Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (6): 129-139.doi: 10.11978/2024002CSTR: 32234.14.2024002
• Marine Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Development of testis and ultrastructure of spermatozoa in Mastigias papua
ZHANG Ruixue1,2( ), YANG Wenhao1,2, CHEN Nan1,2(
), YANG Wenhao1,2, CHEN Nan1,2( ), WANG Shuhong1,2,3
), WANG Shuhong1,2,3
- 1. Fisheries College of Jimei University, Xiamen 361021, China
2. Ornamental Aquarium Engineering Research Centre in University of Fujian Province, Xiamen 361021, China
3. Key Laboratory of Healthy Mariculture for the East China Sea, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Xiamen 361021, China
-
Received:2024-01-02Revised:2024-02-08Online:2024-11-10Published:2024-12-05 -
Contact:CHEN Nan -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Xiamen, China(3502Z202372021); Research Start-up Funds of Jimei University(ZQ2021023)
CLC Number:
- Q958.8
Cite this article
ZHANG Ruixue, YANG Wenhao, CHEN Nan, WANG Shuhong. Development of testis and ultrastructure of spermatozoa in Mastigias papua[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(6): 129-139.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

Fig. 1
Testis morphology changes of Mastigias papua. (a) Testis on the 10th day of the experiment; (b) testis on the 25th day; (c) testis on the 40th day. The lower right corner of (a), (b) and (c) show a partial enlargement of the testis. White arrows show local magnification; white triangles show gastric filaments; white dots show testis"
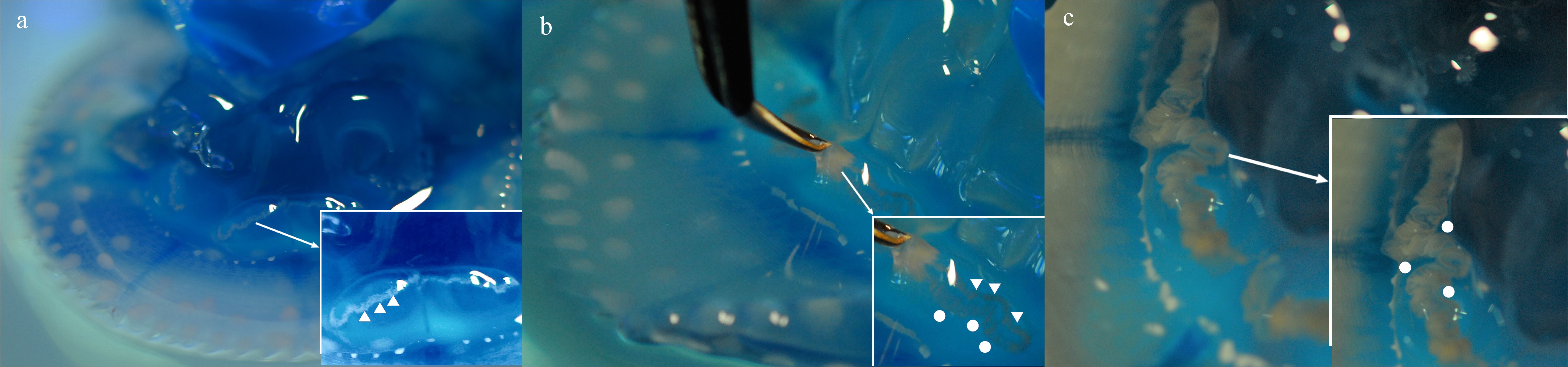
Fig. 2
The testis of Mastigias papua from 1 to 10d of the experiment. (a, c, e) The testis of Mastigias papua sampled from different periods, respectively; (b), (d) and (f) are local enlargements of (a), (c) and (e), respectively. The double arrows show the gap of spermatozoa follicles, the arrow shows typical spermatozoa follicles for this phase"

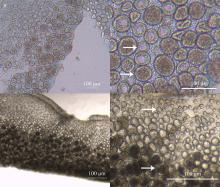
Fig. 3
The testis of Mastigias papua from 11 to 25d of the experiment. (a, c) The testis of Mastigias papua sampled from different period, respectively; (b) and (d) are the enlarged spermatozoa follicles of (a) and (c), respectively. The arrows show typical spermatozoa follicles for this phase"

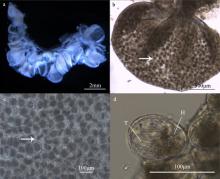
Fig. 4
The testis of Mastigias papua from 26 to 40d of the experiment. (a) Full gonads; (b) the shape of a sac testis; (c) the opaque spermatozoa follicles; (d) spermatozeugmatas in the spermatozoa follicle. H: head of spermatozoa; T: tail of spermatozoa. The arrows show the typical spermatozoa follicles for this phase"

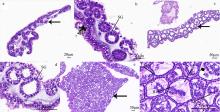
Fig. 5
Histology of various stages of Mastigias papua testis. (a, b) The testis from 1 to 10d of the experiment; (c, d) the testis from 11 to 25d of the experiment; (e, f) the testis from 26 to 40d of the experiment. H: head of spermatozoa; SG: spermatogonia; SZ: spermatozoa; T: tail of spermatozoa. The arrows show the spermatozoa follicles at different stages of testis development"

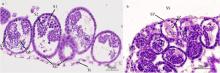
Fig. 6
Spermatozoa follicles structure from testis at different developmental stages (Mastigias papua). (a) Early development of spermatozoa follicles; (b) late development of spermatozoa follicles. SG: spermatogonia; S1: primary spermatocytes; S2: secondary spermatocytes; SZ: spermatozoa; SS: subgenital sinus; SP: spermiation pit; ST: spermatids; Te: testicular epithelium"

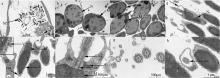
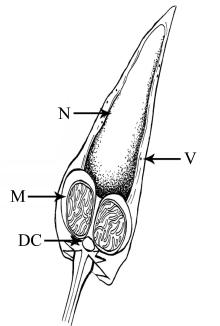
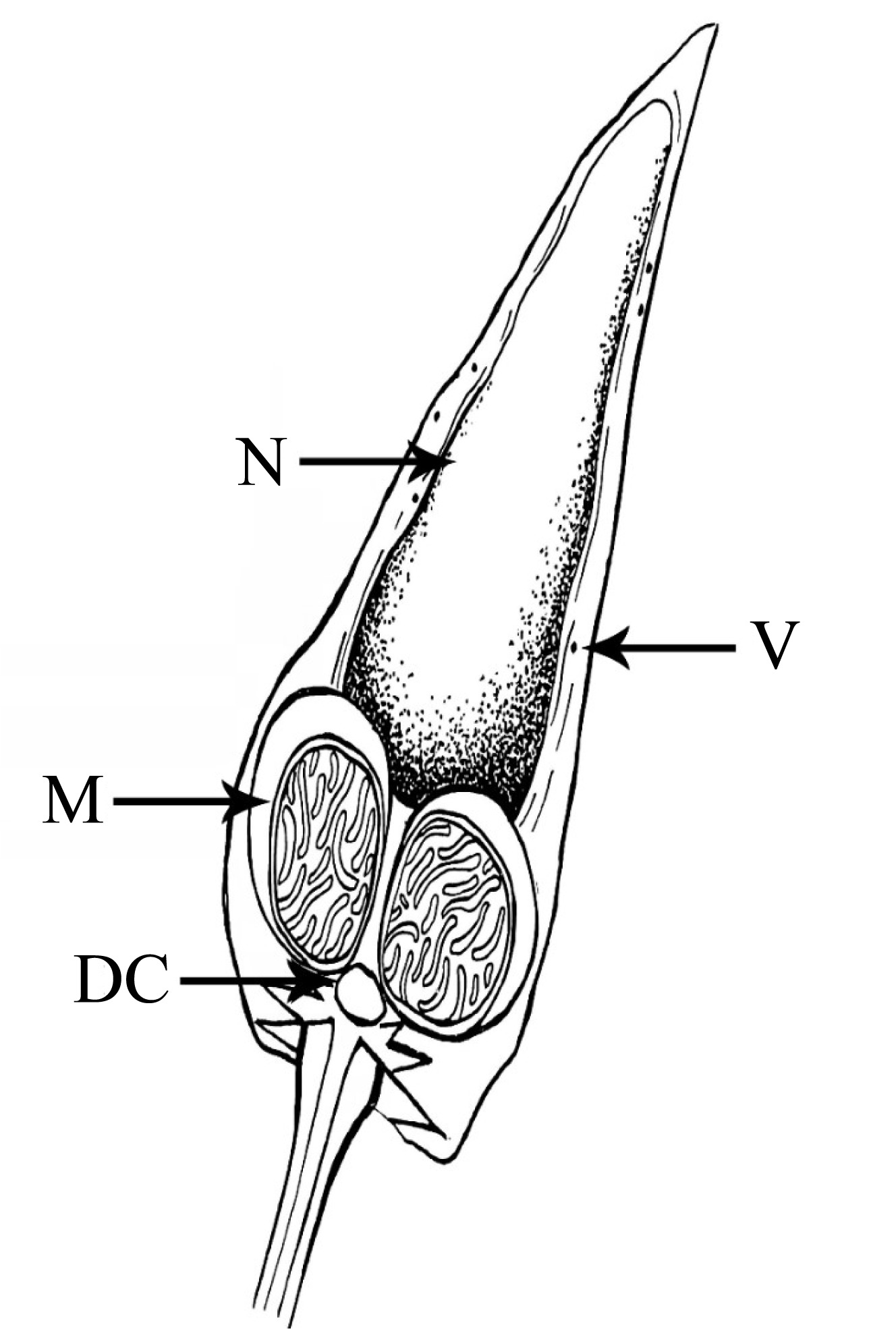
Fig. 8
Untrostructure of spermatozoas from Mastigias papua. (a) Spermatids and mature spermatozoas in the gonad; (b) shows spermatids; (c) shows mature spermatozoas; (d-f) the head and mid-section of mature spermatozoas; (g, h) cross-sections of the tails of mature spermatozoas. Ax: axoneme; DC: distal centriole; S: satellite rays; ST: spermatids; SZ: spermatozoa; PC: proximal centriole; PM: plasma membrane; M: mitochondria; Mi: microtubule; N: nucleus; V: vesicles"

Tab. 1
Development of the testis of Mastigias papua at different stages"
| 精巢分期 | 外部形态 | 光学显微镜下 | 组织切片 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ期 | 肉眼不可见( | 精小囊小而透明, 排列松散( | 由数个细胞核明显的精原细胞组成的球状精小囊, 内部无空腔( |
| Ⅱ期 | 环状乳白色, 由近胃丝处向外性腺透明度降低、颜色加深( | 梯度发育, 由近胃丝处向外精小囊个体变大, 透明度降低( | 远离胃丝的精小囊更大, 排列更紧密, 内部有空腔, 可见明显的由精原细胞整齐排列而成的精小囊壁( |
| Ⅲ期 | 褶皱呈囊状, 浅米黄色( | 处于不同发育阶段的精小囊, 正在进行精子发生的精小囊占绝大多数( | 精小囊内有不同发育阶段的配子细胞, 大量精小囊内充满以精子束存在的成熟精子( |
Tab. 2
Scyphozoa spermatozoa morphology"
| 物种 | 精子头部形态 | 头部长度/μm | 尾部长度/μm | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 夜光游水母 | 短而粗 | <4.00 | — | Franzén( |
| 海月水母 | 长尖辣椒状 | 4.15 | 27.78 | Rouse等( |
| 狮鬃水母 | 细长 | 14.00 | — | Arai( |
| 马赛克水母 | 短而粗 | 2 | 28.00 | Rouse等( |
| 安朵仙水母 | 略微椭圆 | 4.00 | 35.00 | Arai( |
| 煎蛋水母 | 圆柱形 | 6.00 | — | Franzén( |
| 澳洲斑点水母 | 细长 | 6.00 | 42.00 | Rouse等( |
| 巴布亚硝水母 | 尖辣椒状 | 7.61±0.63 | 43.03±4.02 | 本文章 |
| [1] |
陈昭廷, 李琪, 陈四清, 等, 2015. 海月水母精巢发育及排精过程的观察[J]. 动物学杂志, 50(1): 131-140.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈昭廷, 周洋, 顾志峰, 等, 2017. 海月水母(Aurelia aurita)精巢发育及精子的超微结构[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 48(1): 122-129.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
洪惠馨, 2014. 中国海域钵水母生物学及其与人类的关系[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社:60.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
杨翠华, 王玮, 王文章, 2011. 光照和水流对巴布亚硝水母存活时间及存活率的影响[J]. 水产科学, 30(9): 555-558.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
杨翠华, 王玮, 王文章, 等, 2012. 咖啡金黄水母的人工培育及生活史观察[J]. 水产科学, 31(12): 708-712.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
杨文浩, 王淑红, 林子路, 等, 2022. 巴布亚硝水母无性生殖过程及形态变化[J]. 动物学杂志, 57(3): 321-335.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
pmid: 4144098 |
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [1] | WU Tao, PAN Ying, LIU Yiming, LIAN Changpeng, XU Bingjie, WANG Chaoqi, YANG Ling. Testis development, spermatogenesis and sperm ultrastructure of Lutraria sieboldii in the Beibu Gulf, Guangxi [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 69-80. |
|
||