Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2026, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 3-16.doi: 10.11978/2025035CSTR: 32234.14.2025035
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
A review of the Holocene hydroclimate in the arid West Asia
WU Lanjun1,2( ), LI Gang1(
), LI Gang1( ), YANG Menglin1,2
), YANG Menglin1,2
- 1State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 511458, China
2University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2025-03-05Revised:2025-03-31Online:2026-01-10Published:2026-01-30 -
Contact:LI Gang. email:gangli@scsio.ac.cn -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(42176079); National Natural Science Foundation of China(41976062); Independent Deployment Project of South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences(SCSIO2023QY05)
CLC Number:
- P532
Cite this article
WU Lanjun, LI Gang, YANG Menglin. A review of the Holocene hydroclimate in the arid West Asia[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2026, 45(1): 3-16.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
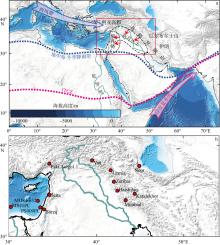
Fig. 1
(a) Schematic map of West Asia illustrating dominant atmospheric circulation patterns; the modern positions of the intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ) and Mediterranean winter precipitation belt are delineated by pink and blue dashed lines, respectively; mid-latitude westerlies and Indian summer monsoon are indicated by blue and pink arrows, respectively; (b) the study area (red rectangle, see detailed view in Fig. 1b) with locations of key paleoclimate archives discussed in this study (red circles): marine sediment records—MS21PC, MD84-632, PS009PC; stalagmite records—Soreq Cave, Jeita Cave, Katalekhor Cave; lake sediment records—Eski Acigöl, Van, Urmia, Zeribar, Mirabad, Haishilan, Neor"

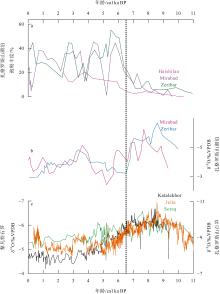
Fig. 2
Comparison of major paleohydrological records in West Asia during the Holocene. (a) Oak pollen abundance records from Lake Zeibar, Lake Mirabad (van Zeist et al, 1977) and Haishilan Wetland (Safaierad et al, 2023); (b) secondary carbonate δ18O records from Lake Zeibar and Lake Mirabad (Stevens et al, 2001; 2006); (c) stalagmite δ18O records from the Levant region [Soreq Cave (Bar-Matthews et al, 2003), Jeita Cave (Cheng et al, 2015)] and Katalekhor Cave in the Zagros Mountains (Andrews et al, 2020)"

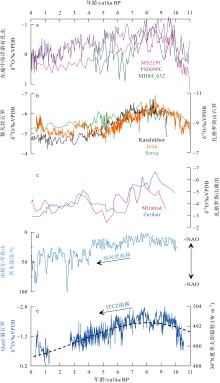
Fig. 3
Comparison of δ18O records from different research archives in West Asia with Indian summer monsoon records. (a) Marine sediment records: MS21PC (Hennekam et al, 2015), MD84-632 (Essallami et al, 2007), PS009PC (Hennekam et al, 2014, 2015); (b) stalagmite δ18O records from the Levant region [Soreq Cave (Bar-Matthews et al, 2003), Jeita Cave (Cheng et al, 2015)] and Katalekhor Cave in the Zagros Mountains (Andrews et al, 2020); (c) lake sediment records: Lake Zeribar (Stevens et al, 2001), Lake Mirabad (Stevens et al, 2006); (d) flood variabilities in southern Alps associated with the North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) (Wirth et al, 2013); (e) summer insolation curves (June-August) for 30°N (Berger et al, 1991) and Qunf Cave stalagmite δ18O records from southern Oman (Fleitmann et al, 2003)"

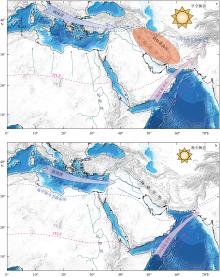
Fig. 4
Schematic models of atmospheric circulation evolution and hydroclimatic system in West Asia during the early Holocene (a) and late Holocene (b). The red shaded area indicates the subtropical high; the pink and blue dashed lines represent the boundary positions of the ITCZ and Mediterranean winter precipitation belt, respectively; the grey-blueish arrows indicate the summer freshwater runoff amount (associated with the δ18O value in the eastern Mediterranean); blue and pink arrows denote the intensity and location of westerlies and Indian summer monsoon, respectively"

| [1] |
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2009.07.017 |
| [2] |
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106433 |
| [3] |
doi: 10.1029/98JD02582 |
| [4] |
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2014.03.001 |
| [5] |
doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.08.005 |
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.1177/0959683610384165 |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(02)01031-1 |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1006/qres.1997.1883 |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1007/s00334-015-0548-5 |
| [11] |
doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(91)90033-Q |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1016/0034-6667(86)90039-4 |
| [13] |
doi: 10.3390/quat2020016 |
| [14] |
doi: 10.1179/146141010X12640787648892 |
| [15] |
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.06.002 |
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1002/2015GL065397 |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1038/srep36975 |
| [19] |
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2015.10.003 |
| [20] |
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2015.07.023 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1177/0959683617721326 |
| [22] |
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2009.12.005 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1177/0959683610362813 |
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.1002/jqs.v22:4 |
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
doi: 10.1175/JHM550.1 |
| [28] |
doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00216-8 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2008.11.007 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2006.04.012 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1126/science.1083130 pmid: 12805545 |
| [32] |
doi: 10.1002/grl.v44.3 |
| [33] |
doi: 10.1006/qres.1998.2031 |
| [34] |
doi: 10.5194/cp-12-273-2016 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1038/nature11593 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1177/0959683608095580 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2015.05.031 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1002/palo.v29.5 |
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2007.01.012 |
| [43] |
doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2007.01.004 |
| [44] |
doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2004.11.022 |
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2003.06.012 |
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
doi: 10.2307/1933099 |
| [50] |
doi: 10.1191/0959683603hl598rp |
| [51] |
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2018.11.010 |
| [52] |
doi: 10.1017/S0003598X0009181X |
| [53] |
doi: 10.1002/jqs.v31.4 |
| [54] |
doi: 10.1191/09596830195744 |
| [55] |
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2017.09.011 |
| [56] |
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2001)014<3192:SAASM>2.0.CO;2 |
| [57] |
doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.01.008 |
| [58] |
doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(95)00070-4 |
| [59] |
doi: 10.1002/joc.v30:7 |
| [60] |
doi: 10.1191/09596830195681 |
| [61] |
doi: 10.1002/jqs.v38.8 |
| [62] |
doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2017.10.001 |
| [63] |
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2015.07.006 |
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
doi: 10.1038/nclimate1592 |
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2006.06.008 |
| [68] |
doi: 10.1191/09596830195762 |
| [69] |
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2009.02.001 |
| [70] |
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2013.02.015 |
| [71] |
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2007.03.014 |
| [72] |
doi: 10.1017/qua.2024.40 |
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
pmid: 17746007 |
| [76] |
doi: 10.1191/0959683605hl846rp |
| [77] |
doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2006.06.006 |
| [78] |
pmid: 17739617 |
| [79] |
doi: 10.1029/2011JD015681 |
| [80] |
doi: 10.1191/0959683603hl653rp |
| [81] |
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2013.09.002 |
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
doi: 10.1038/ngeo3052 |
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
doi: 10.1016/S1040-6182(00)00069-0 |
| [86] |
doi: 10.1126/science.aat9393 |
| [87] |
doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.08.007 |
| [88] |
|
| [1] | LUO Chuanxiu, LIN Gang, THILAKANAYAKA Vidusanka A. M., WEI Haicheng, XIANG Rong, YANG Yiping, WAN Sui, LIANG Shiqing, SU Xiang, DU Shuhuan, ZHANG Lanlan, LIU Jianguo, HUANG Yun, SOE Moe Lwin. Evidence of micro-charcoal deposited in the lower fan of the Bay of Bengal reveals an arid climate during the early Heirich Stadial 1 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2026, 45(1): 117-130. |
| [2] | LUO Chuan-xiu,CHEN Mu-hong,LIU Jian-guo,ZHANG Lan-lan,XIANG Rong,LU Jun. Pollen distribution in marine surface sediments of Guangdong coast and southeast Hainan Island and its environmental significance [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2012, 31(2): 55-61. |
| [3] | ZHANG Yu-lan,PENG Xue-chao,ZHAO Jing. High-resolution palynological record and evolution of vegetation and climate in the low latitude of the South China Sea since 15 kaBP [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2011, 30(5): 67-73. |
|
||

