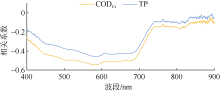
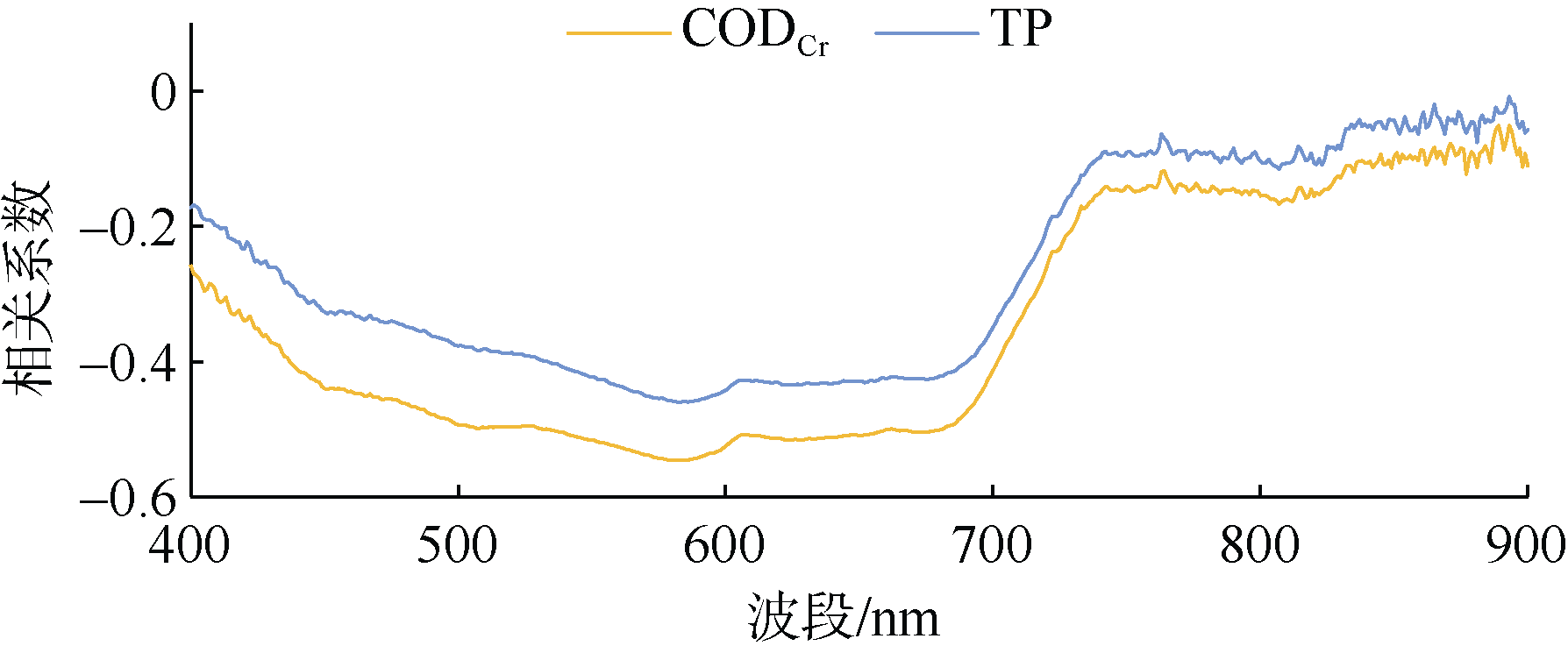
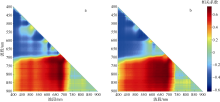
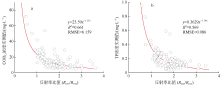
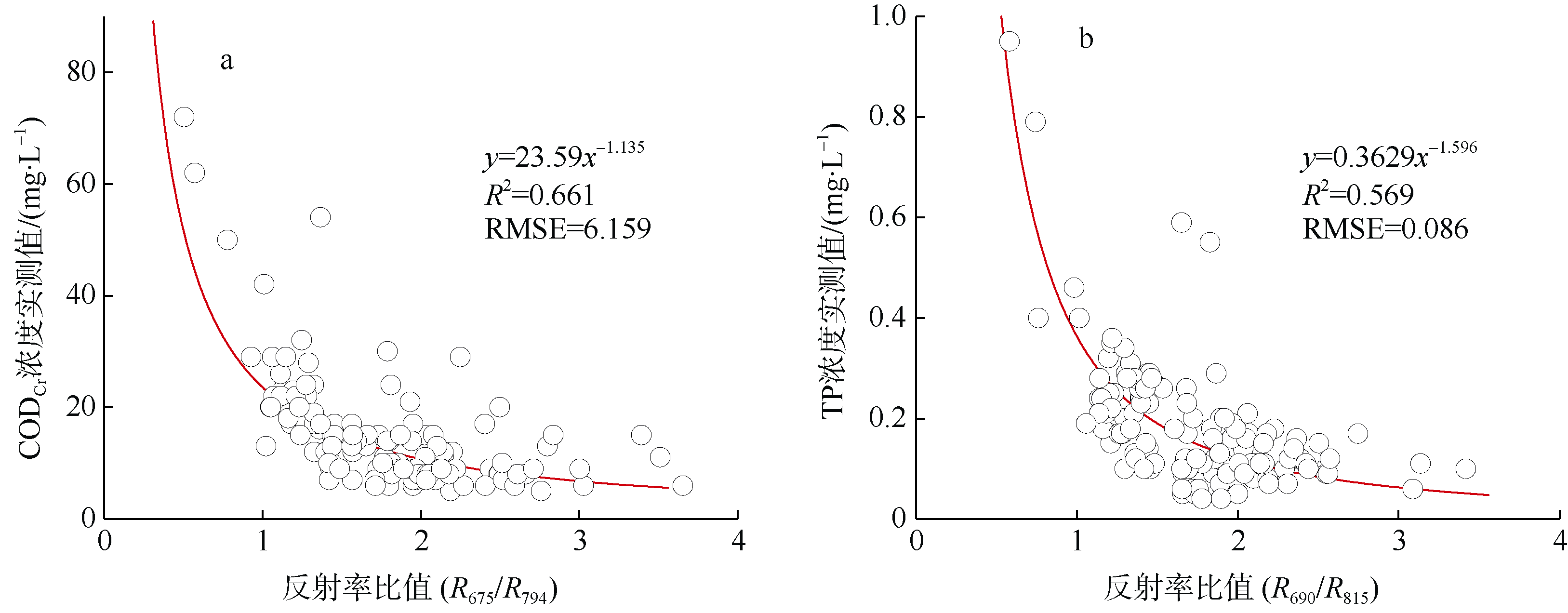
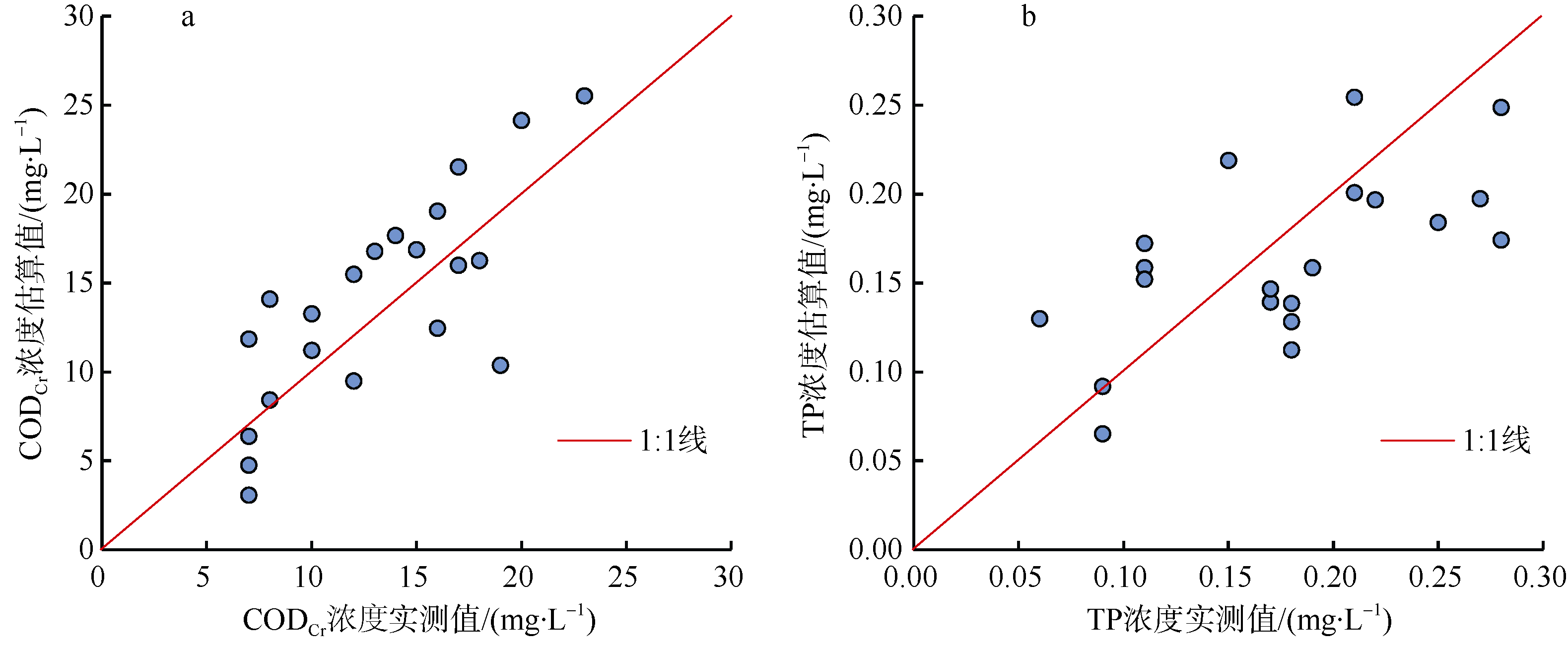
| [1] |
陈楚群, 施平, 毛庆文, 2001. 南海海域叶绿素浓度分布特征的卫星遥感分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 20(2):66-70.
|
|
CHEN CHUQUN, SHI PING, MAO QINGWEN, 2001. Satellite remotely-sensed analysis of distribution characters of chlorophyll concentration in South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 20(2):66-70 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
陈雯扬, 许惠平, 2010. 基于高光谱数据的东海近海悬浮泥沙浓度估测研究木[J]. 水运工程, (2):31-35.
|
|
CHEN WENYANG, XU HUIPING, 2010. Estimation on suspended sedimentation concentration of East Sea based on hyperspectral data[J]. Port & Waterway Engineering, (2):31-35 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
林剑远, 张长兴, 2019. 航空高光谱遥感反演城市河网水质参数[J]. 遥感信息, 34(2):23-29.
|
|
LIN JIANYUAN, ZHANG CHANGXING, 2019. Inversion of water quality parameters of urban river network using airborne hyperspectral remote sensing[J]. Remote Sensing Information, 34(2):23-29 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
刘志国, 周云轩, 沈芳, 2007. 河口水体泥沙浓度的水面光谱统计模式分析[J]. 水利学报, 38(7):799-805.
|
|
LIU ZHIGUO, ZHOU YUNXUAN, SHEN FANG, 2007. Statistic analysis of suspended sediment concentration in offshore waters based on field measurement of reflectance hyper-spectral[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 38(7):799-805 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
彭建, 徐飞雄, 邓凯, 等, 2018. 琅琊山景区不同指标浓度下水质光谱差异分析[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 38(5):1499-1507.
|
|
PENG JIAN, XU FEIXIONG, DENG KAI, et al, 2018. Spectral differences of water quality at different index concentrations: in Langya Mountain scenic area[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 38(5):1499-1507 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
王桂芬, 曹文熙, 杨跃忠, 等, 2010. 珠江口藻华水体总吸收系数的变化特性及高光谱反演模式[J]. 热带海洋学报, 29(2):52-58.
|
|
WANG GUIFEN, CAO WENXI, YANG YUEZHONG, et al, 2010. Variations of absorption coefficient of seawater in the Pearl River Estuary and a hyperspectral retrieval model for an algal bloom[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 29(2):52-58 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
王晓, 逄勇, 沈春其, 等, 2017. 太湖流域跨界水环境动态监测点位优化布局[J]. 水资源保护, 33(5):130-137.
|
|
WANG XIAO, PANG YONG, SHEN CHUNQI, et al, 2017. Layout optimization of water environmental monitoring site of trans-boundary of Taihu Basin[J]. Water Resources Protection, 33(5):130-137 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
邢前国, 2007. 珠江口水质高光谱反演[D]. 广州: 中国科学院研究生院(南海海洋研究所).
|
|
XING QIANGUO, 2007. Retrieval of water quality in the pearl river estuary using hyperspectral technique[D]. Guangzhou: Graduate School of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (South China Sea Institute of Oceanography)(in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
杨锦坤, 陈楚群, 唐世林, 等, 2007. 珠江口水体叶绿素荧光特性研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 26(4):15-20.
|
|
YANG JINKUN, CHEN CHUQUN, TANG SHILIN, et al, 2007. Research on chlorophyll fluorescence properties of water in Zhujiang River estuary[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 26(4):15-20 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
张海威, 张飞, 李哲, 等, 2017. 艾比湖流域地表水水体悬浮物、总氮与总磷光谱诊断及空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 26(6):1042-1050.
|
|
ZHANG HAIWEI, ZHANG FEI, LI ZHE, et al, 2017. Spectral diagnosis and spatial distribution of SS, TN and TP in surface water in Ebinur Lake watershed[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 26(6):1042-1050 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
张雪, 赖积保, 李家国, 等, 2019. 基于高分一号影像的深圳市黑臭水体遥感识别[J]. 科学技术与工程, 19(4):268-274.
|
|
ZHANG XUE, LAI JIBAO, LI JIAGUO, et al, 2019. Remote sensing recognition of black-odor waterbodies in Shenzhen City based on GF-1 satellite[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 19(4):268-274 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
FICHOT C G, DOWNING B D, BERGAMASCHI B A, et al, 2016. High-resolution remote sensing of water quality in the San Francisco Bay-Delta Estuary[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 50(2):573-583.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b03518
pmid: 26651265
|
| [13] |
IQBAL Z, SYED K S, ISHAQ M, 2013. Optimal fin shape in finned double pipe with fully developed laminar flow[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 51(1-2):1202-1223.
doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2012.10.036
|
| [14] |
MOBLEY C D, 1999. Estimation of the remote-sensing reflectance from above-surface measurements[J]. Applied Optics, 38(36):7442-7455.
pmid: 18324298
|
| [15] |
SONG KAISHAN, LI LIN, LI SHUAI, et al, 2012. Hyperspectral remote sensing of total phosphorus (TP) in three central Indiana water supply reservoirs[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 223(4):1481-1502.
|
| [16] |
SUDDUTH K A, JANG G S, LERCH R N, et al, 2015. Long-term agroecosystem research in the central Mississippi river basin: hyperspectral remote sensing of reservoir water quality[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 44(1):71-83.
doi: 10.2134/jeq2014.02.0060
pmid: 25602322
|
| [17] |
WANG XIAOYAN, YANG WU, 2019. Water quality monitoring and evaluation using remote sensing techniques in China: a systematic review[J]. Ecosystem Health and Sustainability, 5(1):47-56.
doi: 10.1080/20964129.2019.1571443
|
| [18] |
WANG YUNPENG, XIA HAO, FU JIAMO, et al, 2004. Water quality change in reservoirs of Shenzhen, China: detection using LANDSAT/TM data[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 328(1-3):195-206.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.02.020
|
 ), LIU Hailong3, JIANG Bo3, CHEN Yinhui1,2, LI Jiehong1,2, WU Sixiao2, LIANG Jianxia2, HUANG Hua4, XING Qianguo3(
), LIU Hailong3, JIANG Bo3, CHEN Yinhui1,2, LI Jiehong1,2, WU Sixiao2, LIANG Jianxia2, HUANG Hua4, XING Qianguo3( )
)