热带海洋学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (6): 171-182.doi: 10.11978/2022016CSTR: 32234.14.2022016
环礁潟湖沉积物重建南沙群岛小冰期以来的热带气旋活动
杨红强1,2,3( ), 谭飞1,2,4, 徐辉龙1,2, 张喜洋1,2, 施祺1,2, 陶士臣1,2
), 谭飞1,2,4, 徐辉龙1,2, 张喜洋1,2, 施祺1,2, 陶士臣1,2
- 1.中国科学院边缘海与大洋地质重点实验室, 中国科学院南海海洋研究所, 中国科学院南海生态环境工程创新研究院, 广东 广州 510301
2.南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州), 广东 广州 511458
3.中国科学院南沙海洋生态环境实验站, 海南 三沙 573199
4.中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
-
收稿日期:2022-01-27修回日期:2022-04-14出版日期:2022-11-10发布日期:2022-04-18 -
通讯作者:杨红强 -
作者简介:杨红强(1980—), 男, 河南省平顶山市人, 博士, 副研究员, 主要从事珊瑚礁现代过程和全球变化记录研究。email:hqyang@scsio.ac.cn -
基金资助:南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州)人才团队引进重大专项(GML2019ZD0206);中国科学院南海生态环境工程创新研究院自主部署项目(ISEE2018PY01);中国科学院战略性先导科技专项(A类)(XDA13010103)
Reconstruction of the tropical cyclones activity in the Nansha Islands since the Little Ice Age from the atoll lagoon sediments
YANG Hongqiang1,2,3( ), TAN Fei1,2,4, XU Huilong1,2, ZHANG Xiyang1,2, SHI Qi1,2, TAO Shichen1,2
), TAN Fei1,2,4, XU Huilong1,2, ZHANG Xiyang1,2, SHI Qi1,2, TAO Shichen1,2
- 1. Key Laboratory of Ocean and Marginal Sea Geology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou 511458, China
3. Nansha Marine Ecological and Environmental Research Station, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Sansha 573199, China
4. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2022-01-27Revised:2022-04-14Online:2022-11-10Published:2022-04-18 -
Contact:YANG Hongqiang -
Supported by:Key Special Project for Introduced Talents Team of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou)(GML2019ZD0206);Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences(ISEE2018PY01);Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences(XDA13010103)
摘要:
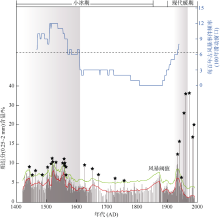
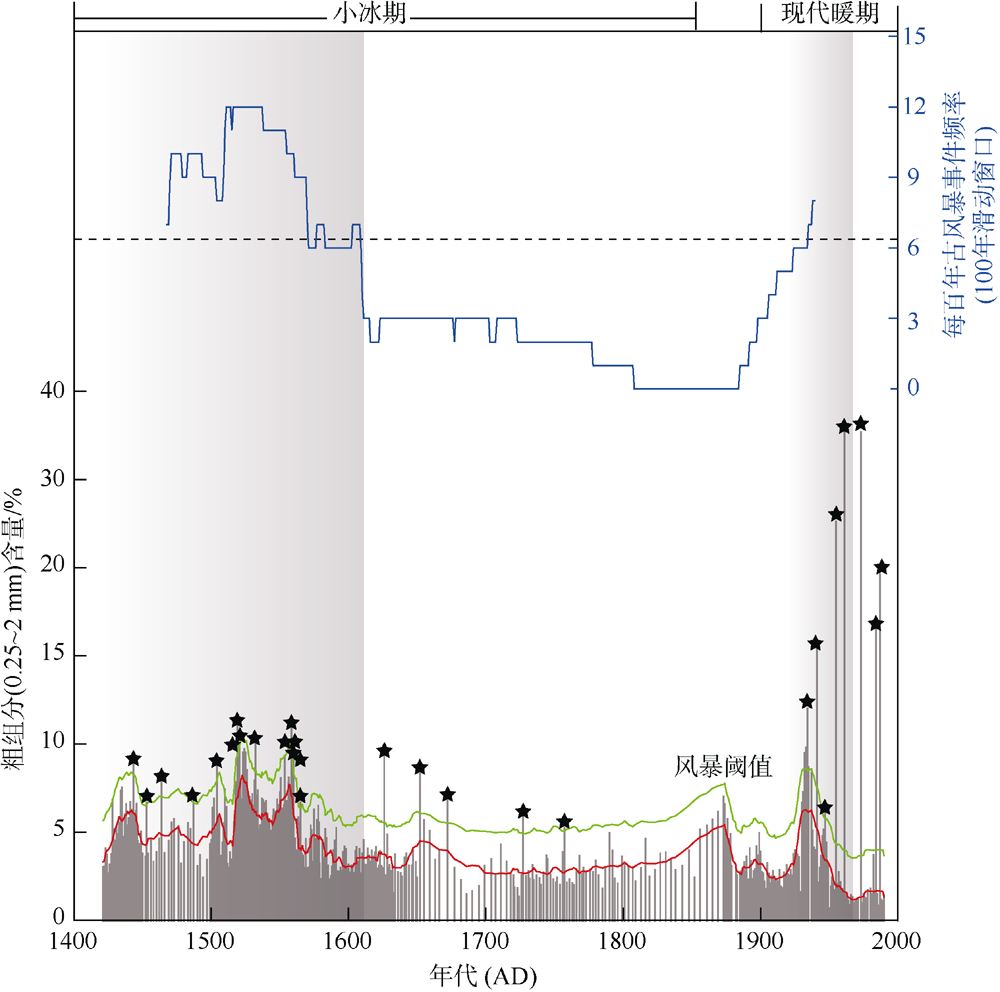
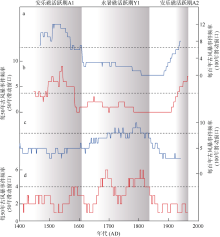
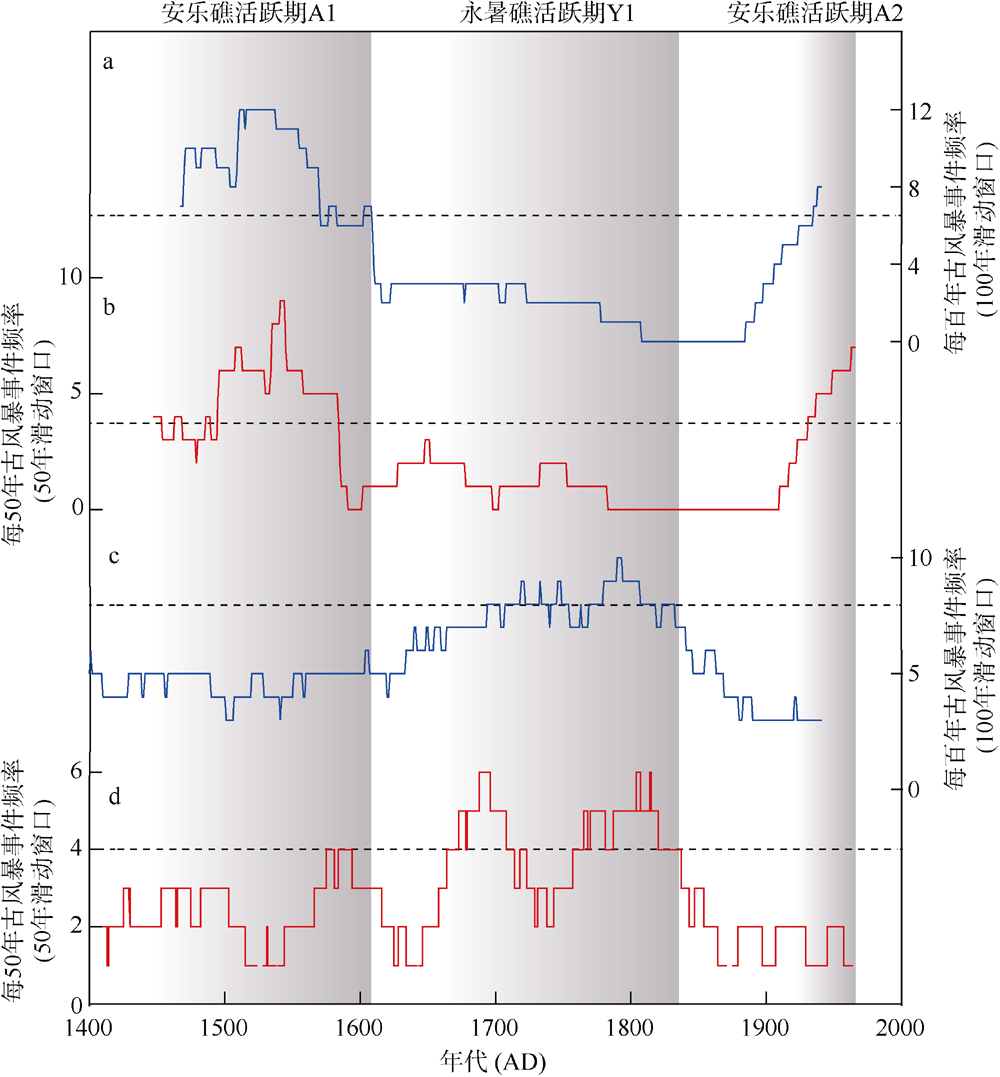
热带气旋活动以及由此产生的风暴潮和强降雨对南海及周边沿海地区社会经济构成巨大威胁。对器测记录之前全新世热带气旋的研究有助于准确预测全球变暖背景下热带气旋活动的变化趋势。本文利用南沙群岛安乐礁潟湖沉积物重建了小冰期以来准年分辨率的热带气旋活动, 共识别28个风暴事件层。研究表明, 小冰期以来, 南沙群岛安乐礁热带气旋活动在年代际到百年尺度上频繁变化, 发育两个主要的风暴活跃期。在小冰期早期(AD 1471—1620)经历了最为强烈的风暴活跃期, 另一个风暴活跃期位于现代暖期的AD 1930—1960, 风暴活动虽有所加强, 但明显低于小冰期早期。与同期永暑礁重建结果的对比表明, 热带气旋活动存在明显的时空差异性, 更多来自相近区域的高分辨率风暴记录可有效降低古风暴活动重建的不确定性, 提高重建记录的准确度。
中图分类号:
- P722.7
引用本文
杨红强, 谭飞, 徐辉龙, 张喜洋, 施祺, 陶士臣. 环礁潟湖沉积物重建南沙群岛小冰期以来的热带气旋活动[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(6): 171-182.
YANG Hongqiang, TAN Fei, XU Huilong, ZHANG Xiyang, SHI Qi, TAO Shichen. Reconstruction of the tropical cyclones activity in the Nansha Islands since the Little Ice Age from the atoll lagoon sediments[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(6): 171-182.
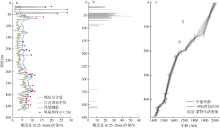
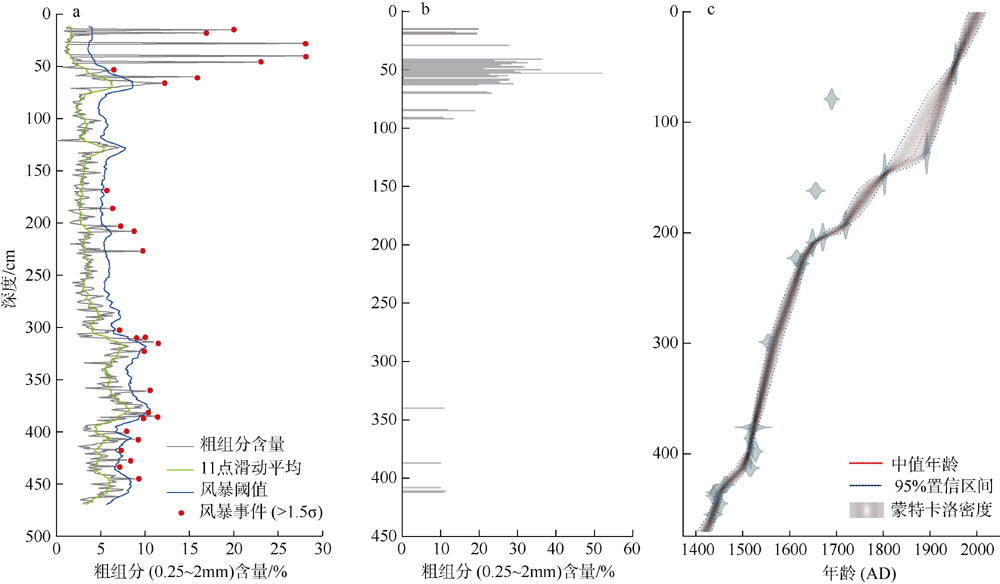
图1
研究区位置及气象和地貌学特征 a. 南海和西北太平洋地理位置及热带气旋历史记录, 该图依据审图号GS(2016)2937号底图制作, 黄色圆圈标注为本研究中的采样位置安乐礁潟湖, 永暑礁NY-4风暴记录以蓝色圆圈表示; b. IBTrACS Hurricane Datase数据库中提供的南沙群岛附近历史热带气旋移动路径(该图来源于 https://coast.noaa.gov/hurricanes/, 图中为热带风暴强度及以上级别热带气旋路径, 白色虚线圆圈代表以安乐礁为中心半径为300km范围内的热带气旋活动路径); c. 安乐礁位置和地貌分区(该图根据google卫星遥感图像制作, 黄色圆圈代表岩心AL-1采集地点, 黄色虚线表示礁坪和潟湖之间的边界)"

表1
1945—2020年登陆南沙群岛安乐礁和永暑礁不同半径范围内的不同强度热带气旋的频率"
| 珊瑚礁区 | 半径范围 | 热带风暴及以上级别热带气旋 | 每百年频率 | ≥cat 1级别热带气旋 | 每百年 频率 | ≥cat 2级别热带气旋 | 每百年 频率 | ≥cat 3级别热带气旋 | 每百年 频率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 安乐礁 | r<300km | 75.0 | 100.0 | 17.0 | 22.7 | 9.0 | 12.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 |
| r=115km | 16.0 | 21.3 | 5.0 | 6.7 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 1.0 | 1.3 | |
| r=60km | 10.0 | 13.3 | 2.0 | 2.7 | 1.0 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 1.3 | |
| 永暑礁 | r<300km | 67.0 | 89.3 | 15.0 | 20.0 | 8.0 | 10.7 | 1.0 | 1.3 |
| r=115km | 18.0 | 24.0 | 6.0 | 8.0 | 2.0 | 2.7 | 1.0 | 1.3 | |
| r=60km | 6.0 | 8.0 | 2.0 | 2.7 | 1.0 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 1.3 |
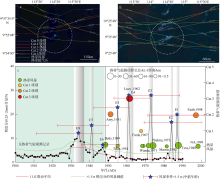
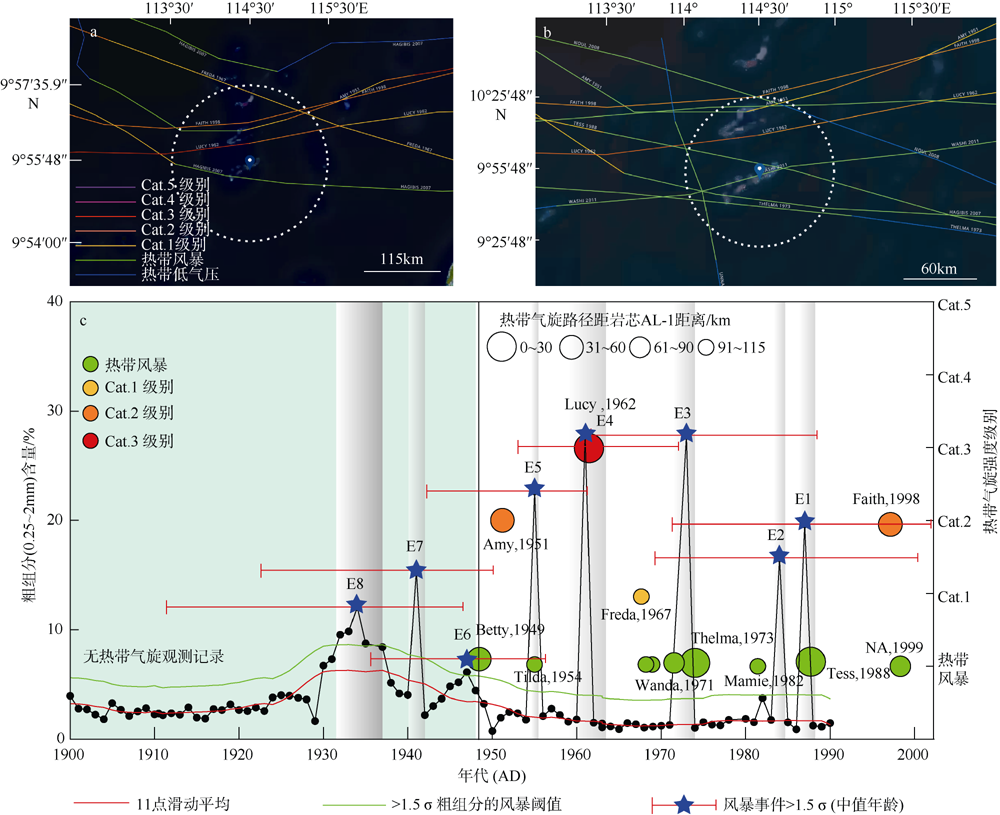
图4
安乐礁现代器测热带气旋移动路径和沉积物记录敏感性校准 a. 经过南海南部安乐礁115km半径范围内的热带气旋活动历史路径; b. 60km范围内近距离影响安乐礁的热带气旋活动路径; c. 岩心顶部1900—2001 AD的粗组分含量百分比与现代热带气旋观测记录的校准和敏感性评估。蓝色五角星代表超过事件阈值的粗粒沉积峰, 其中事件层E8为附近几个小峰的合并; 不同颜色和大小的圆分别代表了某一热带气旋过境安乐礁附近115km范围内的强度和距离安乐礁的最短直线距离, 圆半径越大代表距离安乐礁越近。每个事件层标注了基于贝叶斯模型的2σ年龄误差。现代热带气旋移动路径观测记录来源于 https://coast.noaa.gov/hurricanes/在线数据库网站, 统计时间区间为1945—2020年"
| [1] | 高抒, 贾建军, 杨阳, 等, 2019. 陆架海岸台风沉积记录及信息提取[J]. 海洋学报, 41(10): 141-160. |
| GAO SHU, JIA JIANJUN, et al, 2019. Obtaining typhoon information from sedimentary records in coastal-shelf waters[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 41(10): 141-160. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 廖菲, 李文婷, 张子然, 等, 2019. 1949-2017年南海海域热带气旋强度和路径快速变化统计特征[J]. 海洋学报, 41(9): 126-135. |
| LIAO FEI, LI WENTING, ZHANG ZIRAN, et al, 2019. Analysis of rapid changes of tropical cyclones over the South China Sea for 1949-2017[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 41(9): 126-135. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 陶丽, 张艺帆, 王学兵, 2020. 南海与西北太平洋地区夏季热带气旋潜在生成指数的改进[J]. 大气科学学报, 43(4): 603-616. |
| TAO LI, ZHANG YIFAN, WANG XUEBING, 2020. Improvement of genesis potential index for western North Pacific tropical cyclones[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 43(4): 603-616. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 徐笑梅, 高抒, 周亮, 等, 2019. 海南岛东北部海岸极端波浪事件沉积记录[J]. 海洋学报, 41(6): 48-63. |
| XU XIAOMEI, GAO SHU, ZHOU LIANG, et al, 2019. Sedimentary records of extreme wave events on the northeastern Hainan Island coast, southern China[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 41(6): 48-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] |
张敏, 罗军, 胡金磊, 等, 2019. 雷州市沿海风暴潮淹没危险性评估[J]. 热带海洋学报, 38(2): 1-12.
doi: 10.11978/2018067 |
|
ZHANG MIN, LUO JUN, HU JINLEI, et al, 2019. Inundation risk assessment of storm surge along Lei Zhou coastal areas[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 38(2): 1-12. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi: 10.11978/2018067 |
|
| [6] | 周亮, 高抒, 杨阳, 等, 2015. 海南岛东南部海湾350年古风暴事件沉积与历史文献记录对比[J]. 海洋学报, 37(9): 84-94. |
| ZHOU LIANG, GAO SHU, et al, 2015. Comparison of paleostorm events between sedimentary and historical archives: A 350 year record from southeastern Hainan Island coastal embayments[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 37(9): 84-94. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] |
BACMEISTER J T, REED K A, HANNAY C, et al, 2018. Projected changes in tropical cyclone activity under future warming scenarios using a high-resolution climate model[J]. Climatic Change, 146(3-4): 547-560.
doi: 10.1007/s10584-016-1750-x |
| [8] |
BLAAUW M, CHRISTEN J A, 2011. Flexible paleoclimate age-depth models using an autoregressive gamma process[J]. Bayesian Analysis, 6(3): 457-474.
doi: 10.1214/ba/1339616472 |
| [9] |
BRAITHWAITE C J R, 1973. Settling behaviour related to sieve analysis of skeletal sands[J]. Sedimentology, 20(2): 251-262.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.1973.tb02048.x |
| [10] |
BRAMANTE J F, FORD M R, KENCH P S, et al, 2020. Increased typhoon activity in the Pacific deep tropics driven by Little Ice Age circulation changes[J]. Nature Geoscience, 13(12): 806-811.
doi: 10.1038/s41561-020-00656-2 |
| [11] |
CHEN H-F, LIU Y-C, CHIANG C-W, et al, 2019a. China's historical record when searching for tropical cyclones corresponding to Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) shifts over the past 2 kyr[J]. Climate of the Past, 15(1): 279-289.
doi: 10.5194/cp-15-279-2019 |
| [12] |
CHEN TIANRAN, ROFF G, FENG YUEXING, et al, 2019b. Tropical sand cays as natural Paleocyclone archives[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 46(16): 9796-9803.
doi: 10.1029/2019GL084274 |
| [13] |
CHENG H, EDWARDS R L, HOFF J, et al, 2000. The half-lives of uranium-234 and thorium-230[J]. Chemical Geology, 169(1-2): 17-33.
doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00157-6 |
| [14] |
CLARK T R, ROFF G, ZHAO JIANXIN, et al, 2014. Testing the precision and accuracy of the U-Th chronometer for dating coral mortality events in the last 100 years[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 23: 35-45.
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2014.05.002 |
| [15] |
CONTRERAS-ROSALES L A, JENNERJAHN T, STEINKE S, et al, 2019. Holocene changes in biome size and tropical cyclone activity around the Northern South China Sea[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 215: 45-63.
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2019.05.004 |
| [16] |
DIETRICH W E, 1982. Settling velocity of natural particles[J]. Water Resources Research, 18(6): 1615-1626.
doi: 10.1029/WR018i006p01615 |
| [17] |
DONNELLY J P, HAWKES A D, LANE P, et al, 2015. Climate forcing of unprecedented intense-hurricane activity in the last 2000 years[J]. Earth’s Future, 3(2): 49-65.
doi: 10.1002/2014EF000274 |
| [18] |
ISHIZAWA T, GOTO K, YOKOYAMA Y, et al, 2020. Dating tsunami deposits: Present knowledge and challenges[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 200: 102971.
doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.102971 |
| [19] |
KENCH P S, MCLEAN R F, 1996. Hydraulic characteristics of bioclastic deposits: New possibilities for environmental interpretation using settling velocity fractions[J]. Sedimentology, 43(3): 561-570.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3091.1996.d01-23.x |
| [20] | KENCH P S, BRANDER R W, 2006. Response of reef island shorelines to seasonal climate oscillations: South Maalhosmadulu atoll, Maldives[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 111(F1): F01001. |
| [21] |
KLOSTERMANN L, GISCHLER E, STORZ D, et al, 2014. Sedimentary record of late Holocene event beds in a mid-ocean atoll lagoon, Maldives, Indian Ocean: Potential for deposition by tsunamis[J]. Marine Geology, 348: 37-43.
doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2013.11.014 |
| [22] |
KNUTSON T, CAMARGO S J, CHAN J C L, et al, 2020. Tropical cyclones and climate change assessment: Part II: Projected response to anthropogenic warming[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 101(3): E303-E322.
doi: 10.1175/BAMS-D-18-0194.1 |
| [23] |
KNUTSON T R, SIRUTIS J J, ZHAO Ming, et al, 2015. Global projections of intense tropical cyclone activity for the late twenty-first century from dynamical downscaling of CMIP5/RCP4.5 scenarios[J]. Journal of Climate, 28(18): 7203-7224.
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-15-0129.1 |
| [24] |
LANDSEA C W, HARPER B A, HOARAU K, et al, 2006. Can we detect trends in extreme tropical cyclones?[J]. Science, 313(5786): 452-454.
doi: 10.1126/science.1128448 |
| [25] |
LANE P, DONNELLY J P, WOODRUFF J D, et al, 2011. A decadally-resolved paleohurricane record archived in the late Holocene sediments of a Florida sinkhole[J]. Marine Geology, 287(1-4): 14-30.
doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2011.07.001 |
| [26] |
LIN NING, LANE P, EMANUEL K A, et al, 2014. Heightened hurricane surge risk in northwest Florida revealed from climatological-hydrodynamic modeling and paleorecord reconstruction[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 119(14): 8606-8623.
doi: 10.1002/2014JD021584 |
| [27] |
LIU ENTAO, ZHAO JIANXIN, FENG YUEXING, et al, 2016. U-Th age distribution of coral fragments from multiple rubble ridges within the Frankland Islands, Great Barrier Reef: implications for past storminess history[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 143: 51-68.
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.05.006 |
| [28] |
LIU K B, SHEN CAIMING, LOUIE K S, 2001. A 1,000-year history of typhoon landfalls in Guangdong, southern China, reconstructed from Chinese historical documentary records[J]. Annals of the Association of American Geographers, 91(3): 453-464.
doi: 10.1111/0004-5608.00253 |
| [29] |
MAIKLEM W R, 1968. Some hydraulic properties of bioclastic carbonate grains[J]. Sedimentology, 10(2): 101-109.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.1968.tb01102.x |
| [30] |
MEI WEI, XIE SHANGPING, PRIMEAU F, et al, 2015. Northwestern pacific typhoon intensity controlled by changes in ocean temperatures[J]. Science Advances, 1(4): e1500014.
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1500014 |
| [31] |
PEDUZZI P, CHATENOUX B, DAO H, et al, 2012. Global trends in tropical cyclone risk[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2(4): 289-294.
doi: 10.1038/nclimate1410 |
| [32] |
RODYSILL J R, DONNELLY J P, SULLIVAN R, et al, 2020. Historically unprecedented Northern Gulf of Mexico hurricane activity from 650 to 1250 CE[J]. Scientific Reports, 10(1): 19092.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-75874-0 pmid: 33154412 |
| [33] |
SORIA J L A, SWITZER A D, VILLANOY C L, et al, 2016. Repeat storm surge disasters of typhoon Haiyan and its 1897 predecessor in the Philippines[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 97(1): 31-48.
doi: 10.1175/BAMS-D-14-00245.1 |
| [34] |
SUN LI, BI SHUOBEN, CHEN CHANGCHUN, et al, 2020. Typhoon frequency sequence reconstruction and characteristics analysis in the Southeast coastal area over China during the Ming and Qing dynasties[J]. Natural Hazards, 100(3): 1105-1116.
doi: 10.1007/s11069-019-03851-6 |
| [35] |
TOOMEY M R, DONNELLY J P, WOODRUFF J D, 2013. Reconstructing mid-late Holocene cyclone variability in the Central Pacific using sedimentary records from Tahaa, French Polynesia[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 77: 181-189.
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2013.07.019 |
| [36] |
WALLACE E J, DONNELLY J P, HENGSTUM P J, et al, 2019. Intense Hurricane activity over the past 1500 years at South Andros Island, the Bahamas[J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 34(11): 1761-1783.
doi: 10.1029/2019PA003665 |
| [37] | WALLACE E J, COATS S, EMANUEL K, et al, 2021a. Centennial-scale shifts in storm frequency captured in paleohurricane records from the Bahamas arise predominantly from random variability[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 48(1): e2020GL091145. |
| [38] | WALLACE E J, DONNELLY J P, VAN HENGSTUM P J, et al, 2021b. 1,050 years of hurricane strikes on long island in the Bahamas[J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 36(3): e2020PA004156. |
| [39] |
WINKLER T S, VAN HENGSTUM P J, DONNELLY J P, et al, 2020. Revising evidence of hurricane strikes on Abaco Island (The Bahamas) over the last 700 years[J]. Scientific Reports, 10(1): 16556.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73132-x |
| [40] |
YANG HONGQIANG, YU KEFU, ZHAO MEIXIA, et al, 2015. Impact on the coral reefs at Yongle Atoll, Xisha Islands, South China Sea from a strong typhoon direct sweep: Wutip, September 2013[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 114: 457-466.
doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.04.009 |
| [41] |
YU KEFU, ZHAO JIANXIN, SHI QI, et al, 2009. Reconstruction of storm/tsunami records over the last 4000 years using transported coral blocks and lagoon sediments in the southern South China Sea[J]. Quaternary International, 195(1-2): 128-137.
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2008.05.004 |
| [42] |
YUE YUANFU, YU KEFU, TAO SHICHEN, et al, 2019. 3500-year western Pacific storm record warns of additional storm activity in a warming warm pool[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 521: 57-71.
doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2019.02.009 |
| [43] | ZUKI Z M, LUPO A R, 2008. Interannual variability of tropical cyclone activity in the southern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmosphere, 113(D6): D06106. |
| [1] | 徐超, 龙丽娟, 李莎, 袁丽, 徐晓璐. 南海及其附属岛礁海洋科学考察历史资料系统整编3. 数据共享服务及应用[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 158-165. |
| [2] | 徐超, 龙丽娟, 李莎, 何云开, 袁丽, 徐晓璐. 南海及其附属岛礁海洋科学考察历史资料系统整编1. 资料整编技术及应用[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 143-149. |
| [3] | 徐超, 龙丽娟, 李莎, 徐晓璐, 袁丽. 南海及其附属岛礁海洋科学考察历史资料系统整编2. 数据治理技术与应用[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 150-157. |
| [4] | 柳原, 柯志新, 李开枝, 谭烨辉, 梁竣策, 周伟华. 人类活动和沿岸流影响下的粤东近海浮游动物群落特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [5] | 刘玓玓, 张喜洋, 孙富林, 王明壮, 谭飞, 施祺, 王冠, 杨红强. 南海海滩岩微生物群落结构和特定菌株对其成因机制的启示*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 112-122. |
| [6] | 江绿苗, 陈天然, 赵宽, 张婷, 许莉佳. 南海北部涠洲岛边缘珊瑚礁的生物侵蚀实验研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 155-165. |
| [7] | 许莉佳, 廖芝衡, 陈辉, 王永智, 黄柏强, 林巧云, 甘健锋, 杨静. 南海北部珊瑚群落结构特征及其对海洋热浪事件的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 58-71. |
| [8] | 邱燕, 鞠东, 黄文凯, 王英民, 聂鑫. 南海中央海盆海底初始扩张时间的重新认定[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 154-165. |
| [9] | 赵明辉, 袁野, 张佳政, 张翠梅, 高金尉, 王强, 孙珍, 程锦辉. 南海北部被动陆缘洋陆转换带张裂-破裂研究新进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 173-183. |
| [10] | 韩鼎妍, 李敏, 胡睿, 谢玲玲. 秋季登陆广东热带气旋特征变化及机制分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(1): 64-78. |
| [11] | 黄谕, 王琳, 麦志茂, 李洁, 张偲. 南海热带岛礁生物土壤结皮中细菌的分离及其固砂特性初步研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(6): 101-110. |
| [12] | 田城, 黎鑫, 杜洋, 李明, 谢勇, 夏际炉. 基于贝叶斯网络和GIS的热带气旋灾害风险评估[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(5): 17-29. |
| [13] | 王辰燕, 史敬文, 颜安南, 康亚茹, 王煜轩, 覃素丽, 韩民伟, 张瑞杰, 余克服. 有机磷酸酯在南海长棘海星中的生物富集特征及来源解析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(5): 30-37. |
| [14] | 李牛, 邸鹏飞, 冯东, 陈多福. 冷泉渗漏对海洋沉积物氧化还原环境地球化学识别的影响——以南海东北部F站位活动冷泉为例*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(5): 144-153. |
| [15] | 杨夏玲, 黎树式, 许珊珊, 虞崇熙, 潘洁. 近60年来极端天气影响下南流江入海水沙变化[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(4): 91-103. |
|
||