Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (3): 95-103.doi: 10.11978/2024128CSTR: 32234.14.2024128
• Marine Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Assessment of carbon sequestration capacity of cultivated bivalves and influencing factors in Yantai sea areas
WANG Zheng1( ), YANG Tao2, WANG Yina1, LI Ming3(
), YANG Tao2, WANG Yina1, LI Ming3( ), PEI Pengbing4, DU Hong4, ZHANG Jianbai2(
), PEI Pengbing4, DU Hong4, ZHANG Jianbai2( ), SHEN Pingping1(
), SHEN Pingping1( )
)
- 1. Ocean School, Yantai University, Yantai 264005, China
2. Yantai Marine Economy Research Institute, Yantai 264005, China
3. Yantai Ecological Environment Monitoring Center, Shandong Province, Yantai 264000, China
4. Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Marine Disaster Prediction and Prevention, Shantou University, Shantou 515063, China
-
Received:2024-06-24Revised:2024-08-02Online:2025-05-10Published:2025-06-04 -
Contact:LI Ming, ZHANG Jianbai, SHEN Pingping -
Supported by:Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Marine Disaster Prediction and Prevention, Shantou University(GPKLMD2023001); Open Project of the National Key Laboratory for Environmental Protection of Coastal Ecological Environment(202311); National Natural Science Foundation of China(42376159)
CLC Number:
- X17
Cite this article
WANG Zheng, YANG Tao, WANG Yina, LI Ming, PEI Pengbing, DU Hong, ZHANG Jianbai, SHEN Pingping. Assessment of carbon sequestration capacity of cultivated bivalves and influencing factors in Yantai sea areas[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(3): 95-103.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
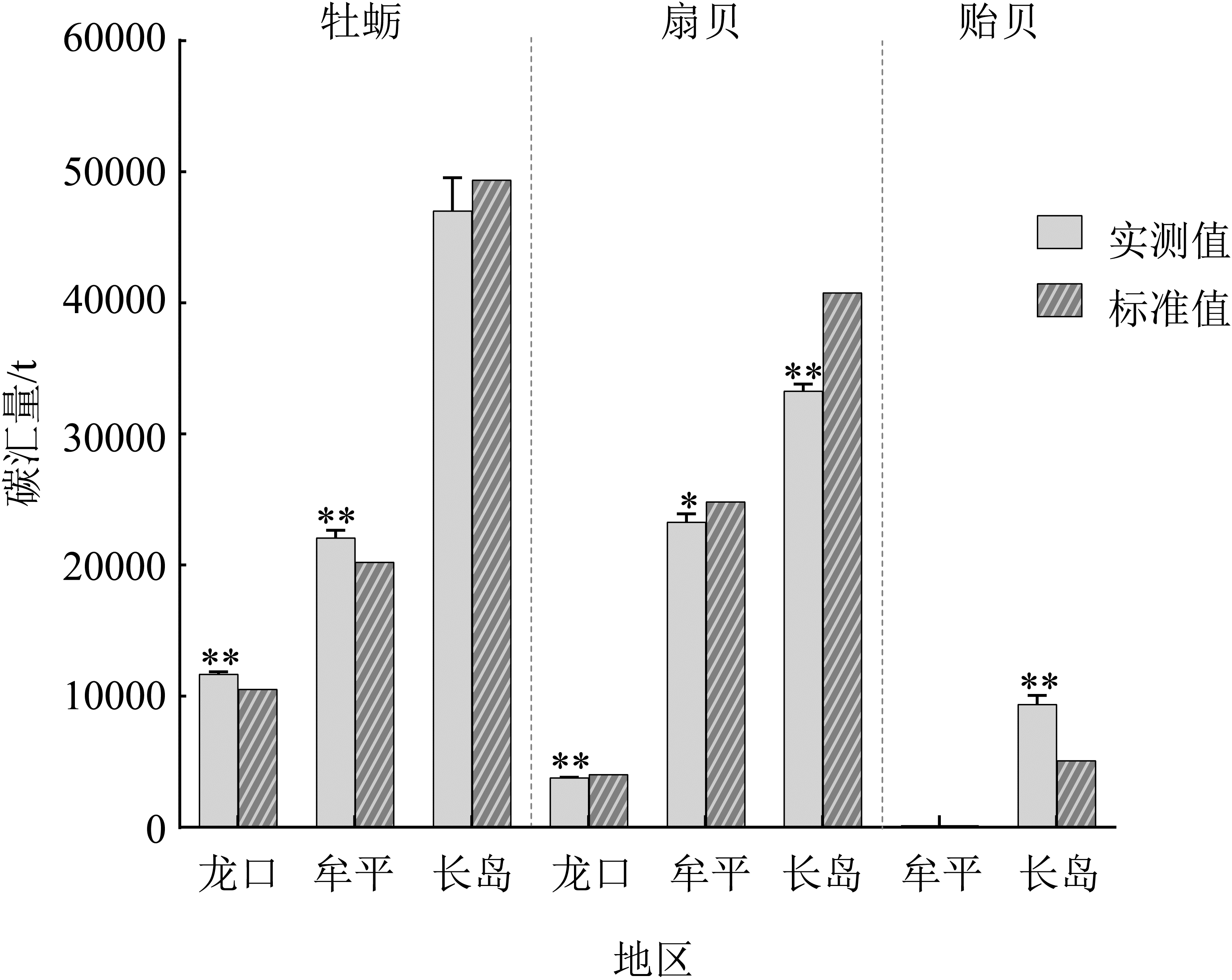
Tab. 1
Dry-wet conversion coefficient and carbon content of bivalves cultivated in Yantai sea areas"
| 贝类 | 体型 | 干湿重转换系数/% | 贝壳含碳率/% | 软体组织含碳率/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 龙口 | 牟平 | 长岛 | 龙口 | 牟平 | 长岛 | 龙口 | 牟平 | 长岛 | ||
| 牡蛎 | 大型 | 76.99 | 76.37 | 76.24 | 12.05 | 12.17 | 9.82 | 46.37 | 45.22 | 41.49 |
| 中型 | 76.47 | 69.99 | 71.06 | 12.09 | 12.14 | 11.82 | 44.64 | 46.52 | 40.27 | |
| 小型 | 73.49 | 74.65 | 72.34 | 13.15 | 12.57 | 12.29 | 45.70 | 44.64 | 39.53 | |
| 平均值 | 75.65 | 73.63 | 73.21 | 12.43 | 12.29 | 11.31 | 45.57 | 45.46 | 40.43 | |
| 扇贝 | 大型 | 53.34 | 45.61 | 54.70 | 14.33 | 15.13 | 12.80 | 41.93 | 46.83 | 37.87 |
| 中型 | 53.36 | 47.27 | 52.21 | 14.28 | 14.40 | 13.05 | 41.88 | 45.67 | 36.13 | |
| 小型 | 60.83 | 49.34 | 56.26 | 13.26 | 14.00 | 12.84 | 43.69 | 43.48 | 36.97 | |
| 平均值 | 55.84 | 47.41 | 54.39 | 13.96 | 14.51 | 12.90 | 42.50 | 45.33 | 36.99 | |
| 贻贝 | 平均值 | - | 56.41 | 53.95 | - | 17.17 | 15.94 | - | 43.33 | 38.35 |
Tab. 2
Carbon sequestration capacity of bivalves cultivated in Yantai sea areas"
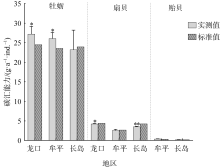
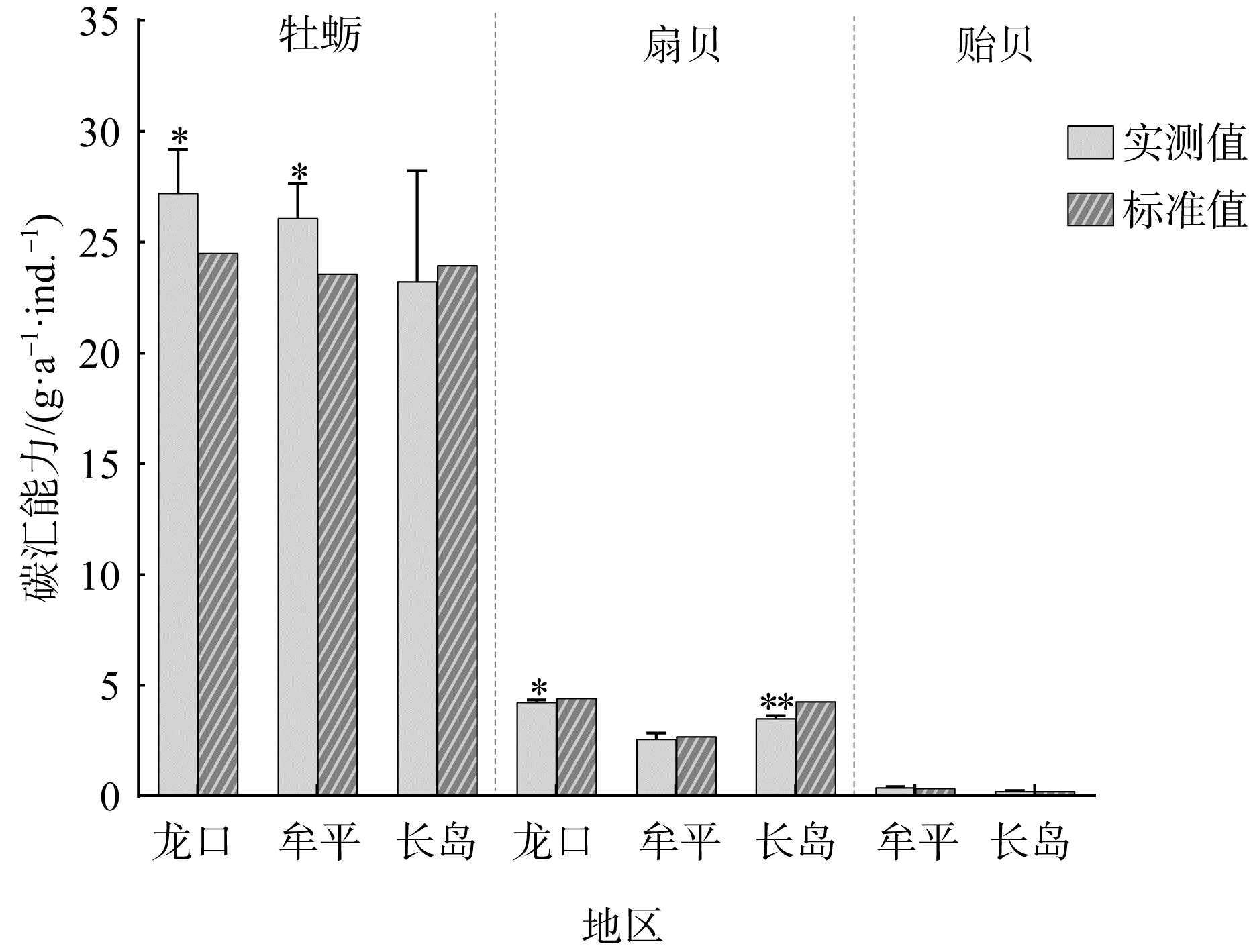
| 贝类 | 体型 | 贝壳固碳能力/(g·a-1·ind.-1) | 软体组织固碳能力(g·a-1·ind.-1) | 总固碳能力(g·a-1·ind.-1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 龙口 | 牟平 | 长岛 | 龙口 | 牟平 | 长岛 | 龙口 | 牟平 | 长岛 | ||
| 牡蛎 | 大型 | 16.12 | 15.14 | 13.82 | 0.52 | 0.59 | 0.35 | 16.64 | 15.73 | 14.17 |
| 中型 | 7.92 | 5.98 | 5.83 | 0.39 | 0.50 | 0.37 | 8.31 | 6.48 | 6.20 | |
| 小型 | 3.23 | 3.69 | 2.74 | 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 3.37 | 3.88 | 2.87 | |
| 平均值 | 9.09 | 8.27 | 7.46 | 0.35 | 0.43 | 0.28 | 9.44 | 8.70 | 7.75 | |
| 扇贝 | 大型 | 1.54 | 0.76 | 1.12 | 0.56 | 0.77 | 0.46 | 2.10 | 1.53 | 1.58 |
| 中型 | 1.00 | 0.43 | 0.86 | 0.37 | 0.44 | 0.23 | 1.37 | 0.86 | 1.08 | |
| 小型 | 0.66 | 0.14 | 0.74 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.78 | 0.21 | 0.87 | |
| 平均值 | 1.07 | 0.44 | 0.91 | 0.35 | 0.43 | 0.27 | 1.42 | 0.87 | 1.17 | |
| 贻贝 | 平均值 | - | 0.29 | 0.20 | - | 0.09 | 0.01 | - | 0.38 | 0.21 |
Tab. 3
The measured and standard reference values of mass ratio of bivalves"
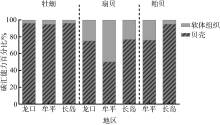
| 贝类 | 体型 | 软体组织质量分数实测值/% | 软体组织质量分数标准参考值/% | 贝壳质量分数实测值/% | 贝壳质量分数标准参考值/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 龙口 | 牟平 | 长岛 | 龙口 | 牟平 | 长岛 | ||||
| 牡蛎 | 大型 | 4.36 | 4.98 | 3.34 | 6.14 | 95.64 | 95.02 | 96.66 | 93.86 |
| 中型 | 5.73 | 7.47 | 6.93 | 94.27 | 92.53 | 93.07 | |||
| 小型 | 5.69 | 5.41 | 6.65 | 94.31 | 94.59 | 93.35 | |||
| 平均值 | 5.26 | 5.95 | 5.64 | 94.74 | 94.05 | 94.36 | |||
| 扇贝 | 大型 | 13.13 | 19.40 | 11.74 | 14.35 | 86.87 | 80.60 | 88.26 | 85.65 |
| 中型 | 12.34 | 18.96 | 9.40 | 87.66 | 81.04 | 90.60 | |||
| 小型 | 8.46 | 13.67 | 7.37 | 91.54 | 86.33 | 92.63 | |||
| 平均值 | 11.31 | 17.34 | 9.50 | 88.69 | 82.66 | 90.50 | |||
| 贻贝 | 平均值 | - | 13.61 | 5.31 | 8.47 | - | 86.39 | 94.69 | 91.53 |
| [1] |
公丕海, 李娇, 关长涛, 等, 2014. 莱州湾增殖礁附着牡蛎的固碳量试验与估算[J]. 应用生态学报, 25(10): 3032-3038.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
顾波军, 朱梓豪, 2021. 浙江省海水贝藻养殖碳汇能力测算及时空演化[J]. 中国渔业经济, 39(6): 88-95.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
郭波, 2015. 中国海水贝藻养殖碳汇潜力的评估研究[J]. 现代农业科技, (19): 226-228.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
贺加贝, 孙俊荣, 赵强, 等, 2022. 烟台市贝藻养殖的碳汇贡献及能力评价[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 44(3): 117-122.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
胡田, 苏洁, 邵魁双, 等, 2024. 贝藻养殖碳汇过程、机制与增汇模式研究进展[J]. 水产科技情报, 51(3): 194-200.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
姜娓娓, 房景辉, 蔺凡, 等, 2022. 胶州湾菲律宾蛤仔生态容量评估及其碳汇功能[J]. 渔业科学进展, 43(5): 61-71.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
蒋增杰, 方建光, 毛玉泽, 等, 2022. 滤食性贝类养殖碳汇功能研究进展及未来值得关注的科学问题[J]. 渔业科学进展, 43(5): 106-114.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
李成林, 宋爱环, 胡炜, 等, 2011. 山东省扇贝养殖产业现状分析与发展对策[J]. 海洋科学, 35(3): 92-98.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
刘超, 2016. 华贵栉孔扇贝不同群体遗传差异分析及生长相关标记筛选[D]. 湛江: 广东海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
罗渡, 汪学杰, 徐猛, 等, 2018. 贝类壳-体质量比和静水沉降特性的相关性[J]. 生态学报, 38(18): 6778-6785.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
聂梦晨, 黄翠玲, 隋琪, 等, 2022. 桑沟湾沉积物有机质的碳氮稳定同位素分析及其来源解析[J]. 渔业科学进展, 43(5): 84-97.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
齐占会, 王珺, 黄洪辉, 等, 2012. 广东省海水养殖贝藻类碳汇潜力评估[J]. 南方水产科学, 8(1): 30-35.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
任黎华, 2014. 桑沟湾筏式养殖长牡蛎及其主要滤食性附着生物固碳功能研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所).
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
唐启升, 方建光, 张继红, 等, 2013. 多重压力胁迫下近海生态系统与多营养层次综合养殖[J]. 渔业科学进展, 34(1): 1-11.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
唐启升, 蒋增杰, 毛玉泽, 2022. 渔业碳汇与碳汇渔业定义及其相关问题的辨析[J]. 渔业科学进展, 43(5): 1-7.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
王俊, 唐启升, 2001. 双壳贝类能量学及其研究进展[J]. 海洋水产研究, 22(3): 80-83.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
温瑞, 2021. 养殖贝类固碳计量与价格核算及对策研究[D]. 厦门: 自然资源部第三海洋研究所.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
徐晓莹, 史文凯, 贺加贝, 等, 2023. 山东省贝藻养殖碳汇能力评估[J]. 中国渔业经济, 41(1): 64-70.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
许瀚之, 张华, 熊盼盼, 等, 2022. 马氏珠母贝异速生长个体对免疫刺激的差异响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 41(5): 180-188.
doi: 10.11978/2021095 |
|
|
|
| [20] |
尹钰文, 车鉴, 魏海峰, 等, 2022. 辽宁省2010-2019年海水养殖贝藻类碳汇能力评估[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 39(9): 17-23.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
于宗赫, 陈康, 杨红生, 等, 2010. 海州湾前三岛海域栉孔扇贝(Chlamys farreri)生长特征与养殖容量的评估[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 41(4): 563-570.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
岳冬冬, 王鲁民, 2012. 我国海水养殖贝类产量与其碳汇的关系[J]. 江苏农业科学, 40(11): 246-248 (in Chinese).
|
| [23] |
张波, 唐启升, 2022. 中国近海渔业生物捕捞群体碳汇评估[J]. 渔业科学进展, 43(5): 126-131.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
张继红, 方建光, 唐启升, 等, 2013. 桑沟湾不同区域养殖栉孔扇贝的固碳速率[J]. 渔业科学进展, 34(1): 12-16.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
张麋鸣, 颜金培, 叶旺旺, 等, 2022. 福建省贝藻类养殖碳汇及其潜力评估[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 41(1): 53-59.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
张明亮, 邹健, 毛玉泽, 等, 2011. 养殖栉孔扇贝对桑沟湾碳循环的贡献[J]. 渔业现代化, 38(4): 13-16, 31.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
张先基, 2013. 基于XRF测碳技术的中国海水贝类养殖碳汇研究[D]. 大连: 辽宁师范大学.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
中华人民共和国自然资源部, 2021. HY/T 0305-2021 养殖大型藻类和双壳贝类碳汇计量方法碳储量变化法[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社.
|
|
Ministry of Natural Resources, People’s Republic of China, 2021a. HY/T 0305-2021 Estimation method of maricultural seaweed and bivalve carbon sink—carbon stock variation method[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China. (in Chinese).
|
|
| [29] |
中华人民共和国自然资源部, 2022. HY/T0349-2022 海洋碳汇核算方法[S] 北京: 中国标准出版社.
|
|
Ministry of Natural Resources, People’s Republic of China, 2022. HY/T0349-2022 Accounting methods for ocean carbon sink[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China. (in Chinese).
|
|
| [30] |
周毅, 杨红生, 刘石林, 等, 2002. 烟台四十里湾浅海养殖生物及附着生物的化学组成、有机净生产量及其生态效应[J]. 水产学报, 26(1): 21-27.
|
|
|
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [1] | ZHAO He, ZHANG Junling, WANG Hao, KE Jingzhao, ZHU Ming, WANG Aimin, LI Xiubao. Preliminary study on carbon sequestration capacity of two hermatypic corals* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 146-154. |
| [2] | ZHOU Linbin, HUANG Liangmin, TAN Yehui. Iron-aluminum hypothesis and the potential of ocean aluminum fertilization as a carbon dioxide removal strategy [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 1-18. |
| [3] | ZHOU Qin, WANG Yu-fen, JIANG Xiu-feng. Giant clam research and prospect of aquaculture in the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2014, 33(2): 87-93. |
|
||