

Journal of Tropical Oceanography >
Comparative genomic analysis of the distribution and evolution of quorum sensing pathways in the Vibrio genus
Copy editor: YAO Yantao
Received date: 2021-02-24
Revised date: 2021-04-15
Online published: 2021-04-22
Supported by
Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou, China(201804010437)
Quorum sensing (QS) is a process of bacterial cell-cell communication in which bacteria can monitor their population density by detection of extracellular autoinducer. QS allows the bacteria to switch between two kinds of gene expression modes: The program is suitable for individual development at low cell density, while favoring community at high cell density. Presently, there are mainly seven kinds of QS signaling molecules, including oligopeptides, AHL (Acylated Homoserine Lactones), AI-2 (Autoinducer-2), CAI-1 (Cholera Autoinducer-1), PQS (Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal), AI-3 (Autoinducer-3), and DSF (Diffusible Signal Factor). Among them, oligopeptides mainly exist in gram-positive bacteria, and the others are commonly found in gram-negative bacteria. Species of the Vibrio genus are important pathogens for human and aquaculture. Since traditional antibiotic treatment has a strong selection pressure leading to increasing number of drug-resistant Vibrio and increasing serious problems, QS quenching is believed as one alternative strategy of the most potential to combat bacterial infection. Thus, it is necessary to investigate the distribution of QS pathways among the Vibrio genus. Among the 46 whole genome sequenced Vibrio species, we found that only three pathways exist in Vibrio species, including AHL, AI-2 and CAI-1 pathways. Specifically, five Vibrio species contain the above three pathways, and 30 strains contain both AI-2 and CAI-1 pathways. However, none of the 46 Vibrio species have the PQS, AI-3 and DSF pathways. In addition, the distribution of QS pathways in Vibrio is related to their phylogeny, suggesting that species with the same QS pathway(s) are close relatives, which indicates that the genes of this pathway evolved from their common ancestor. This study provides useful information for QS quenching against Vibrio pathogens by targeting the AI-2 and CAI-1 QS pathways.
MAO Yingjin , GAO Beile . Comparative genomic analysis of the distribution and evolution of quorum sensing pathways in the Vibrio genus[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022 , 41(1) : 28 -41 . DOI: 10.11978/2021025
表1 革兰氏阴性菌群体感应通路Tab. 1 Quorum sensing pathway of gram-negative bacteria |
| 合成酶 | 信号分子 | 受体蛋白 | 模式菌株 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LuxI | AHL | LuxR | 费氏弧菌 Aliivibrio fischeri | Eberhard et al, 1981 |
| LuxS | AI-2 | LuxPQ/LsrB/RbsB | 霍乱弧菌 Vibrio cholerae | Bassler et al, 1993 |
| CqsA | CAI-1 | CqsS | 霍乱弧菌 Vibrio cholerae | Miller et al, 2002 |
| PqsA/B/C/D/E/H | PQS | PqsR | 铜绿假单胞菌 Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Pesci et al, 1999 |
| LuxS | AI-3 | QseBC/QseEF | 大肠杆菌 Escherichia coli O157:H7 | Sperandio et al, 2003 |
| RpfF | DSF | RpfCG/RpfR | 野油菜黄单胞菌 Xanthomonas campestris | Barber et al, 1997 |
表2 菌株信息Tab. 2 Strain information |
| 物种名称 | 菌株 | 基因组编号 | 基因组大小/Mb | 编码序列数目/个 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vibrio alfacsensis | CAIM 1831 | GCA_003544875.1 | 4.91 | 3830 |
| Vibrio alginolyticus | FA2 | GCA_011801435.1 | 5.25 | 4598 |
| Vibrio anguillarum | VIB12 | GCA_002310335.1 | 4.90 | 4091 |
| Vibrio antiquarius | EX25 | GCA_000024825.1 | 5.09 | 4451 |
| Vibrio aphrogenes | CA-1004 | GCA_002157735.2 | 3.38 | 2881 |
| Vibrio astriarenae | HN897 | GCA_010587385.1 | 4.80 | 4176 |
| Vibrio breoganii | FF50 | GCA_001677275.1 | 4.49 | 3978 |
| Vibrio campbellii | BoB-90 | GCA_002906455.1 | 6.17 | 5407 |
| Vibrio casei | DSM 22364 | GCA_002218025.2 | 4.14 | 3601 |
| Vibrio chagasii | ECSMB14107 | GCA_004022545.1 | 5.55 | 4448 |
| 物种名称 | 菌株 | 基因组编号 | 基因组大小/Mb | 编码序列数目/个 |
| Vibrio cholerae | 10432-62 | GCA_000969265.1 | 4.08 | 3546 |
| Vibrio cidicii | 2756-81 | GCA_009763805.1 | 4.75 | 3492 |
| Vibrio cincinnatiensis | 2070-81 | GCA_009763705.1 | 3.81 | 3284 |
| Vibrio coralliilyticus | RE22 | GCA_003391375.1 | 5.78 | 5064 |
| Vibrio cyclitrophicus | ECSMB14105 | GCA_005144905.1 | 5.07 | 4283 |
| Vibrio diabolicus | FA3 | GCA_011801455.1 | 5.11 | 4501 |
| Vibrio europaeus | NPI-1 | GCA_013154935.1 | 5.45 | 4782 |
| Vibrio fluvialis | FDAARGOS_104 | GCA_001558415.2 | 4.83 | 4338 |
| Vibrio furnissii | FDAARGOS_777 | GCA_006364355.1 | 4.99 | 4466 |
| Vibrio gazogenes | ATCC 43942 | GCA_002196515.1 | 4.79 | 4070 |
| Vibrio harveyi | ATCC 33843 | GCA_000770115.2 | 5.88 | 5166 |
| Vibrio hyugaensis | 090810a | GCA_002906655.1 | 5.61 | 4845 |
| Vibrio jasicida | 090810c | GCA_002887615.1 | 5.99 | 5188 |
| Vibrio mediterranei | QT6D1 | GCA_002214345.1 | 5.81 | 5146 |
| Vibrio metoecus | 08-2459 | GCA_009665275.1 | 3.99 | 3518 |
| Vibrio metschnikovii | 9502-00 | GCA_009763765.1 | 3.62 | 3118 |
| Vibrio mimicus | SCCF01 | GCA_001767355.1 | 4.48 | 3925 |
| Vibrio natriegens | CCUG 16371 | GCA_001680045.1 | 5.16 | 4451 |
| Vibrio navarrensis | 2462-79 | GCA_009763725.1 | 4.78 | 4093 |
| Vibrio nigripulchritudo | SFn1 | GCA_000801275.1 | 6.32 | 5545 |
| Vibrio owensii | XSBZ03 | GCA_002021755.1 | 5.89 | 5112 |
| Vibrio panuliri | JCM 19500 | GCA_009938205.1 | 4.86 | 4235 |
| Vibrio ponticus | DSM 16217 | GCA_009938225.1 | 4.80 | 4098 |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus | VPD14 | GCA_004006515.1 | 5.17 | 4531 |
| Vibrio qinghaiensis | Q67 | GCA_002257545.1 | 4.02 | 3373 |
| Vibrio rotiferianus | B64D1 | GCA_002214395.1 | 5.28 | 4593 |
| Vibrio rumoiensis | FERM P-14531 | GCA_002218045.2 | 4.21 | 3605 |
| Vibrio scophthalmi | VS-12 | GCA_001685465.1 | 4.93 | 4206 |
| Vibrio sp | 2521-89 | GCA_002216685.1 | 4.12 | 3539 |
| Vibrio splendidus | BST398 | GCA_003345295.1 | 5.51 | 4582 |
| Vibrio taketomensis | C4III291 | GCA_009938185.1 | 4.36 | 3526 |
| Vibrio tapetis | CECT4600 | GCA_900233005.1 | 5.73 | 4800 |
| Vibrio tasmaniensis | LGP32 | GCA_000091465.1 | 4.97 | 4169 |
| Vibrio tritonius | JCM 16456 | GCA_001547935.1 | 5.22 | 4549 |
| Vibrio tubiashii | ATCC 19109 | GCA_000772105.1 | 5.54 | 4946 |
| Vibrio vulnificus | 07-2444 | GCA_009764115.1 | 5.23 | 4554 |
表3 查询序列蛋白的结构域组成Tab. 3 Domain composition of the query protein |
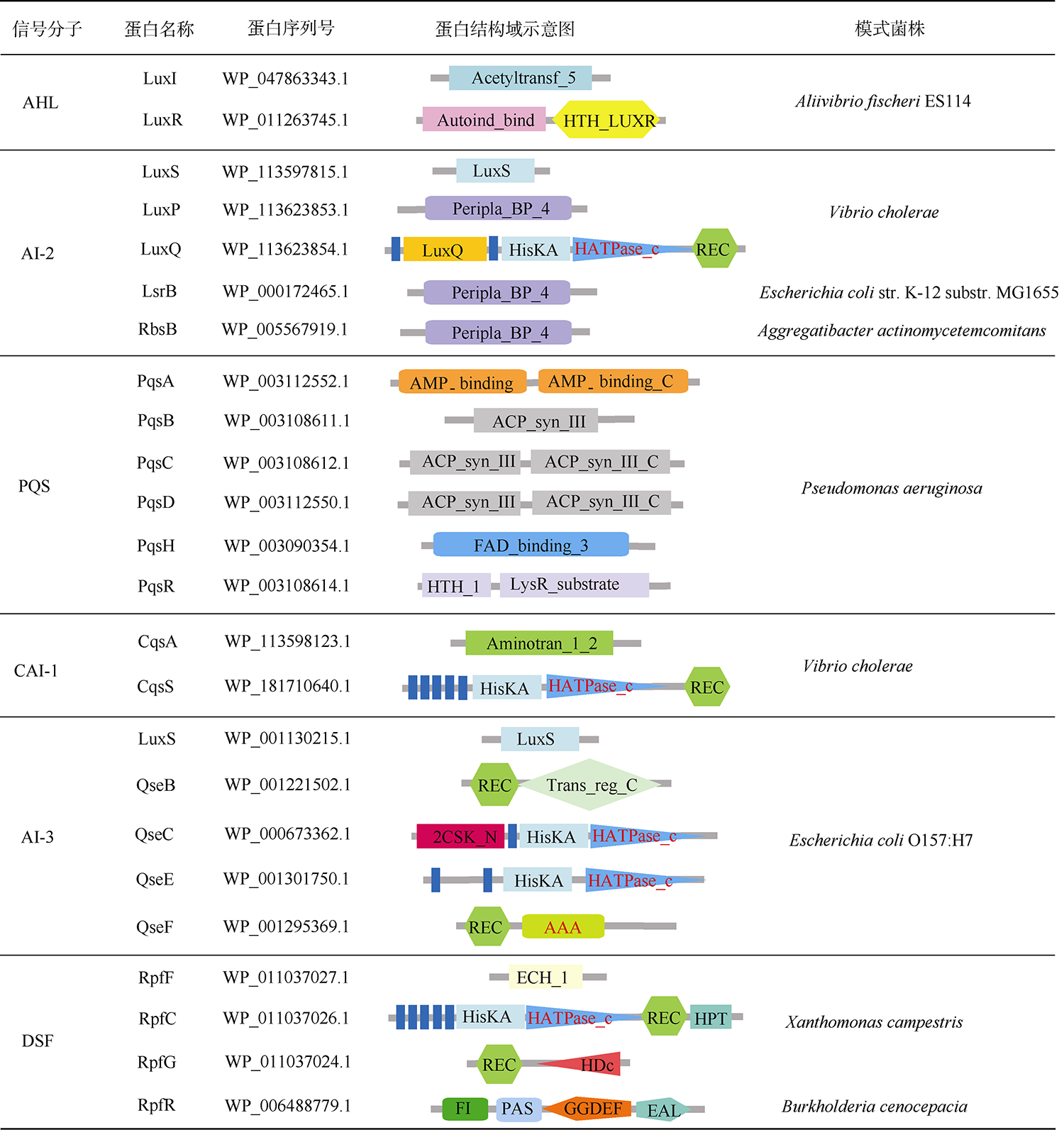 |
注: Acetyltransf_5表示乙酰转移酶结构域(Acetyltransferase domain); Autoind_bind表示自诱导剂结合结构域(Autoinducer binding domain); HTH_LUXR表示Lux操纵子结构域(Helix_turn_helix, Lux Regulon domain); LuxS表示S-核糖基同型半胱氨酸裂解酶结构域(S-ribosylhomocysteine lyase domain); Peripla_BP_4表示周质结合蛋白结构域(Periplasmic binding protein domain); LuxQ表示LuxQ周质空间结构域(LuxQ Periplasmic domain); HisKA表示组氨酸激酶结构域(Histidine kinases domain); HATPase_c表示组氨酸激酶样ATP酶的C端结构域(Histidine kinase-like ATPases C-terminal domain); REC表示CheY同源受体结构域(CheY-homologous receiver domain); AMP_binding表示AMP结合酶结构域(AMP_binding enzyme domain); AMP_binding_C表示AMP结合酶的C端结构域(AMP_binding enzyme C-terminal domain); ACP_syn_Ⅲ表示酰基载体蛋白合成酶Ⅲ结构域(Acyl carrier protein synthase III domain); ACP_syn_Ⅲ_C表示酰基载体蛋白合成酶Ⅲ的C端结构域(Acyl carrier protein synthase III C terminal domain); FAD_binding_3表示单加氧酶结构域(Monooxygenase domain); HTH_1表示螺旋转角螺旋结构域(Helix-turn-helix domain); LysR_substrate表示LysR底物结合结构域(LysR substrate binding domain); Aminotran_1_2表示转氨酶结构域(Aminotransferase domain); Trans_reg_C表示转录调节蛋白的C端结构域(Transcriptional regulatory protein C-terminal domain); 2CSK_N表示双组分系统中激酶的N端结构域(Two-component sensor kinase N-terminal domain); AAA表示与多种细胞活性相关的三磷酸腺苷酶结构域(ATPases associated with a variety of cellular activities domain); ECH_1表示烯醇式辅酶A水合酶/异构酶结构域(Enoyl-CoA hydratase/isomerase domain); HPT表示组氨酸磷酸转移酶结构域(Histidine Phosphotransfer domain); HDc表示金属依赖的磷酸水解酶结构域(Metal dependent phosphohydrolases domain); FI表示RpfF相互作用结构域(RpfF interaction domain); PAS表示PAS结构域(PAS domain); GGDEF表示双鸟苷酸环化酶结构域(Diguanylate cyclase domain); EAL表示双鸟苷酸磷酸二酯酶结构域(Diguanylate phosphodiesterase domain) |
图2 46株弧菌的系统进化树线段0.05代 Fig. 2 Phylogenetic tree of 46 Vibrio species |
表4 AHL信号分子群体感应通路统计Tab. 4 Statistics of quorum sensing pathways directed by AHL signal |
 |
注: 表格中橙色和黄色箭头分别代表AHL信号通路的合成酶和受体蛋白的编码基因, 箭头上标注相应基因的locus tag编号 |
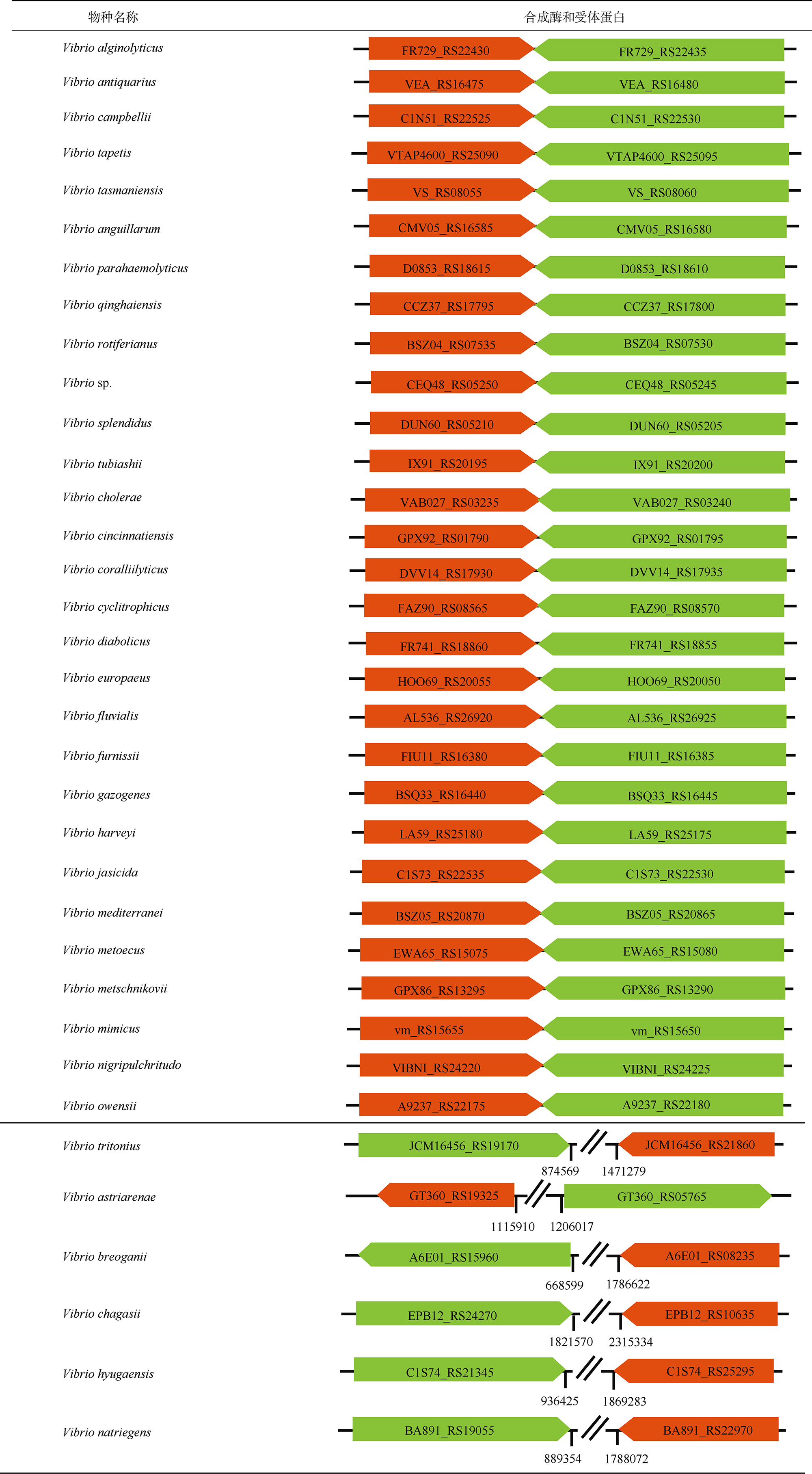
表5 AI-2信号分子群体感应通路统计Tab. 5 Statistics of quorum sensing pathways directed by AI-2 signal |
 |
|---|
 |
注: 表格中的粉色箭头代表AI-2信号通路的合成酶编码基因; 蓝色、绿色和橙色箭头分别代表不同受体蛋白的编码基因, 其中蓝色箭头代表受体蛋白LuxP, 绿色箭头代表受体蛋白LuxQ, 橙色箭头代表受体蛋白RbsB, 箭头上标注的是相应基因的locus tag编号; 灰色箭头代表rbs开放阅读框的其他相关编码基因。双斜线(断开)表示基因间不连续, 双斜线两侧下方数字分别表示基因在基因组上的位置 |
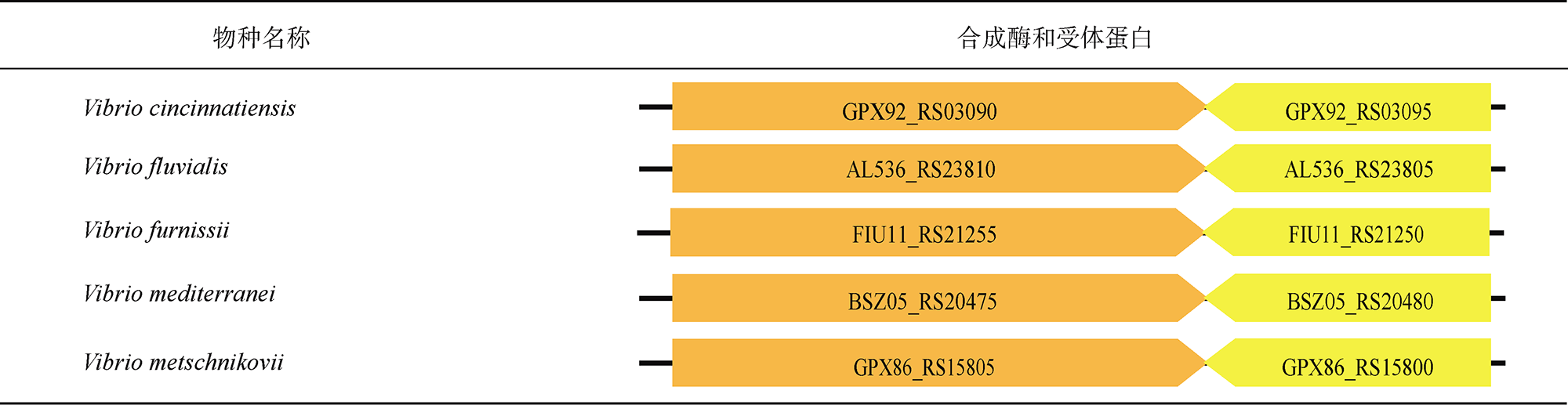
表6 CAI-1信号分子群体感应通路统计Tab. 6 Statistics of quorum sensing pathways directed by CAI-1 signal |
 |
 |
注: 表格中的橙色和绿色箭头分别代表CAI-1信号通路的合成酶和受体蛋白的编码基因, 箭头上标注相应基因的locus tag编号; 双斜线(断开)表示基因间不连续, 双斜线两侧下方数字分别表示基因在基因组上的位置 |
| [1] |
郑林, 祝令伟, 郭学军, 等, 2019. 副溶血性弧菌耐药基因的研究进展[J]. 中国兽药杂志, 53(6): 80-85.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |