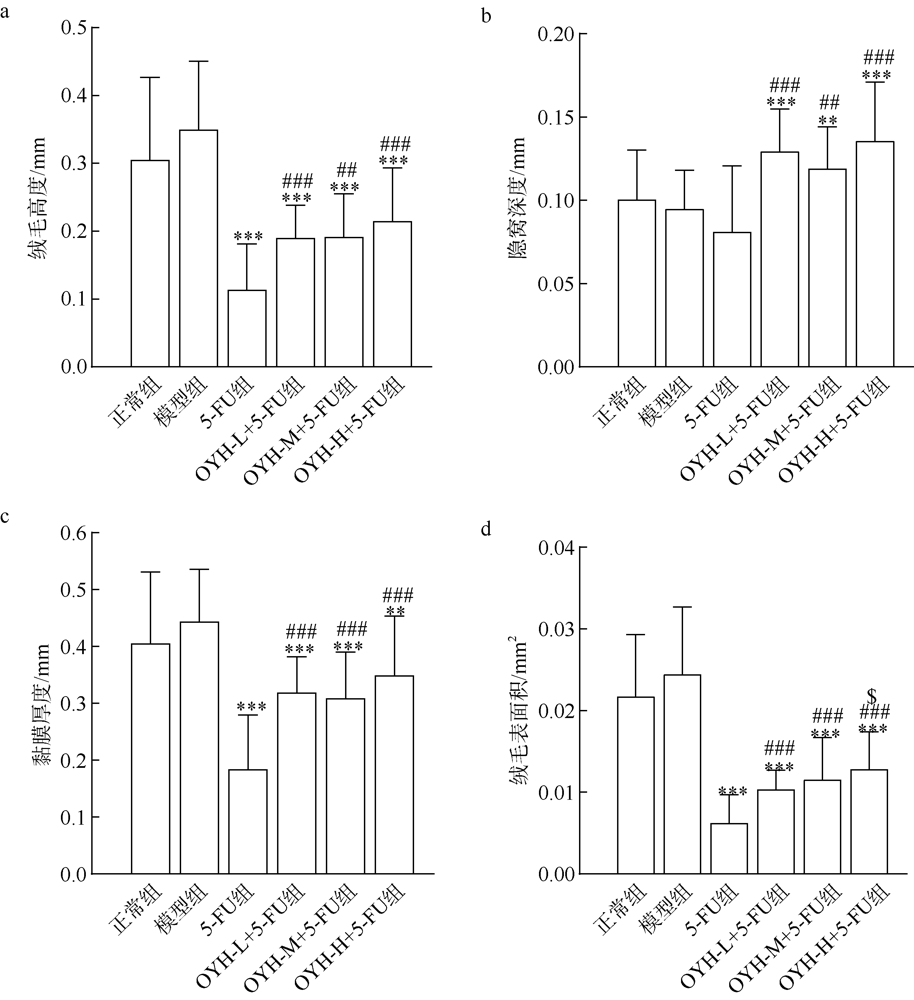
Effects of OYH combined with 5-FU on body weight, tumor weight and tumor inhibition ratio of mice ($\overline{x}$ ± SD, n = 10)"
| 组 别 | 初体重/g | 终体重/g | 瘤重/g | 抑瘤率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常组 | 25.99±1.23 | 29.11±1.50 | — | — |
| 模型组 | 24.27±1.76 | 28.72±2.51 | 1.57±0.30 | — |
| 5-FU组 | 24.14±0.82 | 25.15±1.41***△△△ | 1.09±0.16*** | 31.00 |
| OYH-L+5-FU组 | 24.58±1.41 | 25.95±1.45**△△△ | 0.97±0.18*** | 38.24 |
| OYH-M+5-FU组 | 24.61±2.13 | 26.64±1.65*#△△ | 0.85±0.09***### | 46.27 |
| OYH-H+5-FU组 | 23.94±1.92 | 26.84±1.83#△△ | 0.82±0.19***## | 47.57 |
Tab. 5
Effects of OYH combined with 5-FU on blood routine of mice ($\overline{x}$ ± SD, n = 10)"
| 正常组 | 模型组 | 5-FU组 | OYH-L+5-FU组 | OYH-M+5-FU组 | OYH-H+5-FU组 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白细胞/(×109L-1) | 6.61±2.58*** | 13.22±3.23 | 4.71±0.99*** | 4.25±1.14*** | 4.12±0.46*** | 4.40±0.81*** |
| 红细胞/(×1012L-1) | 10.34±0.46*** | 9.03±0.37 | 8.82±0.44 | 9.12±0.41 | 8.70±0.35$ | 8.72±0.49 |
| 血红蛋白/(g·L-1) | 158.90±6.79*** | 136.20±6.16 | 134.70±5.56 | 138.80±5.12 | 133.00±5.42$ | 133.10±7.46 |
| 红细胞压积/% | 44.93±1.68*** | 39.13±1.27 | 38.53±1.60 | 39.25±1.40 | 37.73±1.51*$ | 37.68±1.99 |
| 血小板/(×109L-1) | 1312.30±149.95*** | 1740.90±169.84 | 1601.50±196.78 | 1747.00±257.28 | 1640.40±170.42 | 1817.30±209.85# |
| 淋巴细胞/% | 80.29±4.17*** | 54.82±6.35 | 62.65±11.25 | 66.71±8.16** | 65.15±6.27** | 65.05±8.91** |
| 中性粒细胞/% | 17.47±4.08*** | 39.43±6.90 | 32.14±9.61 | 28.57±7.54** | 30.95±6.22** | 30.22±8.20* |
| 单核细胞/% | 0.87±0.40*** | 4.98±1.57 | 4.22±2.22 | 3.60±0.66* | 2.99±1.00** | 3.77±1.11 |
| 嗜酸性粒细胞/% | 1.34±0.45** | 0.74±0.19 | 0.99±0.51 | 1.10±0.46* | 0.91±0.48 | 0.89±0.57 |
| 嗜碱性粒细胞/% | 0.03±0.07 | 0.03±0.05 | 0.00±0.00 | 0.02±0.06 | 0.00±0.00 | 0.07±0.12 |
Tab. 6
Effects of OYH combined with 5-FU on serum biochemical indicators of mice ($\overline{x}$±SD, n=10)"
| 正常组 | 模型组 | 5-FU组 | OYH-L+5-FU组 | OYH-M+5-FU组 | OYH-H+5-FU组 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总蛋白/(g·L-1) | 73.83±7.65*** | 57.35±7.11 | 54.72±6.55 | 61.39±6.85# | 64.36±8.95# | 70.56±8.85**###$ |
| 白蛋白/(g·L-1) | 48.41±4.62*** | 36.15±5.41 | 29.90±3.23** | 37.25±8.01# | 38.36±9.21# | 44.58±5.75**###$ |
| 前白蛋白/(mg·L-1) | 3.74±0.70** | 2.71±0.53 | 2.45±0.46 | 2.45±0.53 | 2.47±0.52 | 2.57±0.52 |
| 转铁蛋白/(g·L-1) | 10.31±1.54** | 8.52±1.08 | 8.64±1.21 | 9.25±1.06 | 9.42±1.18 | 9.32±1.00 |
| 补体C3 /(g·L-1) | 2.56±0.61*** | 3.78±0.41 | 3.09±1.12 | 3.70±0.52 | 3.84±0.79 | 3.56±0.88 |
| 补体C4 /(g·L-1) | 0.38±0.07*** | 0.53±0.06 | 0.40±0.08** | 0.43±0.09* | 0.43±0.07** | 0.43±0.08** |
| 免疫球蛋白A /(g·L-1) | 0.37±0.12*** | 0.13±0.03 | 0.12±0.03 | 0.15±0.03# | 0.17±0.03*## | 0.18±0.05*## |
| 免疫球蛋白G /(g·L-1) | 13.54±1.98** | 10.57±2.06 | 10.12±0.98 | 10.71±2.39 | 11.47±2.36 | 11.83±1.77# |
| 免疫球蛋白M /(g·L-1) | 1.72±0.33*** | 1.08±0.19 | 0.99±0.15 | 1.23±0.32# | 1.56±0.26***###$ | 1.64±0.25***### |
| [1] | 杜双双, 2018. 蚕丝蛋白肽免疫调节及与化疗的联合作用[D]. 天津: 天津医科大学:11-13. |
| DU SHUANGSHUANG, 2018. The immunomodulation and combined effect with chemotherapy of silk fibroin peptide[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin Medical University:11-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 胡雪琼, 吴红棉, 刘芷筠, 等, 2009. 近江牡蛎糖胺聚糖的酶解提取及其抗肿瘤活性研究[J]. 食品研究与开发, 30(7): 3-6. |
| HU XUEQIONG, WU HONGMIAN, LIU ZHIJUN, et al, 2009. Study on enzymatic preparation of glycosaminoglycan with anti-tumor activity from Crassostrea rivularis crould[J]. Food Research and Development, 30(7): 3-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 胡雪琼, 吴红棉, 范秀萍, 等, 2014. 近江牡蛎糖胺聚糖的免疫调节活性研究[J]. 现代食品科技, 30(12): 16-24. |
| HU XUEQIONG, WU HONGMIAN, FAN XIUPING, et al, 2014. Immunomodulatory activity of glycosaminoglycans from Jinjiang oyster Crassostrea rivularis[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 30(12): 16-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 李婉, 曹文红, 章超桦, 等, 2017. 牡蛎酶解产物的组成特点及其体外免疫活性[J]. 食品工业科技, 38(16): 35-42. |
| LI WAN, CAO WENHONG, ZHANG CHAOHUA, et al, 2017. Composition characteristics of oyster enzymatic hydrolysate and its immune activity in vitro[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 38(16): 35-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] |
巫楚君, 潘剑宇, 蔡冰娜, 等, 2021. 黄鳍金枪鱼酶解物免疫活性及其氨基酸分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 40(6): 128-134.
doi: 10.11978/2020136 |
| WU CHUJUN, PAN JIANYU, CAI BINGNA, et al, 2021. Immunoactivity and amino acid analysis of enzymatic hydrolysates of Thunnus albacares[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 40(6): 128-134. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 武美彤, 张海欣, 张梦, 等, 2020. 牡蛎酶解物对Lewis肺癌的抑制作用及机制[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 46(11): 98-104, 111. |
| WU MEITONG, ZHANG HAIXIN, ZHANG MENG, et al, 2020. Inhibition and mechanism of oyster enzymatic hydrolysate on Lewis lung cancer[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 46(11): 98-104, 111. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] |
吴园涛, 任小波, 孙恢礼, 2012. 关于我国海洋生物资源领域科技布局的若干思考[J]. 热带海洋学报, 31(1): 79-84.
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2012.01.079 |
| WU YUANTAO, REN XIAOBO, SUN HUILI, 2012. Thoughts on science and technology layout of marine biological resources research in China[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 31(1): 79-84. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 许东晖, 许实波, 王兵, 等, 1999. 皱纹盘鲍多糖抗肿瘤药理作用研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 18(4): 86-90. |
| XU DONGHUI, XU SHIBO, WANG BING, et al, 1999. A study on anti-tumor effects of abalone polysaccharide (AP) from haliotis discus hannai ino[J]. Tropic Oceanology, 18(4): 86-90. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 姚望, 张鑫杰, 姚庆华, 2019. 胃肠道恶性肿瘤化疗患者早期肠内营养干预的临床研究[J]. 中国肿瘤临床, 46(15): 780-784. |
| YAO WANG, ZHANG XINJIE, YAO QINGHUA, 2019. Clinical study of the effect of early enteral nutrition intervention in patients with gastrointestinal malignant tumors undergoing chemotherapy[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Oncology, 46(15): 780-784. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 赵强, 魏祥玲, 孙建安, 等, 2021. 牡蛎资源的综合开发利用研究进展[J]. 中国食品添加剂, 32(7): 150-159. |
| ZHAO QIANG, WEI XIANGLING, SUN JIANAN, et al, 2021. Research progress on comprehensive utilization of oyster resources[J]. China Food Additives, 32(7): 150-159. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局, 2016. 食品安全国家标准食品中氨基酸的测定 GB 5009.6-2016[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| NATIONAL HEALTH AND FAMILY PLANNING COMMISSION OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA, STATE FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION, 2016. National Food Safety Standards Determination of Amino Acids in Foods GB 5009.124-2016[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] |
BALMANT B D, ARAÚJO E O N, YABUKI D, et al, 2018. Effects of L-Arginine supplementation on leukogram, inflammatory bowel infiltrates and immunoglobulins with 5-FU use in rats[J]. Nutrition and Cancer, 70(2): 249-256.
doi: 10.1080/01635581.2018.1424346 |
| [13] | CAI BINGNA, CHEN HUA, SUN HAN, et al, 2016. Production of immunoregulatory polysaccharides from Crassostrea hongkongensis and their positive effects as a nutrition factor in modulating the effectiveness and toxicity of 5-FU chemotherapy in mice[J]. Food & Function, 7(1): 390-397. |
| [14] |
CAI BINGNA, PAN JIANYU, CHEN HUA, et al, 2021. Oyster polysaccharides ameliorate intestinal mucositis and improve metabolism in 5-fluorouracil-treated S180 tumour-bearing mice[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 256: 117545.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117545 |
| [15] |
CHEONG S H, KIM E-K, HWANG J-W, et al, 2013. Purification of a novel peptide derived from a shellfish, Crassostrea gigas, and evaluation of its anticancer property[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 61(47): 11442-11446.
doi: 10.1021/jf4032553 |
| [16] |
COËFFIER M, CLAEYSSENS S, BENSIFI M, et al, 2011. Influence of leucine on protein metabolism, phosphokinase expression, and cell proliferation in human duodenum[J]. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 93(6): 1255-1262.
doi: 10.3945/ajcn.111.013649 |
| [17] | COOL J C, DYER J L, XIAN C J, et al, 2005. Pre-treatment with insulin-like growth factor-Ⅰ partially ameliorates 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis in rats[J]. Growth Hormone & IGF Research, 15(1): 72-82. |
| [18] |
CORREIA-DA-SILVA M, SOUSA E, PINTO M M M, et al, 2017. Anticancer and cancer preventive compounds from edible marine organisms[J]. Seminars in Cancer Biology, 46: 55-64.
doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.03.011 |
| [19] |
DE JESUS L C L, DRUMOND M M, DE CARVALHO A, et al, 2019. Protective effect of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. Lactis CIDCA 133 in a model of 5 fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis[J]. Journal of Functional Foods, 53: 197-207.
doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2018.12.027 |
| [20] |
GAO YUE, XIAO XIANGSHENG, ZHANG CHANGLIN, et al, 2017. Melatonin synergizes the chemotherapeutic effect of 5-fluorouracil in colon cancer by suppressing PI3K / AKT and NF-κB / iNOS signaling pathways[J]. Journal of Pineal Research, 62(2): e12380.
doi: 10.1111/jpi.12380 |
| [21] | HAMOUDA N, SANO T, OIKAWA Y, et al, 2017. Apoptosis, dysbiosis and expression of inflammatory cytokines are sequential events in the development of 5-fluorouracil- induced intestinal mucositis in mice[J]. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology, 121(3): 159-168. |
| [22] |
HAO LILI, WANG XINCEN, CAO YUNRUI, et al, 2022. A comprehensive review of oyster peptides: preparation, characterisation and bioactivities[J]. Reviews in Aquaculture, 14(1): 120-138.
doi: 10.1111/raq.12588 |
| [23] | HE FANG, WU CHENLU, LI PAN, et al, 2018. Functions and signaling pathways of amino acids in intestinal inflammation[J]. Biomed Research International, 2018: 9171905. |
| [24] | JIN QIGUAN, ZHOU MING, HU YULONG, et al, 2021. Inhibitory effect and mechanism of oyster enzymatic hydrolysate on lung metastasis in the subcutaneous Lewis lung cancer model in mice[J]. Kafkas Universitesi Veteriner Fakultesi Dergisi, 27(1): 73-82. |
| [25] |
KATO S, HAYASHI S, KITAHARA Y, et al, 2015. Saireito (TJ-114), a Japanese traditional herbal medicine, reduces 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis in mice by inhibiting cytokine-mediated apoptosis in intestinal crypt cells[J]. PLoS One, 10(1): e0116213.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116213 |
| [26] |
LEVIT R, SAVOY DE GIORI G, DE MORENO DE LEBLANC A, et al, 2021. Evaluation of vitamin-producing and immunomodulatory lactic acid bacteria as a potential co-adjuvant for cancer therapy in a mouse model[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 130(6): 2063-2074.
doi: 10.1111/jam.14918 pmid: 33128836 |
| [27] |
LI WAN, XU CHENG, ZHANG CHAOHUA, et al, 2019. The purification and identification of immunoregulatory peptides from oyster (Crassostrea hongkongensis) enzymatic hydrolysate[J]. RSC Advances, 9(56): 32854-32863.
doi: 10.1039/C9RA04255E |
| [28] |
PAN JIANYU, WAN PENG, CHEN DEKE, et al, 2019. Purification and identification of intestinal mucosal cell proliferation-promoting peptides from Crassostrea hongkongensis[J]. European Food Research and Technology, 245(3): 631-642.
doi: 10.1007/s00217-018-3186-1 |
| [29] |
SINGH K, GOBERT A P, COBURN L A, et al, 2019. Dietary arginine regulates severity of experimental colitis and affects the colonic microbiome[J]. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 9: 66.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00066 pmid: 30972302 |
| [30] |
SOUGIANNIS A T, VANDERVEEN B N, ENOS R T, et al, 2019. Impact of 5 fluorouracil chemotherapy on gut inflammation, functional parameters, and gut microbiota[J]. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, 80: 44-55.
doi: S0889-1591(18)31227-3 pmid: 30807838 |
| [31] |
TAN KARSOON, MA HONGYU, LI SHENGKANG, et al, 2020. Bivalves as future source of sustainable natural omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids[J]. Food Chemistry, 311: 125907.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125907 |
| [32] | TOMÉ D, 2018. The roles of dietary glutamate in the intestine[J]. Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism, 73(S5): 15-20. |
| [33] |
VENUGOPAL V, GOPAKUMAR K, 2017. Shellfish: nutritive value, health benefits, and consumer safety[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 16(6): 1219-1242.
doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12312 |
| [34] |
VIEIRA DE BARROS P A, RABELO ANDRADE M E, DE VASCONCELOS GENEROSO S, et al, 2018. Conjugated linoleic acid prevents damage caused by intestinal mucositis induced by 5-fluorouracil in an experimental model[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 103: 1567-1576.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.04.133 |
| [35] |
WANG HAIBO, LIU YULAN, SHI HAIFENG, et al. 2017. Aspartate attenuates intestinal injury and inhibits TLR4 and NODs / NF-κB and p38 signaling in weaned pigs after LPS challenge[J]. European Journal of Nutrition, 56(4): 1433-1443.
doi: 10.1007/s00394-016-1189-x |
| [36] |
WANG LIANG, SONG BAOHUI, HU YAN, et al, 2021. Puerarin ameliorates 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis in mice by inhibiting JAKs[J]. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 379(2): 147-155.
doi: 10.1124/jpet.121.000677 pmid: 34400527 |
| [37] |
WANG YUKAI, HE HAILUN, WANG GUOFAN, et al, 2010. Oyster (Crassostrea gigas) hydrolysates produced on a plant scale have antitumor activity and immunostimulating effects in BALB / c mice[J]. Marine Drugs, 8(2): 255-268.
doi: 10.3390/md8020255 |
| [38] |
WANG ZHENGHUI, WU BAOJUN, ZHANG XIANGHONG, et al, 2012. Purification of a polysaccharide from Boschniakia rossica and its synergistic antitumor effect combined with 5-fluorouracil[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 89(1): 31-35.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.02.024 |
| [39] |
XIA MI, YE LULU, HOU QIHANG, et al, 2016. Effects of arginine on intestinal epithelial cell integrity and nutrient uptake[J]. British Journal of Nutrition, 116(10): 1675-1681.
doi: 10.1017/S000711451600386X |
| [40] |
XIANG DAOCHUN, YANG JINYU, XU YANJIAO, et al, 2020. Protective effect of Andrographolide on 5-Fu induced intestinal mucositis by regulating p38 MAPK signaling pathway[J]. Life Sciences, 252: 117612.
doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117612 |
| [41] | XIE CHENGLIANG, KANG SANGSOO, LU CIYONG, et al, 2018. Quantification of multifunctional dipeptide YA from oyster hydrolysate for quality control and efficacy evaluation[J]. Biomed Research International, 2018: 8437379. |
| [42] |
YAN XIAOXIA, LI HAILONG, ZHANG YITING, et al, 2020. A new recombinant MS-superoxide dismutase alleviates 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis in mice[J]. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 41(3): 348-357.
doi: 10.1038/s41401-019-0295-8 |
| [43] |
YIM S K, KIM K M, LEE C H, et al, 2021. The superoxide dismutase mimetic M40403, improves 5-fluorouracil-induced small intestinal mucositis in a mouse model[J]. In Vivo, 35(3): 1485-1497.
doi: 10.21873/invivo.12401 pmid: 33910826 |
| [44] |
ZEESHAN M, ATIQ A, UL AIN Q, et al, 2021. Evaluating the mucoprotective effects of glycyrrhizic acid-loaded polymeric nanoparticles in a murine model of 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis via suppression of inflammatory mediators and oxidative stress[J]. Inflammopharmacology, 29(5): 1539-1553.
doi: 10.1007/s10787-021-00866-z pmid: 34420176 |
| [45] | ZHANG PAN, LAI ZELIN, CHEN HUIFEN, et al, 2017. Curcumin synergizes with 5-fluorouracil by impairing AMPK / ULK1-dependent autophagy, AKT activity and enhancing apoptosis in colon cancer cells with tumor growth inhibition in xenograft mice[J]. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 36(1): 190. |
| [46] |
ZHANG YUNCHANG, MU TIANQI, JIA HAI, et al, 2021. Protective effects of glycine against lipopolysaccharide- induced intestinal apoptosis and inflammation[J]. Amino Acids, 54(3): 353-364.
doi: 10.1007/s00726-021-03011-w |
| [47] |
ZHENG HONG, GAO JING, MAN SHULI, et al, 2019. The protective effects of Aquilariae Lignum Resinatum extract on 5-fuorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis in mice[J]. Phytomedicine, 54: 308-317.
doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.07.006 |
| [48] |
ZHENG JINLING, ZHANG TINGTING, FAN JIAN, et al, 2021. Protective effects of a polysaccharide from Boletus aereus on S180 tumor-bearing mice and its structural characteristics[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 188: 1-10.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.07.191 |
| [1] | WEI Xue, QIN Xiaoming, CHEN Suhua, ZHANG Kaijia, LIN Haisheng, ZHENG Huina, GAO Jialong. Study on the effect of Oyster hydrolysates on improving Lactation function in Postpartum hypogalactism [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(2): 141-152. |
|
||