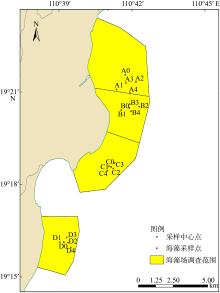
| [1] |
高洁, 余克服, 许慎栋, 等, 2024. 西沙群岛永乐环礁礁外坡沉积物中有机碳的含量与来源分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 43(3): 131-145.
|
|
GAO JIE, YU KEFU, XU SHENDONG, et al, 2024. Content and source analysis of organic carbon in the outer slope sediments of the Yongle Atoll, Xisha Islands[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 43(4): 131-145 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
胡闪闪, 邹定辉, 周凯, 等, 2024. 深圳东部海域海藻场大型海藻生态服务价值评估[J]. 生态学杂志, 43(1): 224-233.
|
|
HU SHANSHAN, ZOU DINGHUI, ZHOU KAI, et al, 2024. Evaluation for ecological services of macroalgae in the seaweed beds of the eastern coastal waters of Shenzhen, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 43(1): 224-233 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
江小芳, 2020. 中国红树林植被和土壤碳储量及其影响因子[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学.
|
|
JIANG XIAOFANG, 2020. The biomass and soil carbon stocks and their influencing factors of mangrove forests in China[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
李梦, 2018. 广西海草床沉积物碳储量研究[D]. 南宁: 广西师范学院.
|
|
LI MENG, 2018. Carbon storage in the seagrass sediments of Guangxi, China[D]. Nanning: Guangxi Teachers Education University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
彭承祥, 孙林, 孙晨晨, 等, 2024. 环境变化对海藻场碳汇能力的影响[J]. 天津科技, 51(2): 45-50.
|
|
PENG CHENGXIANG, SUN LIN, SUN CHENCHEN, et al, 2024. Effects of environmental changes on capacity of carbon sequestration in seaweed farms[J]. Tianjin Science & Technology, 51(2): 45-50 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
钱树本, 刘东艳, 孙军, 2005. 海藻学[M]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学出版社.
|
|
QIAN SHUBEN, LIU DONGYAN, SUN JUN, 2005. Marine phycology[M]. Qingdao: China Ocean University Press (in Chinese).
|
| [7] |
曲元凯, 2015. 三种马尾藻的生长繁殖和人工藻场的构建[D]. 湛江: 广东海洋大学.
|
|
QU YUANKAI, 2015. The growth, reproduction and artificial seaweeds beds construction of three species of Sargassum[D]. Zhanjiang: Guangdong Ocean University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
权伟, 应苗苗, 康华靖, 等, 2014a. 中国近海海藻养殖及碳汇强度估算[J]. 水产学报, 38(4): 509-514.
|
|
QUAN WEI, YING MIAOMIAO, KANG HUAJING, et al, 2014a. Marine algae culture and the estimation of carbon sink capacity in the coastal areas of China[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 38(4): 509-514 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
权伟, 应苗苗, 康华靖, 等, 2014b. 基于时间序列模型的洞头大型藻类碳汇强度预测分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 30(8): 63-67.
|
|
QUAN WEI, YING MIAOMIAO, KANG HUAJING, et al, 2014b. Carbon sink capacity forecast of macroscopic algae in the coastal areas of Dongtou county based on time series model[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 30(8): 63-67 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
宋金明, 李学刚, 袁华茂, 等, 2008. 中国近海生物固碳强度与潜力[J]. 生态学报, 28(2): 551-558.
|
|
SONG JINMING, LI XUEGANG, YUAN HUAMAO, et al, 2008. Carbon fixed by phytoplankton and cultured algae in China coastal seas[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28(2): 551-558 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
夏艳芳, 2021. 大型海藻植株和碎屑沉降特征研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学.
|
|
XIA YANFANG, 2021. Study on the settlement characteristics of macro-seaweed plants and debris[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
邢珊珊, 2016. 匍枝马尾藻有性繁育及环境因子对其幼苗生长的影响[D]. 海口: 海南大学.
|
|
XING SHANSHAN, 2016. Study on sexual reproduction and effect of environment factors on the growth of Sargssum polycystum[D]. Haikou: Hainan University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [13] |
颜葵, 2016. 海南东寨港红树林湿地碳储量及固碳价值评估[D]. 海口: 海南师范大学.
|
|
YAN KUI, 2016. Carbon storage and evaluation of mangrove wetlands in Dongzhaigang, Hainan[D]. Haikou: Hainan Normal University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [14] |
严立文, 黄海军, 陈纪涛, 等, 2011. 我国近海藻类养殖的碳汇强度估算[J]. 海洋科学进展, 29(4): 537-545.
|
|
YAN LIWEN, HUANG HAIJUN, CHEN JITAO, et al, 2011. Estimation of carbon sink capacity of algal mariculture in the coastal areas of China[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 29(4): 537-545 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [15] |
杨熙, 余威, 何静, 等, 2022. 海南黎安港海草床碳储量评估[J]. 海洋科学, 46(11): 116-125.
|
|
YANG XI, YU WEI, HE JING, et al, 2022. Carbon storage in the seagrass beds of Li’an Bay, Hainan[J]. Marine Sciences, 46(11): 116-125 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [16] |
杨宇峰, 罗洪添, 王庆, 等, 2021. 大型海藻规模栽培是增加海洋碳汇和解决近海环境问题的有效途径[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 36(3): 259-269.
|
|
YANG YUFENG, LUO HONGTIAN, WANG QING, et al, 2021. Large-scale cultivation of seaweed is effective approach to increase marine carbon sequestration and solve coastal environmental problems[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 36(3): 259-269 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [17] |
杨宇峰, 邹立功, 贺志理, 等, 2024. 大型海藻负排放理论技术研究与应用展望[J]. 热带海洋学报, 43(6): 27-36.
|
|
YANG YUFENG, ZOU LIGONG, HE ZHILI, et al, 2024. A prospectus for the theory, technology and application of seaweed negative emissions[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 43(6): 27-36 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [18] |
姚丹丹, 2022. 海南青葛海藻场马尾藻分类鉴定及多样性分析[D]. 佳木斯: 佳木斯大学.
|
|
YAO DANDAN, 2021. Taxonomic identification and diversity analysis of Sargassum in Qingge Seaweed Bed, Hainan[D]. Jiamusi: Jiamusi University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [19] |
中国海洋工程咨询协会, 2021. 海岸带生态系统现状调查与评估技术导则第6部分海草床T/CAOE 20. 6-2020 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社.
|
|
China Association of Oceanic Engineering, 2021. Technical guideline for investigation and assessment of coastal ecosystem-Part 6: Seagrass bed T/CAOE 20. 6-2020 [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China (in Chinese).
|
| [20] |
中国科学院中国孢子植物志编辑委员会, 1999. 中国海藻志[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
|
|
Consilio Florarum Cryptogamarum Sinicarum Academiae Sinicae Edita, 1999. Flora algarum marinarum sinicarum[M]. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese).
|
| [21] |
国家海洋局, 2013. 海洋监测技术规程HYT 147. 1-2013 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 26-28.
|
|
State Oceanic Administration, 2013. Code of practice for marine monitoring technology Part 1: seawater HYT 147. 1-2013 [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 26-28 (in Chinese).
|
| [22] |
中华人民共和国自然资源部, 2021. 养殖大型藻类和双壳贝类碳汇计量方法碳储量变化法HY/T 0305-2021 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社.
|
|
Ministry of Natural Resources, 2021. Estimation method of maricultural seaweed and bivalve carbon sink-carbon stock variation method HY/T 0305-2021 [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China (in Chinese).
|
| [23] |
周曦杰, 2018. 藻场碎屑产生机制及岛礁生态养护功能实现途径研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学.
|
|
ZHOU Xijie, 2018. Formational mechanism of detritus in seaweed bed and ecological conservation function application of island reef water[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [24] |
CLARKE K R, 1993. Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure[J]. Australian Journal of Ecology, 18(1): 117-143.
|
| [25] |
DUARTE C M, CHISCANO C L, 1999. Seagrass biomass and production: a reassessment[J]. Aquatic Botany, 65(1-4): 159-174.
|
| [26] |
DUARTE C M, WU JIAPING, XIAO XI, et al, 2017. Can seaweed farming play a role in climate change mitigation and adaptation?[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 4: 00100.
|
| [27] |
JIAO N, ROBINSON C, AZAM F, et al, 2014. Mechanisms of microbial carbon sequestration in the ocean-future research directions[J]. Biogeosciences, 11(19): 5285-5306.
|
| [28] |
JIANG Z, LIU S, ZHANG J, et al. Newly discovered seagrass beds and their potential for blue carbon in the coastal seas of Hainan Island, South China Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 125(1/2): 513-521.
|
| [29] |
KRAUSE-JENSEN D, LAVERY P, SERRANO O, et al, 2018. Sequestration of macroalgal carbon: the elephant in the Blue Carbon room[J]. Biology Letters, 14(6): 20180236.
|
| [30] |
PIANKA E R, 1973. The structure of lizard communities[J]. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 4: 53-74.
|
 ), CHEN Xian2, CHEN Dandan1, CHEN Xiaohui1, LIANG Jilin1(
), CHEN Xian2, CHEN Dandan1, CHEN Xiaohui1, LIANG Jilin1( )
)