Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (5): 115-123.doi: 10.11978/2022243CSTR: 32234.14.2022243
• Marine Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Physiological and biochemical responses of different species of chlorophyta to simulated acid rain stress
DU Xiang( ), LUO Qijun(
), LUO Qijun( ), CHEN Haimin
), CHEN Haimin
- School of Marine Sciences, Ningbo University, Ningbo 315211, China
-
Received:2022-11-14Revised:2023-01-07Online:2023-09-10Published:2023-01-10 -
Supported by:China Agriculture Research System(CARS-50); Nanji Islands National Marine Nature Reserve Administration Project(H202200074)
Cite this article
DU Xiang, LUO Qijun, CHEN Haimin. Physiological and biochemical responses of different species of chlorophyta to simulated acid rain stress[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 115-123.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Fig. 1
Effects of simulated acid rain stress on Fv/Fm at different pH levels of eight species of green seaweeds. (a) U. prolifera; (b) U. indicate; (c) U. lactuca; (d) U. stenophylla; (e) U. pertusa; (f) U. conglobata; (g) C. stimpsonii; (h) C. fragile. * and ** indicate significant difference among different treatments at 0.05 and 0.01 levels"
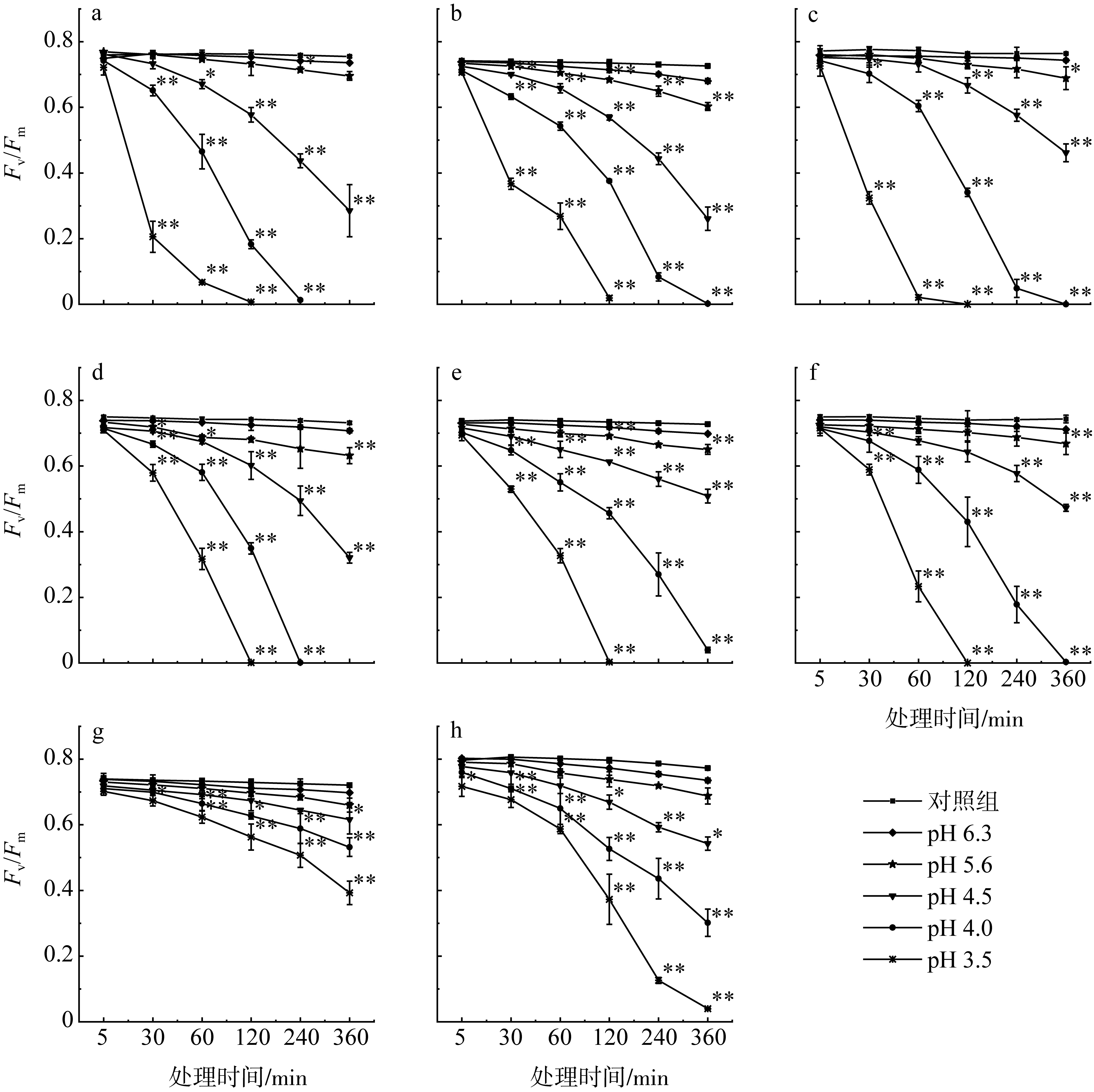
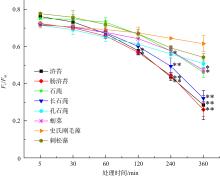
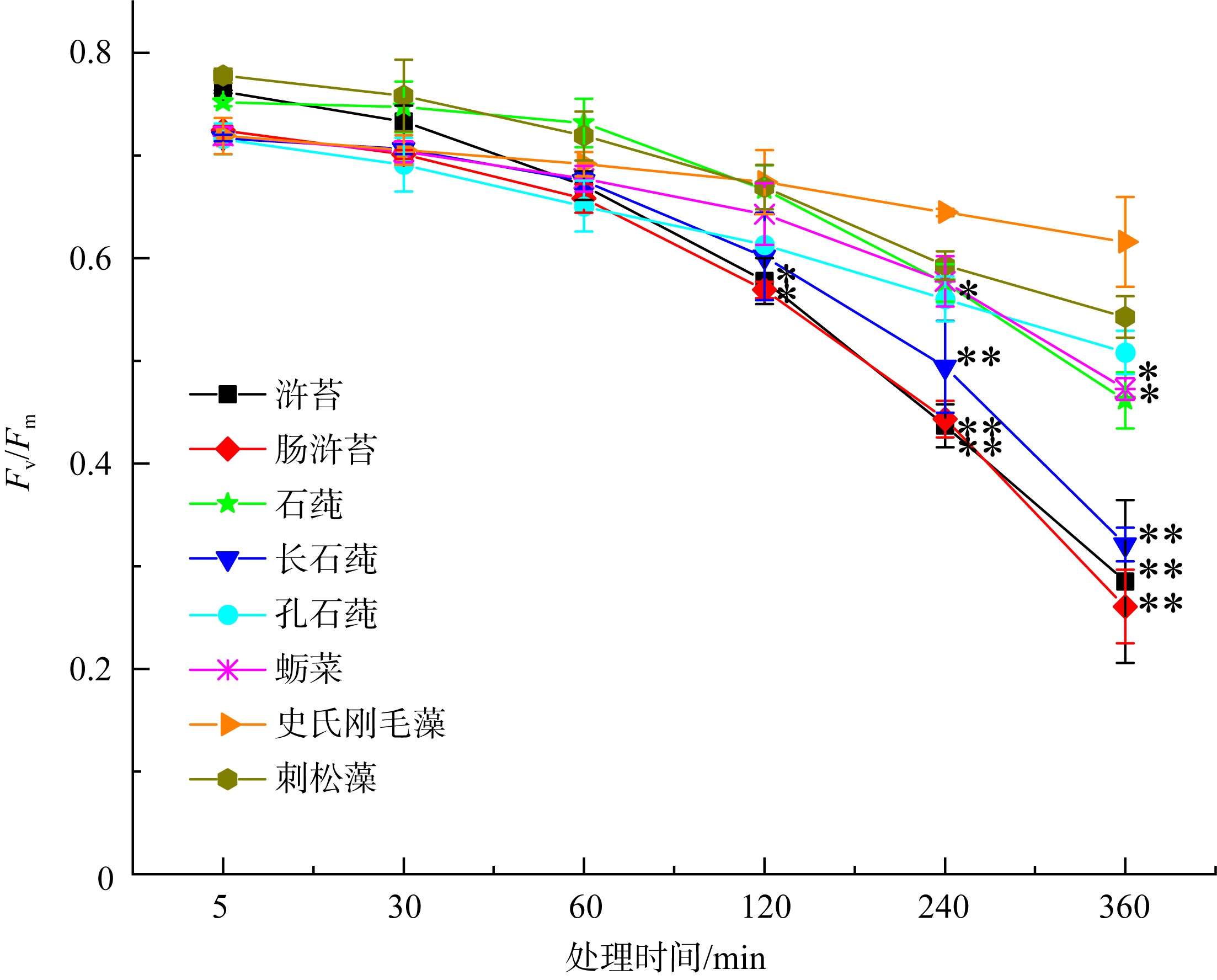
Fig. 2
Effects of simulated acid rain (pH 4.5) stress with different treatment times on Fv/Fm of eight species of green seaweeds. * and ** indicate that there are significant differences among U. prolifera, U. intestinalis, U. lactuca, U. stenophylla, U. pertusa, U. conglobata, C. fragile and C. stimpsonii at the level of 0.05 and 0.01. C. stimpsonii is control"
Tab. 1
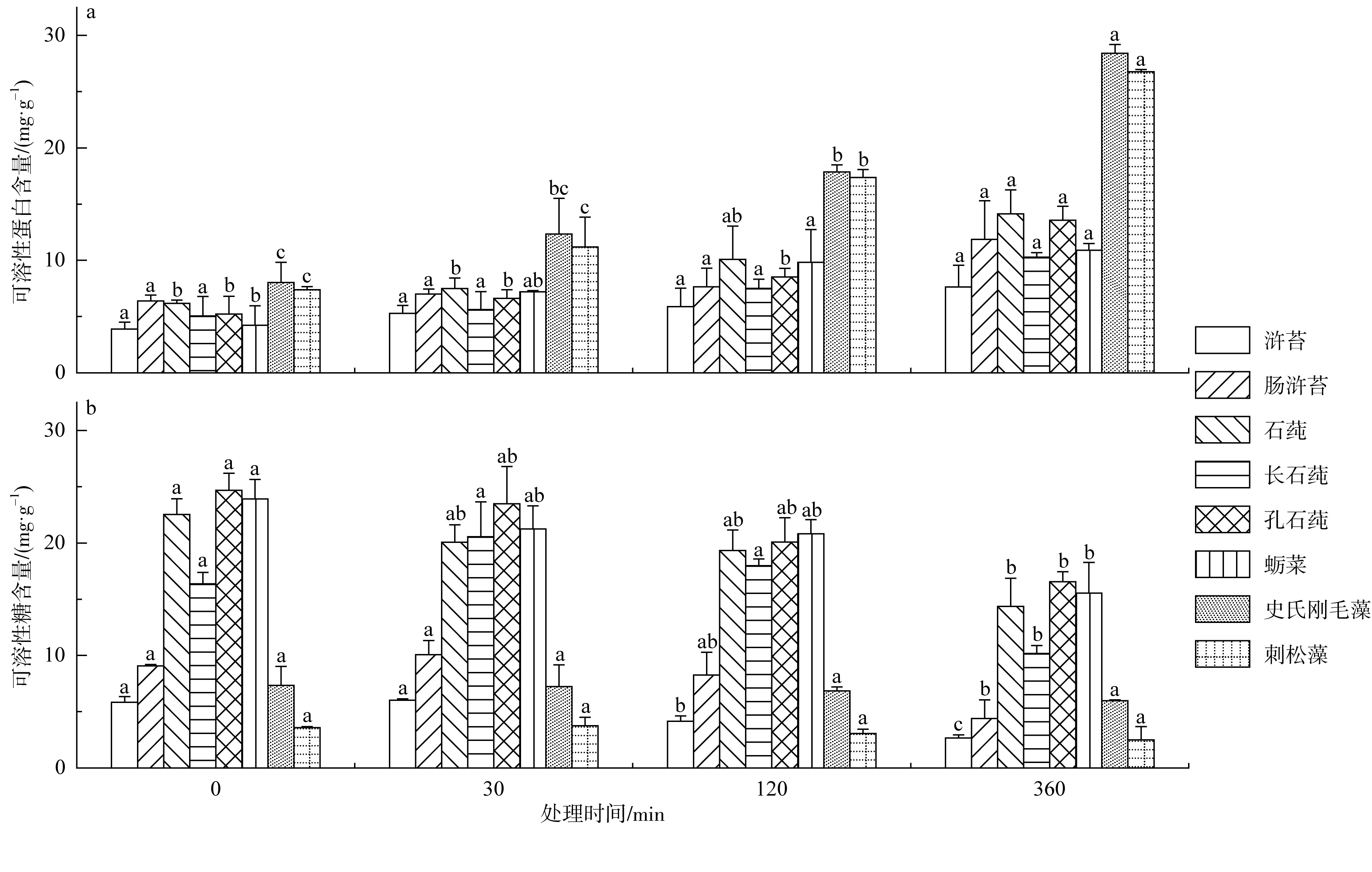
Stress response of chlorophyll a content (unit: mg·g-1) to different treatment times of simulated acid rain"
| 绿藻种类 | 0min | 30min | 60min | 120min | 240min | 360min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 浒苔 | 0.735±0.005 a | 0.728±0.010 a | 0.678±0.018 ab | 0.627±0.060 bc | 0.545±0.001 c | 0.446±0.010 d |
| 肠浒苔 | 0.479±0.005 a | 0.416±0.014 b | 0.401±0.017 bc | 0.370±0.007 bc | 0.356±0.022 cd | 0.312±0.021 d |
| 石莼 | 0.735±0.053 a | 0.733±0.021 a | 0.714±0.007 ab | 0.642±0.078 abc | 0.549±0.029 bc | 0.525±0.066 c |
| 长石莼 | 0.678±0.024 a | 0.674±0.039 a | 0.660±0.020 ab | 0.634±0.021 ab | 0.578±0.023 b | 0.479±0.034 c |
| 孔石莼 | 0.698±0.011 a | 0.702±0.032 a | 0.687±0.036 a | 0.664±0.012 a | 0.578±0.003 b | 0.514±0.011 b |
| 蛎菜 | 0.512±0.009 a | 0.477±0.010 ab | 0.444±0.034 ab | 0.420±0.012 ab | 0.410±0.008 ab | 0.366±0.093 b |
| 史氏刚毛藻 | 0.671±0.033 a | 0.672±0.012 a | 0.636±0.051 a | 0.616±0.009 a | 0.574±0.003 ab | 0.505±0.039 b |
| 刺松藻 | 0.675±0.009 a | 0.671±0.014 a | 0.660±0.018 a | 0.646±0.006 a | 0.586±0.016 b | 0.499±0.016 c |
Tab. 2
Stress response of carotenoids content (unit: mg·g-1) to different treatment times of simulated acid rain"
| 绿藻种类 | 0min | 30min | 60min | 120min | 240min | 360min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 浒苔 | 0.444±0.017 a | 0.442±0.028 ab | 0.402±0.008 ab | 0.377±0.031 b | 0.303±0.021 c | 0.281±0.002 c |
| 肠浒苔 | 0.347±0.006 a | 0.313±0.008 ab | 0.305±0.012 b | 0.284±0.008 bc | 0.265±0.004 cd | 0.228±0.021 d |
| 石莼 | 0.470±0.033 a | 0.475±0.002 a | 0.450±0.019 a | 0.421±0.051 ab | 0.385±0.042 ab | 0.332±0.033 b |
| 长石莼 | 0.217±0.013 a | 0.212±0.003 ab | 0.188±0.012 bc | 0.171±0.006 cd | 0.155±0.003 d | 0.147±0.009 d |
| 孔石莼 | 0.567±0.031 a | 0.541±0.001 ab | 0.551±0.001 ab | 0.508±0.003 b | 0.448±0.001 c | 0.406±0.007 c |
| 蛎菜 | 0.284±0.017 a | 0.274±0.011 a | 0.270±0.001 a | 0.249±0.002 a | 0.233±0.014 a | 0.212±0.053 a |
| 史氏刚毛藻 | 0.396±0.041 a | 0.392±0.009 a | 0.388±0.008 ab | 0.372±0.017 ab | 0.365±0.022 ab | 0.313±0.026 b |
| 刺松藻 | 0.406±0.002 a | 0.400±0.005 a | 0.388±0.033 ab | 0.361±0.007 ab | 0.341±0.009 bc | 0.302±0.006 c |
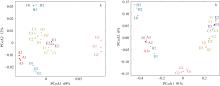
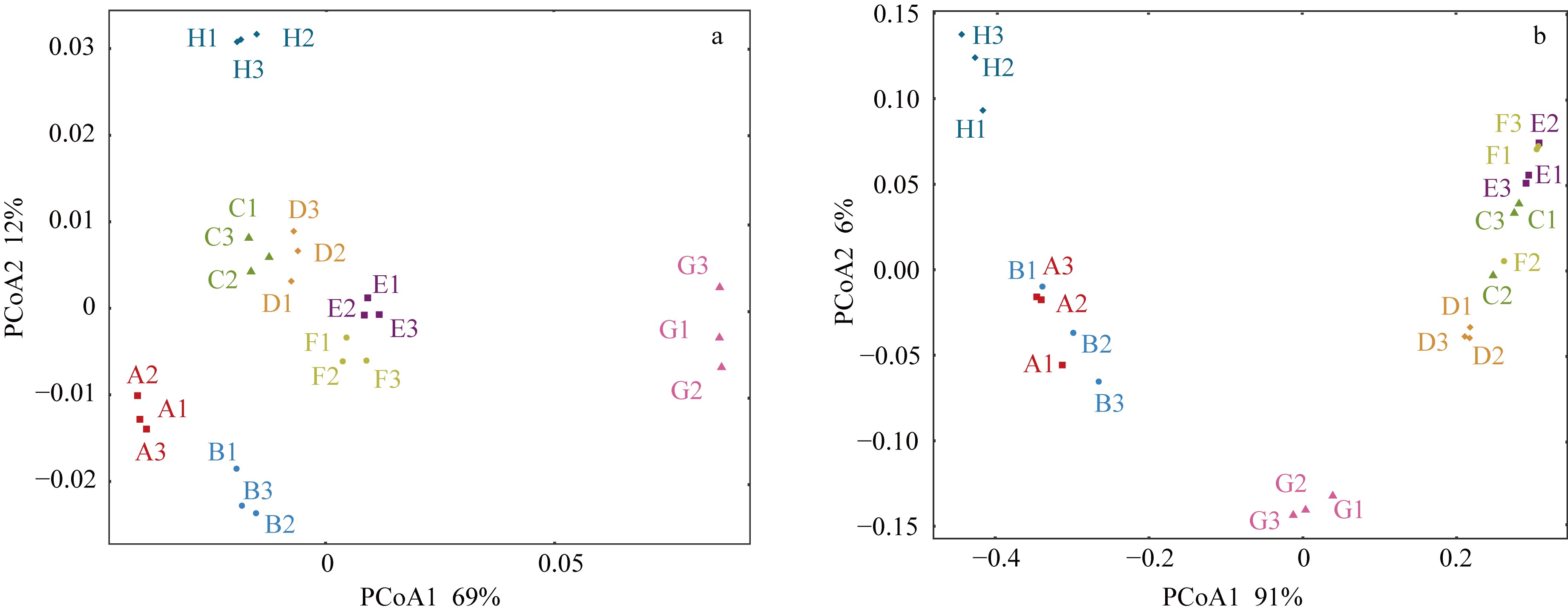
Fig. 5
PcoA of Fv/Fm and soluble sugar content in green seaweeds. (a) PcoA of Fv/Fm in green seaweeds; (b) PcoA of soluble sugar content in green seaweeds. A1~A3: U. prolifera; B1~B3: U. intestinalis; C1~C3: U. lactuca; D1~D3: U. stenophylla; E1~E3: U. pertusa; F1~F3: U. congbata; G1~G3: C. stimpsonii; H1~H3: C. fragile"
| [1] |
卞雅姣, 黄洁, 孙其松, 等, 2013. 模拟酸雨对小麦产量及籽粒蛋白质和淀粉含量及组分的影响[J]. 生态学报, 33(15): 4623-4630.
|
|
doi: 10.5846/stxb |
|
| [2] |
丁兰平, 栾日孝, 2013. 中国海藻志: 第四卷绿藻门(第一册)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 44- 69, 135-137.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
姜芳燕, 杨宁, 菅盼盼, 等, 2018. 基于 rbcL 和 tufA 基因的石莼和浒苔系统发育分析[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 37(7): 228-234.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
李合生, 2000. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社: 182- 186, 194-203.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
李信书, 徐军田, 何培民, 2011. 干燥和模拟酸雨胁迫对条斑紫菜光合作用的影响[J]. 水产科学, 30(5): 260-264.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
连纲, 罗涛, 傅智慧, 等, 2021. 2001—2018 年浙江省酸雨变化特征及影响因素分析[J]. 中国环境监测, 37(4): 104-110.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
廖源林, 蔡仕珍, 叶充, 等, 2015. 模拟酸雨对苦楝生理生态特性的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 34(10): 2764-2770.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
刘华, 吴国荣, 周耀民, 等, 2003. 模拟酸雨引起水体 pH 下降导致 Zn 对金鱼藻的毒害[J]. 环境科学学报, 23(4): 525-529.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
宁波市生态环境局, 2022. 2021年宁波市生态环境状况公报[N]. 宁波日报, 2022-06-05(004).
|
|
NINGBO MUNICIPAL BUREAU OF ECOLOGY AND ENVIRONMENT, 2022. 2021 Ningbo ecological environment status bulletin[N]. Ningbo Daily, 2022-06-05(004) (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
|
| [10] |
齐泽民, 王玄德, 宋光煜, 2004. 酸雨对植物影响的研究进展[J]. 世界科技研究与发展, 26(2): 36-41.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
水德聚, 王晓艳, 邵勤, 等, 2016. 模拟酸雨胁迫对油冬菜生理特性的影响[J]. 南方农业学报, 47(7): 1155-1158.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
万文琴, 杜响, 秦欣, 等, 2022. 坛紫菜对干出和酸雨胁迫的生理响应[J]. 宁波大学学报(理工版), 35(2): 1-7.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
王春燕, 2017. 不同模拟酸雨不同处理方式对华重楼生理特性的影响[D]. 成都: 四川师范大学.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
王文彦, 2020. 模拟酸雨对玉米种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 东北农业科学, 45(1): 21-24, 78.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
王自发, 高超, 谢付莹, 2007. 中国酸雨模式研究回顾与所面临的挑战[J]. 自然杂志, 29(2): 78-82.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
徐德才, 1995. 酸雨污染与防治: 浙江区域酸雨趋势与防治对策[J]. 能源环境保护, 9(4): 25-28.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
徐晓婷, 李亚鹤, 王东, 等, 2016. 低盐胁迫下模拟酸雨对裂片石莼光合作用生理特性的影响[J]. 水产学报, 40(5): 731-739.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
张银, 李文杰, 李玲丽, 等, 2020. 模拟酸雨对3种红豆杉幼苗生理指标的影响[J]. 西部林业科学, 49(1): 120-127.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
张志良, 瞿伟菁, 2003. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 第3版. 北京: 高等教育出版社: 121-127, 268-270.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
赵会杰, 邹琦, 于振文, 2000. 叶绿素荧光分析技术及其在植物光合机理研究中的应用[J]. 河南农业大学学报, 34(3): 248-251.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
周原也, 易晓芹, 周跃斌, 等, 2019. 模拟酸雨对茶树叶片光合色素含量及光合作用 CO2 响应的影响[J]. 分子植物育种, 17(21): 7201-7206.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.044 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2015.11.019 |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1080/1364253031000136321 |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1016/S0168-9452(03)00222-X |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1007/s11099-017-0689-0 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.69.6.1376 |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.1023/A:1020470224740 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a029256 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.32615/ps.2020.035 |
|
||