Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2021, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5): 123-133.doi: 10.11978/2020137CSTR: 32234.14.2020137
• Marine Environment Protection • Previous Articles Next Articles
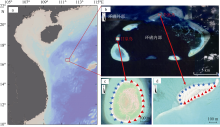
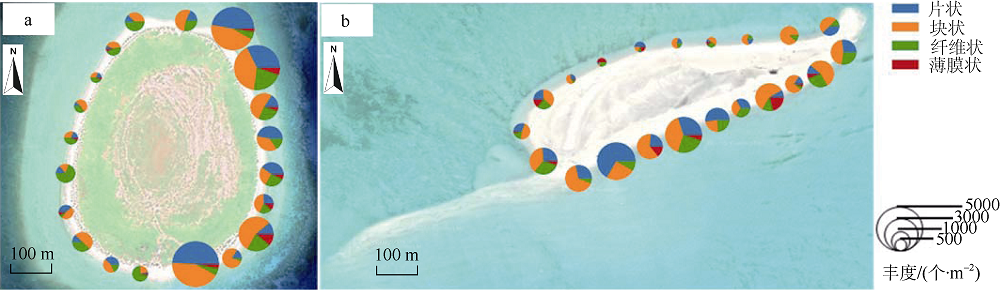
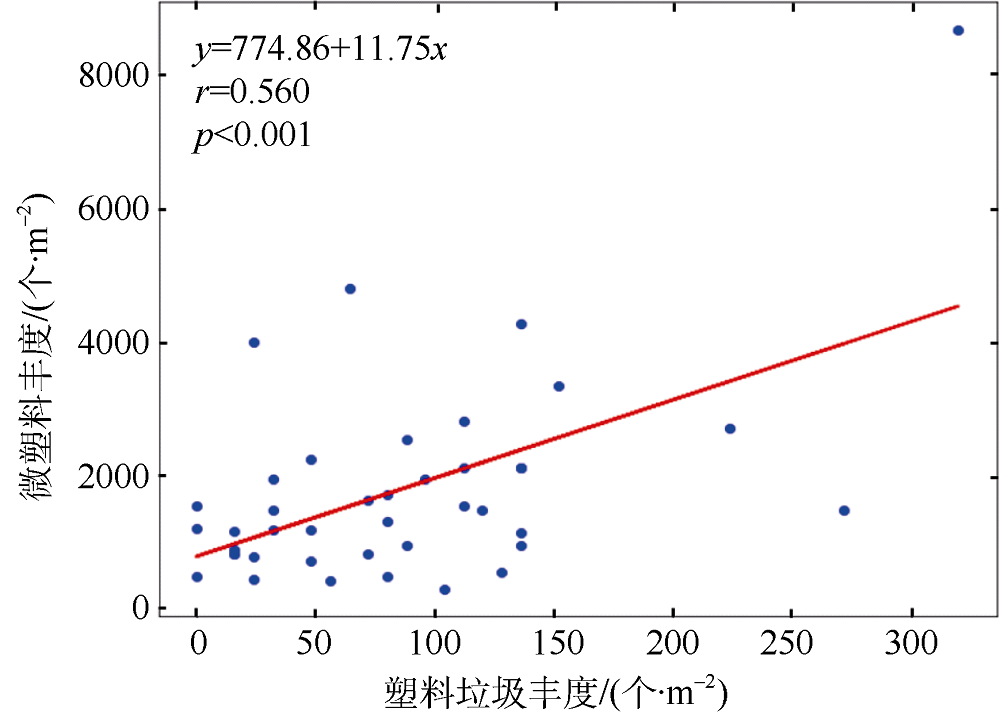
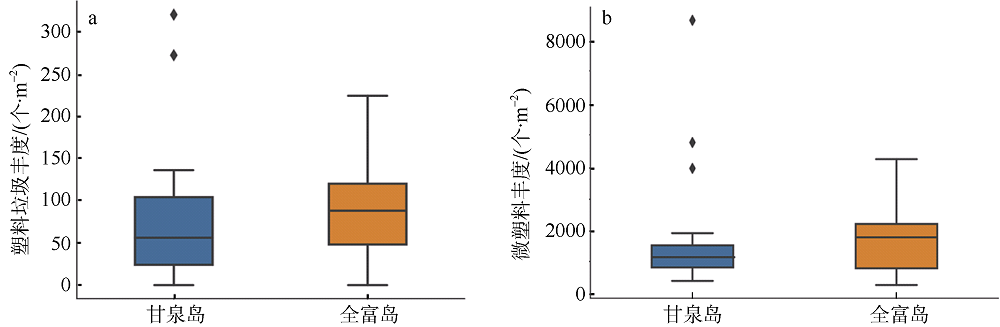
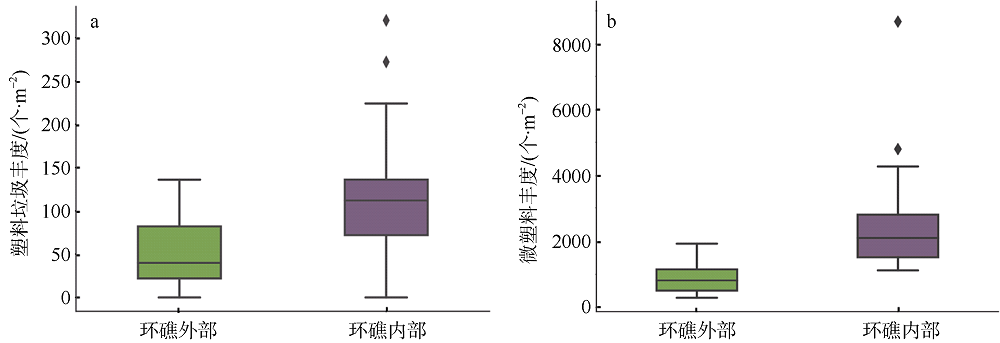
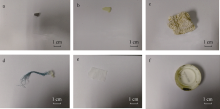
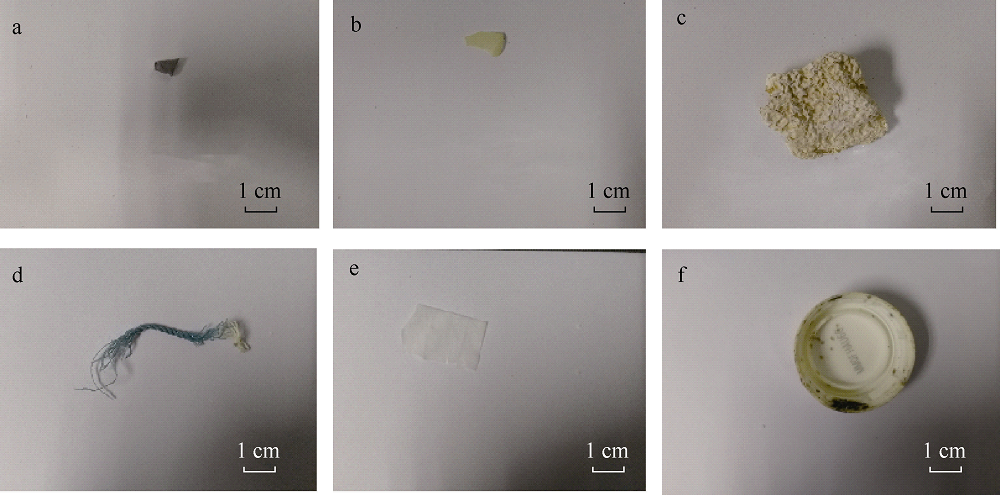
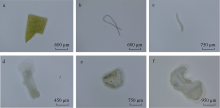
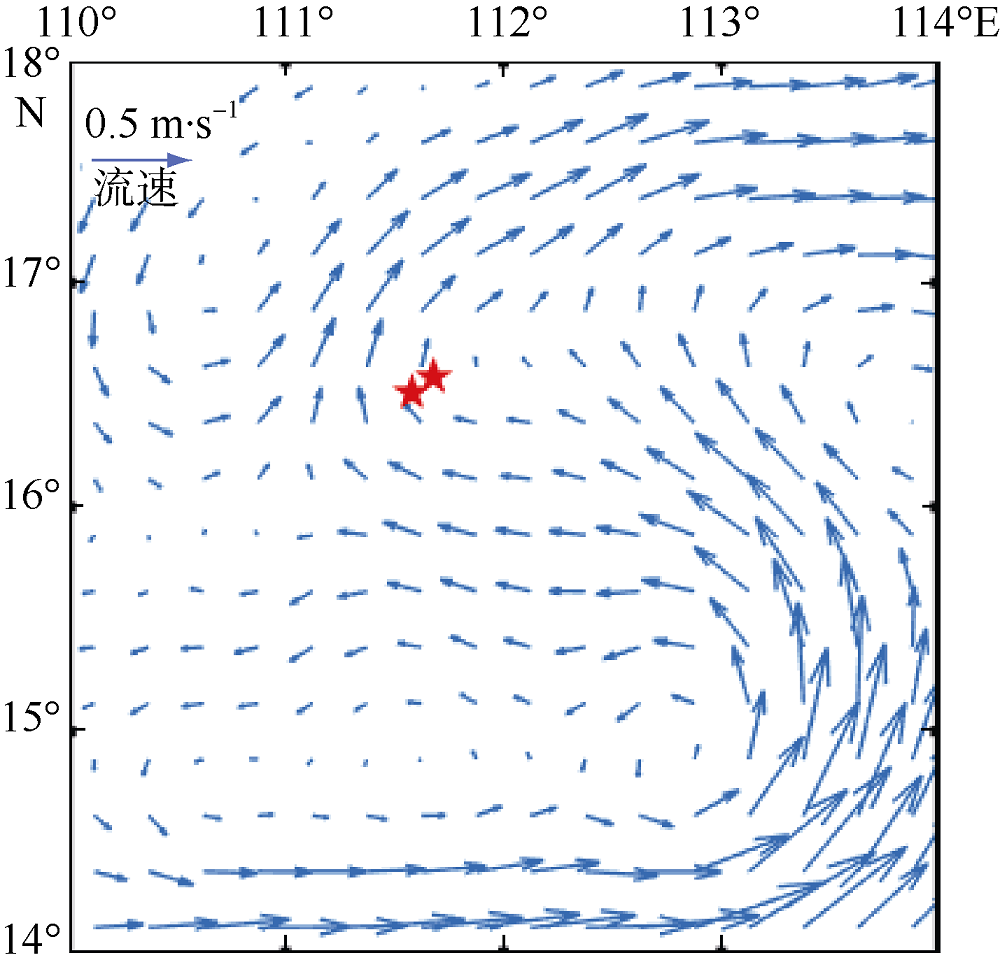
Distribution characteristics of plastic debris and microplastics on the beaches of Ganquan Island and Quanfu Island in Xisha Sea
FANG Zhou1,4( ), TAN Fei1,4, YANG Hongqiang1,3,5(
), TAN Fei1,4, YANG Hongqiang1,3,5( ), XU Huilong1, XU Xiangrong2,3, LI Hengxiang2,3(
), XU Huilong1, XU Xiangrong2,3, LI Hengxiang2,3( )
)
- 1. Key Laboratory of Ocean and Marginal Sea Geology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
3. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou 511458, China
4. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
5. Nansha Marine Ecological and Environmental Research Station, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Sansha 573199, China
-
Received:2020-11-20Revised:2021-03-02Online:2021-09-10Published:2021-03-10 -
Contact:YANG Hongqiang,LI Hengxiang E-mail:13763057862@163.com;hqyang@scsio.ac.cn;hxli@scsio.ac.cn -
Supported by:Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences(XDA13010103);Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences(XDA13020101);Key Special Project for Introduced Talents Team of Southern Marine Science and Engineering, Guangdong Laboratory(Guangzhou)(GML2019ZD0404);Key Special Project for Introduced Talents Team of Southern Marine Science and Engineering, Guangdong Laboratory(Guangzhou)(GML2019ZD0206);Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences(ISEE2019ZR03);Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences(ISEE2018PY01)
CLC Number:
- P762.9
Cite this article
FANG Zhou, TAN Fei, YANG Hongqiang, XU Huilong, XU Xiangrong, LI Hengxiang. Distribution characteristics of plastic debris and microplastics on the beaches of Ganquan Island and Quanfu Island in Xisha Sea[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(5): 123-133.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
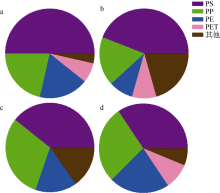
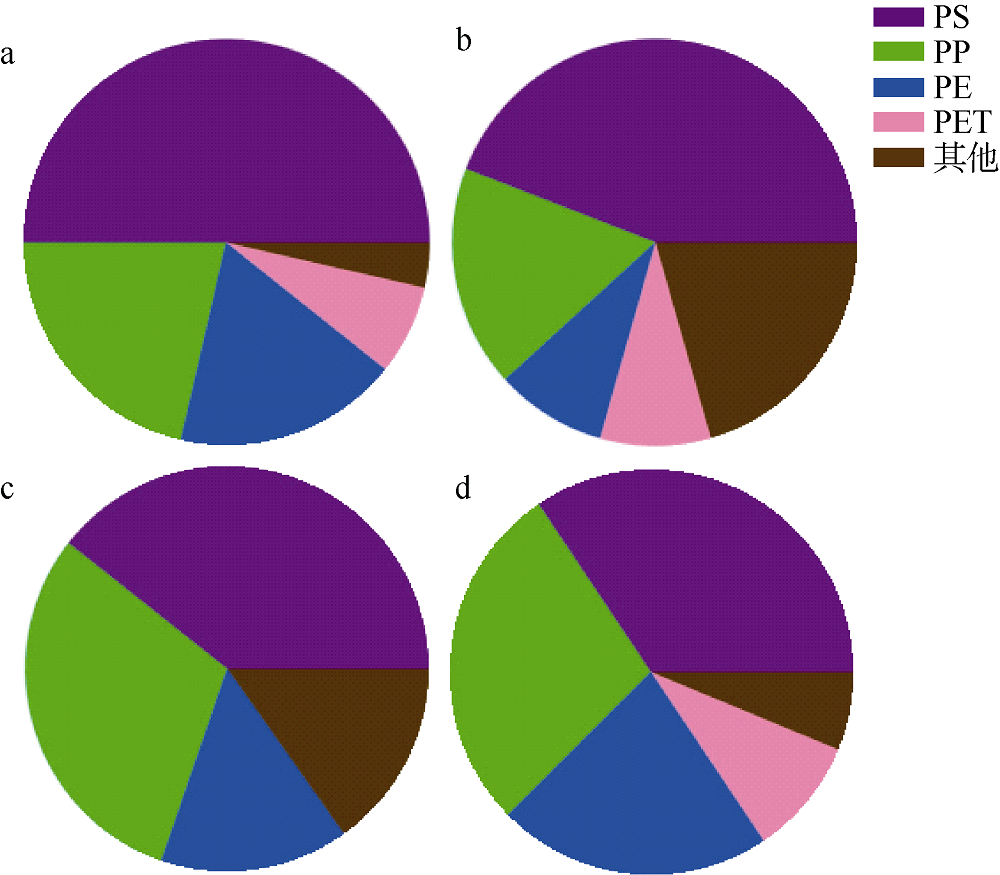
Tab. 1
Comparison of beach microplastics in different studies"
| 调查区域 | 滤膜孔径/μm | 微塑料丰度 | 微塑料主要成分 | 微塑料主要形状 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中国香港沿岸 | 315 | 5595个∙m-2 | EPS | 泡沫、碎片 | |
| 马尔代夫 | 50 | 22.7个∙m-2 | PE、PP、PS | 碎片、泡沫 | |
| 马尔代夫 | 0.2 | 1029个∙m-2 | PS、PE、PP | 泡沫、碎片、薄膜 | |
| 秘鲁沿岸 | 1000 | 174.1个∙m-2 | PS | 泡沫、碎片 | |
| 韩国沿岸 | 1000 | 918.7个∙m-2 | PS | 泡沫、纤维 | |
| 危地马拉沿岸 | 1000 | 279个∙m-2 | PS、PP、PE | 泡沫、碎片 | |
| 新西兰沿岸 | 300 | 459个∙m-2 | 纤维素、PE | 纤维、碎片、薄膜 | |
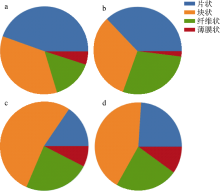
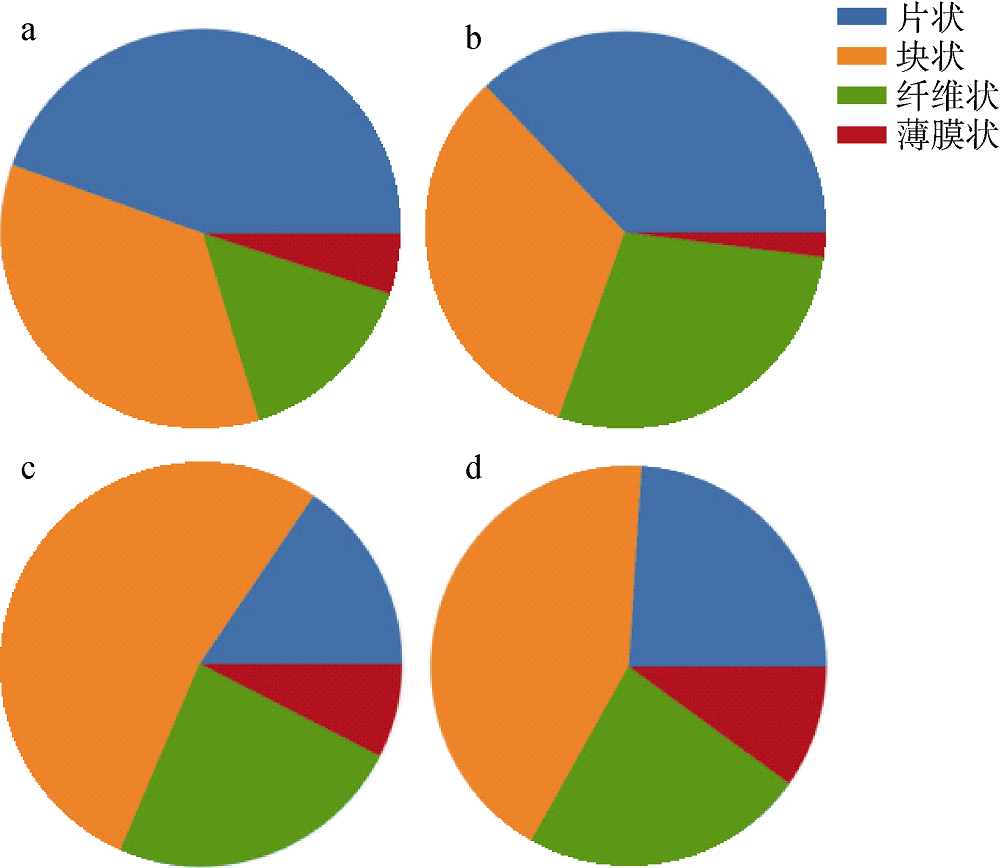
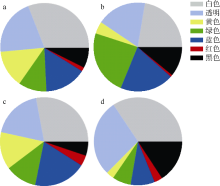
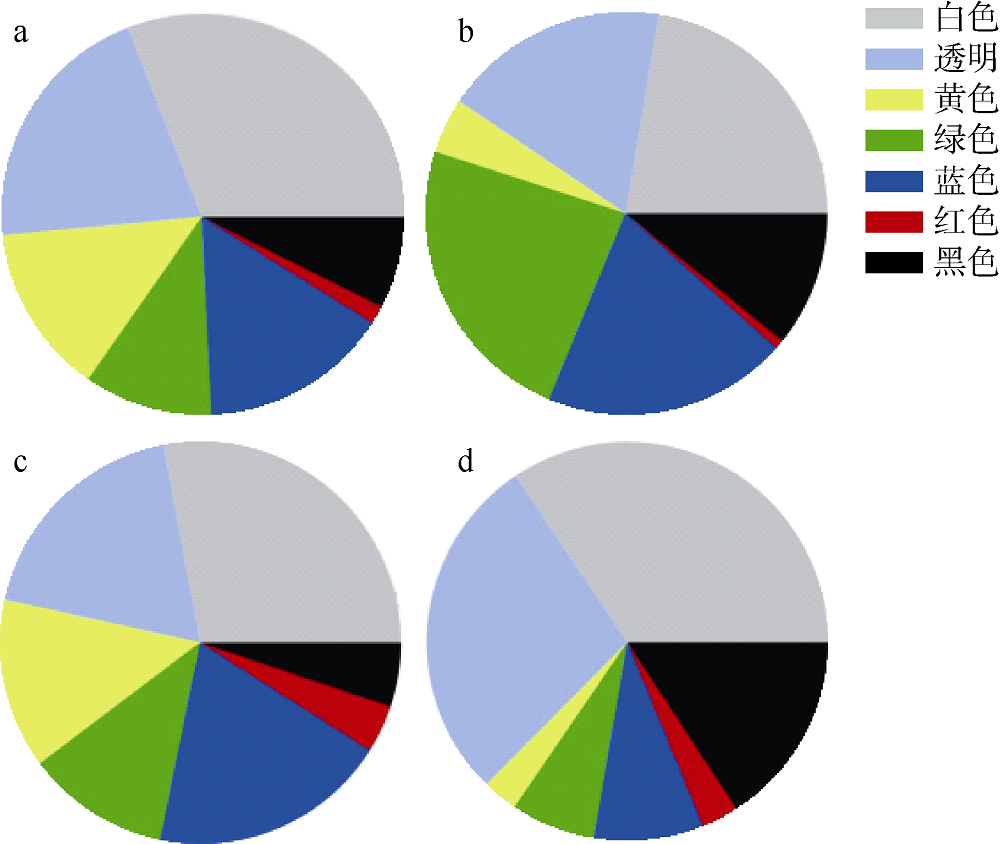
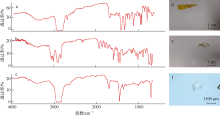
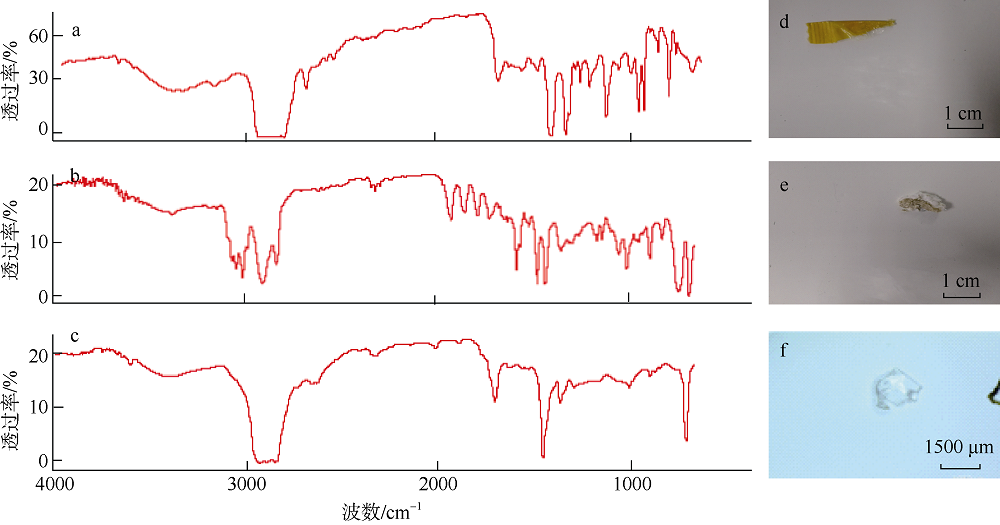
| 西沙偏远海岛 | 20 | 1774.75个∙m-2 | PS、PE、PP | 泡沫、碎片、纤维 | 本研究 |
| 渤海沿岸 | 10 | 102.9~163.3个∙kg-1 | PEVA、LDPE、 PS | 碎片、薄片 | |
| 厦门湾沿岸 | / | 28.1~312. 7个∙kg-1 | PE、PS | 泡沫、碎片、纤维 | |
| 象山港沿岸 | 10 | 1739个∙kg-1 | PE泡沫、PE渔网 | 泡沫 | |
| 长江口沿岸 | 20 | 121个∙kg-1 | 尼龙、PE | 纤维 | |
| 加勒比海沿岸 | 0.45 | 261个∙kg-1 | / | 纤维 | |
| 西沙偏远海岛 | 20 | 100.82个∙kg-1 | PS、PE、PP | 泡沫、碎片、纤维 | 本研究 |
| [1] | 何蕾, 黄芳娟, 殷克东, 等, 2018. 海洋微塑料作为生物载体的生态效应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 37(4):1-8. |
| HE LEI, HUANG FANGJUAN, YIN KEDONG, et al, 2018. The ecological effect of marine microplastics as a biological vector[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 37(4):1-8 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [2] | 刘启明, 梁海涛, 锡桂莉, 等, 2019. 厦门湾海滩微塑料污染特征[J]. 环境科学, 40(3):1217-1221. |
| LIU QIMING, LIANG HAITAO, XI GUILI, et al, 2019. Microplastic pollution of the beaches in Xiamen Bay, China[J]. Environmental Science, 40(3):1217-1221 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
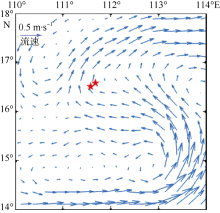
| [3] | 王道儒, 侍茂崇, 南峰, 2012. 西沙群岛潮、余流特征研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 42(10):1-9. |
| WANG DAORU, SHI MAOCHONG, NAN FENG, 2012. Study on features of tide and residual currents in the region of Paracel islands[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 42(10):1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [4] | 赵新月, 熊宽旭, 周倩, 等, 2020. 黄海桑沟湾潮滩塑料垃圾与微塑料组成和来源研究[J]. 海洋环境科学, 39(4):529-536. |
| ZHAO XINYUE, XIONG KUANXU, ZHOU QIAN, et al, 2020. Compositions and sources of plastic debris and microplastics in different sizes from the Sanggou bay beaches, Yellow Sea, China[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 39(4):529-536 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [5] | ARTHUR C, BAKER J, BAMFORD H, 2009. International research workshop on the occurrence, effects and fate of microplastic marine debris[R]. Maryland: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: 1-41. |
| [6] | BORRELLE S B, RINGMA J, LAW K L, et al. Predicted growth in plastic waste exceeds efforts to mitigate plastic pollution[J]. Science, 369. |
| [7] |
BOSKER T, GUAITA L, BEHRENS P, 2018. Microplastic pollution on Caribbean beaches in the Lesser Antilles[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 133:442-447.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.05.060 |
| [8] |
BRIDSON J H, PATEL M, LEWIS A, et al, 2020. Microplastic contamination in Auckland (New Zealand) beach sediments[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 151:110867.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110867 |
| [9] |
BROWNE M A, GALLOWAY T S, THOMPSON R C, 2010. Spatial patterns of plastic debris along estuarine shorelines[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(9):3404-3409.
doi: 10.1021/es903784e |
| [10] |
CHEN MINGLONG, JIN MING, TAO PEIRAN, et al, 2018. Assessment of microplastics derived from mariculture in Xiangshan Bay, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 242:1146-1156.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.07.133 |
| [11] |
DE-LA-TORRE G E, DIOSES-SALINAS D C, CASTRO J M, et al, 2020. Abundance and distribution of microplastics on sandy beaches of Lima, Peru[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 151:110877.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110877 |
| [12] |
DING JINFENG, JIANG FENGHUA, LI JINGXI, et al, 2019. Microplastics in the coral reef systems from Xisha Islands of South China Sea[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 53(14):8036-8046.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.9b01452 |
| [13] |
FOK L, CHEUNG P K, 2015. Hong Kong at the Pearl River Estuary: A hotspot of microplastic pollution[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 99(1-2):112-118.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.07.050 |
| [14] |
IMHOF H K, SIGL R, BRAUER E, et al, 2017. Spatial and temporal variation of macro-, meso- and microplastic abundance on a remote coral island of the Maldives, Indian Ocean[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 116(1-2):340-347.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.01.010 |
| [15] |
JAMBECK J R, GEYER R, WILCOX C, et al, 2015. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean[J]. Science, 347(6223):768-771.
doi: 10.1126/science.1260352 |
| [16] |
LEE J, LEE J S, JANG Y C, et al, 2015. Distribution and size relationships of plastic marine debris on beaches in South Korea[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 69:288-298.
doi: 10.1007/s00244-015-0208-x |
| [17] |
LI JIA, ZHANG HUA, ZHANG KAINA, et al, 2018. Characterization, source, and retention of microplastic in sandy beaches and mangrove wetlands of the Qinzhou Bay, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 136:401-406.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.09.025 |
| [18] | LI W C, TSE H F, FOK L, 2016. Plastic waste in the marine environment: A review of sources, occurrence and effects[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 566- 567:333-349. |
| [19] |
LO H S, XU XIAOYU, WONG C Y, et al, 2018. Comparisons of microplastic pollution between mudflats and sandy beaches in Hong Kong[J]. Environmental Pollution, 236:208-217.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.01.031 |
| [20] |
MAZARIEGOS-ORTÍZ C, DE LOS ÁNGELES ROSALES M, CARRILLO-OVALLE L, et al, 2020. First evidence of microplastic pollution in the El Quetzalito sand beach of the Guatemalan Caribbean[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 156:111220.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111220 |
| [21] |
MCDERMID K J, MCMULLEN T L, 2004. Quantitative analysis of small-plastic debris on beaches in the Hawaiian archipelago[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 48(7-8):790-794.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2003.10.017 |
| [22] |
NIE HUAYUE, WANG JUN, XU KAIHANG, et al, 2019. Microplastic pollution in water and fish samples around Nanxun Reef in Nansha Islands, South China Sea[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 696:134022.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134022 |
| [23] |
PENG GUYU, ZHU BANGSHANG, YANG DONGQI, et al, 2017. Microplastics in sediments of the Changjiang Estuary, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 225:283-290.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.12.064 |
| [24] |
SALIU F, MONTANO S, GARAVAGLIA M G, et al, 2018. Microplastic and charred microplastic in the Faafu Atoll, Maldives[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 136:464-471.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.09.023 |
| [25] |
SONG Y K, HONG S H, EO S, et al, 2018. Horizontal and vertical distribution of microplastics in Korean coastal waters[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 52(21):12188-12197.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b04032 |
| [26] |
TAN FEI, YANG HONGQIANG, XU XIANGRONG, et al, 2020. Microplastic pollution around remote uninhabited coral reefs of Nansha Islands, South China Sea[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 725:138383.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138383 |
| [27] |
VIDYASAKAR A, NEELAVANNAN K, KRISHNAKUMAR S, et al, 2018. Macrodebris and microplastic distribution in the beaches of Rameswaram Coral Island, Gulf of Mannar, Southeast coast of India: A first report[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 137:610-616.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.11.007 |
| [28] |
YAO PIAO, ZHOU BIN, LU YUEHAN, et al, 2019. A review of microplastics in sediments: Spatial and temporal occurrences, biological effects, and analytic methods[J]. Quaternary International, 519:274-281.
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2019.03.028 |
| [29] |
YU XUBIAO, PENG JUNPING, WANG JUNDONG, et al, 2016. Occurrence of microplastics in the beach sand of the Chinese inner sea: the Bohai Sea[J]. Environmental Pollution, 214:722-730.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.04.080 |
| [30] |
ZHANG LINLIN, ZHANG SHUAIPENG, WANG YINGHUI, et al, 2019. The spatial distribution of microplastic in the sands of a coral reef island in the South China Sea: Comparisons of the fringing reef and atoll[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 688:780-786.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.178 |
| [31] |
ZHANG ZHIWEI, WU HUI, PENG GUYU, et al, 2020. Coastal ocean dynamics reduce the export of microplastics to the open ocean[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 713:136634.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136634 |
| [32] |
ZHU CHUNYOU, LI DANING, SUN YUXIN, et al, 2019. Plastic debris in marine birds from an island located in the South China Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 149:110566.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110566 |
| [1] | ZHAO Zhongwei, WU Lingyun, GAO Weijian, LI Wei. A study of the effect of shore platform morphology on coastal erosion of rocky cliffs in the Wucaiwan Bay, E’man, Hainan Island [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 106-115. |
| [2] | WANG Jiaxi, LU Humu, QI Xin, GAO Chenghai, LIU Yonghong, LUO Xiaowei. Study on the secondary metabolites from the Weizhou Island coral Acropora austera associated fungus Arachniotus ruber GXIMD 02510 and their antibacterial activity [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 174-180. |
| [3] | XI Chen, LIN Zongxuan, SA Rula, DENG Xi, LIU Qiang, NI Liang, LUO Laicai, MA Teng, XIE Zhijie, CHEN Siruo, CHEN Songze. Analysis of water environmental changes and influencing factors in the southwestern waters of the Daya Bay based on continuous monitoring data from dual buoys [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 153-164. |
| [4] | GAO Jie, YU Kefu, XU Shendong, HUANG Xueyong, CHEN Biao, WANG Yonggang. Content and source analysis of organic carbon in the outer slope sediments of the Yongle Atoll, Xisha Islands [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 131-145. |
| [5] | ZHANG Yuyang, LIU Chengyue, YU Xiaolei, LUO Yong, ZHOU Tiancheng, LIAN Jiansheng, HUANG Hui. Study on relocation effect of scleractinian coral in the Fenghuang Island, Sanya* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 177-186. |
| [6] | LEI Mingfeng, YU Kefu, LIAO Zhiheng, CHEN Biao, HUANG Xueyong, CHEN Xiaoyan. The rapid ecological degradation and its impact on fish of the Yinyu Island in the Xisha Islands [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 87-99. |
| [7] | LIANG Yuxian, LIU Chengyue, YU Xiaolei, ZHANG Yuyang, LIAN Wenke, CHEN Lunju, HUANG Hui. Focusing on supplementing and restoring degraded coral reefs with key groups of reef-building coral - paradigms in the restoration of Xidao Island’s coral reef [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 166-176. |
| [8] | CHEN Shu, XU Hong, LU Shushen, Zhang Haiyang, MA Yazeng, LUO Jinxiong. The framework, reservoir characteristics and reef formation model of Miocene algal reef dolomite in the Xisha Islands* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 140-153. |
| [9] | CHEN Junqiang, WANG Wenbo, WANG Qing, YANG Yufeng. Species diversity and habitat preference of bdelloid rotifers in the Weizhou island, Guangxi [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 81-91. |
| [10] | ZHAO Jinfa, LIU Yong, LI Chunhou, WANG Teng, SHI Juan, XIAO Yayuan, WU Peng, SONG Xiaoyu. Study on species composition and distribution of fish eggs in Yongle Atoll and Dongdao Island by high-throughput sequencing technology [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 127-136. |
| [11] | ZENG Weite, ZHANG Dongqiang, LIU Bing, YANG Yongpeng, ZHANG Hangfei, WU Duoyu, WANG Xiaolin. Distribution, main controlling factors and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface seawater of the Northern Bay of Hainan Island, south China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 156-167. |
| [12] | XING Nannan, REN Runxin, TANG Zhenzhou, LUO Zhihong, XIA Chenxi, LIU Yonghong, PENG Liang, CHEN Xianqiang. Study on the secondary metabolites of fungus Aspergillus sp. GXIMD02003 derived from marine sediment in the Weizhou island [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 154-160. |
| [13] | GUO Jianlin, SUN Xian, YANG Yufeng, WANG Qing. The succession characteristics of copepod community structure in the seaweed bed and its adjacent waters in the Weizhou Island, Guangxi Province [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 155-165. |
| [14] | XING Jianwei, SONG Jinming. Atmospheric deposition and its eco-environmental effects on the South China Sea* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 19-39. |
| [15] | WANG Pengxia, ZHAO Yi, DU Xiaofei, WANG Weiquan, WANG Xiaoxue. Identification and functional study of the genomic island GIPspSM9913 in Pseudoalteromonas sp. SM9913 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(2): 45-53. |
|
||