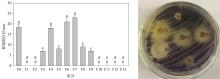
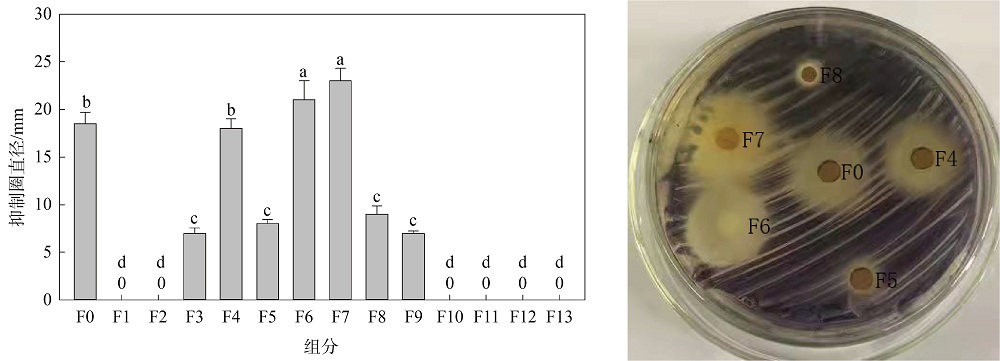
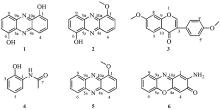
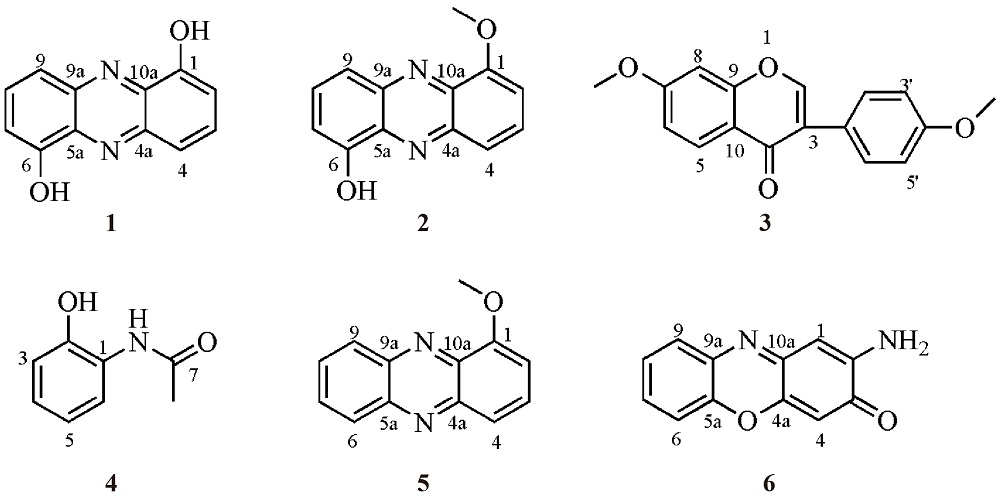
| [1] |
李德利, 丁鹏敏, 刘双月, 等, 2020. 人肠道微生物中抗菌活性菌株的筛选及其代谢产物研究[J]. 中国现代中药, 22(1): 26-34.
|
|
LI DELI, DING PENGMIN, LIU SHUANGYUE, et al, 2020. Screening of an antibacterial strain from human intestinal microbes and investigation on its active metabolites[J]. Modern Chinese Medicine, 22(1): 26-34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [2] |
李艳群, 陈柔雯, 林宗豪, 等, 2021. 一株群体感应抑制活性海洋放线菌的筛选与鉴定[J]. 热带海洋学报, 40(1): 75-81.
doi: 10.11978/2020011
|
|
LI YANQUN, CHEN ROUWEN, LIN ZONGHAO, et al, 2021. Screening and identification of a quorum sensing inhibitory actinomycetes derived from marine sediments[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 40(1): 75-81. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi: 10.11978/2020011
|
| [3] |
刘海珊, 朱国良, 赵水鸽, 等, 2019. 海绵放线菌Nocardiopsis dassonvillei OUCMDZ-4534的活性天然产物[J]. 有机化学, 39(2): 507-514.
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201806045
|
|
LIU HAISHAN, ZHU GUOLIANG, ZHAO SHUIGE, et al, 2019. Bioactive natural products from the marine sponge-derived Nocardiopsis dassonvillei OUCMDZ-4534[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 39(2): 507-514. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201806045
|
| [4] |
马忠俊, 孟大利, 王玉霞, 等, 2003. 苦马豆根和茎中化学成分的研究[J]. 沈阳药科大学学报, 20(2): 104-106.
|
|
MA ZHONGJUN, MENG DALI, WANG YUXIA, et al, 2003. Study on the chemical constituents from the roots and stems of Sphaerophysa salsula (Pall.) DC[J]. Journal of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, 20(2): 104-106. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [5] |
裴召苓, 陈雷, 许嘉磊, 等, 2017. 2株海鞘来源放线菌Streptomyces coelicoflavus和Nocardiopsis dassonvillei的次级代谢产物及其生物活性研究[J]. 中国海洋药物, 36(2): 55-60.
|
|
PEI ZHAOLING, CHEN LEI, XU JIALEI, et al, 2017. Secondary metabolites and their biological activities of two actinomycetes Streptomyces coelicoflavus and Nocardiopsis dassonvillei associated with ascidians Styela clava and Botryllus schlosseri[J]. Chinese Journal of Marine Drugs, 36(2): 55-60. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [6] |
王聪, 雷福厚, 谭学才, 等, 2019. 海洋拟诺卡菌来源的天然产物[J]. 中国抗生素杂志, 44(7): 763-769.
|
|
WANG CONG, LEI FUHOU, TAN XUECAI, et al, 2019. New natural products from the marine-derived Nocardiopsis spp.[J]. Chinese Journal of Antibiotics, 44(7): 763-769. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [7] |
王柯, 李元, 吴剑波, 2007. 微生物来源白细胞介素-4受体拮抗剂的筛选[J]. 中国新药杂志, 16(14): 1088-1090.
|
|
WANG KE, LI YUAN, WU JIANBO, 2007. Screening of IL-4 receptor antagonist from microbial origin[J]. Chinese Journal of New Drugs, 16(14): 1088-1090. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [8] |
周恒, 2020. 海洋底泥放线菌抗群体感应活性及次级代谢产物的研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学.
|
|
ZHOU HENG, 2020. Study on anti-quorum sensing active and secondary metabolites of marine sediment actinomycetes[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [9] |
CHEN JIANWEI, WANG BIXIA, LU YAOJIA, et al, 2019. Quorum sensing inhibitors from marine microorganisms and their synthetic derivatives[J]. Marine Drugs, 17(2): 80.
doi: 10.3390/md17020080
|
| [10] |
GRAF E, SCHNEIDER K, NICHOLSON G, et al, 2007. Elloxazinones A and B, New aminophenoxazinones from Streptomyces griseus Acta 2871[J]. Journal of Antibiotics, 60(4): 277-284.
doi: 10.1038/ja.2007.35
|
| [11] |
HAQUE S, AHMAD F, DAR S A, et al, 2018. Developments in strategies for quorum sensing virulence factor inhibition to combat bacterial drug resistance[J]. Microbial Pathogenesis, 121: 293-302.
doi: S0882-4010(18)30537-0
pmid: 29857121
|
| [12] |
HU LINFANG, CHEN XIAO, HAN LI, et al, 2019. Two new phenazine metabolites with antimicrobial activities from soil-derived Streptomyces species[J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 72(7): 574-577.
doi: 10.1038/s41429-019-0163-2
|
| [13] |
LAURSEN J B, NIELSEN J, 2004. Phenazine natural products: biosynthesis, synthetic analogues, and biological activity[J]. Chemical Reviews, 104(3): 1663-1686.
doi: 10.1021/cr020473j
pmid: 15008629
|
| [14] |
LU CHUNHUA, LI YAOYAO, WANG HAOXIN, et al, 2013. A new phenoxazine derivative isolated from marine sediment actinomycetes, Nocardiopsis sp. 236[J]. Drug Discoveries & Therapeutics, 7(3): 101-104.
|
| [15] |
MANIVASAGAN P, KANG K H, SIVAKUMAR K, et al, 2014. Marine actinobacteria: An important source of bioactive natural products[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 38(1): 172-188.
doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2014.05.014
pmid: 24959957
|
| [16] |
MASKEY R P, LI FUCHAO, QIN SONG, et al, 2003. Chandrananimycins A-C: Production of novel anticancer antibiotics from a marine Actinomadura sp. isolate M048 by variation of medium composition and growth conditions[J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 56(7): 622-629.
doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.56.622
|
| [17] |
MAVRODI D V, PAREJKO J A, MAVRODI O V, et al, 2013. Recent insights into the diversity, frequency and ecological roles of phenazines in fluorescent Pseudomonas spp.[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2013, 15(3): 675-686.
doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2012.02846.x
|
| [18] |
MIAO LI, QIAN SHENGHUI, QI SHUHUA, et al, 2021. Culture medium optimization and active compounds investigation of an anti-quorum sensing marine actinobacterium Nocardiopsis dassonvillei JS106[J]. Microbiology, 90(1): 112-123.
doi: 10.1134/S0026261721010070
|
| [19] |
MOGOŞANU G D, GRUMEZESCU A M, BEJENARU L E, et al, 2016. Marine natural products in fighting microbial infections[M]// KONK, RAIM. Antibiotic resistance: mechanisms and new antimicrobial approaches. San Diego: Academic Press: 351-375.
|
| [20] |
MUKHERJEE S, BASSLER B L, 2019. Bacterial quorum sensing in complex and dynamically changing environments[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 17(6): 371-382.
doi: 10.1038/s41579-019-0186-5
pmid: 30944413
|
| [21] |
PANDEY M K, PANDEY R, SINGH V P, et al, 2002. Antifungal activity of 4', 7-dimethoxyisoflavone against some fungi[J]. Mycobiology, 30(1): 55-56.
doi: 10.4489/MYCO.2002.30.1.055
|
| [22] |
PRIYANKA S, JAYASHREE M, SHIVANI R, et al, 2019. Characterisation and identification of antibacterial compound from marine actinobacteria: In vitro and in silico analysis[J]. Journal of Infection and Public Health, 12(1): 83-89.
doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2018.09.005
|
| [23] |
RÉMY B, MION S, PLENER L, et al, 2018. Interference in bacterial quorum sensing: a biopharmaceutical perspective[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 9: 203, doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00203.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00203
pmid: 29563876
|
| [24] |
SELIM M S M, ABDELHAMID S A, MOHAMED S S, 2021. Secondary metabolites and biodiversity of actinomycetes[J]. Journal of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, 19(1): 72.
doi: 10.1186/s43141-021-00156-9
|
| [25] |
XIAO JUN, THWE A A, LIU TINGTING, et al, 2021. Anti-inflammatory effects of an extract from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its purified product 1-hydroxyphenazine on RAW264. 7 cells[J]. Current Microbiology, 78(7): 2762-2773.
doi: 10.1007/s00284-021-02544-3
|
| [26] |
XIONG YANGHUI, LIU YU, 2010. Biological control of microbial attachment: a promising alternative for mitigating membrane biofouling[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 86(3): 825-837.
doi: 10.1007/s00253-010-2463-0
pmid: 20169341
|
| [27] |
YANG CHENGFANG, QIAN RUI, XU YAO, et al, 2019. Marine actinomycetes-derived natural products[J]. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, 19(31): 2868-2918.
doi: 10.2174/1568026619666191114102359
pmid: 31724505
|
| [28] |
ZOU GE, LIAO XIAOJIAN, PENG QI, et al, 2017. A new α-pyrone from the deep-sea actinomycete Nocardiopsis dassonvillei subsp. dassonvillei DSM 43111(T)[J]. Journal of Asian Natural Products Research, 19(12): 1232-1238.
doi: 10.1080/10286020.2017.1307186
|
 ), QIAN Jiaxing, MO Jie, ZHOU Heng, QIAN Shenghui, DONG Kunming(
), QIAN Jiaxing, MO Jie, ZHOU Heng, QIAN Shenghui, DONG Kunming( )
)