热带海洋学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (4): 136-145.doi: 10.11978/2021172CSTR: 32234.14.2021172
夏季南海北部粤东陆架锋面的动力特征分析*
曾毅港1,2( ), 经志友1, 黄小龙1,2, 郑瑞玺1,2
), 经志友1, 黄小龙1,2, 郑瑞玺1,2
- 1.热带海洋环境国家重点实验室(中国科学院南海海洋研究所), 广东 广州 510301
2.中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
-
收稿日期:2021-12-04修回日期:2022-02-16出版日期:2022-07-10发布日期:2022-02-21 -
通讯作者:曾毅港 -
作者简介:曾毅港(1997—), 男, 湖南省湘潭市人, 硕士研究生, 主要从事锋面观测研究。email:2873417616@qq.com -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(92058201);国家自然科学基金项目(41776040);国家自然科学基金项目(41949907);国家自然科学基金项目(42149907);中国科学院基础前沿科学研究计划原始创新项目(ZDBS-LY-DQC011);广州市科学研究计划(201904010420)
Analysis of the dynamic characteristics of the east Guangdong shelf front in the northern South China Sea in summer
ZENG Yigang1,2( ), JING Zhiyou1, HUANG Xiaolong1,2, ZHENG Ruixi1,2
), JING Zhiyou1, HUANG Xiaolong1,2, ZHENG Ruixi1,2
- 1. State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography (South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2021-12-04Revised:2022-02-16Online:2022-07-10Published:2022-02-21 -
Contact:ZENG Yigang -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(92058201);National Natural Science Foundation of China(41776040);National Natural Science Foundation of China(41949907);National Natural Science Foundation of China(42149907);Original Innovation Project of Basic Frontier Scientific Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences(ZDBS-LY-DQC011);Guangzhou Science and Technology Project(201904010420)
摘要:
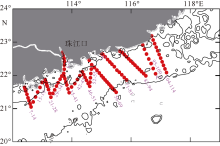
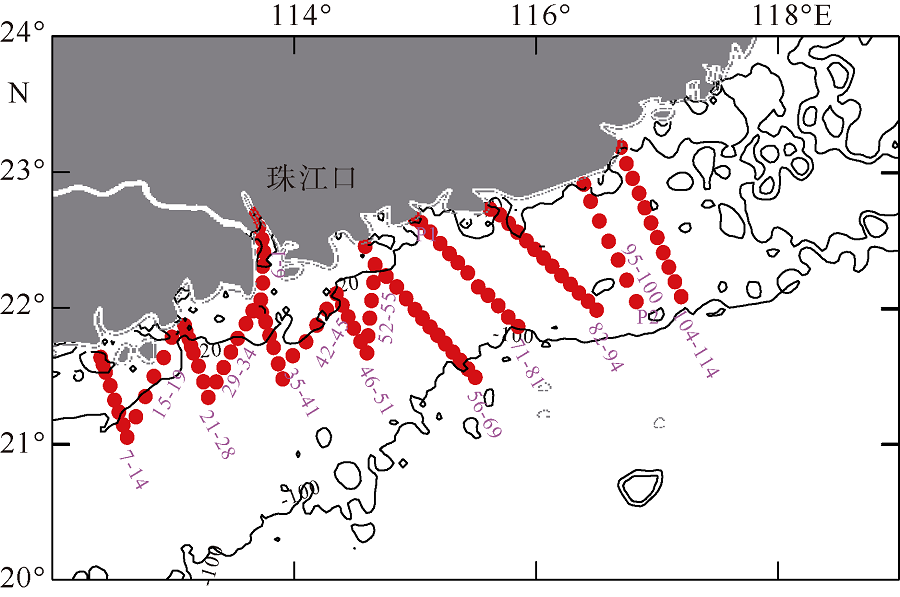
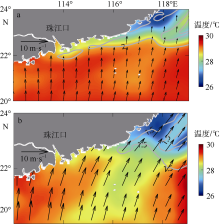
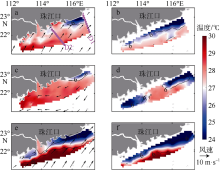
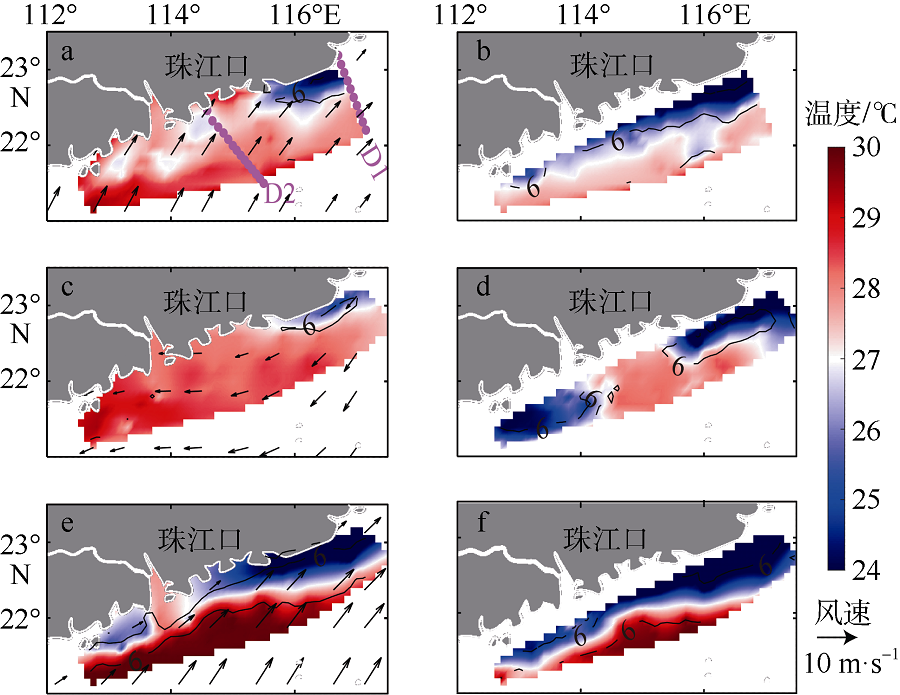
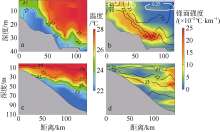
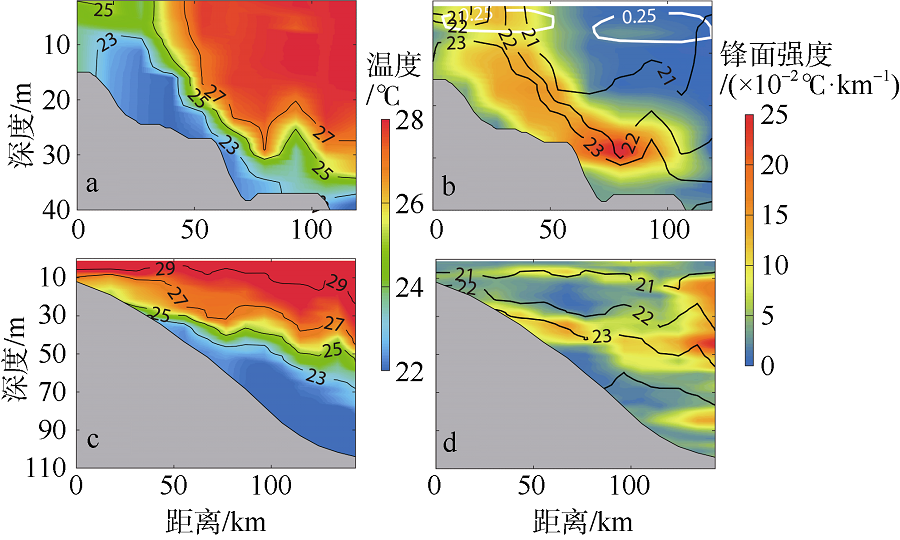
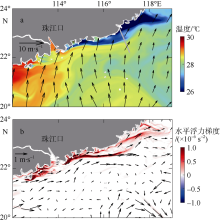
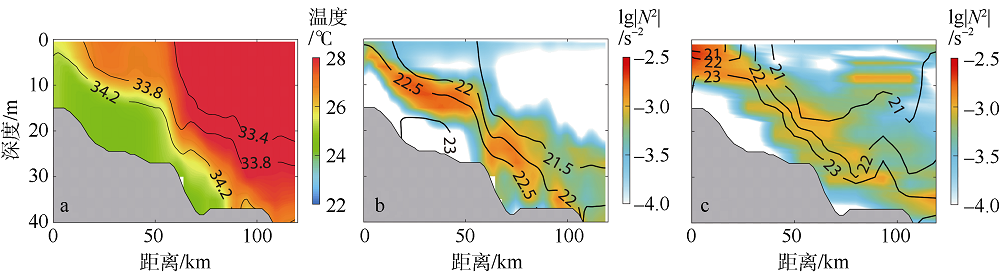
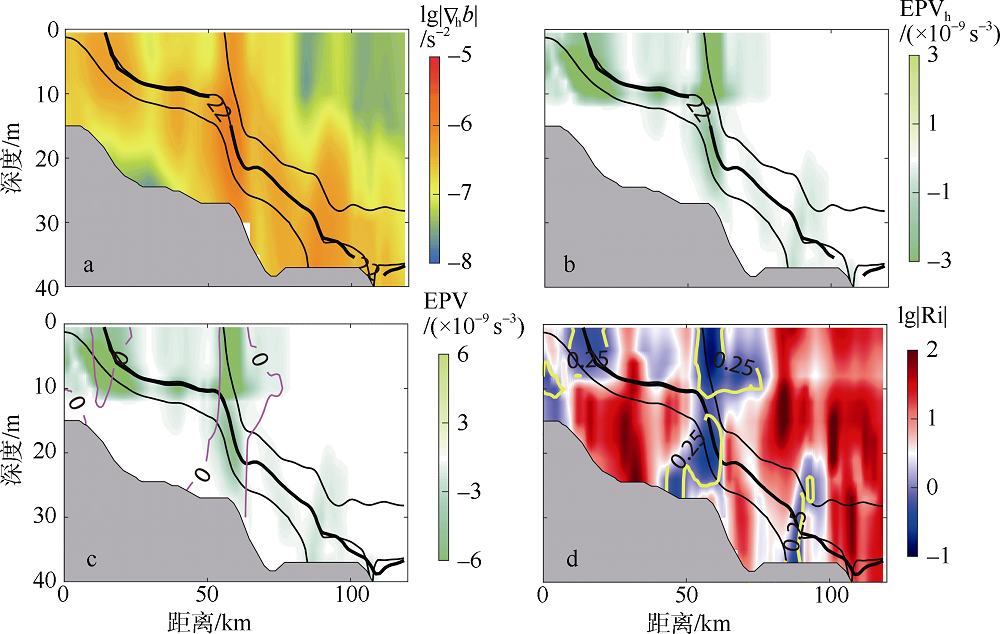
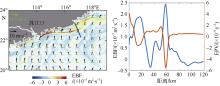
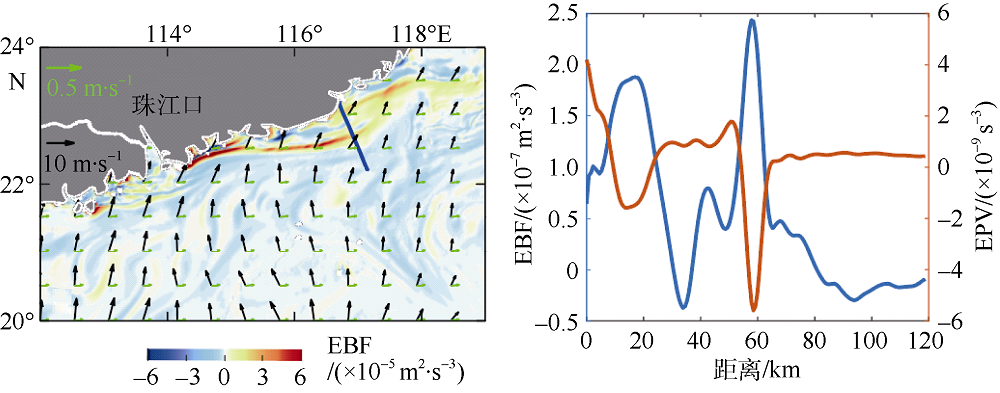
本文利用现场观测资料和卫星遥感数据, 并结合ROMS(regional ocean modeling system)数值模拟对南海北部粤东陆架的锋面特征及其影响因素进行探讨。观测结果显示, 夏季南海北部陆架存在活跃的上升流温度锋面, 其水平尺度约为50km, 强度达到0.06℃∙km-1, 大于同时期卫星遥感观测结果, 垂向影响深度超过20m, 且具有一阶理查森数(Richardson number, Ri)的典型动力学特征。进一步的ROMS 模式诊断分析结果显示, 锋面处水平梯度增强, 且动力学上表现出一阶Ri数, 为锋面不稳定的发生提供了有利条件。高分辨率模拟结果显示, 在夏季西南风的驱动下, 沿锋面地转流方向的风应力引起的跨陆架Ekman输运将锋面处冷水向暖水运移, 导致水平浮力梯度和锋面强度增强并形成负Ertel位涡(Ertel potential vorticity, EPV)。因此, 夏季风场强迫引起的Ekman浮力通量(Ekman buoyancy flux, EBF)可能是南海北部锋面不稳定现象的主要贡献者, 对局地动力环境有重要影响。
中图分类号:
- P731.2
引用本文
曾毅港, 经志友, 黄小龙, 郑瑞玺. 夏季南海北部粤东陆架锋面的动力特征分析*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(4): 136-145.
ZENG Yigang, JING Zhiyou, HUANG Xiaolong, ZHENG Ruixi. Analysis of the dynamic characteristics of the east Guangdong shelf front in the northern South China Sea in summer[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 136-145.
| [1] | 经志友, 齐义泉, 华祖林, 2008. 南海北部陆架区夏季上升流数值研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 27(3): 1-8. |
| JING ZHIYOU, QI YIQUAN, HUA ZULIN, 2008. Numerical study on summer upwelling over northern continental shelf of South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 27(3): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 李立, 1990. 珠江口以西陆架夏季上升流的研究[J]. 台湾海峡, 9(4): 338-346. |
| LI LI, 1990. A study on the summer upwellings in shelf waters west to Zhujiang River mouth[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 9(4): 338-346. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 吴日升, 李立, 2003. 南海上升流研究概述[J]. 台湾海峡, 22(2): 269-277. |
| WU RISHENG, 2003. Summarization of study on upwelling system in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 22(2): 269-277. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 夏华永, 刘长建, 王东晓, 2018. 2006年夏季珠江冲淡水驱动的上升流[J]. 海洋学报, 40(7): 43-54. |
| XIA HUAYONG, LIU CHANGJIAN, WANG DONGXIAO, 2018. The upwelling driven by the Zhujiang River runoff in 2006 summer[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 40(7): 43-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 徐闯, 许永基, 胡嘉镗, 等, 2019. 基于高精度海洋动力模型的珠江口羽状流季节和年际变化规律研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 38(3): 43-52. |
| XU CHUANG, XU YONGJI, HU JIATANG, et al, 2019. Study on the seasonal and interannual variability of river plume in the Pearl River Estuary based on a high-resolution ocean dynamic model[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 38(3): 43-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 杨阳, 孟强, 夏华永, 等, 2010. 2006年夏季珠江冲淡水扩展及生态响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 29(6): 15-21. |
| MENG QIANG, XIA HUAYONG, et al, 2010. Expansion of the Pearl River diluted water in 2006 and its ecological response[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 29(6): 15-21. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 张燕, 夏华永, 钱立兵, 等, 2011. 2006年夏、冬季珠江口附近海域水文特征调查分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 30(1): 20-28. |
| ZHANG YAN, XIA HUAYONG, QIAN LIBING, et al, 2011. Analysis on hydrological characteristics off the Pearl River Estuary in summer and winter of 2006[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 30(1): 20-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 郑瑞玺, 经志友, 罗士浩, 2018. 南海北部反气旋涡旋边缘的次中尺度动力过程分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 37(3): 19-25. |
| ZHENG RUIXI, JING ZHIYOU, LUO SHIHAO, 2018. Analysis of sub-mesoscale dynamic processes in the periphery of anticyclonic eddy in the northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 37(3): 19-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 庄伟, 王东晓, 吴日升, 等, 2005. 2000年夏季福建、广东沿海上升流的遥感与船舶观测分析[J]. 大气科学, 29(3): 438-444. |
| ZHUANG WEI, WANG DONGXIAO, WU RISHENG, et al, 2005. Coastal upwelling off eastern Fujian-Guangdong detected by remote sensing[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 29(3): 438-444. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] |
ATLAS R, HOFFMAN R N, ARDIZZONE J, et al, 2011. A cross-calibrated, multiplatform ocean surface wind velocity product for meteorological and oceanographic applications[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 92(2): 157-174.
doi: 10.1175/2010BAMS2946.1 |
| [11] |
BOCCALETTI G, FERRARI R, FOX-KEMPER B, 2007. Mixed layer instabilities and restratification[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 37(9): 2228-2250.
doi: 10.1175/JPO3101.1 |
| [12] |
BRANNIGAN L, MARSHALL D P, NA VEIRA GARABA TO A C, et al, 2017. Submesoscale instabilities in mesoscale eddies[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 47(12): 3061-3085.
doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-16-0178.1 |
| [13] | BODNER A S, FOX-KEMPER B, 2020. A breakdown in potential vorticity estimation delineates the submesoscale-to-turbulence boundary in large eddy simulations[J]. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, 12(10): e2020MS002049. |
| [14] |
CAPET X, MCWILLIAMS J C, MOLEMAKER M J, et al, 2008. Mesoscale to submesoscale transition in the California current system. Part Ⅱ: frontal processes[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 38(1): 44-64.
doi: 10.1175/2007JPO3672.1 |
| [15] |
CARTON J A, CHEPURIN G, CAO XIANHE, 2000. A simple Ocean Data Assimilation analysis of the global upper ocean 1950-95. Part Ⅱ: results[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 30(2): 311-326.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(2000)030<0311:ASODAA>2.0.CO;2 |
| [16] | CHEN GENGXIN, HOU YIJUN, CHU XIAOQING, 2011. Mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea: Mean properties, spatiotemporal variability, and impact on thermohaline structure[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 116(C6): C06018. |
| [17] |
D'ASARO E, LEE C, RAINVILLE L, et al, 2011. Enhanced turbulence and energy dissipation at ocean fronts[J]. Science, 332(6027): 318-322.
doi: 10.1126/science.1201515 |
| [18] |
DONLON C J, MARTIN M, STARK J, et al, 2012. The Operational Sea Surface Temperature and Sea Ice Analysis (OSTIA) system[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 116: 140-158.
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2010.10.017 |
| [19] | FANG GUOHONG, WANG GANG, FANG YUE, et al, 2012. A review on the South China Sea western boundary current[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 31(5): 1-10. |
| [20] |
FOX-KEMPER B, FERRARI R, HALLBERG R, 2008. Parameterization of mixed layer eddies. Part I: Theory and diagnosis[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 38(6): 1145-1165.
doi: 10.1175/2007JPO3792.1 |
| [21] |
GAN JIANPING, WANG DONGXIAO, et al, 2009a. Interaction of a river plume with coastal upwelling in the northeastern South China Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 29(4): 728-740.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2008.12.002 |
| [22] | GAN JIANPING, CHEUNG A, GUO XIAOGANG, et al, 2009b. Intensified upwelling over a widened shelf in the northeastern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 114(C9): C09019. |
| [23] |
GUO LIN, XIU PENG, CHAI FEI, et al, 2017. Enhanced chlorophyll concentrations induced by kuroshio intrusion fronts in the Northern South China Sea[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 44(22): 11565-11572.
doi: 10.1002/2017GL075336 |
| [24] |
HANEY S, FOX-KEMPER B, JULIEN K, et al, 2015. Symmetric and geostrophic instabilities in the wave-forced ocean mixed Layer[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 45(12): 3033-3056.
doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-15-0044.1 |
| [25] | HORII T, UEKI I, ANDO K, 2020. Coastal upwelling events, salinity stratification, and barrier layer observed along the southwestern coast of Sumatra[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research. 125(12): e2020JC016287. |
| [26] |
HU JIANYU, WANG XIAOHUA, 2016a. Progress on upwelling studies in the China seas[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 54(3): 653-673.
doi: 10.1002/2015RG000505 |
| [27] |
HU ZIFENG, PAN DELU, HE XIANQIANG, et al, 2016b. Diurnal variability of turbidity fronts observed by geostationary satellite ocean color remote sensing[J]. Remote Sensing, 8(2): 147.
doi: 10.3390/rs8020147 |
| [28] | HUANG XIAOLONG, JING ZHIYOU, ZHENG RUIXI, et al, 2020. Dynamical analysis of submesoscale fronts associated with wind-forced offshore jet in the western South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 39(11): 1-12. |
| [29] | JING ZHIYOU, QI YIQUAN, DU YAN, 2011. Upwelling in the continental shelf of northern South China Sea associated with 1997-1998 El Niño[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 116(C2): C02033. |
| [30] | JING ZHIYOU, QI YIQUAN, DU YAN, et al, 2015. Summer upwelling and thermal fronts in the northwestern South China Sea: Observational analysis of two mesoscale mapping surveys[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 120(3): 1993-2006. |
| [31] | JING ZHIYOU, QI YIQUAN, FOX-KEMPER B, et al, 2016. Seasonal thermal fronts on the northern South China Sea shelf: satellite measurements and three repeated field surveys[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 121(3): 1914-1930. |
| [32] |
JING ZHIYOU, FOX-KEMPER B, CAO HAIJIN, et al, 2021. Submesoscale fronts and their dynamical processes associated with symmetric instability in the northwest Pacific Subtropical Ocean[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 51(1): 83-100.
doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-20-0076.1 |
| [33] |
LARGE W G, MCWILLIAMS J C, DONEY S C, 1994. Oceanic vertical mixing: a review and a model with a nonlocal boundary layer parameterization[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 32(4): 363-403.
doi: 10.1029/94RG01872 |
| [34] |
LETELIER J, PIZARRO O, NUÑEZ S, 2009. Seasonal variability of coastal upwelling and the upwelling front off central Chile[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 114(C12): C12009.
doi: 10.1029/2008JC005171 |
| [35] |
LIN HONGYANG, LIU ZHIYU, HU JIANYU, et al, 2020. Characterizing meso- to submesoscale features in the South China Sea[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 188: 102420.
doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2020.102420 |
| [36] |
MCWILLIAMS J C, MOLEMAKER M J, YAVNEH I, 2004. Ageostrophic, anticyclonic instability of a geostrophic, barotropic boundary current[J]. Physics of Fluids, 16(10): 3720-3725.
doi: 10.1063/1.1785132 |
| [37] |
NAN FENG, XUE HUIJIE, YU FEI, 2015. Kuroshio intrusion into the South China Sea: A review[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 137: 314-333.
doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2014.05.012 |
| [38] |
OU SUYING, ZHANG HONG, WANG DONGXIAO, 2009. Dynamics of the buoyant plume off the Pearl River Estuary in summer[J]. Environmental Fluid Mechanics, 9(5): 471-492.
doi: 10.1007/s10652-009-9146-3 |
| [39] |
QIU CHUNHUA, MAO HUABIN, LIU HAILONG, et al, 2019. Deformation of a warm eddy in the northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 124(8): 5551-5564.
doi: 10.1029/2019JC015288 |
| [40] |
REN SHIHE, XIE JIPING, ZHU JIANG, 2014. The roles of different mechanisms related to the tide-induced fronts in the Yellow Sea in summer[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 31(5): 1079-1089.
doi: 10.1007/s00376-014-3236-y |
| [41] |
RISIEN C M, CHELTON D B, 2008. A global climatology of surface wind and wind stress fields from eight years of QuikSCAT Scatterometer data[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 38(11): 2379-2413.
doi: 10.1175/2008JPO3881.1 |
| [42] |
SHU YEQIANG, CHEN JU, YAO JINGLONG, et al, 2014. Effects of the Pearl River plume on the vertical structure of coastal currents in the Northern South China Sea during summer 2008[J]. Ocean Dynamics, 64(12): 1743-1752.
doi: 10.1007/s10236-014-0779-5 |
| [43] |
STONE P H, 1966. On non-geostrophic baroclinic stability[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 23(4): 390-400.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1966)023<0390:ONGBS>2.0.CO;2 |
| [44] |
STONE P H, 1970. On non-geostrophic baroclinic stability: Part Ⅱ[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 27(5): 721-726.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1970)027<0721:ONGBSP>2.0.CO;2 |
| [45] |
TANG DANLING, Kester D R, Ni I H, et al, 2002. Upwelling in the Taiwan Strait during the summer monsoon detected by satellite and shipboard measurements[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 83(3): 457-471.
doi: 10.1016/S0034-4257(02)00062-7 |
| [46] |
THOMAS L N, 2005. Destruction of potential vorticity by winds[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 35(12): 2457-2466.
doi: 10.1175/JPO2830.1 |
| [47] | THOMAS L N, TAYLOR J R, FERRARI R, et al, 2013. Symmetric instability in the Gulf Stream[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 91: 96-110. |
| [48] |
WANG DONGXIAO, LIU YUN, QI YIQUAN, et al, 2001. Seasonal variability of thermal fronts in the northern South China Sea from satellite data[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 28(20): 3963-3966.
doi: 10.1029/2001GL013306 |
| [49] | WANG DONGXIAO, SHU YEQIANG, XUE HUIJIE, et al, 2014. Relative contributions of local wind and topography to the coastal upwelling intensity in the northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 119(4): 2550-2567. |
| [50] |
WANG GUIHUA, SU JILAN, CHU P C, 2003. Mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea observed with altimeter data[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 30(21): 2121.
doi: 10.1029/2003GL018532 |
| [51] |
WANG GUIHUA, WANG CHUNZAI, HUANG RUIXIN, 2010. Interdecadal Variability of the Eastward Current in the South China Sea Associated with the Summer Asian Monsoon[J]. Journal of Climate, 23(22): 6115-6123.
doi: 10.1175/2010JCLI3607.1 |
| [52] | WANG GUIHUA, LI JIAXUN, WANG CHUNZAI, et al, 2012. Interactions among the winter monsoon, ocean eddy and ocean thermal front in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 117(C8): C08002. |
| [53] |
XIE SHANGPING, 2004. Satellite observations of cool ocean-atmosphere interaction[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 85(2): 195-208.
doi: 10.1175/BAMS-85-2-195 |
| [54] |
XIU PENG, CHAI FEI, 2011. Modeled biogeochemical responses to mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 116(C10): C10006.
doi: 10.1029/2010JC006800 |
| [55] |
YANG QINGXUAN, ZHAO WEI, LIANG XINFENG, et al, 2017. Elevated mixing in the periphery of mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 47(4): 895-907.
doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-16-0256.1 |
| [56] |
ZU TINGTING, WANG DONGXIAO, GAN JIANPING, et al, 2014. On the role of wind and tide in generating variability of Pearl River plume during summer in a coupled wide estuary and shelf system[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 136: 65-79.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2014.03.005 |
| [1] | 柳原, 柯志新, 李开枝, 谭烨辉, 梁竣策, 周伟华. 人类活动和沿岸流影响下的粤东近海浮游动物群落特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [2] | 江绿苗, 陈天然, 赵宽, 张婷, 许莉佳. 南海北部涠洲岛边缘珊瑚礁的生物侵蚀实验研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 155-165. |
| [3] | 许莉佳, 廖芝衡, 陈辉, 王永智, 黄柏强, 林巧云, 甘健锋, 杨静. 南海北部珊瑚群落结构特征及其对海洋热浪事件的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 58-71. |
| [4] | 赵明辉, 袁野, 张佳政, 张翠梅, 高金尉, 王强, 孙珍, 程锦辉. 南海北部被动陆缘洋陆转换带张裂-破裂研究新进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 173-183. |
| [5] | 李骏旻, 李博, 陈武阳, 刘军亮. 三亚近岸海浪观测特征及其对台风过程的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(4): 25-35. |
| [6] | 杨一凯, 曾丽丽. 挟带黑潮高盐水的中尺度涡在南海北部的时空特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 75-85. |
| [7] | 张金尚, 邹定辉, 马玉, 李锐祥, 刘愉强, 孟强, 刘同木, 史华明. 南海北部水团及中尺度现象对营养盐时空分布的影响*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(1): 168-181. |
| [8] | 马梦真, 李芊, 吴正超, 陈寅超, 俞建成. 南海北部最小含氧带水下滑翔机观测结果初步分析*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(1): 131-142. |
| [9] | 王仁政, 单正垛, 孟思雨, 宫响. 南海北部次表层叶绿素最大值年际变化特征分析*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(6): 63-75. |
| [10] | 王剑, 陈楚群, 周伟华, 李祥付, 吴颉, 叶海彬, 唐世林. 利用遥感技术估算南海北部表层异养细菌丰度*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(5): 53-62. |
| [11] | 苏晓康, 赵明辉, 李子正, 袁野, 王星月, 程锦辉, 张佳政. 南海北部陆缘OBS2018-H2测线地壳结构初步结果*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(5): 111-122. |
| [12] | 蔡树群, 牛建伟, 何映晖, 陈学彬, 张永康, 许洁馨, 陈植武, 林世柽, 谢皆烁. 基于海上风电场构建海洋水文同步实时现场观测系统的思考[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(3): 96-102. |
| [13] | 黄小龙, 经志友, 郑瑞玺, 张旭. 南海西部夏季上升流锋面的次中尺度特征分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(3): 1-9. |
| [14] | 舒婵, 耿兵绪, 房巍巍, 修鹏. 南海北部海洋生态模型的参数分析及遗传算法优化[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(2): 98-106. |
| [15] | 杨威, 董园, 俎婷婷, 刘长建, 修鹏. 南海北部夏季叶绿素a分布规律及影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(6): 9-20. |
|
||