Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2018, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (6): 49-62.doi: 10.11978/2018011CSTR: 32234.14.2018011
• Marine Geology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of carbonates in Liyue Basin and their tectonic implications
Donghai XU1,2( ), Lijie WANG1,2, Yongjian YAO3, Zhen SUN1(
), Lijie WANG1,2, Yongjian YAO3, Zhen SUN1( ), Ning QIU1
), Ning QIU1
- 1. CAS Key Laboratory of Ocean and Marginal Sea Geology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3. Guangzhou Marine Geological Survey, Guangzhou 510760, China
-
Received:2018-01-15Online:2018-11-20Published:2018-12-24 -
Supported by:National NSFC & Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (U1301233);Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2017A030312002);Marine geological survey of southern South China Sea (DD20160138-04)
CLC Number:
- P588.24
Cite this article
Donghai XU, Lijie WANG, Yongjian YAO, Zhen SUN, Ning QIU. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of carbonates in Liyue Basin and their tectonic implications[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(6): 49-62.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
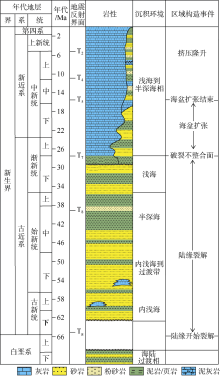
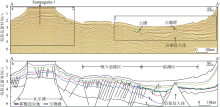
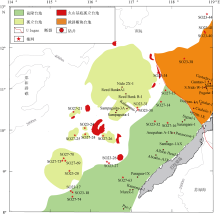
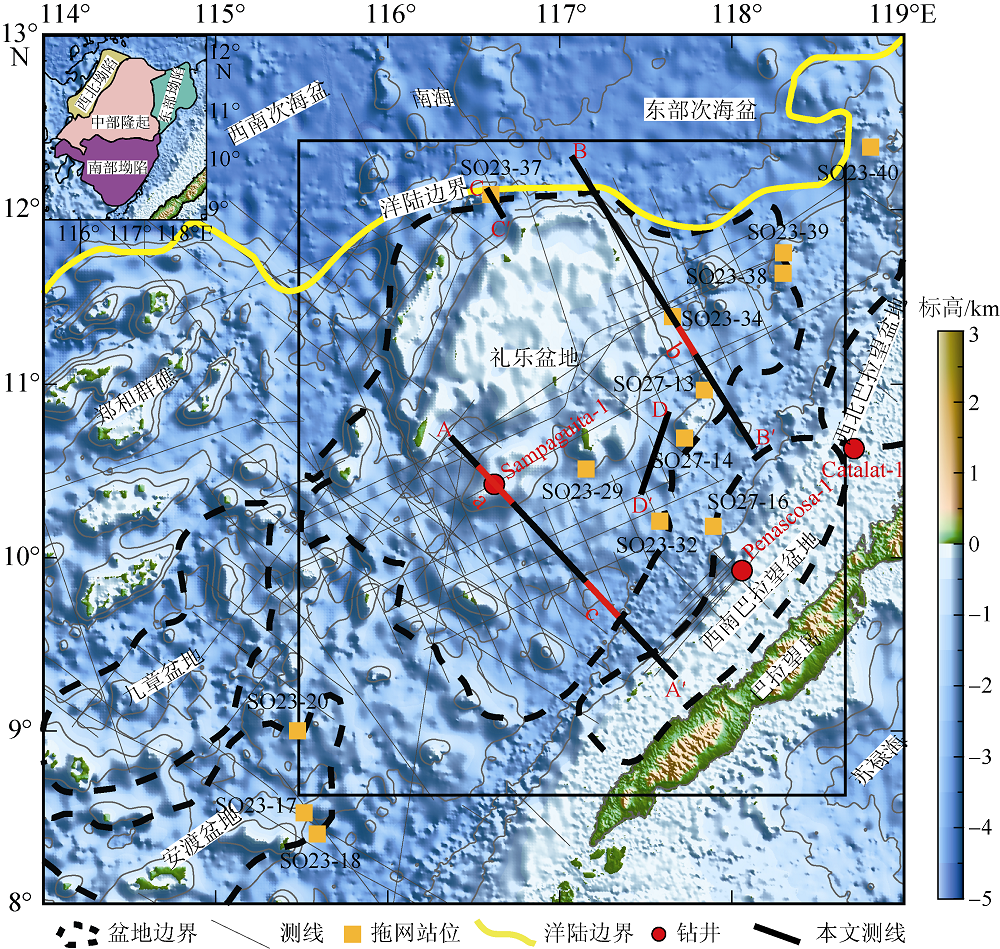
Fig. 1
Locations of Liyue Basin, survey lines, wells, and dredge samples. The basin boundary, COB, survey line data are from Yao et al (2012), the dredging locations are referenced to Kudrass et al (1986). The bathymetric data are from http//www. ngdc.noaa.gov/mgg/bathymetry/relief.html. The Generic Mapping Tools (GMT) software (Wessel et al, 2013) was used in this study"
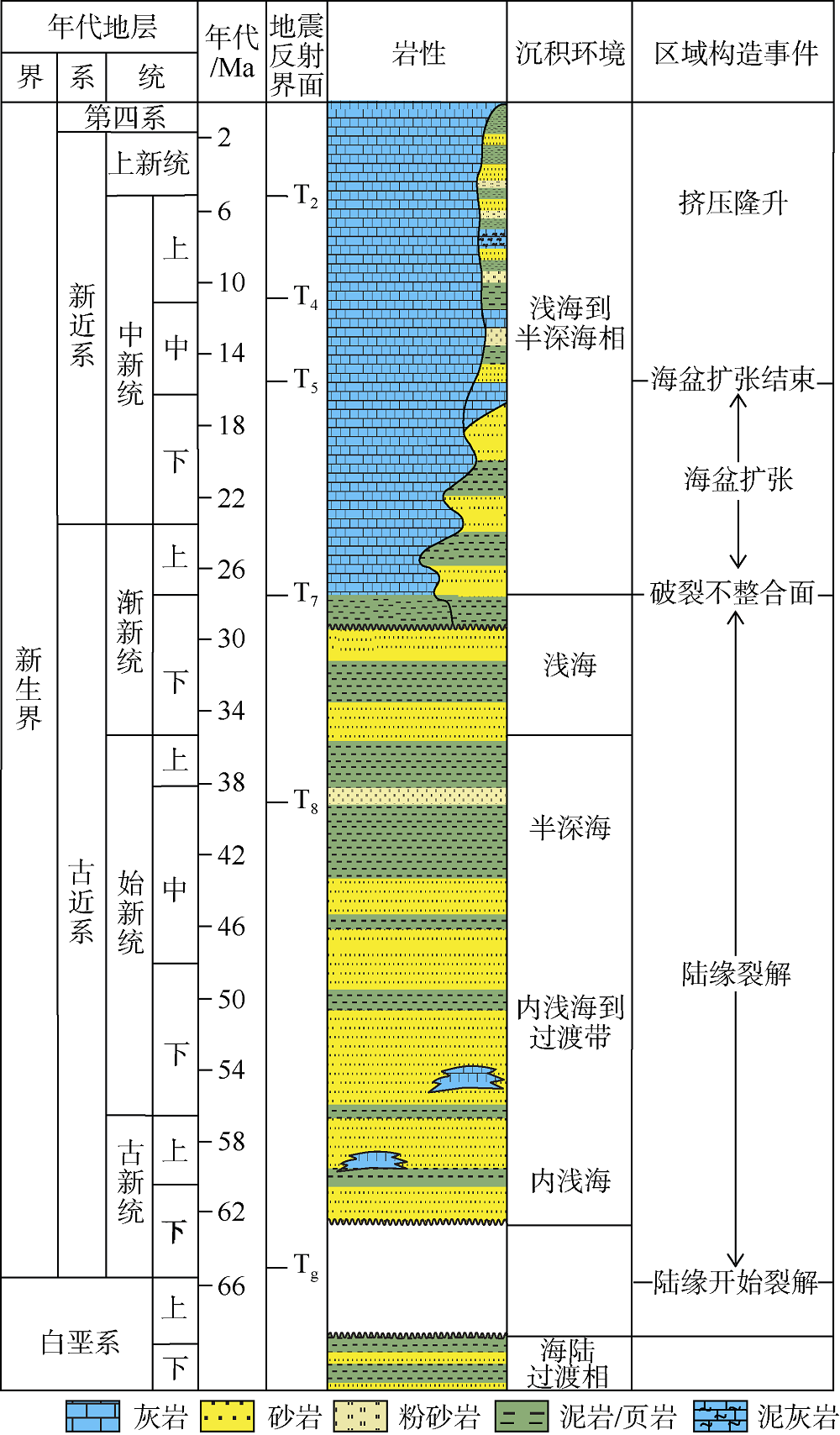
Tab. 1
The dredged samples in Liyue Basin. After Kudrass et al (1986)"
| 拖网站位 | 岩性 | 年代 | 沉积环境 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SO23-39 | 颗粒灰岩、泥质颗粒灰岩 | 早—中中新世 | 浅海相、潟湖相 |
| SO23-38 | 多孔含红藻-圆盾虫粒泥灰岩、生物碎屑粒泥灰岩 | 晚渐新世—中中新世 | 开阔浅海相 |
| SO23-37 | 黏结灰岩、颗粒质泥灰岩 | 中新世 | 开阔浅海相 |
| SO23-34 | 含生物碎屑泥质颗粒灰岩 | 中中新世 | 开阔浅海相 |
| SO23-32 | 颗粒灰岩、内碎屑泥质颗粒灰岩、含超微化石泥灰岩 | 早—中中新世 | 开阔浅海相、半深海相 |
| SO23-29 | 含有孔虫化石泥质颗粒灰岩 | 早—中中新世 | 开阔浅海相 |
| SO23-20 | 黏结灰岩、泥质颗粒灰岩 | 中新世 | 礁相 |
| SO23-18 | 印模粒泥灰岩 | 早—中中新世 | 开阔浅海相 |
| SO23-17 | 颗粒灰岩 | 早中新世早期 | 开阔浅海相 |
| SO27-16 | 印模粒泥灰岩、内碎屑泥粒灰岩 | 晚渐新世—中中新世 | 开阔浅海相 |
| SO27-13 | 富红藻颗粒灰岩、泥灰岩 | 早—中中新世 | 开阔浅海相 |
| SO27-14 | 生物碎屑灰岩、泥灰岩 | 早—中中新世 | 开阔浅海相 |
| SO23-37 | 多孔玄武岩 | 0.4Ma | — |
| SO23-38 | 橄榄玄武岩 | 0.5Ma | — |
| SO23-40 | 多孔斑状玄武岩 | 2.7Ma | — |
| SO27-15 | 斑状安山岩 | 14.7Ma | — |
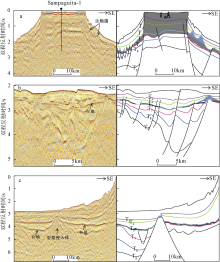
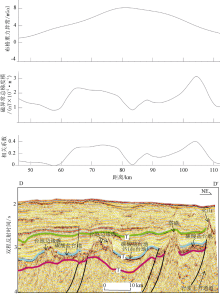
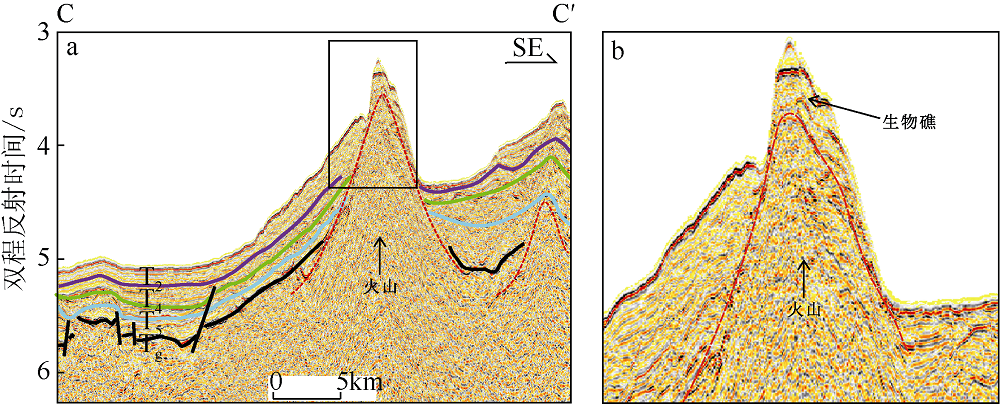
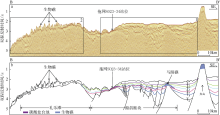
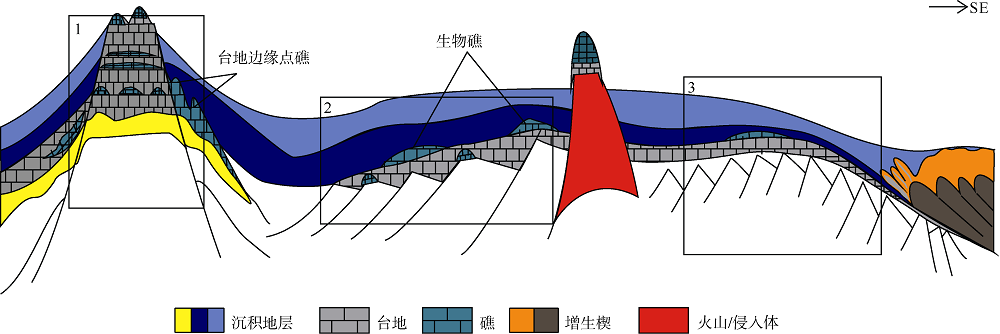
Fig. 4
Three types carbonate platforms in Liyue Basin and their seismic reflection characteristics. a) isolate platform; b) fault-block platform; c) forebulge platform. The seismic characteristics are displayed on the left; the interpretation is on the right. The grey area is platform and the blue is reef."

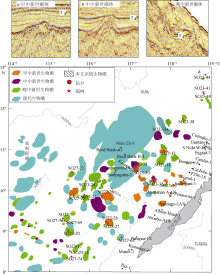
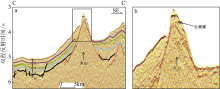
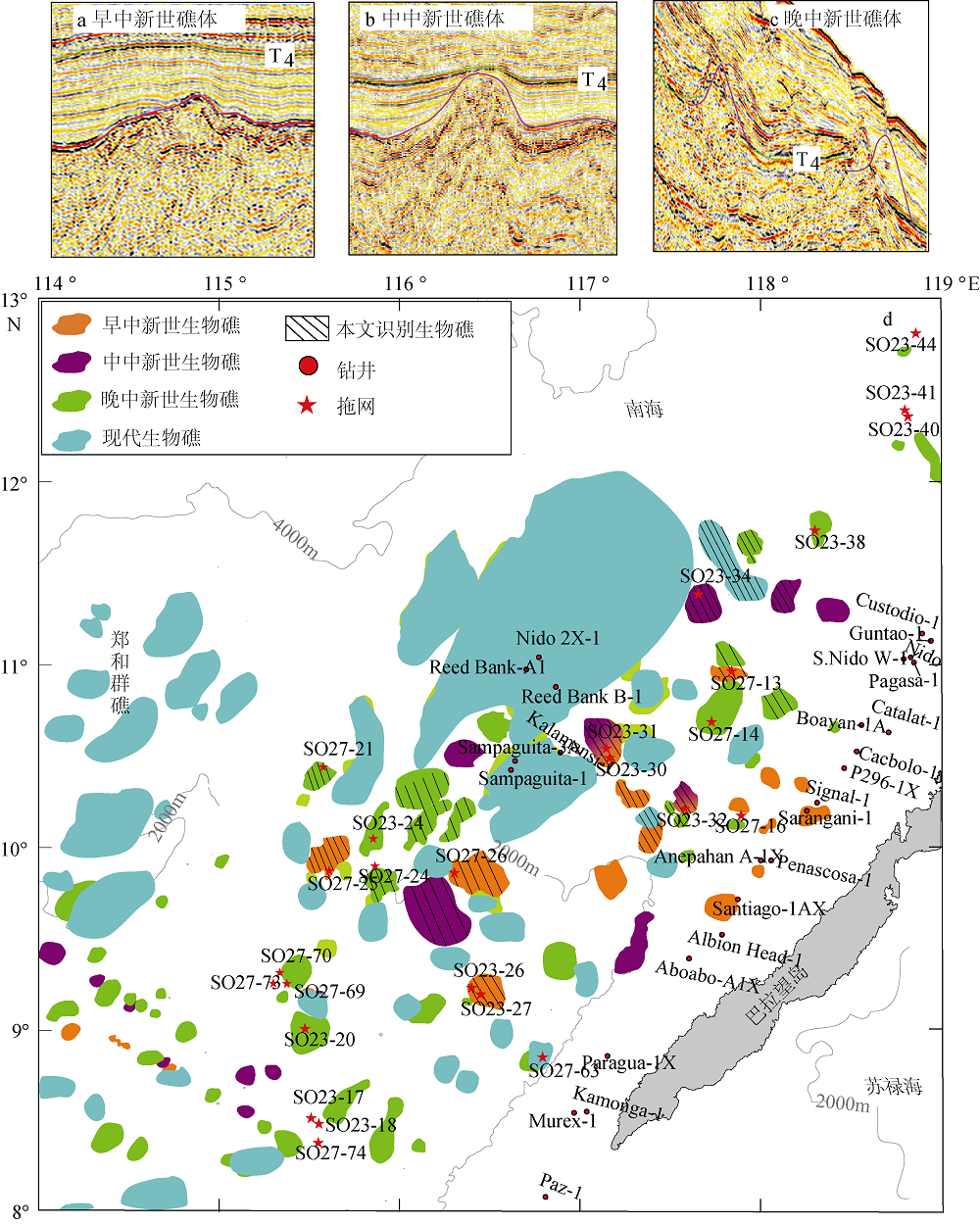
Fig. 9
Distributions of reefs in different stages (a, b, c) from the Miocene till now in Liyue Basin and its surrounding area (d). The reef we interpreted is displayed in the dash area; the Miocene reef is from Letouzey et al (1988) and Steuer et al (2014). The modern reef is from Wu et al (2015)"
| [1] | 陈平, 陆永潮, 许红, 2003. 南沙海域第三纪生物礁层序构成和演化[J]. 地质科学, 38(4): 514-518. |
| CHEN PING, LU YONGCHAO, XU HONG, 2003. Sequence stratigraphy and development of the tertiary reefs in marine area of the Nansha islands[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 38(4): 514-518 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [2] | 丁巍伟, 李家彪, 黎明碧, 2011. 南海南部陆缘礼乐盆地新生代的构造-沉积特征及伸展机制: 来自NH973-2多道地震测线的证据[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 36(5): 895-904. |
| DING WEIWEI, LI JIABIAO, LI MINGBI, 2011. Seismic stratigraphy, tectonic structure and extension model across the Reed Bank Basin in the south margin of South China Sea: evidence from NH973-2 multichannel seismic profile[J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 36(5): 895-904 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [3] | 方鹏高, 丁巍伟, 方银霞, 等, 2015. 南海礼乐滩碳酸盐台地的发育及其新生代构造响应[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 40(12): 2052-2076. |
| FANG PENGGAO, DING WEIWEI, FANG YINXIA, et al, 2015. Development of carbonate platform and its response to Cenozoic tectonic in Reed Bank area, the South China Sea[J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 40(12): 2052-2076 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [4] | 郭建宇, 马朋善, 胡平忠, 等, 2006. 地震-地质方法识别生物礁[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 41(5): 587-591. |
| GUO JIANYU, MA PENGSHAN, HU PINGZHONG, et al, 2006. Identification of reefs by seismic-geologic interpretation approach[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 41(5): 587-591 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [5] | 郭令智, 施央申, 马瑞士, 1983. 西太平洋中、新生代活动大陆边缘和岛弧构造的形成及演化[J]. 地质学报, 57(1): 11-21. |
| GUO LINGZHI, SHI YANGSHEN, MA RUISHI, 1983. On the formation and evolution of the Mesozoic-Cenozoic active continental margin and island arc tectonics of the Western Pacific Ocean[J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 57(1): 11-21 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [6] | 金振奎, 石良, 高白水, 等, 2013. 碳酸盐岩沉积相及相模式[J]. 沉积学报, 31(6): 965-979. |
| JIN ZHENKUI, SHI LIANG, GAO BAISHUI, et al, 2013. Carbonate facies and facies models[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 31(6): 965-979 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [7] | 李文成, 严俊嵩, 王立飞, 等, 2003. 礼乐盆地中生界初探[J]. 南海地质研究, 102-107. |
| LI WENEHENG, YAN JUNSONG, WANG LIFEI, et al, 2003. On the Mesozoic of Liyue Basin, South China Sea[J]. Gresearchof Eological South China Sea, 102-107 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [8] | 林自强, 1994. 地震剖面上的生物礁[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, (1): 127. |
| [9] | 马玉波, 吴时国, 张功成, 等, 2009. 南海北部陆缘深水区礁相碳酸盐岩的地球物理特征[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 33(4): 33-39. |
| MA YUBO, WU SHIGUO, ZHANG GONGCHENG, et al, 2009. Geophysical characteristics of biohermal carbonate in the northern margin deep water area of South China Sea[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum, 33(4): 33-39 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [10] | 邱燕, 1999. 生物礁的地震鉴别方法[J]. 海洋地质, (2): 12-21.邱燕, 王立飞, 黄文凯, 等2016. 中国海域中新生代沉积盆地[M]. 北京: 地质出版社 |
| [11] | 孙珍, 赵中贤, 李家彪, 等, 2011. 南沙地块内破裂不整合与碰撞不整合的构造分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(12): 3196-3209. |
| SUN ZHEN, ZHAO ZHONGXIAN, LI JIABIAO, et al, 2011. Tectonic analysis of the breakup and collision unconformities in the Nansha[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(12): 3196-3209 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [12] | 汪瑞良, 周小康, 曾驿, 等, 2011. 珠江口盆地东部东沙隆起中新世碳酸盐岩与生物礁地震响应特征及其识别[J]. 石油天然气学报(江汉石油学院学报), 33(8): 63-68. |
| WANG RUILIANG, ZHOU XIAOKANG, ZENG YI, et al, 2011. Seismic response characteristics and identification of Miocene carbonate rocks in Dongsha Uplift of Pearl River-month Basin[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology (Journal of Jianghan Petroleum Institute), 33(8): 63-68 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [13] | 王一博, 张功成, 赵志刚, 等, 2016. 南海边缘海构造旋回对沉积充填的控制——以礼乐盆地新生代沉积为例[J]. 石油学报, 37(4): 474-482. |
| WANG YIBO, ZHANG GONGCHENG, ZHAO ZHIGANG, et al, 2016. The control for tectonic cycle of marginal sea on sedimentary fill in South China Sea: a case study of Cenozoic sediment in Lile Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 37(4): 474-482 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [14] | 魏喜, 邓晋福, 谢文彦, 等, 2005. 南海盆地演化对生物礁的控制及礁油气藏勘探潜力分析[J]. 地学前缘, 12(3): 245-252. |
| WEI XI, DENG JINFU, XIE WENYAN, et al, 2005. Constraints on biogenetic reef formation during evolution of the South China Sea and exploration potential analysis[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 12(3): 245-252 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [15] | 吴时国, 赵学燕, 董冬冬, 等, 2011. 南沙海区礼乐盆地碳酸盐台地地震响应及发育演化[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 36(5): 807-814. |
| WU SHIGUO, ZHAO XUEYAN, DONG DONGDONG, et al, 2011. Seismic response and development of carbonate platform in Liyue Basin, Nansha Sea area[J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 36(5): 807-814 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [16] | 吴时国, 张新元, 2015. 南海共轭陆缘新生代碳酸盐台地对海盆构造演化的响应[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 40(2): 234-248. |
| WU SHIGUO, ZHANG XINYUAN, 2015. Response of cenozoic carbonate platform on tectonic evolution in the conjugated margin of South China Sea[J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 40(2): 234-248 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [17] | 阎贫, 刘海龄, 2005. 南海及其周缘中新生代火山活动时空特征与南海的形成模式[J]. 热带海洋学报, 24(2): 33-41. |
| YAN PIN, LIU HAILING, 2005. Temporal and spatial distributions of Meso-Cenozoic igneous rocks over South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 24(2): 33-41 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [18] | 姚伯初, 1994. 中美合作调研南海地质专报[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社. |
| YAO BOCHU, 1994. The geological memoir of South China Sea surveyed jointly by China & USA[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geoscience Press (in Chinese). | |
| [19] | 姚永坚, 杨楚鹏, 李学杰, 等, 2013. 南海南部海域中中新世(T3界面)构造变革界面地震反射特征及构造含义[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(4): 1274-1286. |
| YAO YONGJIAN, YANG CHUPENG, LI XUEJIE, et al, 2013. The seismic reflection characteristics and tectonic significance of the tectonic revolutionary surface of mid-Miocene (T3 seismic interface) in the southern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 56(4): 1274-1286 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [20] | 张广旭, 吴时国, 朱伟林, 等, 2011. 南海北部陆坡流花碳酸盐台地地球物理响应[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 31(4): 105-112. |
| ZHANG GUANGXU, WU SHIGUO, ZHU WEILIN, et al, 2011. Geophysical response of the Liuhua carbonate platform in northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 31(4): 105-112 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [21] | 张莉, 李文成, 曾祥辉, 2003. 礼乐盆地地层发育特征及其与油气的关系[J]. 石油实验地质, 25(5): 469-472, 480. |
| ZHANG LI, LI WENCHENG, ZENG XIANGHUI, 2003. Stratigraphic sequence and hydrocarbon potential in Lile Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Expeximent, 25(5): 469-472, 480 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [22] | 张莉, 李文成, 李国英, 等, 2004. 礼乐盆地生烃系统特征[J]. 天然气工业, 24(6): 22-24. |
| ZHANG LI, LI WENCHENG, LI GUOYING, et al, 2004. Hydrocarbon-generation system characteristics of Lile Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 24(6): 22-24 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [23] | 张永贵, 宋在超, 周小进, 等, 2011. 琼东南盆地南部中新统生物礁的识别[J]. 石油实验地质, 33(3): 307-309, 313. |
| ZHANG YONGGUI, SONG ZAICHAO, ZHOU XIAOJIN, et al, 2011. Identification of reef in Miocene, South of Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 33(3): 307-309, 313 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [24] | 周蒂, 刘海龄, 陈汉宗, 2005. 南沙海区及其周缘中-新生代岩浆活动及构造意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 29(3): 354-363. |
| ZHOU DI, LIU HAILING, CHEN HANZONG, 2005. Mesozoic-Cenozoic magmatism in southern South China Sea and its surrounding areas and its implications to tectonics[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 29(3): 354-363 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [25] | 朱伟林, 1987. 珠江口盆地中新世碳酸盐岩及生物礁相研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 7(2): 11-20. |
| ZHU WEILIN, 1987. Study of Miocene carbonate and reef facies in the Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 7(2): 11-20 (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | AURELIO M A, FORBES M T, TAGUIBAO K J L, et al, 2014. Middle to Late Cenozoic tectonic events in south and central Palawan (Philippines) and their implications to the evolution of the south-eastern margin of South China Sea: Evidence from onshore structural and offshore seismic data[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 58: 658-673. |
| [27] | AURELIO M A, TAGUIBAO K J L, MORADO A A, et al, 2015. Twisted Nido limestone: mark of a mid tertiary bimodal deformation at the thinned SE edge of Sundaland [G]. Kota Kinabalu, Sabah, Malaysia: Tectonic Evolution and Sedimentation ofSouth China Sea Region. |
| [28] | BRIAIS A, PATRIAT P, TAPPONNIER P, 1993. Updated interpretation of magnetic anomalies and seafloor spreading stages in the South China Sea: implications for the Tertiary tectonics of Southeast Asia[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 98(B4): 6299-6328. |
| [29] | CHANG J H, HSU H H, LIU C S, et al, 2017. Seismic sequence stratigraphic analysis of the carbonate platform, north offshore Taiping Island, Dangerous Grounds, South China Sea[J]. Tectonophysics, 702: 70-81. |
| [30] | CULLEN A B, 2010. Transverse segmentation of the Baram- Balabac Basin, NW Borneo: refining the model of Borneo's tectonic evolution[J]. Petroleum Geoscience, 16(1): 3-29. |
| [31] | DING WEIWEI, LI JIABIAO, DONG CONGZHI, et al, 2014. Carbonate platforms in the Reed Bank area, South China Sea: seismic characteristics, development and controlling factors[J]. Energy Exploration & Exploitation, 32(1): 243-262. |
| [32] | DING WEIWEI, LI JIABIAO, DONG CONGZHI, et al, 2015. Oligocene-Miocene carbonates in the Reed Bank area, South China Sea, and their Tectono-sedimentary evolution[J]. Marine Geophysical Research, 36(2-3): 149-165. |
| [33] | DU BOIS E P, 1981. Review of principal hydrocarbon- bearing basins of the South China Sea area[J]. Energy, 6(11): 1113-1140. |
| [34] | DUNG T T, QUE B C, MINH N Q, 2016. Distribution of eruptive volcanic basalt in the South China Sea and adjacent areas by interpreting gravity, magnetic and seismic data[J]. Russian Journal of Pacific Geology, 10(1): 1-12. |
| [35] | DUNG T T, QUE B C, PHUONG N H, 2013. Cenozoic basement structure of the South China Sea and adjacent areas by modeling and interpreting gravity data[J]. Russian Journal of Pacific Geology, 7(4): 227-236. |
| [36] | FOURNIER F, MONTAGGIONI L, BORGOMANO J, 2004. Paleoenvironments and high-frequency cyclicity from Cenozoic South-East Asian shallow-water carbonates: a case study from the Oligo-Miocene buildups of Malampaya (Offshore Palawan, Philippines)[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 21(1): 1-21. |
| [37] | FRANKE D, SAVVA D, PUBELLIER M, et al, 2014. The final rifting evolution in the South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 58: 704-720. |
| [38] | FULTHORPE C S, SCHLANGER S O, 1989. Paleo- oceanographic and tectonic settings of early Miocene reefs and associated carbonates of offshore Southeast Asia[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 73(6): 729-756. |
| [39] | HALL R, ALI J R, ANDERSON C D, 1995. Cenozoic motion of the Philippine Sea Plate: palaeomagnetic evidence from eastern Indonesia[J]. Tectonics, 14(5): 1117-1132. |
| [40] | HAQ B U, HARDENBOL J, VAIL P R, 1987. Chronology of fluctuating sea levels since the Triassic[J]. Science, 235(4793): 1156-1167. |
| [41] | HINZ K, SCHLÜTER H U, 1985. Geology of the dangerous grounds, South China Sea, and the continental margin off Southwest Palawan: results of SONNE cruises SO-23 and SO-27[J]. Energy, 10(3-4): 297-315. |
| [42] | HOLLOWAY N, 1981. The North Palawan Block, Philippines: its relation to the Asian Mainland and its role in the evolution of the South China Sea[J]. Geological Society of Malaysia Bulletin, 14: 19-58. |
| [43] | HUTCHISON C S, 1991. Neogene arc—continent collision in Sabah, Northern Borneo (Malaysia)—Comment[J]. Tectonophysics, 200(1-3): 325-329. |
| [44] | KUDRASS H R, WIEDICKE M, CEPEK P, 1986. Mesozoic and Cainozoic rocks dredged from the South China Sea (Reed Bank area) and Sulu Sea and their significance for plate- tectonic reconstructions[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 3(1): 19-30. |
| [45] | LETOUZEY J, SAGE L, MÜLLER C, 1988. Geological and structural map of eastern Asia, 1:2,500,000: introductory notes[J]. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin. |
| [46] | LI CHUNFENG, ZHOU ZUYI, LI JIABIAO, et al, 2008. Magnetic zoning and seismic structure of the South China Sea Ocean basin[J]. Marine Geophysical Researches, 29(4): 223-238. |
| [47] | LI SHULING, MENG XIAOHONG, GUO LIANGHUI, et al, 2010. Gravity and magnetic anomalies field characteristics in the South China Sea and its application for interpretation of igneous rocks[J]. Applied Geophysics, 7(4): 295-305. |
| [48] | RANGIN C, BELLON H, BENARD F, et al, 1990. Neogene arc-continent collision in Sabah, Northern Borneo (Malaysia)[J]. Tectonophysics, 183(1-4): 305-319. |
| [49] | REHM S K, 2003. The Miocene carbonates in time and space on-and offshore SW Palawan, Philippines[D]. Kiel: Christian- Albrechts Universität Kiel. |
| [50] | SALDIVAR-SALI A, CAAGUSAN N L, RIEZA R S, 1981. Paleogene petroleum possibilities in the Philippines[J]. Energy, 6(11): 1207-1224. |
| [51] | SALES A O, JACOBSEN E C, MORADO JR A A, et al, 1997. The petroleum potential of deep-water northwest Palawan Block GSEC 66[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 15(2-3): 217-240. |
| [52] | SCHLÜTER H U, HINZ K, BLOCK M, 1996. Tectono- stratigraphic terranes and detachment faulting of the South China Sea and Sulu Sea[J]. Marine Geologys, 130(1-2): 39-51, 58-78. |
| [53] | SONG XIAOXIAO, LI CHUNFENG, YAO YONGJIAN, et al, 2017. Magmatism in the evolution of the South China Sea: Geophysical characterization[J]. Marine Geology, 394: 4-15. |
| [54] | STEUER S, FRANKE D, MERESSE F, et al, 2013. Time constraints on the evolution of southern Palawan Island, Philippines from onshore and offshore correlation of Miocene limestones[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 76: 412-427. |
| [55] | STEUER S, FRANKE D, MERESSE F, et al, 2014. Oligocene- Miocene carbonates and their role for constraining the rifting and collision history of the Dangerous Grounds, South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 58: 644-657. |
| [56] | TAMAKI K, 1995. Opening tectonics of the Japan Sea[M]//TAYLOR B. Backarc Basins: Tectonics and Magmatism. Boston, MA:Springer : 407-420. |
| [57] | TAYLOR B, HAYES D E, 1980. The tectonic evolution of the South China Basin[M]//HAYES D E. The Tectonic and Geologic Evolution of Southeast Asian Seas and Islands, Volume 23. Washington: American Geophysical Union: 89-104. |
| [58] | TAYLOR B, HAYES D E, 1983. Origin and history of the South China Sea basin[M]//HAYES D E. The Tectonic and Geologic Evolution of Southeast Asian Seas and Islands: Part 2, Volume 27. Washington: American Geophysical Union: 23-56. |
| [59] | WANG HONGLI, ZHAO QIANG, WU SHIGUO, et al, 2018. Post-rifting magmatism and the drowned reefs in the Xisha Archipelago domain[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 17(1): 195-208. |
| [60] | WESSEL P, SMITH W H F, SCHARROO R, et al, 2013. Generic mapping tools: improved version released[J]. EOS, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 94(45): 409-410. |
| [61] | WILLIAMS H H, 1997. Play concepts-northwest Palawan, Philippines[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 15(2-3): 251-273. |
| [62] | WOLFART R, CEPEK P, GRAMANN F, et al, 1986. Stratigraphy of Palawan island, Philippines[J]. Newsletters on Stratigraphy, 16: 19-48. |
| [63] | YAO YONGJIAN, LIU HAILING, YANG CHUPENG, et al, 2012. Characteristics and evolution of Cenozoic sediments in the Liyue Basin, SE South China Sea[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 60: 114-129. |
| [1] | LI Ao, FENG Yang, WANG Yuntao, XUE Huijie. Spatiotemporal variation of water area with high chlorophyll a concentration in the South China Sea based on OC-CCI data* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 77-89. |
| [2] | ZHANG Yun-fan, HU Deng-ke, WANG Wan-yin, QIU Zhi-yun, LI Fu-cheng. A comparison of crustal stretching characteristics between northern and southern slopes of the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2012, 31(3): 137-143. |
|
||