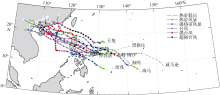
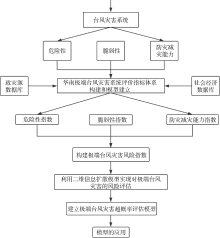
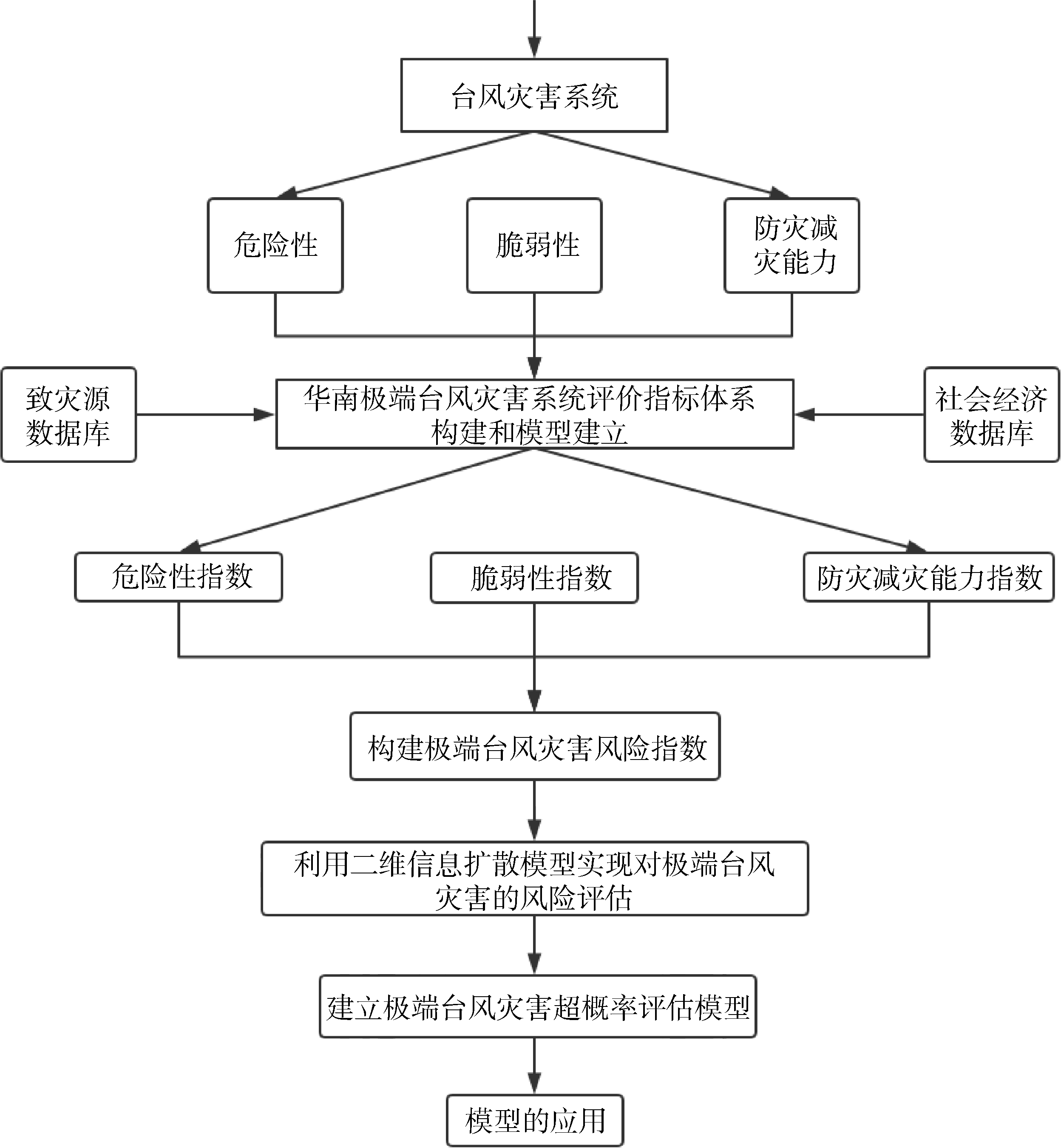
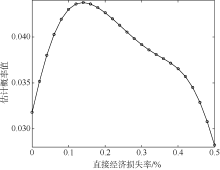
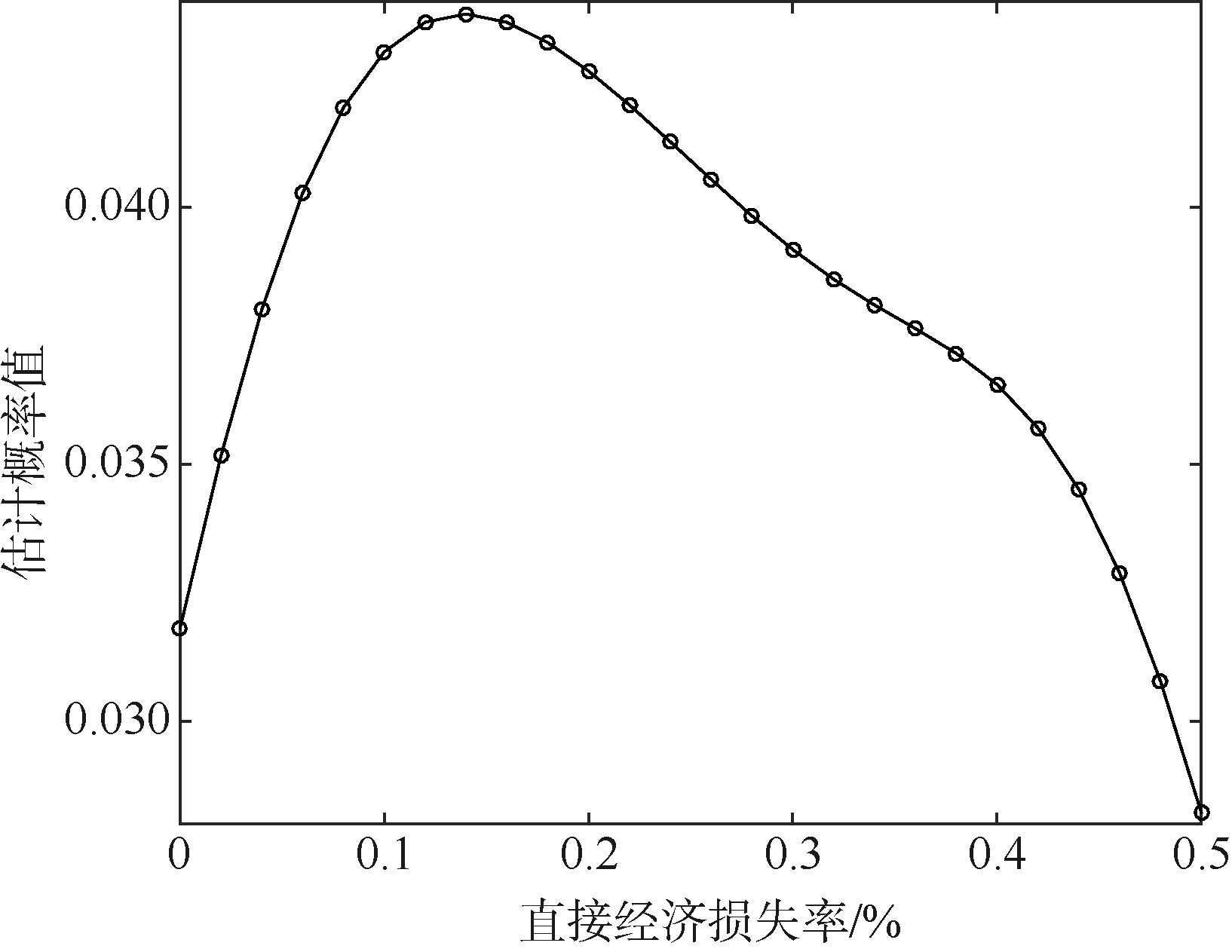
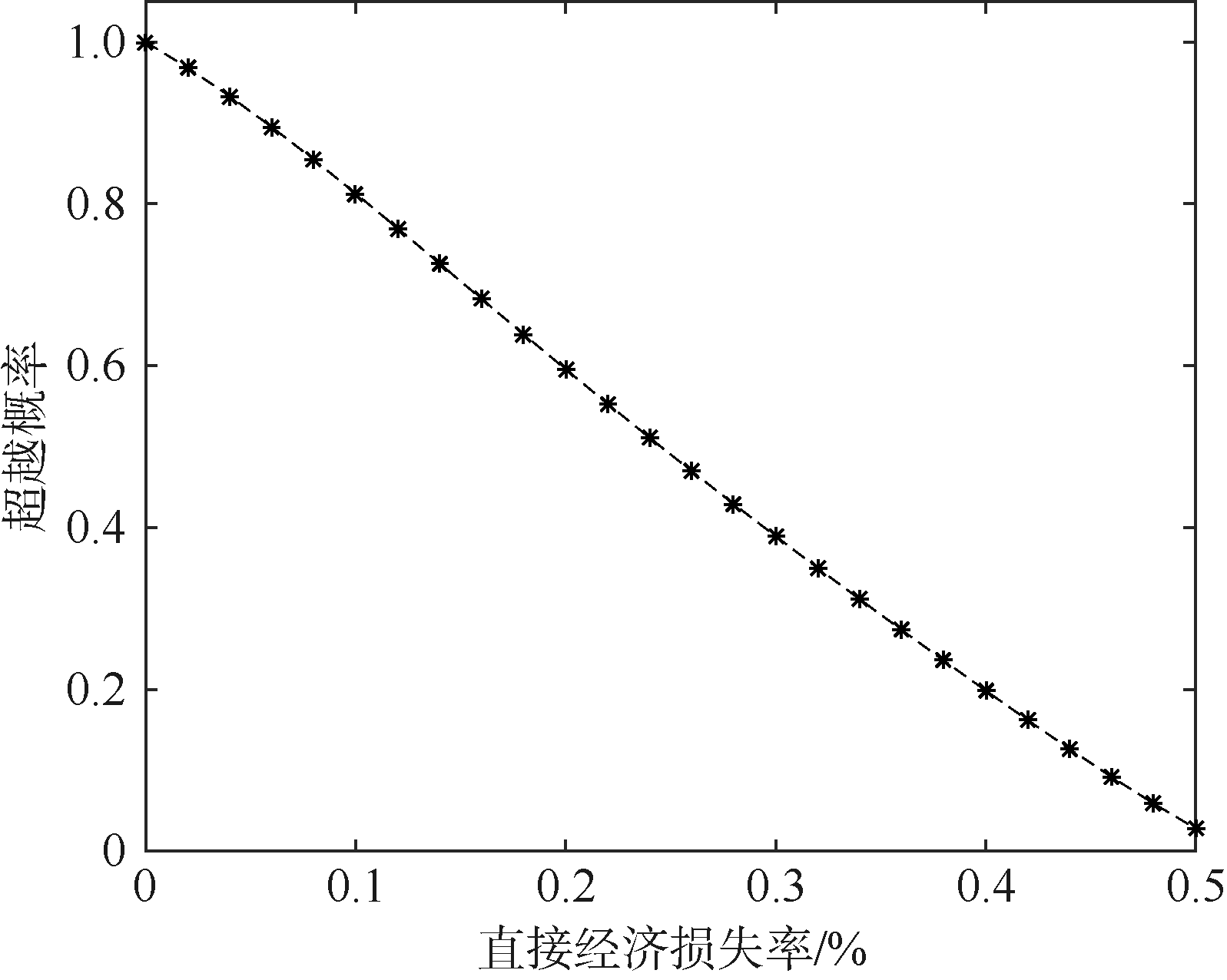
| 1 |
白海玲, 黄崇福 , 2000. 自然灾害的模糊风险[J]. 自然灾害学报, 9(1):47-53.
|
|
BAI HAILING, HUANG CHONGFU , 2000. Fuzzy risk of natural disasters[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 9(1):47-53(in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 2 |
陈佩燕, 杨玉华, 雷小途 , 等, 2009. 我国台风灾害成因分析及灾情预估[J]. 自然灾害学报, 18(1):64-73.
|
|
CHEN PEIYAN, YANG YUHUA, LEI XIAOTU , et al, 2009. Cause analysis and preliminary hazard estimate of typhoon disaster in China[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 18(1):64-73 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 3 |
陈香 , 2007. 福建省台风灾害风险评估与区划[J]. 生态学杂志, 26(6):961-966.
|
|
CHEN XIANG , 2007. Risk assessment and zonation of typhoon disasters in Fujian province[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 26(6):961-966 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 4 |
丁燕, 史培军 , 2002. 台风灾害的模糊风险评估模型[J]. 自然灾害学报, 11(1):34-43.
|
|
DING YAN, SHI PEIJUN , 2002. Fuzzy risk assessment model of typhoon hazard[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 11(1):34-43 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 5 |
黄崇福, 刘新立, 周国贤 , 等, 1998. 以历史灾情资料为依据的农业自然灾害风险评估方法[J]. 自然灾害学报, 7(2):1-9.
|
|
HUANG CHONGFU, LIU XINLI, ZHOU GUOXIAN , et al, 1998. Agricultural natural Disater risk assessment method according to the historic disaster data[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 7(2):1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 6 |
黄崇福 , 2005. 自然灾害风险评价: 理论与实践[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
|
|
HUANG CHONGFU , 2005. Risk assessment of natural disaster[M]. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese).
|
| 7 |
黄崇福 , 2006. 自然灾害风险分析的信息矩阵方法[J]. 自然灾害学报, 15(1):1-10.
|
|
HUANG CHONGFU , 2006. Information matrix method for risk analysis of natural disaster[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 15(1):1-10 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 8 |
黄崇福 , 2009. 自然灾害基本定义的探讨[J]. 自然灾害学报, 18(5):41-50.
|
|
HUANG CHONGFU , 2009. A discussion on basic definition of natural disaster[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 18(5):41-50 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 9 |
黄崇福 , 2018. 用信息扩散模型改进台风风险估计[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 38(9):2315-2325.
|
|
HUANG CHONGFU , 2018. Improving estimation of typhoon risk by using information diffusion model[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 38(9):2315-2325 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 10 |
刘合香, 徐庆娟 , 2011. 基于r维正态扩散的区域热带气旋灾害模糊风险分析[J]. 数学的实践与认识, 41(3):150-159.
|
|
LIU HEXIANG, XU QINGJUAN , 2011. Based on r-dimensional normal proliferation fuzzy risk analysis of regional tropical cyclone disasters[J]. Mathematics in Practice and Theory, 41(3):150-159 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 11 |
毛熙彦, 蒙吉军, 康玉芳 , 2012. 信息扩散模型在自然灾害综合风险评估中的应用与扩展[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 48(3):513-518.
|
|
MAO XIYAN, MENG JIJUN, KANG YUFANG , 2012. Application and extension of information diffusion model in comprehensive risk assessment of natural disasters[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 48(3):513-518 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 12 |
史培军 , 1996. 再论灾害研究的理论与实践[J]. 自然灾害学报, 5(4):6-17.
|
|
SHI PEIJUN , 1996. Theory and practice of disaster study[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 5(4):6-17 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 13 |
史培军 , 2002. 三论灾害研究的理论与实践[J]. 自然灾害学报, 11(3):1-9.
|
|
SHI PEIJUN , 2002. Theory on disaster science and disaster dynamics[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 11(3):1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 14 |
史培军 , 2005. 四论灾害系统研究的理论与实践[J]. 自然灾害学报, 14(6):1-7.
|
|
SHI PEIJUN , 2005. Theory and practice on disaster system research in a fourth time[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 14(6):1-7 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 15 |
史培军 , 2009. 五论灾害系统研究的理论与实践[J]. 自然灾害学报, 18(5):1-9.
|
|
SHI PEIJUN , 2009. Theory and practice on disaster system research in a fifth time[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 18(5):1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 16 |
吴联要, 雷小途 , 2012. 内核及外围尺度与热带气旋强度关系的初步研究[J]. 热带气象学报, 28(5):719-725.
|
|
WU LIANYAO, LEI XIAOTU , 2012. Preliminary research on the size of inner core and periphery and their relationship with the intensity of tropical cyclones[J]. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 28(5):719-725 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 17 |
于小兵, 俞显瑞, 吉中会 , 等, 2019. 基于信息扩散的东南沿海台风灾害风险评估[J]. 灾害学, 34(1):73-77.
|
|
YU XIAOBING, YU XIANRUI, JI ZHONGHUI , et al, 2019. Risk assessment of typhoon disaster in China's south-east coastal areas——based on information diffusion theory[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 34(1):73-77 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 18 |
张俊香, 李平日, 黄光庆 , 等, 2007. 基于信息扩散理论的中国沿海特大台风暴潮灾害风险分析[J]. 热带地理, 27(1):11-14.
|
|
ZHANG JUNXIANG, LI PINGRI, HUANG GUANGQING , et al, 2007. Risk assessment of swingeing storm surge disaster in coastal area of China induced by typhoon based on information diffusion method[J]. Tropical Geography, 27(1):11-14 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 19 |
张韧, 徐志升, 申双和 , 等, 2013. 基于小样本案例的自然灾害风险评估——信息扩散概率模型[J]. 系统科学与数学, 33(4):445-456.
|
|
ZHANG REN, XU ZHISHENG, SHEN SHUANGHE , et al, 2013. An unsymmetrical information diffusion probability model-for risk evaluation of natural disaster based on rare sample cases[J]. Journal of Systems Science and Mathematical Sciences, 33(4):445-456 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 20 |
HUANG CHONGFU , 1997. Principle of information diffusion[J]. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 91(1):69-90.
doi: 10.1016/S0165-0114(96)00257-6
|
| 21 |
HUANG CHONGFU , 2001. Information matrix and application[J]. International Journal of General Systems, 30(6):603-622.
doi: 10.1080/03081070108960737
|
| 22 |
LIU HEXIANG, ZHANG DALIN , 2012. Analysis and prediction of hazard risks caused by tropical cyclones in Southern China with fuzzy mathematical and grey models[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 36(2):626-637.
doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2011.07.024
|
| 23 |
WANG PEIZHUANG , 1990. A factor spaces approach to knowledge representation[J]. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 36(1):113-124.
doi: 10.1016/0165-0114(90)90085-K
|
 ), Yaojian LU, Meng WANG, Guangtao LI
), Yaojian LU, Meng WANG, Guangtao LI