Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 91-107.doi: 10.11978/2025051CSTR: 32234.14.2025051
Previous Articles Next Articles
Integrated analysis of phytoplankton community structure in mussel aquaculture areas using net sampling with microscopy and LISST Holo2
YANG Tianwei1( ), LIN Jun1,2,3,4(
), LIN Jun1,2,3,4( ), JIAO Junpeng1, WU Yue1
), JIAO Junpeng1, WU Yue1
- 1
College of Oceanography and Ecological Science ,Shanghai Ocean University
2Marine Ranching Engineering Technology Research Center ,Shanghai Ocean University
3National Engineering Research Center for Special Equipment and Power Systems of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering
4Key Laboratory of Marine Ecological Monitoring and Restoration Technology ,Ministry of Natural Resources, Shanghai Ocean University
-
Received:2025-04-04Revised:2025-05-23Online:2025-11-10Published:2025-12-03 -
Contact:LIN Jun. email: jlin@shou.edu.cn -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(42376207); National Key Research and Development Program of China(2023YFD2401902)
CLC Number:
- Q948.8
Cite this article
YANG Tianwei, LIN Jun, JIAO Junpeng, WU Yue. Integrated analysis of phytoplankton community structure in mussel aquaculture areas using net sampling with microscopy and LISST Holo2[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(6): 91-107.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
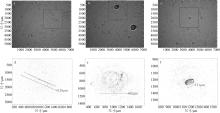
Fig. 4
Hologram of LISST Holo2. (a) Particle image showing Skeletonema costatum; (b) particle image showing Noctiluca scintillans; (c) particle image showing Coscinodiscus spp.; (d) reconstructed image of Skeletonema costatum; (e) reconstructed image of Noctiluca scintillans; (f) reconstructed image of Coscinodiscus spp. The boxes in the image indicate particles suspected to be phytoplankton"

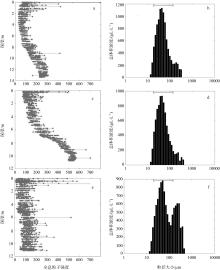
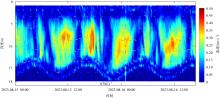
Fig. 7
Organic particle size distribution based on LISST Holo2. (a) Holographic particle intensity variation with depth at 09:00; (b) concentration of suspended particles of different sizes at 09:00; (c) holographic particle intensity variation with depth at 13:00; (d) concentration of suspended particles of different sizes at 13:00; (e) holographic particle intensity variation with depth at 17:00; (f) concentration of suspended particles of different sizes at 17:00. The solid line represents the size range of small phytoplankton (20-200 μm)"

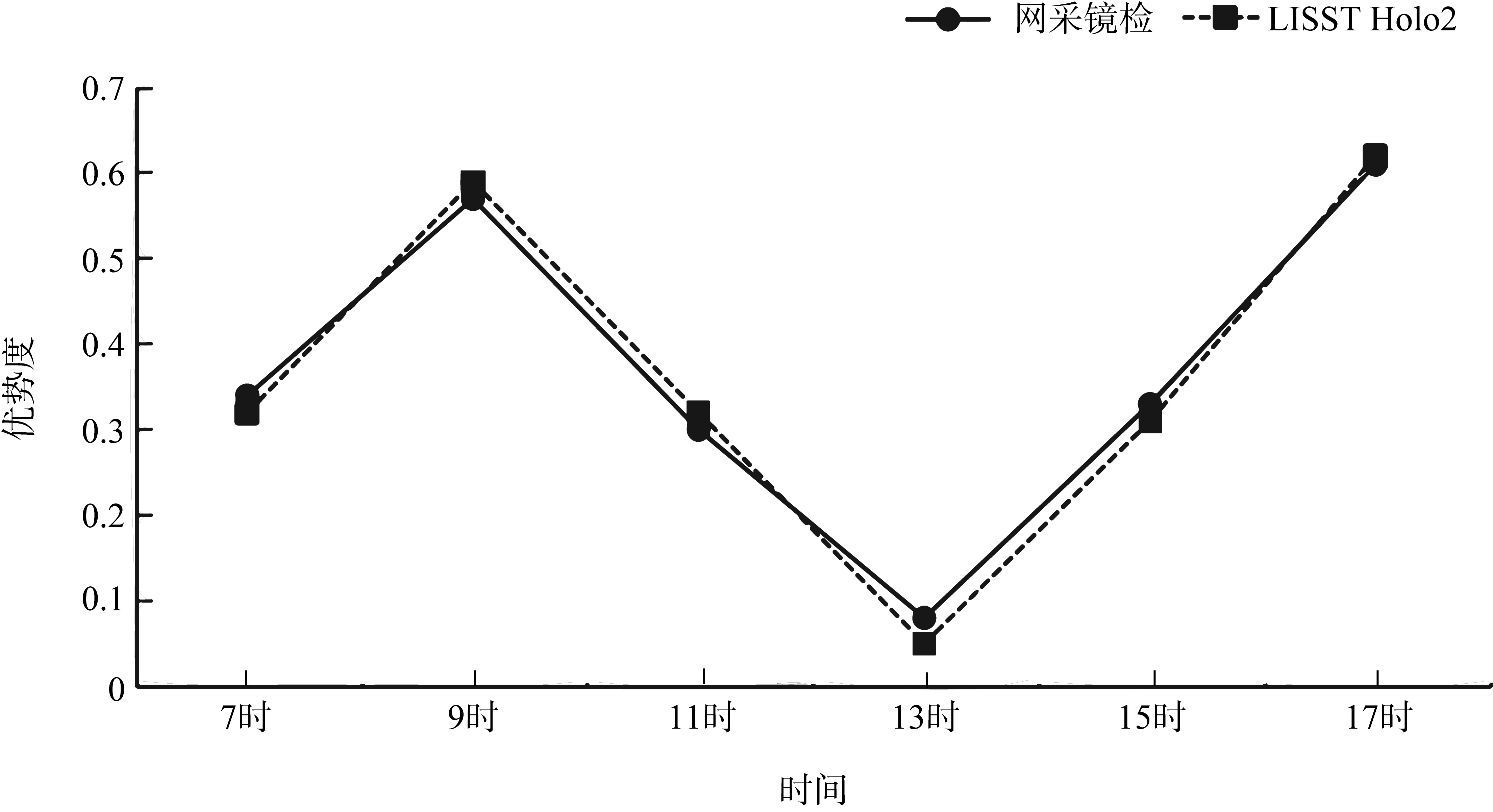
Tab. 2
Dominance of dominant phytoplankton species"
| 编号 | 优势种 | 优势度 | 粒径大小 | 形态特征 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贻贝养殖层 | 全水层 | ||||
| A1 | 中肋骨条藻(Skeletonema costatum) | / | 0.04 | 直径6~22μm | 单个细胞近似球形, 链长2~8个细胞 |
| A2 | 笔尖形根管藻(Rhizosolenia styliformis) | 0.35 | 0.36 | 直径5~15μm,长200~500μm | 细胞呈长圆柱形, 末端尖锐 |
| A3 | 洛氏角毛藻(Chaetoceros lorenzianus) | / | 0.04 | 长约20~50μm, 宽约10~30μm | 细胞呈圆柱形或椭圆形通常形成短链, 由 2~6个细胞组成 |
| A4 | 尖刺伪菱形藻(Pseudo-nitzschia pungens) | 0.03 | / | 宽2~5μm, 长70~130μm | 细长针形 |
| A5 | 柔软伪菱形藻(Pseudo-nitzschia delicatissima) | 0.06 | 0.05 | 宽1.5~3μm, 长30~80μm | 较尖刺伪菱形藻更纤细 |
| A6 | 佛氏海线藻(Thalassionema frauenfeldii | / | 0.02 | 宽2~5μm, 长20~60μm | 线状或短棒状, 常形成星形群体 |
| B1 | 夜光藻(Noctiluca scintillans) | 0.31 | 0.29 | 直径200~2000μm | 球形或肾形 |
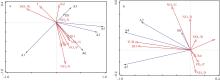
Fig. 10
Redundancy analysis of phytoplankton and environmental factors. (a) RDA analysis of dominant phytoplankton species and environmental factors in the entire water column; (b) RDA analysis of dominant phytoplankton species and environmental factors in the aquaculture water layer. T denotes temperature, Sal denotes salinity, DO denotes dissolved oxygen, TUB denotes turbidity, SiO3-Si denotes silicate, NH4-N denotes ammoniacal nitrogen, NO2-N denotes nitrite, NO3-N denotes nitrate, PO4-P denotes phosphate. A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, and B1 are shown in Tab. 2"

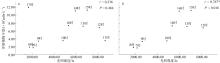
Fig. 11
Correlation analysis between phytoplankton abundance and light intensity. (a) Scatter plot and correlation coefficient between phytoplankton abundance and light intensity from 7:00 to 17:00, which includes two outlier data points; (b) scatter plot and correlation coefficient between phytoplankton abundance and light intensity after removing the two outliers"

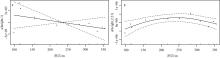
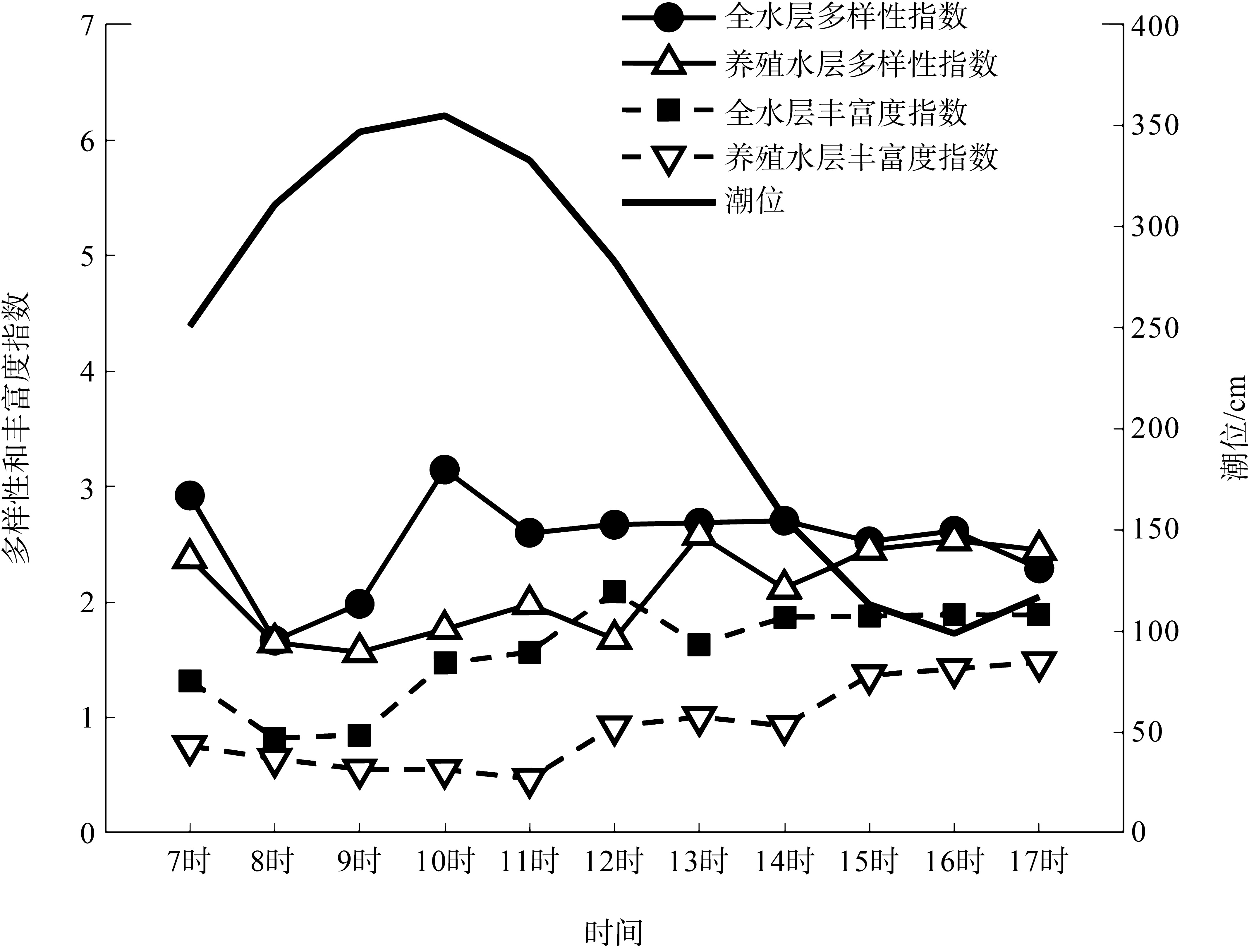
Fig. 13
Correlation analysis between phytoplankton abundance and tidal height based on GAM. (a) Correlation analysis between phytoplankton abundance in the entire water column and tidal height; (b) correlation analysis between phytoplankton abundance in the aquaculture layer and tidal height. The vertical axis represents the effect of tidal height on phytoplankton abundance. The solid line shows the smoothed fit between tidal height and phytoplankton abundance, and the dashed lines indicate the upper and lower bounds of the confidence interval"

| [1] |
毕远溥, 董婧, 蒋双, 等, 2002. 小窑湾双壳贝类筏式养殖对海域环境的影响[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 8(3): 270-275.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈丹丹, 庞巧珠, 涂志刚, 等, 2021. 后水湾深水网箱养殖区浮游植物群落季节变化及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 海洋环境科学, 40(1): 73-80.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
陈奕帆, 王君玥, 王英豪, 等, 2024. 典型赤潮生物夜光藻研究进展[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 39(6): 1075-1086.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
代鲁平, 李超伦, 王世伟, 等, 2016. 基于ZooScan图像技术的南黄海夏季浮游动物群落结构分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 47(4): 764-773.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
段晓萌, 秦华伟, 马浩阳, 等, 2023. 黄河口及莱州湾海域磷的时空分布及浮游生物对低磷胁迫的响应[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 53(11): 87-98.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
凡仁福, 魏皓, 赵亮, 2015. 高生产力区LISST-100和OBS对悬浮颗粒物测量的比较研究[J]. 海洋科学进展, 33(4): 492-500.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
关莹莹, 林军, 焦俊鹏, 等, 2022. 高滤食压力下贻贝筏式养殖场及周边海域浮游植物群落特征[J]. 海洋环境科学, 41(4): 543-553.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
关莹莹, 2021. 规模化贻贝养殖海域浮游植物群落结构及其环境影响因子研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
霍笑康, 王永刚, 周灵同, 等, 2024. 结合生态网络解析白洋淀浮游生物生态位和种间联结性特征[J]. 环境科学, 45(9): 5298-5307.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
焦念志, 杨燕辉,
|
| [11] |
李红飞, 林森杰, 2019. 南海浮游植物生态学研究进展[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 58(1): 1-10.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
李立群, 王艳, 王彪, 等, 2024. 2009—2021年夏季长江口海域浮游生物群落结构时空分布特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 37(2): 233-245.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
李斯远, 2022. 厚壳贻贝的摄食选择偏好及其食物识别机制研究[D]. 舟山: 浙江海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
梁文钊, 唐丹玲, 2017. 南海西部夏季表层浮游植物粒径结构分布特征分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 36(4): 93-101.
doi: 10.11978/2016104 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2016104 |
|
| [15] |
陆斗定, 张志道, 朱根海, 等, 1994. 浙江近海夜光藻的分布及其生态学特点[J]. 东海海洋, 12(3): 62-69.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
施玉珍, 张才学, 张际标, 等, 2017. 水东湾海域浮游植物潮汐分布特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态学报, 37(18): 5981-5992.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
孙晓霞, 郭术津, 刘梦坛, 等, 2021. 印太交汇区浮游植物和浮游动物生态学研究进展[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 52(2): 323-331.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
孙东, 赵冬至, 文世勇, 等, 2010. 夜光藻赤潮与环境因子关系的模糊分析[J]. 海洋环境科学, 29(1): 70-75.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
宋书群, 孙军, 俞志明, 2009. 长江口及其邻近水域叶绿素a的垂直格局及成因初析[J]. 植物生态学报, 33(2): 369-379.
doi: 10.3773/j.issn.1005-264x.2009.02.015 |
|
doi: 10.3773/j.issn.1005-264x.2009.02.015 |
|
| [20] |
唐启升, 蒋增杰, 毛玉泽, 2022. 渔业碳汇与碳汇渔业定义及其相关问题的辨析[J]. 渔业科学进展, 43(5): 1-7.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
唐紫琦, 宋敏杰, 王馨, 等, 2024. 2022年南黄海绿潮分布与浮游生物群落关系初探[J]. 海洋科学, 48(3): 26-41.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
谭益国, 钟威, 林军, 等, 2024. 浮筏式贻贝养殖设施阻流效应的数值模拟[J/OL]. 水产学报: 1-13. (2024-02-19) [2025-04-04]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/31.1283.S.20240207.1550.002.html
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
陶宗娅, 邹琦, 1999. 植物光合作用光抑制分子机理及其光保护机制[J]. 西南农业学报, 12(S2): 9-18.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
王旭, 赵旭, 章守宇, 等, 2015. 枸杞岛贻贝养殖水域碳氮磷分布格局[J]. 水产学报, 39(11): 1650-1664.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
吴晓凡, 汪振华, 章守宇, 等, 2024. 大规模筏式贻贝养殖区浮游植物群落结构昼夜变化特征[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 33(5): 1211-1222.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
温英, 林军, 杨冠林, 等, 2022. 贻贝浮筏养殖设施水动力效应及附生海藻碎屑输运的数值模拟[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 31(6): 1549-1561.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
徐亚军, 赵亮, 原野, 2016. 基于声学仪器与粒径分析仪研究东海浮游动物昼夜垂直迁移过程[J]. 海洋学报, 38(8): 123-130.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
徐兆礼, 高文烨, 2004. 东海赤潮高发区夜光藻数量分布与环境关系的研究[C]// 中国水产学会. 中国水产学会第五届青年学术年会摘要集, 上海: 中国水产学会: 135.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
杨冠林, 2022. 典型贻贝浮筏式养殖海域物理—生态—贝类生长耦合数值模型的构建及应用[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [30] |
岳新利, 张梦柯, 谷利德, 等, 2023. 福建平潭外海域夜光藻赤潮期营养元素和溶解态痕量金属动态与响应[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 62(3): 375-384.
|
|
|
|
| [31] |
赵文, 2005. 水生生物学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社 (in Chinese).
|
| [32] |
周曦杰, 2014. 枸杞岛典型生境螺贝类代表种—角蝾螺、紫贻贝摄食生态初步研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.3800/pbr.8.9 |
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
doi: 10.1038/334340a0 |
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
doi: 10.1007/s12601-015-0008-2 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.170343 |
| [39] |
doi: 10.1016/0025-326X(94)00105-I |
| [40] |
doi: 10.3354/meps062283 |
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.973155 |
| [1] | XIANG Chenhui, LIU Jiaxing, KE Zhixin, ZHOU Linbin, TAN Yehui. Phytoplankton responses to Dan’ao River estuary water enrichment in terms of size structure and community composition* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(2): 49-60. |
|
||