Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (3): 19-39.doi: 10.11978/2022212CSTR: 32234.14.2022212
Special Issue: 全球变化专题
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Atmospheric deposition and its eco-environmental effects on the South China Sea*
XING Jianwei1,2,3,4( ), SONG Jinming1,2,3,4(
), SONG Jinming1,2,3,4( )
)
- 1. CAS Key Laboratory of Marine Ecology and Environmental Sciences, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao 266071, China
2. Laboratory for Marine Ecology and Environmental Science, Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology (Qingdao), Qingdao 266237, China
3. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
4. Center for Ocean Mega-Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao 266071, China
-
Received:2022-10-07Revised:2022-11-11Online:2023-05-10Published:2022-11-14 -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Program(2022YFC3104305); National Natural Science Foundation of China(41906035); Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation(ZR2019BD068); The “Huiquan Young Scholar” Talent Program supported by the Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences; Open Fund of State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography (SCSIO, CAS)(LTO1903)
Cite this article
XING Jianwei, SONG Jinming. Atmospheric deposition and its eco-environmental effects on the South China Sea*[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 19-39.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
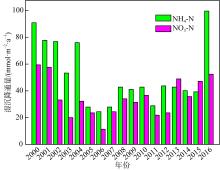
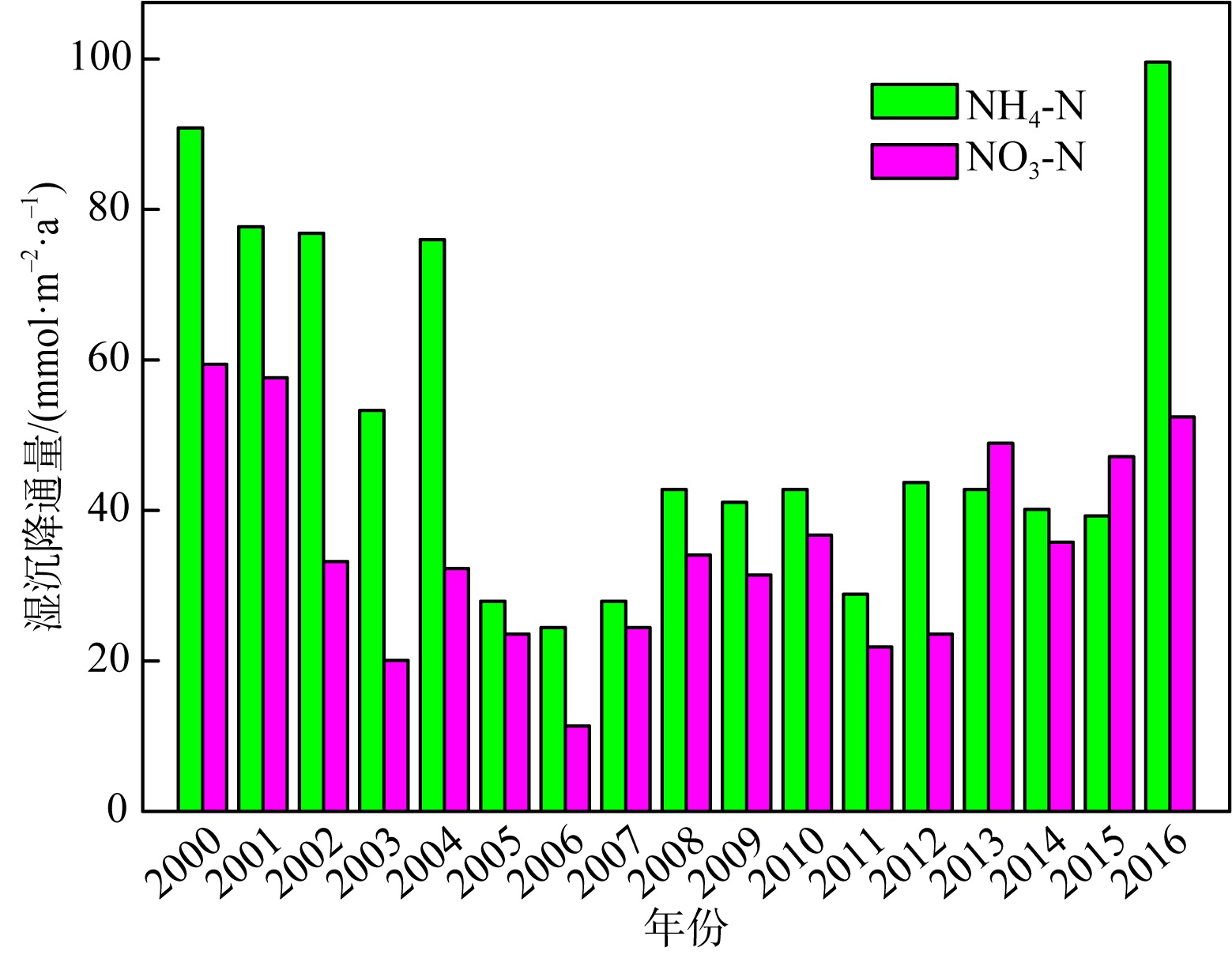
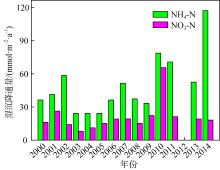
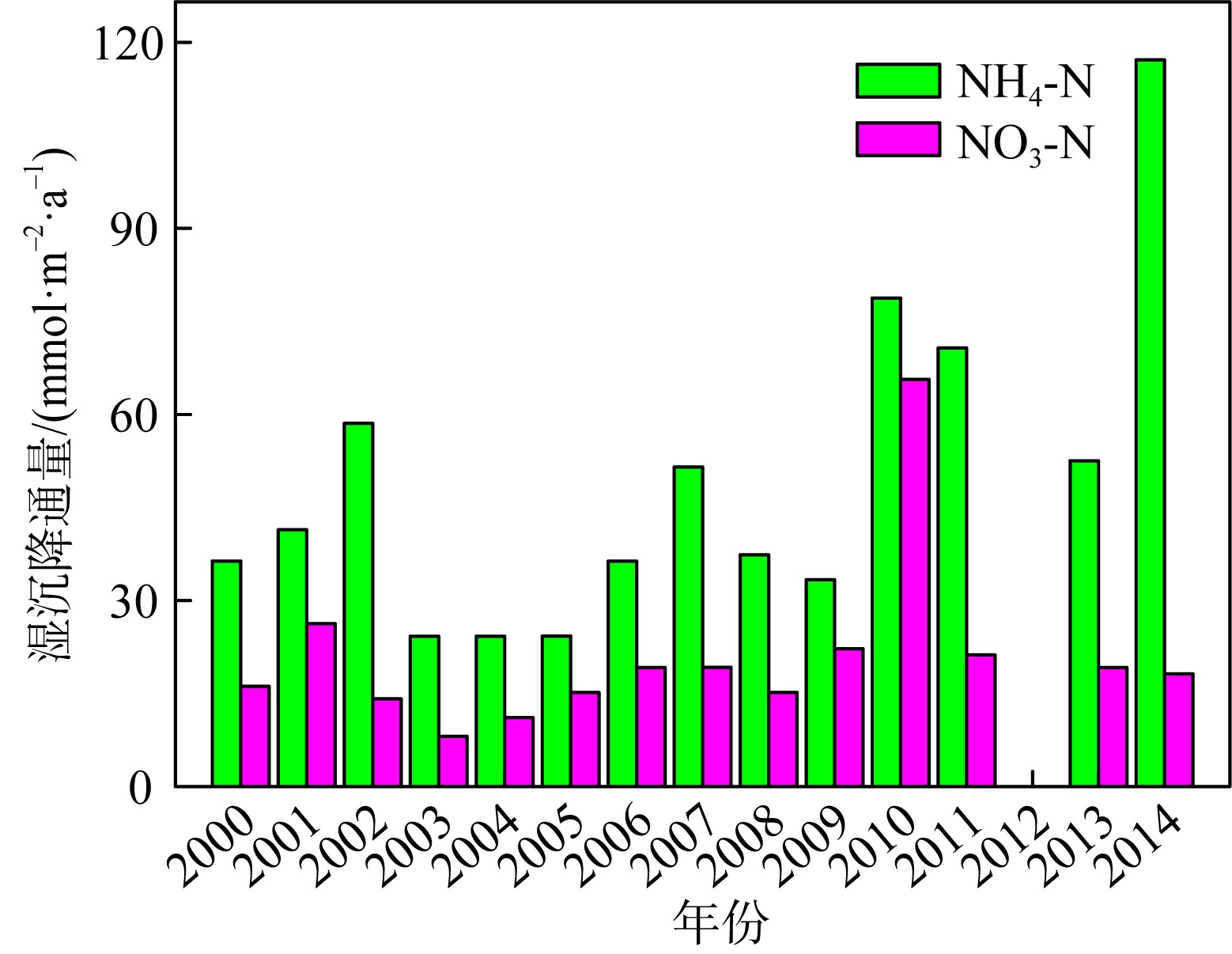
Tab. 1
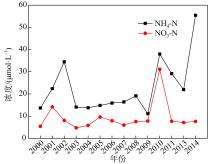
Concentrations of various nutrients in aerosols in different areas of South China Sea"
| 区域 | 浓度/(nmol·m-3) | 文献 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH4-N | NO3-N | NO2-N | DIN | DON | DIP | DOP | DSi | ||
| 大亚湾 | 5.42 | 13.51 | — | 18.93 | 33.21 | 0.78 | 0.61 | 2.63 | Wu et al, |
| 南海北部 | 52.3 | 14.5 | — | 66.8 | — | 0.97 | — | — | Qi et al, |
| 西沙永兴岛 | 3.89 | 31.45 | — | 35.34 | — | — | — | — | Xiao et al, |
| 南海整体 | 90~148.6 | 7.14~15.7 | <1.43 | — | — | 0.50 | — | — | 于丽敏 等, |
Tab. 2
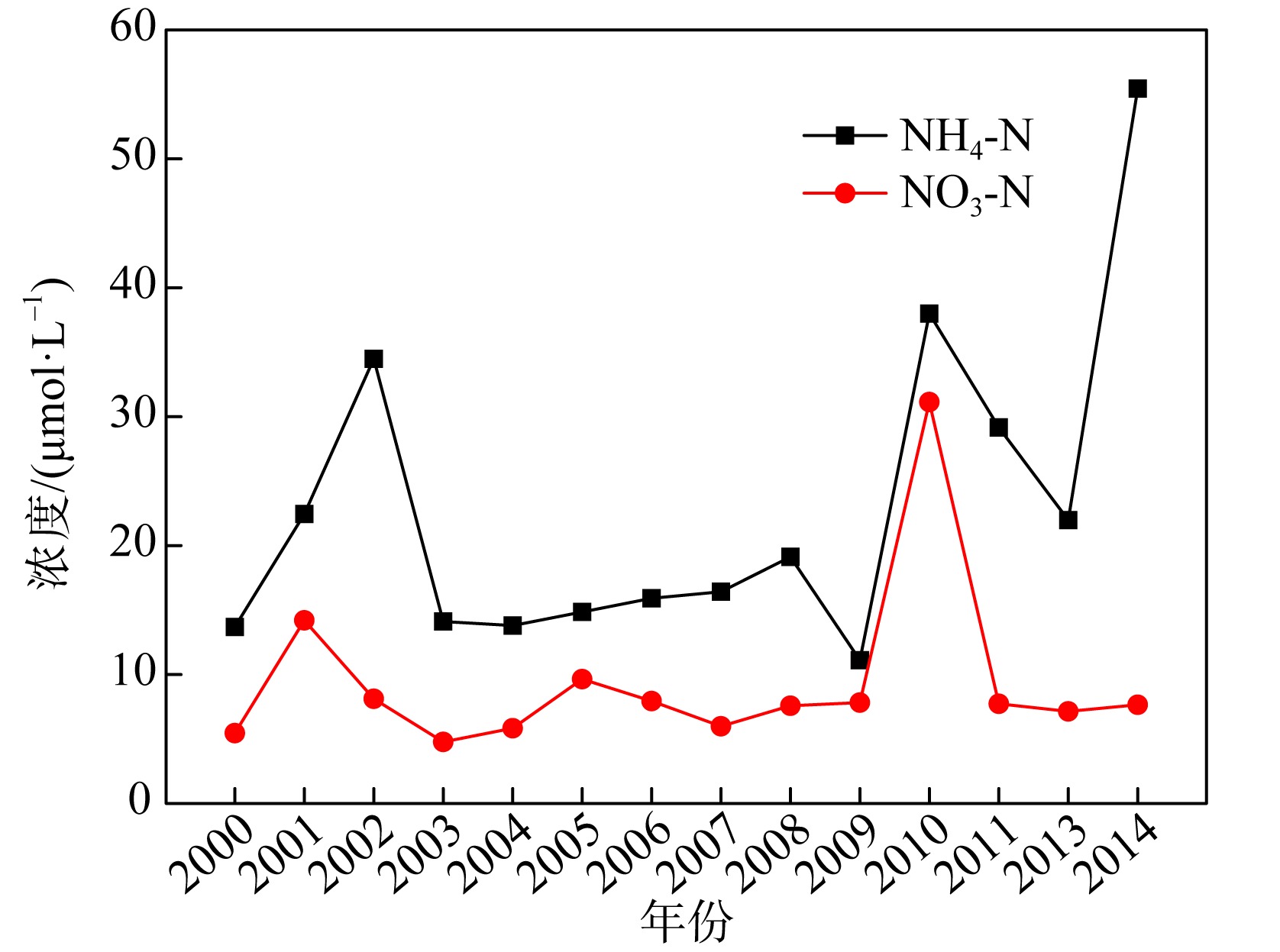
Concentrations of various nutrients in rainwater in different areas of South China Sea"
| 区域 | 营养盐浓度/(μmol·L-1) | 参考文献 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH4-N | NO3-N | NO2-N | DIN | DON | DIP | DOP | DSi | ||
| 珠江口 | 58.57 | 37.14 | — | 95.71 | 57.15 | — | — | — | 樊敏玲 等, |
| 北部湾西部 | 27 | 15 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 陈法锦 等, |
| 湛江湾 | — | 19.50 | 0.14 | — | — | 0.25 | — | 1.56 | 陈法锦 等, |
| 大亚湾 | 33.86 | 38.28 * | — | 72.14 | 15.72 | — | — | — | 陈瑾 等, |
| 大亚湾 | 7.16 | 26.43 | 0.39 | 33.98 | 20.33 | 0.75 | 0.38 | 6.82 | Wu et al, |
| 西沙永兴岛 | 8.7 | 8.9 | — | 17.6 | — | — | — | — | 肖红伟 等, |
| 南海东北部 | 11.67 | 30.16 | — | — | — | 0.04 | — | — | 林久人 等, |
| 南海东部 | 23.2 | 9.6 | — | 32.8 | — | — | — | — | 劳齐斌 等, |
Tab. 3
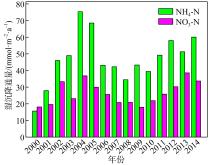
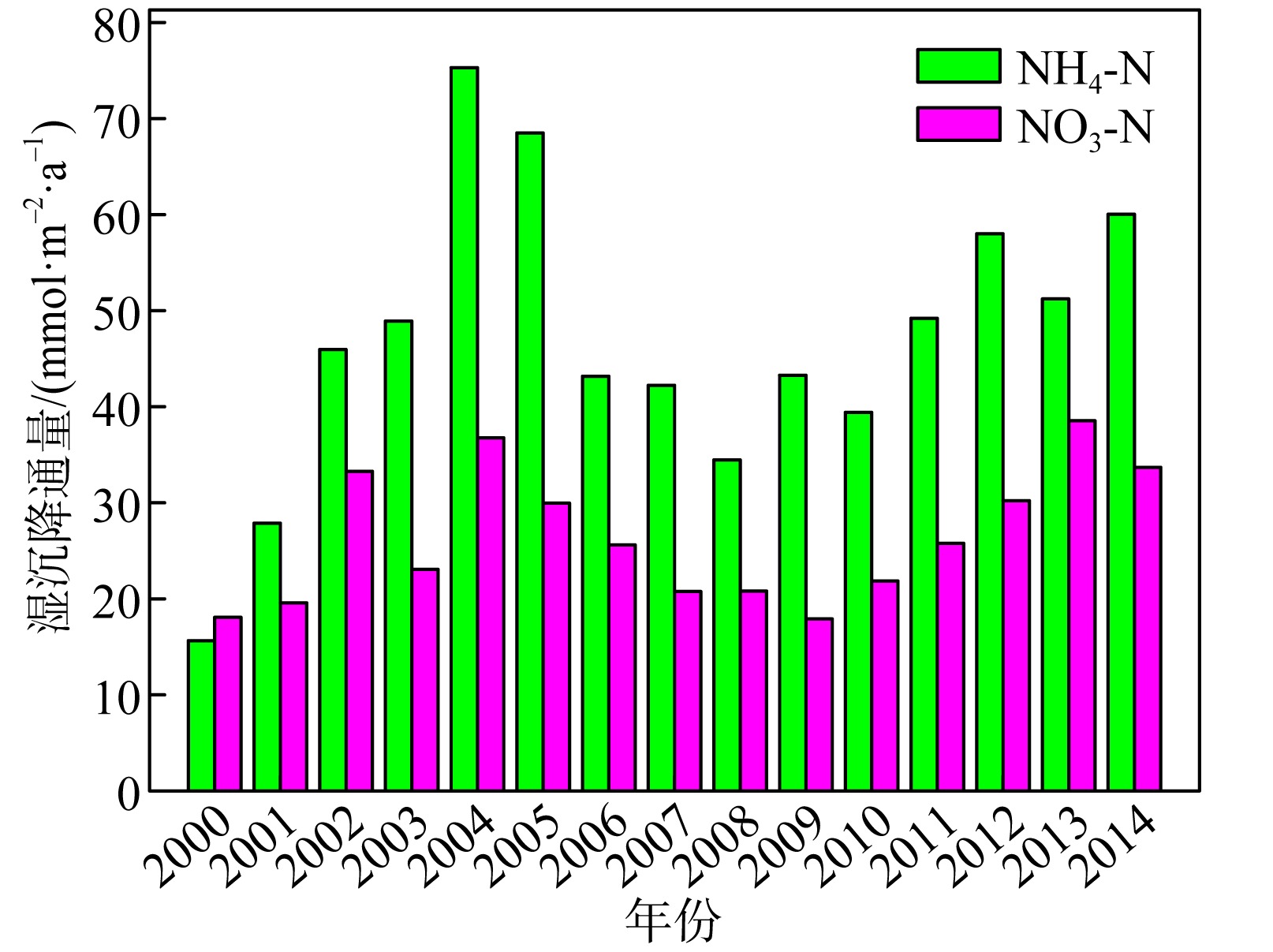
Dry and wet deposition fluxes of various nutrients in different areas of South China Sea"
| 区域 | 营养盐 | 参考文献 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH4-N | NO3-N | NO2-N | DIN | DON | DIP | DOP | DSi | |||
| 干沉降通量/(mmol·m-2·a-1) | 珠江口 | 43.66 | 25.92 | — | 69.58 | 27.87 | — | — | — | 陈中颖 等, |
| 大亚湾 | 7.17 | 20.14 | 2.41 | 29.72 | 9.26 | 0.093 | 0.124 | — | 陈瑾 等, | |
| 大亚湾 | 0.934 | 8.46 | 0.046 | 9.44 | 16.33 | 0.057 | 0.032 | 0.338 | Wu et al, | |
| 湿沉降通量/(mmol·m-2·a-1) | 珠江口 | 60.51 | 40.98* | — | 101.5 | 57.18 | — | — | — | 陈中颖 等, |
| 大亚湾 | 68.25 | 84.51 | 4.81 | 157.6 | 19.78 | 0.244 | 0.233 | — | 陈瑾 等, | |
| 大亚湾 | 17.5 | 64.4 | 0.97 | 82.87 | 49.7 | 0.133 | 0.068 | 1.19 | Wu et al, | |
| 北部湾西部 | 46.44 | 25.92 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 陈法锦 等, | |
| 湛江湾 | — | 42.62 | 0.297 | — | — | 0.535 | — | 3.338 | 陈法锦 等, | |
| 总(干+湿)沉降通量/(mmol·m-2·a-1) | 珠江口 | 104.2 | 66.90 | — | 171.1 | 85.05 | — | — | — | 陈中颖 等, |
| 大亚湾 | 75.42 | 104.6 | 7.22 | 187.3 | 29.04 | 0.337 | 0.357 | — | 陈瑾 等, | |
| 大亚湾 | 18.43 | 72.86 | 1.02 | 92.31 | 66.03 | 0.190 | 0.100 | 1.528 | Wu et al, | |
Tab. 4
Concentrations (ng·m-3) and dry deposition fluxes (mg·m-2·a-1) of dissolved trace elements in the aerosol of the Daya Bay"
| 参数 | 元素 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | Fe | Mn | Cu | Ni | Zn | Pb | Cd | Cr | As | Se | V | Mo | Ba | Co | |
| 溶解态浓度 | 203.5 | 110.7 | 16.16 | 9.58 | 3.54 | 881.7 | 3.01 | 0.62 | 3.12 | 38.9 | 0.42 | 1.29 | 2.04 | 151.8 | 0.08 |
| 干沉降通量 | 37.54 | 20.07 | 6.02 | 0.70 | 0.21 | 9.46 | 0.84 | 0.0375 | 0.27 | 0.44 | 0.055 | 0.154 | 0.091 | 24.05 | 0.022 |
Tab. 5
Concentrations (μg·L-1) and wet deposition fluxes (mg·m-2·a-1) of trace elements in precipitation in South China Sea"
| 海区 | 参数 | 元素 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | Fe | Mn | Cu | Ni | Zn | Pb | Cd | Cr | As | Se | V | Mo | Ba | Co | ||
| 深圳近海* | 溶解态浓度 | 22.86 | — | 3.34 | 1.85 | 0.44 | 22.54 | 1.81 | 0.10 | 0.21 | 0.72 | — | 0.19 | — | — | 0.03 |
| 大亚湾** | 总浓度 | 2800 | 1130 | 230 | 24.9 | 10.1 | 510 | 40 | 7.6 | 16 | 20 | 3.2 | 13 | 8.1 | 1320 | 0.87 |
| 深圳近海* | 湿沉降通量 | — | — | — | 2.94 | 1.23 | 26.74 | 2.71 | 0.742 | 0.857 | 1.445 | — | 2.16 | — | — | 0.678 |
| 大亚湾** | 湿沉降通量 | 439.9 | 189.3 | 47.4 | 3.97 | 1.70 | 84.5 | 6.79 | 0.12 | 2.68 | 3.20 | 0.51 | 2.26 | 1.32 | 125.7 | 0.16 |
| [1] |
陈法锦, 陈淳青, 周凤霞, 等, 2017. 湛江湾大气湿沉降中营养盐的研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 37(6): 2055-2063.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈法锦, 劳齐斌, 李志阳, 等, 2018a. 近15年北部湾西部近岸大气湿沉降中无机氮的研究[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 37(1): 69-74.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
陈法锦, 孟亚飞, 劳齐斌, 等, 2018b. 2003-2014年珠江口香洲大气无机氮湿沉降变化研究[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 38(1): 54-62.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
陈瑾, 刘思言, 邓鉴峰, 等, 2014a. 惠州大亚湾大气湿沉降中氮营养盐变化特征的研究[J]. 华南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 46(4): 70-75.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
陈瑾, 卢平, 陈中颖, 等, 2014b. 惠州大亚湾春夏季大气氮磷沉降的研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 33(2): 109-114.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
陈中颖, 李开明, 林文实, 等, 2010. 珠江口大气氮磷干湿沉降通量及其污染特征[J]. 环境污染与防治, 32(11): 53-57.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
邓银银, 2014. 基于卫星数据的中国近海氮沉降通量估算研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 1-65.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
丁晓君, 代威力, 龙爱民, 等, 2022. 南海气溶胶中溶解性无机磷的空间和季节分布特征[J]. 环境化学, 41(7): 2347-2355.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
樊敏玲, 王雪梅, 王茜, 等, 2010. 珠江口横门大气氮、磷干湿沉降的初步研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 29(1): 51-56.
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2010.01.051 |
|
|
|
| [10] |
蒋冰艳, 何龙, 陈德华, 等, 2018. 深圳近海区域降水中重金属湿沉降通量及源解析[J]. 环境化学, 37(7): 1460-1473.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
劳齐斌, 朱庆梅, 周欣, 等, 2018. 南海东部大气湿沉降中无机氮的研究[J]. 地球与环境, 46(1): 33-42.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
林久人, 祁建华, 谢丹丹, 等, 2017. 海洋降水中无机离子浓度及湿沉降通量——中国海及西北太平洋降水的研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 37(5): 1706-1715.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
牟英春, 褚强, 张潮, 等, 2018. 南海浮游植物对沙尘和灰霾添加的响应[J]. 中国环境科学, 38(9): 3512-3523.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
石金辉, 2011. 中国近海大气沉降中氮组分的分布特征及对春季水华事件的影响分析[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学: 1-131.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
宋金明, 段丽琴, 2017. 渤黄东海微/痕量元素的环境生物地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 1-463.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
宋金明, 李学刚, 袁华茂, 等, 2019. 渤黄东海生源要素的生物地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 1-870.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
宋金明, 李学刚, 袁华茂, 等, 2020. 海洋生物地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 1-690.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
宋金明, 王启栋, 2021. 近40年来对南海化学海洋学研究的新认知[J]. 热带海洋学报, 40(3): 15-24.
doi: 10.11978/YG2020010 |
|
doi: 10.11978/YG2020010 |
|
| [19] |
宋金明, 邢建伟, 2022. 大气干湿沉降及其对海洋生态环境的影响[M]//李乃胜, 宋金明, 经略海洋, 189-205,
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
田媛, 涂晨, 周倩, 等, 2020. 环渤海海岸大气微塑料污染时空分布特征与表面形貌[J]. 环境科学学报, 40(4): 1401-1409.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
王国祯, 刘偲嘉, 于兴娜, 2021. 珠海市降水化学与沉降特征[J]. 环境科学研究, 34(7): 1612-1620.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
王梦梦, 原梦云, 苏德纯, 2017. 我国大气重金属干湿沉降特征及时空变化规律[J]. 中国环境科学, 37(11): 4085-4096.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
王茜, 王雪梅, 钟流举, 等, 2009. 珠江口无机氮湿沉降规律及大气输送的研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 29(6): 1156-1163.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
王少锋, 冯新斌, 仇广乐, 等, 2006. 大气汞的自然来源研究进展[J]. 地球与环境, 34(2): 1-11.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
王欣睿, 刘梦南, 董燕红, 等, 2014. 珠江口海域气溶胶中重金属含量的时间变化特征及入海通量初步估算[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 33(1): 133-139.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
王赞红, 王保民, 崔鹏飞, 等, 2011. 渤海近海大气颗粒物金属元素的入海通量[J]. 海洋环境科学, 30(1): 86-89.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
吴兑, 1990. 西沙群岛旱季小阵雨的酸度及化学成分[J]. 气象, 16(9): 18-22.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
吴兑, 1995. 南海北部大气气溶胶水溶性成分谱分布特征[J]. 大气科学, 19(5): 615-622.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
吴兑, 项培英, 常业谛, 等, 1989. 西沙永兴岛降水的酸度及其化学组成[J]. 气象学报, 47(3): 381-384.
|
|
|
|
| [30] |
吴俊晖, 劳齐斌, 曾珍, 等, 2021. 珠江口湿沉降化学特征及其变化趋势[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 41(3): 60-66.
|
|
|
|
| [31] |
肖红伟, 龙爱民, 谢露华, 等, 2014. 中国南海大气降水化学特征[J]. 环境科学, 35(2): 475-480.
|
|
|
|
| [32] |
肖红伟, 肖化云, 张忠义, 等, 2016. 西沙永兴岛大气降水化学特征及来源分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 36(11): 3237-3244.
|
|
|
|
| [33] |
邢建伟, 宋金明, 袁华茂, 等, 2017. 胶州湾生源要素的大气沉降及其生态效应研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 28(1): 353-366.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.201701.006 |
|
|
|
| [34] |
邢建伟, 宋金明, 袁华茂, 等, 2020. 胶州湾大气活性硅酸盐干沉降特征及其生态效应[J]. 生态学报, 40(9): 3096-3104.
|
|
|
|
| [35] |
徐玲玲, 赵金平, 徐亚, 等, 2011. 大气汞的来源及其浓度分布特征研究进展[J]. 环境污染与防治, 33(11): 82-88, 92.
|
|
|
|
| [36] |
徐向荣, 孙承君, 季荣, 等, 2018. 加强海洋微塑料的生态和健康危害研究提升风险管控能力[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 33(10): 1003-1011.
|
|
|
|
| [37] |
杨一超, 薛金林, 任景玲, 等, 2020. 夏季南海气溶胶微量元素浓度、溶解度及干沉降通量[J]. 环境科学学报, 40(7): 2365-2374.
|
|
|
|
| [38] |
于丽敏, 祁建华, 孙娜娜, 等, 2007. 南、黄海及青岛地区大气气溶胶中无机氮组分的研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 27(2): 319-325.
|
|
|
|
| [39] |
周佳佳, 2015. 中国近海大气气溶胶中有机胺的浓度分布及来源[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学: 1-64.
|
|
|
|
| [40] |
周卫文, 李芊, 葛在名, 等, 2020. 珠江口羽流锋浮游植物群落对大气沉降的生态响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 39(4): 50-60.
doi: 10.11978/2019101 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2019101 |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
doi: 10.1038/s41561-019-0335-5 |
| [43] |
doi: 10.1029/2002GB001964 |
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00437-3 pmid: 28894096 |
| [46] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2018.07.008 |
| [47] |
doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2005.06.006 |
| [48] |
CHEN YUH-LING LEE,
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2003.12.006 |
| [49] |
doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(99)00343-X |
| [50] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2016.02.011 |
| [51] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26728-4 |
| [52] |
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2019.06.015 |
| [53] |
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2021.118389 |
| [54] |
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2020.117261 |
| [55] |
doi: 10.1126/science.1150369 pmid: 18487184 |
| [56] |
doi: 10.1029/91GB01778 |
| [57] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17201-9 pmid: 32665541 |
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
doi: 10.5194/bg-10-653-2013 |
| [60] |
doi: 10.1029/2009JD012958 |
| [61] |
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2020.117484 |
| [62] |
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2019.02.033 |
| [63] |
doi: 10.1029/2021JD034590 |
| [64] |
doi: 10.5194/acp-6-729-2006 |
| [65] |
doi: 10.1093/plankt/fbt002 |
| [66] |
doi: 10.5194/bg-9-1519-2012 |
| [67] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2014.04.003 |
| [68] |
doi: 10.1002/2013GL058796 |
| [69] |
doi: 10.1002/jgrd.50405 |
| [70] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2008.10.003 |
| [71] |
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.06.006 |
| [72] |
doi: 10.1038/srep03763 pmid: 24441731 |
| [73] |
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.07.029 |
| [74] |
doi: 10.1002/2014GL059665 |
| [75] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150767 |
| [76] |
doi: 10.1029/2020GL090383 |
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
doi: 10.1029/2009GL037484 |
| [79] |
doi: 10.1002/2013GB004795 |
| [80] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123223 |
| [81] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.9b03427 |
| [82] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153604 |
| [83] |
doi: 10.1029/2002JD003051 |
| [84] |
doi: 10.1038/nature06316 |
| [85] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.339 |
| [86] |
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0811486106 |
| [87] |
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2020.105076 |
| [88] |
doi: 10.1126/science.aal3869 pmid: 28522534 |
| [89] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.04.022 |
| [90] |
doi: 10.1029/2019JG005490 |
| [91] |
doi: 10.1029/2004JD004598 |
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
doi: S0269-7491(18)30281-1 pmid: 30093156 |
| [94] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2018.06.005 |
| [95] |
doi: 10.1080/02786820119445 |
| [96] |
doi: S0269-7491(16)30197-X pmid: 26975003 |
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2019.109092 |
| [99] |
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.12.041 |
| [100] |
doi: 10.1029/2011GL050415 |
| [101] |
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2022.106089 |
| [102] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.01.019 |
| [103] |
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.03.037 |
| [104] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.12.046 |
| [105] |
doi: 10.1029/2019JC015663 |
| [106] |
|
| [107] |
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.03.006 |
| [108] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151772 |
| [109] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157130 |
| [110] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.134 |
| [111] |
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.02.004 |
| [112] |
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2018.03.001 |
| [113] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109371 |
| [114] |
doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-2810-2 |
| [115] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.149 |
| [116] |
doi: 10.5194/bg-11-1833-2014 |
| [117] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c00706 |
| [118] |
doi: 10.1029/2004JD005411 |
| [119] |
|
| [120] |
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.06.031 |
| [121] |
doi: 10.1029/2009JD012814 |
| [122] |
doi: 10.5094/APR.2015.023 |
| [123] |
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.03.069 |
| [124] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.07.127 |
| [125] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2005.05.007 |
| [126] |
doi: 10.1029/2006JD007074 |
| [127] |
doi: 10.1002/lno.v66.4 |
| [128] |
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.08.023 |
| [129] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.07.033 |
| [130] |
doi: 10.1002/2016JG003393 |
| [131] |
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.12.028 |
| [1] | ZHAO Hongwuyi, ZHOU Wen, ZENG Kai, DENG Lin, LIAO Jianzu, CAO Wenxi. A study of the regional size-fractionated primary production algorithm based on phytoplankton absorption coefficient and photosynthetically active radiation in the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(1): 43-55. |
| [2] | WANG Zhaohui, ZHANG Yuning, WANG Wenting, XIE Changliang, CHEN Jiazhuo, ZHENG Hu, WANG Junxing. Distribution of dinoflagellate cysts in surface sediments on the Dongshan Bay, Fujian province, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 154-162. |
| [3] | LI Yao, XIANG Chenhui, JIANG Zhijian, SONG Xingyu. Production and metabolism characteristics of planktonic community and their influencing factors in Daya Bay during summer* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(6): 83-92. |
| [4] | FANG Zhou, TAN Fei, YANG Hongqiang, XU Huilong, XU Xiangrong, LI Hengxiang. Distribution characteristics of plastic debris and microplastics on the beaches of Ganquan Island and Quanfu Island in Xisha Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(5): 123-133. |
| [5] | CHEN Huanhuan, WANG Yuntao, QI Yiquan, CHAI Fei. Temporal and spatial patterns of dust deposition in the North Pacific Ocean and its potential impact on ecosystem in the subarctic ocean [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(1): 21-30. |
| [6] | Weiwen ZHOU, Qian LI, Zaiming GE, Zijia LIU, Yiping SHUAI, Mengzhen MA. Response of phytoplankton community to atmospheric deposition along Pearl River plume front [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(4): 50-60. |
| [7] | Lei HE, Fangjuan HUANG, Kedong YIN. The ecological effect of marine microplastics as a biological vector [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(4): 1-8. |
| [8] | Huajian LIU, Liangmin HUANG, Yehui TAN, Zhixin KE, Jiaxing LIU, Chunyu ZHAO, Junxing WANG. Seasonal variations of chlorophyll a and primary production and their influencing factors in the Pearl River Estuary [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2017, 36(1): 81-91. |
| [9] | LIU Jiaxing, ZHOU Linbin, LI Gang, TAN Yehui, LIU Huajian, ZHAO Chunyu, KE Zhixin, LI Jiajun, JIANG Xin. Nitrogen fixation and its contribution of nitrogen to primary production in the surface waters of the northeastern South China Sea during October 2014 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2016, 35(5): 38-47. |
| [10] | CHEN Jin, LU Ping, CHEN Zhong-ying, YAN Hui-hua, LI Lai-sheng. Atmospheric deposition of nitrogen and phosphorus at Daya Bay in Huizhou during spring and summer [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2014, 33(2): 109-114. |
|
||