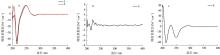
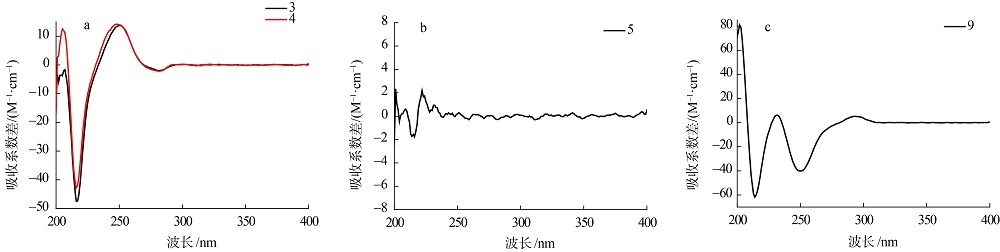
| [1] |
尚卓, 王斌贵, 2012. 海洋真菌来源的抗菌活性物质研究: 方法与进展[J]. 生命科学, 24(9): 997-1011.
|
|
SHANG ZHUO, WANG BINGUI, 2012. Methods and advances in studies on antimicrobial substances of marine-derived fungi[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 24(9): 997-1011. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [2] |
余玥, 林文翰, 2011. 海洋Penicillium属化学成分与生物活性的研究[J]. 哈尔滨商业大学学报(自然科学版), 27(4): 517-523, 527.
|
|
YU YUE, LIN WENHAN, 2011. Study on chemical composition and bioactivity of marine Penicillium genus[J]. Journal of Harbin University of Commerce (Natural Sciences Edition), 27(4): 517-523, 527. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [3] |
朱伟明, 王俊锋, 2011. 海洋真菌生物活性物质研究之管见[J]. 菌物学报, 30(2): 218-228.
|
|
ZHU WEIMING, WANG JUNFENG, 2011. A review on studies of secondary metabolites from marine fungi[J]. Mycosystema, 30(2): 218-228. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [4] |
朱伟明, 2019. 海洋天然产物的高效发现与成药性研究[J]. 中草药, 50(23): 5645-5652.
|
|
ZHU WEIMING, 2019. Efficient discovery and medicinal research of marine natural products[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 50(23): 5645-5652. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [5] |
ARAI K, KIMURA K, MUSHIRODA T, et al, 1989. Structures of fructigenines A and B, new alkaloids isolated from Penicillium fructigenum Takeuchi[J]. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 37(11): 2937-2939.
|
| [6] |
BAI JING, ZHANG PENG, BAO GUANHU, et al, 2018. Imaging mass spectrometry-guided fast identification of antifungal secondary metabolites from Penicillium polonicum[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 102(19): 8493-8500.
doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9218-8
|
| [7] |
BLUNT J W, COPP B R, KEYZERS R A, et al, 2017. Marine natural products[J]. Natural Product Reports, 34(3): 235-294.
doi: 10.1039/c6np00124f
pmid: 28290569
|
| [8] |
BUROV O N, KLETSKII M E, GULEVSKAYA A V. 2013. Quantum chemical studies of the oxidative alkylamination of diazinones[J]. Russian Chemical Bulletin, 62(5): 1156-1163.
doi: 10.1007/s11172-013-0158-2
|
| [9] |
CARROLL A R, COPP B R, DAVIS R A, et al, 2020. Marine natural products[J]. Natural Product Reports, 37(2): 175-223.
doi: 10.1039/c9np00069k
pmid: 32025684
|
| [10] |
CHAI YUNJING, CUI CHENGBIN, LI CHANGWEI, et al, 2012. Activation of the dormant secondary metabolite production by introducing gentamicin-resistance in a marine-derived Penicillium purpurogenum G59[J]. Marine Drugs, 10(3): 559-582.
doi: 10.3390/md10030559
|
| [11] |
JOHNSON K F, VAN ZEELAND R, STANLEY L M, 2013. Palladium-catalyzed synthesis of N-tert-prenylindoles[J]. Organic Letters, 15(11): 2798-2801.
doi: 10.1021/ol4011344
|
| [12] |
LI JING, WANG JUN, JIANG CHENGSHI, et al, 2014. (+)-Cyclopenol, a new naturally occurring 7-membered 2, 5-dioxopiperazine alkaloid from the fungus Penicillium sclerotiorum endogenous with the Chinese mangrove Bruguiera gymnorrhiza[J]. Journal of Asian Natural Products Research, 16(5): 542-548.
doi: 10.1080/10286020.2014.911290
|
| [13] |
LUCKNER M, 1967. Zur bildung von chinolinalkaloiden in pflanzen. 2. Die fermentative umwandlung der Penicillium-alkaloide cyclopenin und cyclopenol in viridicatin und viridicatol[J]. European Journal of Biochemistry, 2(1): 74-78.
doi: 10.1111/ejb.1967.2.issue-1
|
| [14] |
LUO HAN, LI XIAOMING, LI CHUNSHUN, et al, 2014. Diphenyl ether and benzophenone derivatives from the marine mangrove-derived fungus Penicillium sp. MA-37[J]. Phytochemistry Letters, 9: 22-25.
doi: 10.1016/j.phytol.2014.03.012
|
| [15] |
MENG LINGHONG, LI XIAOMING, LIU YANG, et al, 2014. Penicibilaenes A and B, sesquiterpenes with a tricyclo[6. 3. 1. 01, 5]dodecane skeleton from the marine isolate of Penicillium bilaiae MA-267[J]. Organic Letters, 16(23): 6052-6055.
doi: 10.1021/ol503046u
|
| [16] |
MENG LINGHONG, ZHANG PENG, LI XIAOMING, et al, 2015. Penicibrocazines A-E, five new sulfide diketopiperazines from the marine-derived endophytic fungus Penicillium brocae[J]. Marine Drugs, 13(1): 276-287.
doi: 10.3390/md13010276
|
| [17] |
RUAN XIANGCHUN, DENG XIAOLING, TAN MEILING, et al, 2021. In vitro antibiofilm activity of resveratrol against avian pathogenic Escherichia coli[J]. BMC Veterinary Research, 17(1): 249.
doi: 10.1186/s12917-021-02961-3
|
| [18] |
SHU ZHENDAN, LIU QINGMEI, XING CUIPING, et al, 2020. Viridicatol isolated from deep-sea Penicillium griseofulvum alleviates anaphylaxis and repairs the intestinal barrier in mice by suppressing mast cell activation[J]. Marine Drugs, 18(10): 517.
doi: 10.3390/md18100517
|
| [19] |
WANG JUNFENG, HE WEIJUN, HUANG XIAOLONG, et al, 2016. Antifungal new oxepine-containing alkaloids and xanthones from the deep-sea-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor SCSIO 05879[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 64(14): 2910-2916.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b00527
|
| [20] |
WANG LIYAN, LI MENGJIE, LIN YINZHI, et al, 2020. Inhibition of cellular inflammatory mediator production and amelioration of learning deficit in flies by deep sea Aspergillus-derived cyclopenin[J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 73(9): 622-629.
doi: 10.1038/s41429-020-0302-9
|
| [21] |
YANG HAIBIN, LI FANG, JI NAIYUN, 2016. Alkaloids from an algicolous strain of Talaromyces sp.[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 34(2): 367-371.
doi: 10.1007/s00343-015-4316-2
|
 ), MOU Pengyun1,4(
), MOU Pengyun1,4( ), ZHANG Qingbo1,2,3, ZHANG Changsheng1,2,3
), ZHANG Qingbo1,2,3, ZHANG Changsheng1,2,3