Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 28-41.doi: 10.11978/2021025CSTR: 32234.14.2021025
• Marine Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparative genomic analysis of the distribution and evolution of quorum sensing pathways in the Vibrio genus
MAO Yingjin1,2( ), GAO Beile1(
), GAO Beile1( )
)
- 1. CAS Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, Guangdong Key Laboratory of Marine Materia Medica, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049
-
Received:2021-02-24Revised:2021-04-15Online:2022-01-10Published:2021-04-22 -
Contact:GAO Beile E-mail:maoyingjin18@mails.ucas.edu.cn;gaob@scsio.ac.cn -
Supported by:Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou, China(201804010437)
CLC Number:
- P735.51
Cite this article
MAO Yingjin, GAO Beile. Comparative genomic analysis of the distribution and evolution of quorum sensing pathways in the Vibrio genus[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(1): 28-41.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
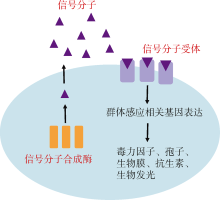
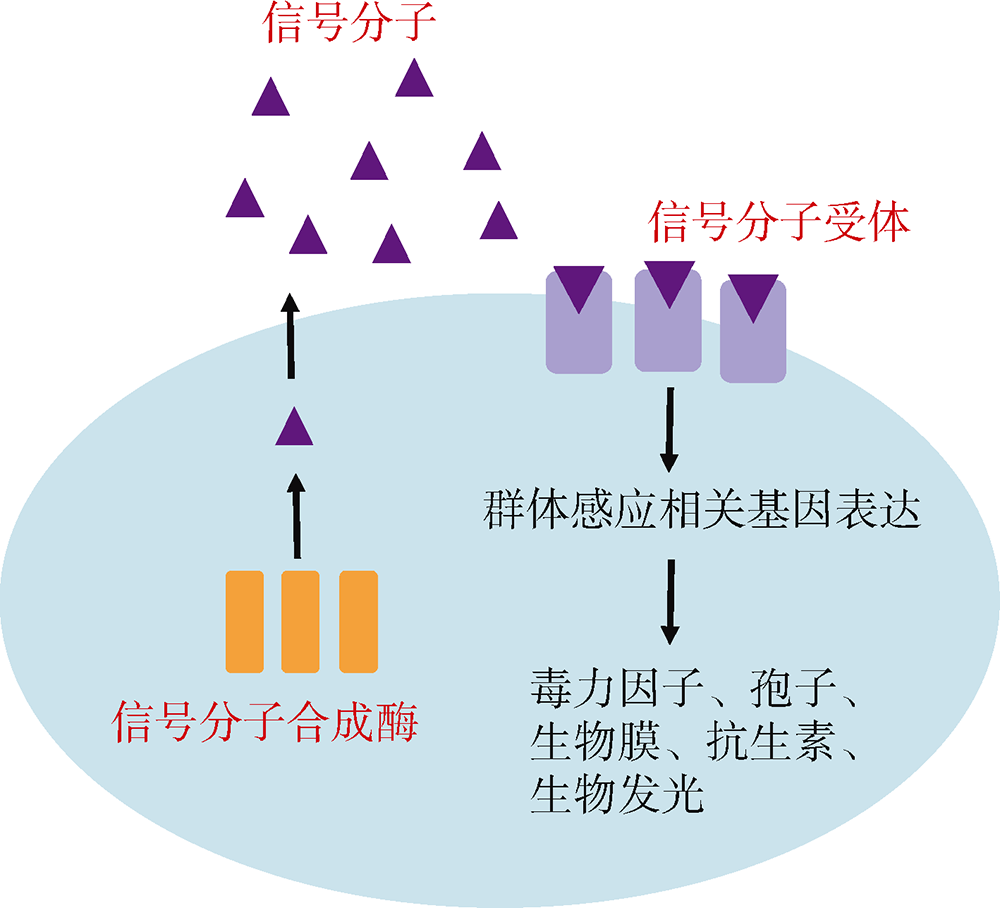
Tab. 1
Quorum sensing pathway of gram-negative bacteria"
| 合成酶 | 信号分子 | 受体蛋白 | 模式菌株 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LuxI | AHL | LuxR | 费氏弧菌 Aliivibrio fischeri | Eberhard et al, |
| LuxS | AI-2 | LuxPQ/LsrB/RbsB | 霍乱弧菌 Vibrio cholerae | Bassler et al, |
| CqsA | CAI-1 | CqsS | 霍乱弧菌 Vibrio cholerae | Miller et al, |
| PqsA/B/C/D/E/H | PQS | PqsR | 铜绿假单胞菌 Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Pesci et al, |
| LuxS | AI-3 | QseBC/QseEF | 大肠杆菌 Escherichia coli O157:H7 | Sperandio et al, |
| RpfF | DSF | RpfCG/RpfR | 野油菜黄单胞菌 Xanthomonas campestris | Barber et al, |
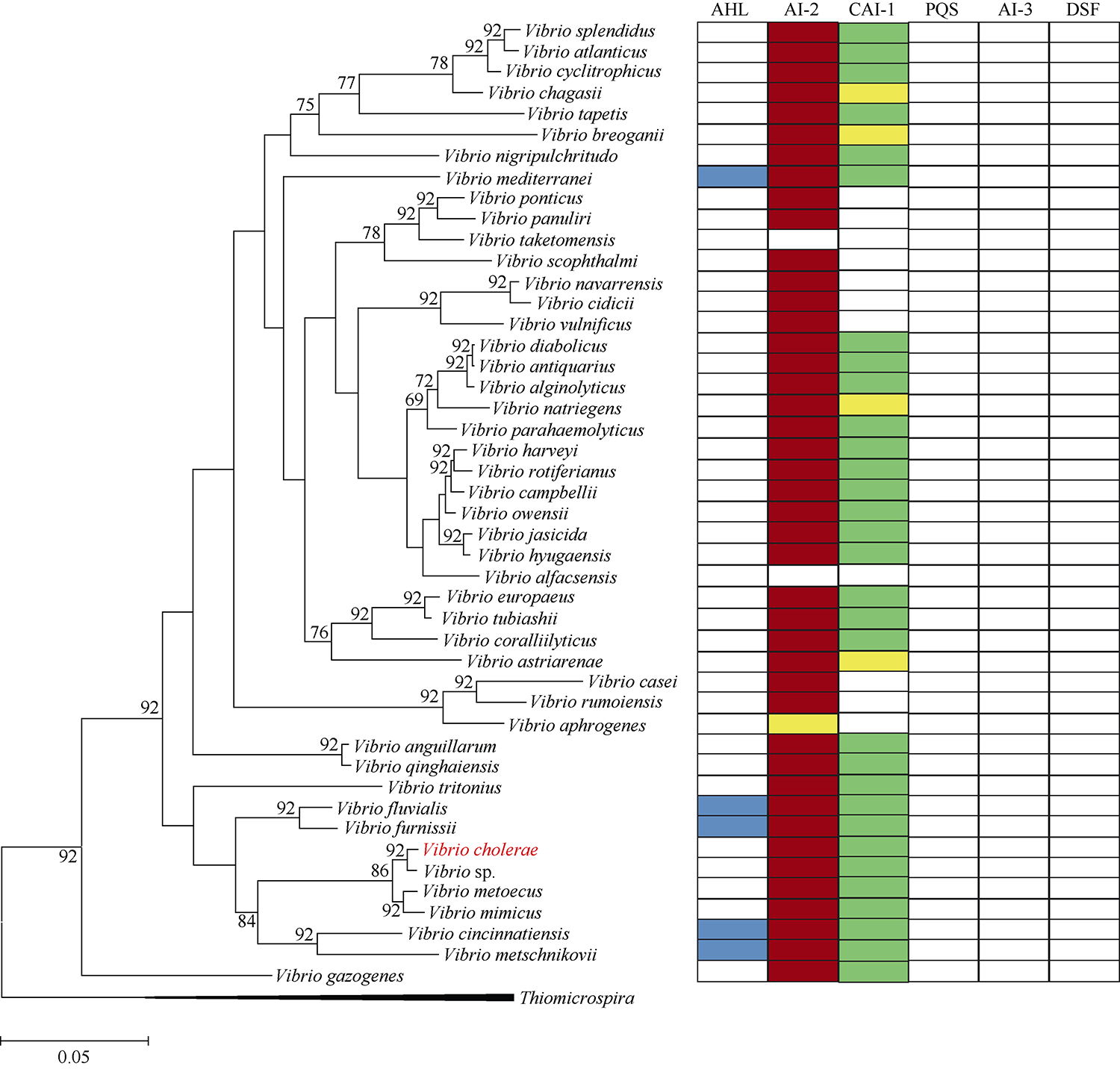
Tab. 2
Strain information"
| 物种名称 | 菌株 | 基因组编号 | 基因组大小/Mb | 编码序列数目/个 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vibrio alfacsensis | CAIM 1831 | GCA_003544875.1 | 4.91 | 3830 |
| Vibrio alginolyticus | FA2 | GCA_011801435.1 | 5.25 | 4598 |
| Vibrio anguillarum | VIB12 | GCA_002310335.1 | 4.90 | 4091 |
| Vibrio antiquarius | EX25 | GCA_000024825.1 | 5.09 | 4451 |
| Vibrio aphrogenes | CA-1004 | GCA_002157735.2 | 3.38 | 2881 |
| Vibrio astriarenae | HN897 | GCA_010587385.1 | 4.80 | 4176 |
| Vibrio breoganii | FF50 | GCA_001677275.1 | 4.49 | 3978 |
| Vibrio campbellii | BoB-90 | GCA_002906455.1 | 6.17 | 5407 |
| Vibrio casei | DSM 22364 | GCA_002218025.2 | 4.14 | 3601 |
| Vibrio chagasii | ECSMB14107 | GCA_004022545.1 | 5.55 | 4448 |
| 物种名称 | 菌株 | 基因组编号 | 基因组大小/Mb | 编码序列数目/个 |
| Vibrio cholerae | 10432-62 | GCA_000969265.1 | 4.08 | 3546 |
| Vibrio cidicii | 2756-81 | GCA_009763805.1 | 4.75 | 3492 |
| Vibrio cincinnatiensis | 2070-81 | GCA_009763705.1 | 3.81 | 3284 |
| Vibrio coralliilyticus | RE22 | GCA_003391375.1 | 5.78 | 5064 |
| Vibrio cyclitrophicus | ECSMB14105 | GCA_005144905.1 | 5.07 | 4283 |
| Vibrio diabolicus | FA3 | GCA_011801455.1 | 5.11 | 4501 |
| Vibrio europaeus | NPI-1 | GCA_013154935.1 | 5.45 | 4782 |
| Vibrio fluvialis | FDAARGOS_104 | GCA_001558415.2 | 4.83 | 4338 |
| Vibrio furnissii | FDAARGOS_777 | GCA_006364355.1 | 4.99 | 4466 |
| Vibrio gazogenes | ATCC 43942 | GCA_002196515.1 | 4.79 | 4070 |
| Vibrio harveyi | ATCC 33843 | GCA_000770115.2 | 5.88 | 5166 |
| Vibrio hyugaensis | 090810a | GCA_002906655.1 | 5.61 | 4845 |
| Vibrio jasicida | 090810c | GCA_002887615.1 | 5.99 | 5188 |
| Vibrio mediterranei | QT6D1 | GCA_002214345.1 | 5.81 | 5146 |
| Vibrio metoecus | 08-2459 | GCA_009665275.1 | 3.99 | 3518 |
| Vibrio metschnikovii | 9502-00 | GCA_009763765.1 | 3.62 | 3118 |
| Vibrio mimicus | SCCF01 | GCA_001767355.1 | 4.48 | 3925 |
| Vibrio natriegens | CCUG 16371 | GCA_001680045.1 | 5.16 | 4451 |
| Vibrio navarrensis | 2462-79 | GCA_009763725.1 | 4.78 | 4093 |
| Vibrio nigripulchritudo | SFn1 | GCA_000801275.1 | 6.32 | 5545 |
| Vibrio owensii | XSBZ03 | GCA_002021755.1 | 5.89 | 5112 |
| Vibrio panuliri | JCM 19500 | GCA_009938205.1 | 4.86 | 4235 |
| Vibrio ponticus | DSM 16217 | GCA_009938225.1 | 4.80 | 4098 |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus | VPD14 | GCA_004006515.1 | 5.17 | 4531 |
| Vibrio qinghaiensis | Q67 | GCA_002257545.1 | 4.02 | 3373 |
| Vibrio rotiferianus | B64D1 | GCA_002214395.1 | 5.28 | 4593 |
| Vibrio rumoiensis | FERM P-14531 | GCA_002218045.2 | 4.21 | 3605 |
| Vibrio scophthalmi | VS-12 | GCA_001685465.1 | 4.93 | 4206 |
| Vibrio sp | 2521-89 | GCA_002216685.1 | 4.12 | 3539 |
| Vibrio splendidus | BST398 | GCA_003345295.1 | 5.51 | 4582 |
| Vibrio taketomensis | C4III291 | GCA_009938185.1 | 4.36 | 3526 |
| Vibrio tapetis | CECT4600 | GCA_900233005.1 | 5.73 | 4800 |
| Vibrio tasmaniensis | LGP32 | GCA_000091465.1 | 4.97 | 4169 |
| Vibrio tritonius | JCM 16456 | GCA_001547935.1 | 5.22 | 4549 |
| Vibrio tubiashii | ATCC 19109 | GCA_000772105.1 | 5.54 | 4946 |
| Vibrio vulnificus | 07-2444 | GCA_009764115.1 | 5.23 | 4554 |
| [1] | 郑林, 祝令伟, 郭学军, 等, 2019. 副溶血性弧菌耐药基因的研究进展[J]. 中国兽药杂志, 53(6): 80-85. |
| ZHENG LIN, ZHU LINGWEI, GUO XUEJUN, et al, 2019. Advances in antimicrobial resistance genes in Vibrio parahaemolyticus[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Drug, 53(6): 80-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] |
ALTSCHUL S F, MADDEN T L, SCHÄFFER A A, et al, 1997. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 25(17): 3389-3402.
doi: 10.1093/nar/25.17.3389 |
| [3] |
BARBER C E, TANG J L, FENG J X, et al, 1997. A novel regulatory system required for pathogenicity of Xanthomonas campestris is mediated by a small diffusible signal molecule[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 24(3): 555-566.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1997.3721736.x |
| [4] |
BARNARD A M L, BOWDEN S D, BURR T, et al, 2007. Quorum sensing, virulence and secondary metabolite production in plant soft-rotting bacteria[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 362(1483): 1165-1183.
doi: 10.1098/rstb.2007.2042 |
| [5] |
BASSLER B L, WRIGHT M, SHOWALTER R E, et al, 1993. Intercellular signalling in Vibrio harveyi: sequence and function of genes regulating expression of luminescence[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 9(4): 773-786.
doi: 10.1111/mmi.1993.9.issue-4 |
| [6] | CAO HUI, KRISHNAN G, GOUMNEROV B, et al, 2001. A quorum sensing-associated virulence gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa encodes a LysR-like transcription regulator with a unique self-regulatory mechanism[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98(25): 14613-14618. |
| [7] |
CHEN XIN, SCHAUDER S, POTIER N, et al, 2002. Structural identification of a bacterial quorum-sensing signal containing boron[J]. Nature, 415(6871): 545-549.
doi: 10.1038/415545a |
| [8] |
CORNFORTH D M, FOSTER K R, 2013. Competition sensing: the social side of bacterial stress responses[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 11(4): 285-293.
doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2977 |
| [9] |
DE KIEVIT T R, IGLEWSKI B H, 2000. Bacterial quorum sensing in pathogenic relationships[J]. Infection and Immunity, 68(9): 4839-4849.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.9.4839-4849.2000 |
| [10] |
DEFOIRDT T, 2018. Quorum-sensing systems as targets for antivirulence therapy[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 26(4): 313-328.
doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2017.10.005 |
| [11] |
EBERHARD A, BURLINGAME A L, EBERHARD C, et al, 1981. Structural identification of autoinducer of Photobacterium fischeri luciferase[J]. Biochemistry, 20(9): 2444-2449.
doi: 10.1021/bi00512a013 |
| [12] |
GROISMAN E A, 2016. Feedback control of two-component regulatory systems[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 70: 103-124.
doi: 10.1146/micro.2016.70.issue-1 |
| [13] |
GUPTA A, REIZMAN I M B, REISCH C R, et al, 2017. Dynamic regulation of metabolic flux in engineered bacteria using a pathway-independent quorum-sensing circuit[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 35(3): 273-279.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.3796 |
| [14] |
HANCOCK R E W, 2014. Collateral damage[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 32(1): 66-68.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.2779 |
| [15] |
HIBBING M E, FUQUA C, PARSEK M R, et al, 2010. Bacterial competition: surviving and thriving in the microbial jungle[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 8(1): 15-25.
doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2259 |
| [16] |
HIGGINS D A, POMIANEK M E, KRAML C M, et al, 2007. The major Vibrio cholerae autoinducer and its role in virulence factor production[J]. Nature, 450(7171): 883-886.
doi: 10.1038/nature06284 |
| [17] |
KELLY R C, BOLITHO M E, HIGGINS D A, et al, 2009. The Vibrio cholerae quorum-sensing autoinducer CAI-1: analysis of the biosynthetic enzyme CqsA[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 5(12): 891-895.
doi: 10.1038/nchembio.237 |
| [18] |
KUMAR S, STECHER G, TAMURA K, 2016. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 33(7): 1870-1874.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw054 |
| [19] |
LEE J, WU JIEN, DENG YINYUE, et al, 2013. A cell-cell communication signal integrates quorum sensing and stress response[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 9(5): 339-343.
doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1225 |
| [20] | LETUNIC I, BORK P, 2018. 20 years of the SMART protein domain annotation resource[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 46(D1): D493-D496. |
| [21] |
MILLER M B, BASSLER B L, 2001. Quorum sensing in bacteria[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 55: 165-199.
doi: 10.1146/micro.2001.55.issue-1 |
| [22] |
MILLER M B, SKORUPSKI K, LENZ D H, et al, 2002. Parallel quorum sensing systems converge to regulate virulence in Vibrio cholerae[J]. Cell, 110(3): 303-314.
doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00829-2 |
| [23] |
MITRA A, HERREN C D, PATEL I R, et al, 2016. Integration of AI-2 based cell-cell signaling with metabolic cues in Escherichia coli[J]. PLoS One, 11(6): e0157532.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157532 |
| [24] | MONNET V, JUILLARD V, GARDAN R, 2016. Peptide conversations in Gram-positive bacteria[J]. Critical Reviews in Microbiology, 42(3): 339-351. |
| [25] | MOREIRA C G, SPERANDIO V, 2016. The Epinephrine/ Norepinephrine/Autoinducer-3 interkingdom signaling system in Escherichia coli O157:H7[M]//LYTE M. Microbial endocrinology:interkingdom signaling in infectious disease and health. Cham: Springer, 874: 247-261. |
| [26] |
MUKHERJEE S, BASSLER B L, 2019. Bacterial quorum sensing in complex and dynamically changing environments[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 17(6): 371-382.
doi: 10.1038/s41579-019-0186-5 |
| [27] |
NA S I, KIM Y O, YOON S H, et al, 2018. UBCG: Up-to-date bacterial core gene set and pipeline for phylogenomic tree reconstruction[J]. Journal of Microbiology, 56(4): 280-285.
doi: 10.1007/s12275-018-8014-6 |
| [28] |
NG W L, BASSLER B L, 2009. Bacterial quorum-sensing network architectures[J]. Annual Review of Genetics, 43: 197-222.
doi: 10.1146/genet.2009.43.issue-1 |
| [29] |
NG W L, PEREZ L J, WEI YUNZHOU, et al, 2011. Signal production and detection specificity in Vibrio CqsA/CqsS quorum-sensing systems[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 79(6): 1407-1417.
doi: 10.1111/mmi.2011.79.issue-6 |
| [30] |
NOVAK E A, SHAO HANJUAN, DAEP C A, et al, 2010. Autoinducer-2 and QseC control biofilm formation and in vivo virulence of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans[J]. Infection and Immunity, 78(7): 2919-2926.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.01376-09 |
| [31] |
PAPENFORT K, BASSLER B L, 2016. Quorum sensing signal-response systems in Gram-negative bacteria[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 14(9): 576-588.
doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.89 |
| [32] |
PEREIRA C S, DE REGT A K, BRITO P H, et al, 2009. Identification of functional LsrB-like autoinducer-2 receptors[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 191(22): 6975-6987.
doi: 10.1128/JB.00976-09 |
| [33] |
PEREIRA C S, THOMPSON J A, XAVIER K B, 2013. AI-2-mediated signalling in bacteria[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 37(2): 156-181.
doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2012.00345.x |
| [34] | PESCI E C, MILBANK J B J, PEARSON J P, et al, 1999. Quinolone signaling in the cell-to-cell communication system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 96(20): 11229-11234. |
| [35] |
RAINEY P B, RAINEY K, 2003. Evolution of cooperation and conflict in experimental bacterial populations[J]. Nature, 425(6953): 72-74.
doi: 10.1038/nature01906 |
| [36] |
RAJEEV L, GARBER M E, MUKHOPADHYAY A, 2020. Tools to map target genes of bacterial two-component system response regulators[J]. Environmental Microbiology Reports, 12(3): 267-276.
doi: 10.1111/emi4.v12.3 |
| [37] |
SCHÄFFER A A, ARAVIND L, MADDEN T L, et al, 2001. Improving the accuracy of PSI-BLAST protein database searches with composition-based statistics and other refinements[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 29(14): 2994-3005.
doi: 10.1093/nar/29.14.2994 |
| [38] | SCHOLZ R L, GREENBERG E P, 2017. Positive autoregulation of an acyl-homoserine lactone quorum-sensing circuit synchronizes the population response[J]. mBio, 25; 8(4): e01079-17. |
| [39] | SPERANDIO V, TORRES A G, JARVIS B, et al, 2003. Bacteria-host communication: the language of hormones[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100(15): 8951-8956. |
| [40] |
STEPHENS K, BENTLEY W E, 2020. Synthetic biology for manipulating quorum sensing in microbial consortia[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 28(8): 633-643.
doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2020.03.009 |
| [41] |
TAGA M E, MILLER S T, BASSLER B L, 2003. Lsr-mediated transport and processing of AI-2 in Salmonella typhimurium[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 50(4): 1411-1427.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03781.x |
| [42] |
TANG J L, LIU Y N, BARBER C E, et al, 1991. Genetic and molecular analysis of a cluster of rpf genes involved in positive regulation of synthesis of extracellular enzymes and polysaccharide in Xanthomonas campestris pathovar campestris[J]. Molecular and General Genetics MGG, 226(3): 409-417.
doi: 10.1007/BF00260653 |
| [43] |
URBANCZYK H, AST J C, HIGGINS M J, et al, 2007. Reclassification of Vibrio fischeri, Vibrio logei, Vibrio salmonicida and Vibrio wodanis as Aliivibrio fischeri gen. nov., comb. nov., Aliivibrio logei comb. nov., Aliivibrio salmonicida comb. nov. and Aliivibrio wodanis comb. nov[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 57(12): 2823-2829.
doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.65081-0 |
| [44] |
VON BODMAN S B, WILLEY J M, DIGGLE S P, 2008. Cell-cell communication in bacteria: united we stand[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 190(13): 4377-4391.
doi: 10.1128/JB.00486-08 |
| [45] |
WANG FANGFANG, QIAN WEI, 2019. The roles of histidine kinases in sensing host plant and cell-cell communication signal in a phytopathogenic bacterium[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 374(1767): 20180311.
doi: 10.1098/rstb.2018.0311 |
| [46] | WANG YANG, LIU BAOBAO, GRENIER D, et al, 2019. Regulatory mechanisms of the LuxS/AI-2 system and bacterial resistance[J]. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 63(10): e01186-19. |
| [47] |
WEI YUNZHOU, NG W L, CONG JIANPING, et al, 2012. Ligand and antagonist driven regulation of the Vibrio cholerae quorum-sensing receptor CqsS[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 83(6): 1095-1108.
doi: 10.1111/mmi.2012.83.issue-6 |
| [48] |
WEST S A, GRIFFIN A S, GARDNER A, et al, 2006. Social evolution theory for microorganisms[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 4(8): 597-607.
doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1461 |
| [49] |
WHITELEY M, DIGGLE S P, GREENBERG E P, 2017. Progress in and promise of bacterial quorum sensing research[J]. Nature, 551(7680): 313-320.
doi: 10.1038/nature24624 |
| [50] |
WINZER K, HARDIE K R, BURGESS N, et al, 2002a. LuxS: its role in central metabolism and the in vitro synthesis of 4-hydroxy-5-methyl-3(2H)-furanone[J]. Microbiology, 148(4): 909-922.
doi: 10.1099/00221287-148-4-909 |
| [51] |
WINZER K, HARDIE K R, WILLIAMS P. 2002b. Bacterial cell-to-cell communication: sorry, can't talk now - gone to lunch![J]. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 5(2): 216-222.
doi: 10.1016/S1369-5274(02)00304-1 |
| [52] |
WU SHENGBO, LIU JIAHENG, LIU CHUNJIANG, et al, 2020. Quorum sensing for population-level control of bacteria and potential therapeutic applications[J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 77(7): 1319-1343.
doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03326-8 |
| [53] |
ZIMMERMANN L, STEPHENS A, NAM S Z, et al, 2018. A completely reimplemented MPI bioinformatics toolkit with a new HHpred server at its core[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 430(15): 2237-2243.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2017.12.007 |
| [1] | MU Rong, ZHU Zhu, ZHANG Ruifeng. Adaptive mechanisms of iron limitation on the marine Synechococcus based on comparative genomics [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 89-100. |
| [2] | LI Yanqun, CHEN Rouwen, LIN Zonghao, TIAN Xinpeng, YIN Hao. Screening and identification of a quorum sensing inhibitory actinomycetes derived from marine sediments [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(1): 75-81. |
|
||