Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (1): 162-171.doi: 10.11978/2024193
• Marine Environmental Science • Previous Articles Next Articles
Study of acute toxicity of Karenia hui on Artemia salina and its hemolytic activity
CHEN Shibing1( ), HUANG Bozhu2, XIE Xuedong2, ZHAO Jinping2, LYU Songhui1, CEN Jingyi1(
), HUANG Bozhu2, XIE Xuedong2, ZHAO Jinping2, LYU Songhui1, CEN Jingyi1( )
)
- 1. Research Center of Harmful Algae and Marine Biology, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
2. Guangdong Ecological and Environmental Monitoring Center, Guangzhou 510308, China
-
Received:2024-10-15Revised:2024-10-23Online:2025-01-10Published:2025-02-10 -
Contact:CEN Jingyi -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Program of China(2022YFC3105201); Construction of a Phytoplankton Biodiversity Database for Typical Water Sources Based on Environmental DNA Technology; Guangdong Provincial Key R&D Program(2023B1111050011)
CLC Number:
- Q89
Cite this article
CHEN Shibing, HUANG Bozhu, XIE Xuedong, ZHAO Jinping, LYU Songhui, CEN Jingyi. Study of acute toxicity of Karenia hui on Artemia salina and its hemolytic activity[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(1): 162-171.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 1
The specific death rate of Artemia salina under exposure to different concentrations of Karenia hui (h-1)"
| 时间段 | 比死亡速率(h-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低密度组 | 中密度组 | 高密度组 | 对照组 | 饥饿组 | |
| 0—24h | 0.11±0.03a | 0.19±0.04b | 0.26±0.02c | 0.03±0.02d | 0.03±0.02d |
| 24—48h | 0.10±0.02a | 0.11±0.04a | 0.13±0.03a | 0.01±0.02b | 0.04±0.03b |
| 48—72h | 0.12±0.04a | 0.08±0.04a | 0.02±0.02b | 0.02±0.02b | 0.01±0.01b |
| 72—96h | 0.08±0.03a | 0.03±0.03bc | 0.00±0.00b | 0.04±0.03c | 0.02±0.02bc |
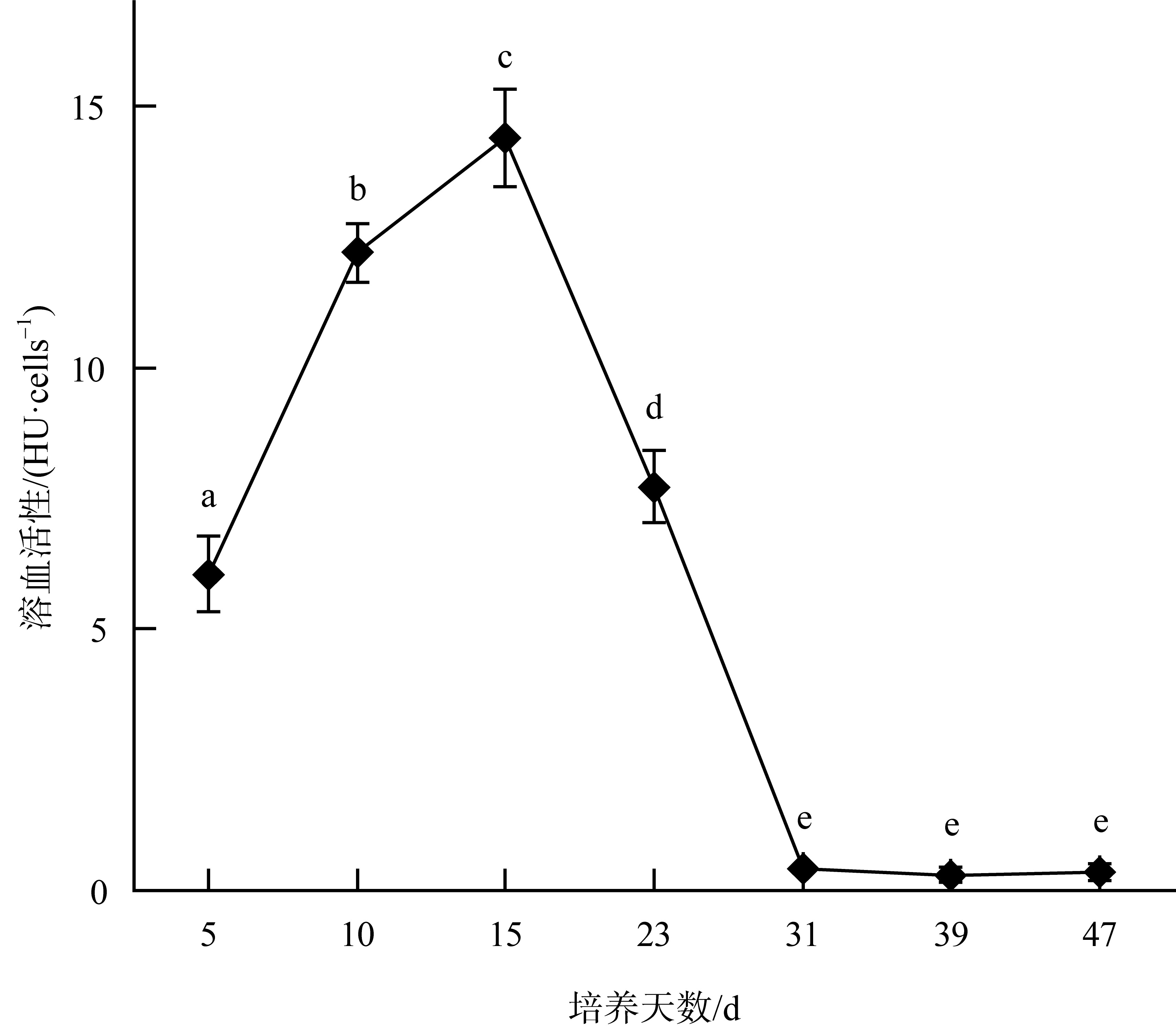
Fig. 4
The death rate of Artemia salina exposed to Karenia hui at different growth stages. “*” indicates significant difference between the study group and the control group (P<0.05), a−f represent the death rates of Artemia salina exposed to K. hui on day 5, 10, 15, 23, 31, and 39 of cultivation, respectively"

Tab. 2
The specific death rate of Artemia salina exposure to Karenia hui for different culture days (h-1)"
| 时间段 | 密度 组别 | 不同培养天数下的比死亡速率(h-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5d | 10d | 15d | 23d | 31d | 39d | ||
| 0—24h | 低 | 0.13±0.03a | 0.13±0.04a | 0.15±0.04a | 0.19±0.02b | 0.12±0.03a | 0.13±0.05a |
| 高 | 0.18±0.02ab | 0.17±0.03ab | 0.20±0.03bc | 0.22±0.03c | 0.15±0.03a | 0.17±0.03ab | |
| 24—48h | 低 | 0.11±0.04a | 0.13±0.06a | 0.13±0.07a | 0.10±0.04a | 0.15±0.03a | 0.14±0.06a |
| 高 | 0.12±0.04a | 0.13±0.03a | 0.11±0.07a | 0.10±0.06a | 0.15±0.03a | 0.13±0.05a | |
| 48—72h | 低 | 0.06±0.06ab | 0.06±0.04a | 0.10±0.02abc | 0.10±0.04abc | 0.11±0.03bc | 0.13±0.05c |
| 高 | 0.06±0.04a | 0.07±0.04a | 0.08±0.07a | 0.08±0.07a | 0.08±0.06a | 0.09±0.03a | |
| 72—96h | 低 | 0.10±0.07a | 0.10±0.03a | 0.03±0.04b | 0.01±0.02b | 0.04±0.04b | 0.03±0.02b |
| 高 | 0.04±0.03a | 0.04±0.04a | 0.02±0.02a | 0.01±0.02c | 0.03±0.03a | 0.02±0.02a | |
| [1] |
曹洁茹, 桓清柳, 吴霓, 等, 2015. 光照、温度和氮磷限制对6种典型鱼毒性藻类生长及产毒的影响[J]. 海洋环境科学, 34(3): 321-329.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈宝红, 谢尔艺, 高亚辉, 等, 2015. 米氏凯伦藻对海洋生物致毒作用的研究进展[J]. 福建水产, 37(3): 241-249.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
崔伟民, 杨维东, 刘洁生, 等, 2009. 米氏凯伦藻溶血毒素的溶血反应特征[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 17(3): 237-241.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
江涛, 吴霓, 钟艳, 等, 2012. 卵圆卡盾藻溶血毒素产毒的影响因素研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 12(2): 1-5.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
林雅柔, 岑竞仪, 王建艳, 等, 2020. 中国南海四种凯伦藻种间作用与溶血活性初步研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 51(6): 1402-1411.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
彭喜春, 杨维东, 刘洁生, 等, 2005. 实验室培养球形棕囊藻溶血毒素的提取、分离及其生成特征[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 13(1): 25-28.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
彭颖慧, 刘洁生, 李宏业, 等, 2009. 赤潮藻溶血活性测定标准的建立[J]. 卫生研究, 38(6): 653-656.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
孙科, 颜天, 周名江, 等, 2010. 米氏凯伦藻对褶皱臂尾轮虫、卤虫和黑褐新糠虾存活的影响[J]. 海洋科学, 34(9): 76-81.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
王朝晖, 尹伊伟, 齐雨藻, 等, 2001. 珠海桂山岛米氏裸甲藻赤潮对鱼鳃损伤的病理学组织观察[J]. 海洋学报, 23(1): 133-137.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
严冰, 岑竞仪, 吕颂辉, 2022. 有害甲藻米氏凯伦藻(Karenia mikimotoi)对海洋青鳉鱼(Oryzias melastigm)的急性毒性效应研究[J]. 海洋环境科学, 41(3): 402-407, 415.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
周成旭, 傅永静, 严小军, 2007. 4种典型有害赤潮原因种的溶血特性研究[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2(1): 78-82.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [1] | ZHOU Jie,YU Ke-fu,LI Shu,CHEN Tian-ran,ZHAO Mei-xia,SHI Qi. Experimental study of the impact of heavy metal copper on reef coral growth [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2011, 30(2): 57-66. |
|
||