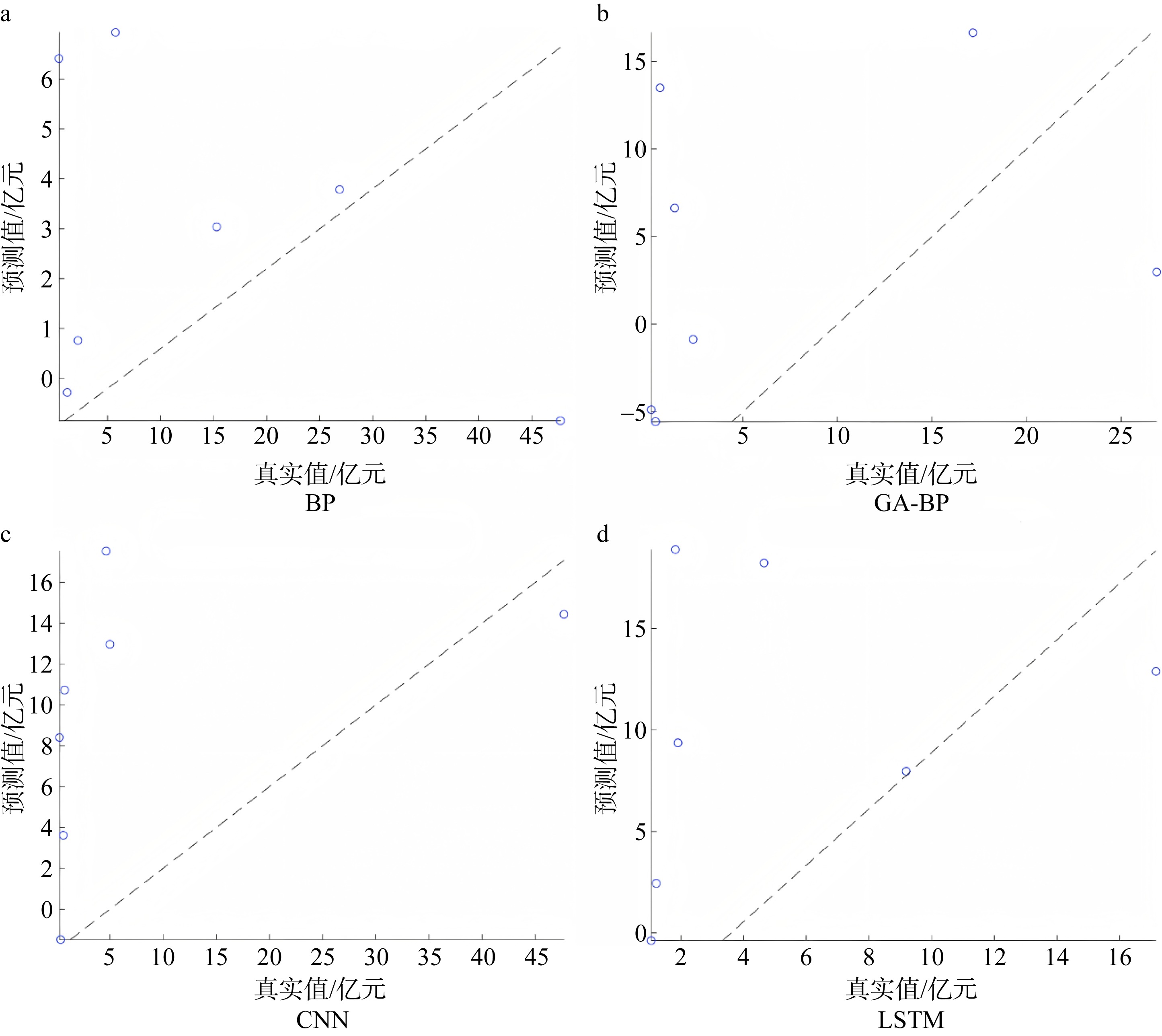
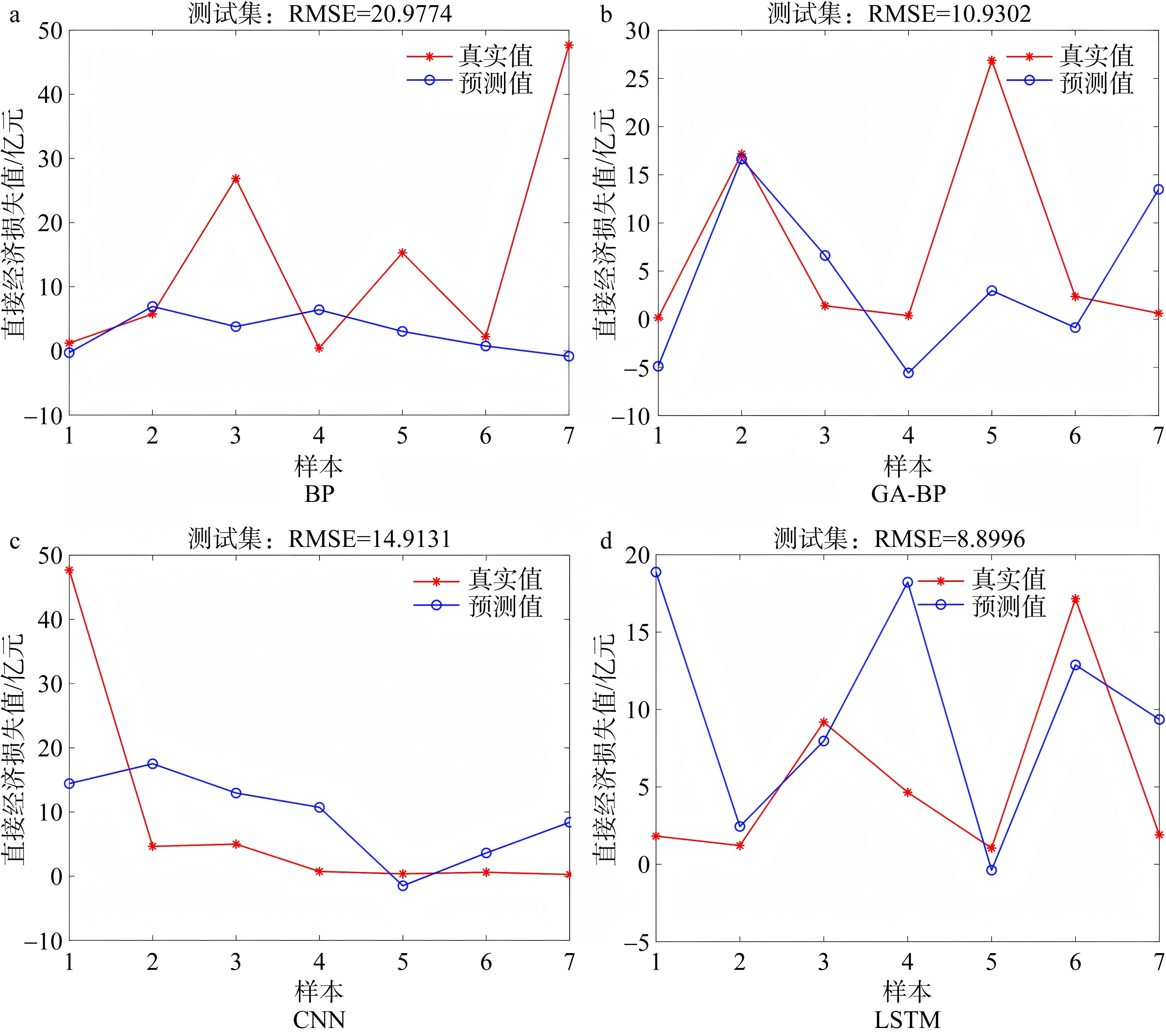
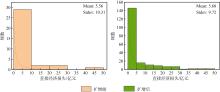
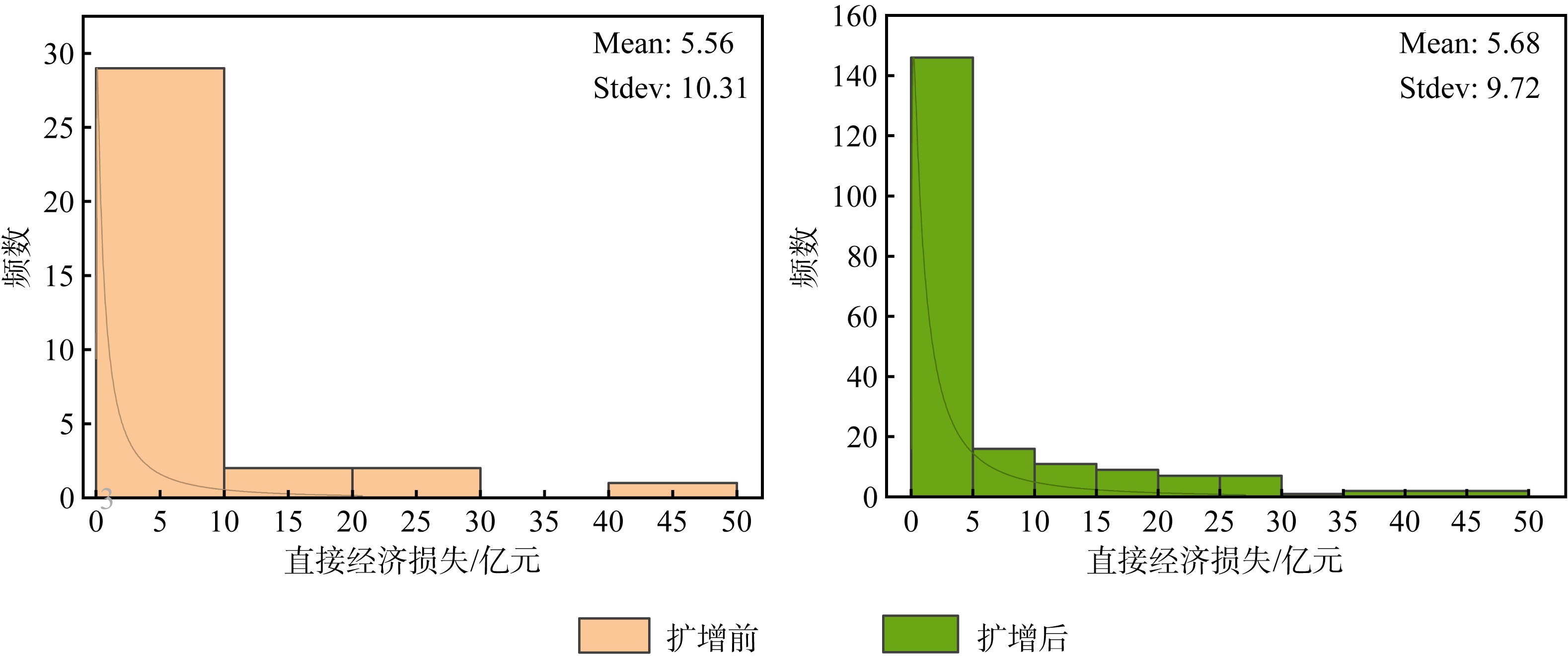
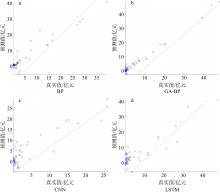
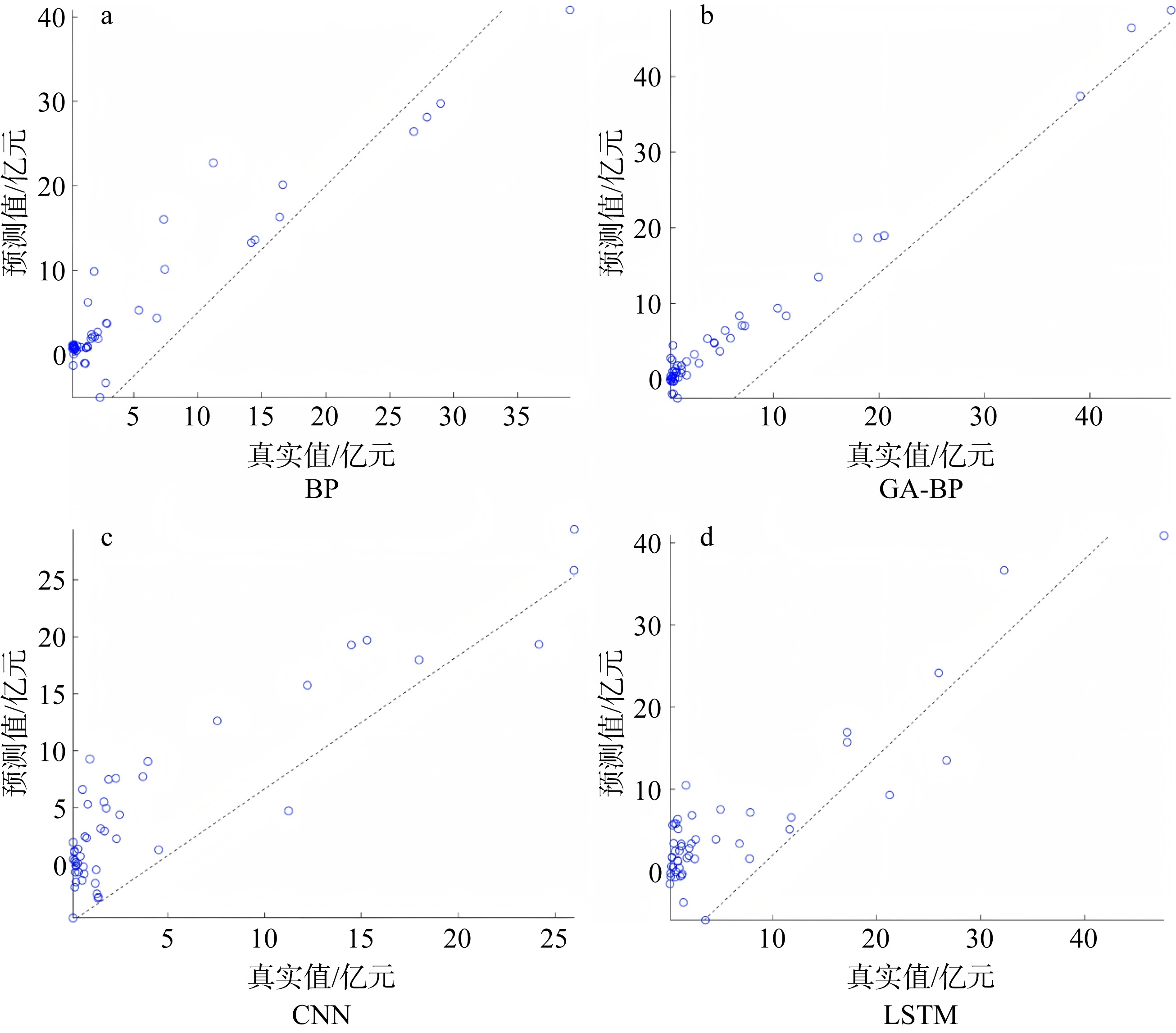
Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 56-66.doi: 10.11978/2024191
Special Issue: 海洋大数据及应用
• Marine Meteorology • Previous Articles Next Articles
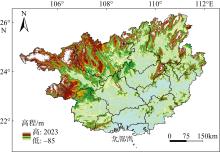
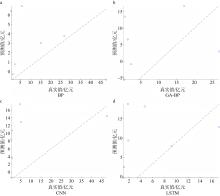
Research on a prediction model for direct economic losses caused by typhoons in Guangxi
HUANG Zhaoyong1( ), XU Guilin2, MO Zhiming3(
), XU Guilin2, MO Zhiming3( )
)
- 1. School of Geography and Planning, Nanning Normal University, Nanning 530001, China
2. Key Laboratory of Environmental Change and Resources Use in Beibu Gulf, Ministry of Education, Nanning Normal University, Nanning 530001, China
3. Economic and Trade College, Guangxi University of Finance and Economics, Nanning 530007, China
-
Received:2024-10-14Revised:2024-11-08Online:2025-07-10Published:2025-07-31 -
Contact:MO Zhiming -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Program of China(2022YFD2401200); Key Project of Joint Fund for Regional Innovation and Development of National Natural Science Foundation of China(U20A20105); Major Science and Technology Projects in Guangxi(Guike)(AA22067072-5)
CLC Number:
- P429
Cite this article
HUANG Zhaoyong, XU Guilin, MO Zhiming. Research on a prediction model for direct economic losses caused by typhoons in Guangxi[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(4): 56-66.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 2
Indicator system for typhoon disaster impact factors in Guangxi"
| 指标层 | 指标因子 |
|---|---|
| 致灾因子危险性 | 最大风速/(m·s-1) (X1) |
| 最大降雨量/mm (X2) | |
| 中心气压/hPa (X3) | |
| 最大增水/cm (X4) | |
| 总水位/m (X5) | |
| 有效波高/m (X6) | |
| 平均波长/cm (X7) | |
| 平均波周期/s (X8) | |
| 承灾体脆弱性 | 人口密度/每平方千米人数 (X9) |
| 经济密度/(108 yuan·km-2) (X10) | |
| 城镇化率/% (X11) | |
| 农作物播种面积/1000hm2 (X12) | |
| 全区电力消费量/108 kWh (X13) | |
| 防灾减灾能力 | 每千人拥有病床数 (X14) |
| 每千人拥有卫生技术人员数 (X15) | |
| 卫生机构数量 (X16) | |
| 境内公路里程/km (X17) | |
| 境内铁路营业里程/km (X18) |
Tab. 3
Importance levels of various indicators"
| 指标 | 重要性程度 |
|---|---|
| 最大风速(X1) | 32.48% |
| 农作物播种面积(X12) | 21.07% |
| 中心气压(X3) | 9.02% |
| 总水位(X5) | 8.02% |
| 人口密度(X9) | 7.95% |
| 最大降雨量(X2) | 5.26% |
| 最大增水(X4) | 4.32% |
| 卫生机构数量(X16) | 4.04% |
| 境内铁路营业里程(X18) | 2.20% |
| 每千人拥有病床数量(X14) | 1.28% |
| 每千人拥有卫生技术人员数量(X15) | 1.23% |
| 城镇化率(X11) | 0.76% |
| 平均波长(X7) | 0.48% |
| 平均波周期(X8) | 0.47% |
| 经济密度(X10) | 0.44% |
| 有效波高(X6) | 0.41% |
| 全区电力消费量(X13) | 0.35% |
| 境内公路里程(X17) | 0.22% |
| [1] |
丁宏飞, 李演洪, 刘博, 等, 2016. 基于BP神经网络与SVM的快速路行程时间组合预测研究[J]. 计算机应用研究, 33(10): 2929-2932, 2936.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
冯倩, 刘强, 2017. 基于SVM-BP神经网络的风暴潮灾害损失预评估[J]. 海洋环境科学, 36(4): 615-621.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
韩鹏, 郭桂祯, 李鑫磊, 等, 2023. 基于地理探测器的福建省台风灾情影响因素分析[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 38(2): 487-495.
doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2023.2.0487 |
|
|
|
| [4] |
韩鹏, 郭桂祯, 孙宁, 等, 2022. 广东省台风灾害时空格局及影响因素研究[J]. 灾害学, 37(3): 112-117.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
李艳兰, 金龙, 史旭明, 等, 2021. 基于遗传—神经网络方法的广西台风灾害评估模型研究[J]. 气象与环境学报, 37(3): 139-144.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
李志娟, 2016. 台风灾害损失预测方法研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
林沛延, 林陪晖, 王俊, 等, 2023. 基于机器学习方法的浙江省台风灾害风险评估和动态风险预报[J]. 自然灾害学报, 32(4): 13-24.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
刘玉函, 唐晓春, 宋丽莉, 2003. 广东台风灾情评估探讨[J]. 热带地理, 23(2): 119-122.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
毛嘉铭, 刘光宇, 罗凯元, 2024. 结合数据增强及组合算法的短期光伏功率预测[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 36(8): 133-141.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
牛海燕, 刘敏, 陆敏, 等, 2011. 中国沿海地区台风灾害损失评估研究[J]. 灾害学, 26(3): 61-64.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
邱军, 孙力勇, 樊庆东, 2023. 一种基于三次样条插值的风电场出力预测评估方法[J]. 电气开关, 61(3): 16-18, 23.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
汪路, 卢莹, 赵海坤, 2023. 台风灾害时空特征分析与评估模型构建[J]. 灾害学, 38(4): 187-194.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
王阳, 陈薇伊, 马军山, 2022. 基于卷积神经网络的乳腺癌良恶性诊断[J]. 软件工程, 25(1): 6-9.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
温姗姗, 翟建青,
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
徐金鹏, 郭新峰, 王瑞波, 等, 2023. 基于GAN数据增强的软件缺陷预测聚合模型[J]. 计算机科学, 50(12): 24-31.
doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.221100171 |
|
doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.221100171 |
|
| [16] |
杨帆, 夏鸿崚, 2024. 基于数据集扩充的即时软件缺陷预测方法[J]. 南通大学学报(自然科学版), 23(1): 58-65.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
张恺, 杨隆浩, 高建清, 等, 2024. 基于累积置信规则库推理的台风灾害直接经济损失预测[J]. 灾害学, 39(1): 64-68, 74.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
赵飞, 廖永丰, 张妮娜, 等, 2011. 登陆中国台风灾害损失预评估模型研究[J]. 灾害学, 26(2): 81-85.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [1] | LI Shuzhao, WEI Che, SHEN Chen, SUN Guodong, YANG Yetao, LUO Jinhua, WANG Jiaolong. A machine learning-based method for predicting shallow subsurface CPT parameters in offshore wind farms [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(4): 14-24. |
| [2] | Xuyang CHEN, Baoliang LIU. Application of Real-time monitoring buoy in monitoring red tide [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(5): 20-24. |
| [3] | Chaoyu YANG, Danling TANG, Haibin YE. A study on retrieving chlorophyll concentration by using GF-4 data [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2017, 36(5): 33-39. |
| [4] |
HUANG Hu,DAI Zhi-jun,SHI Wei-yong,SHENG Kai.
Deposition characteristics of beach profile in strong-tidal environment − A case study of Yintan, Guangxi during spring [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2011, 30(4): 71-76. |
|
||