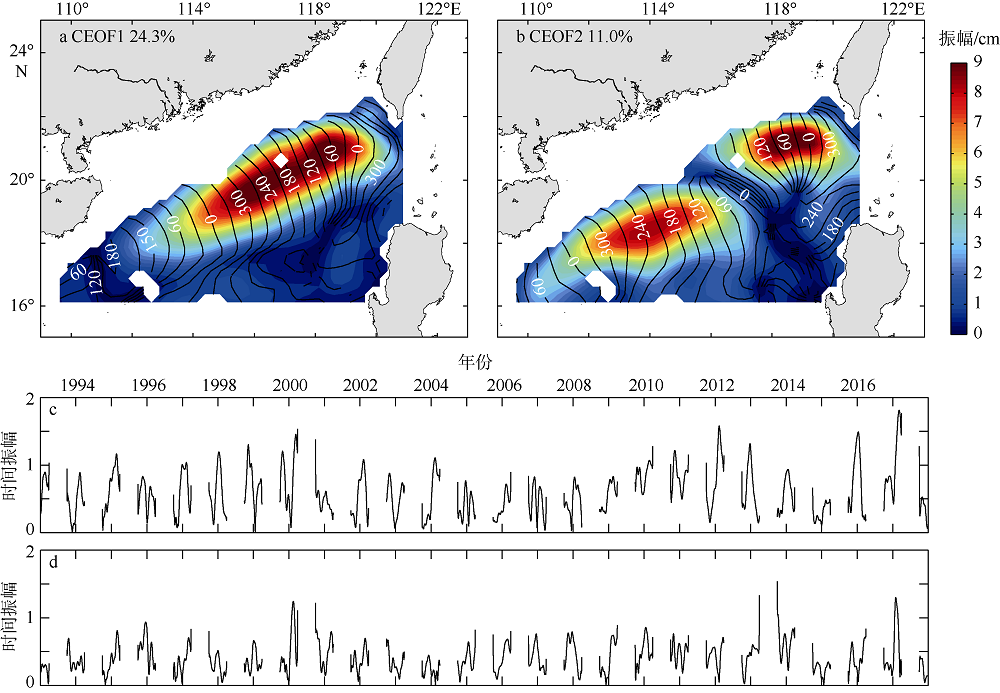
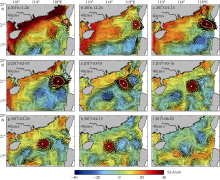
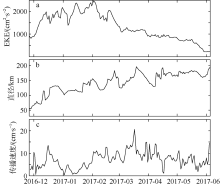
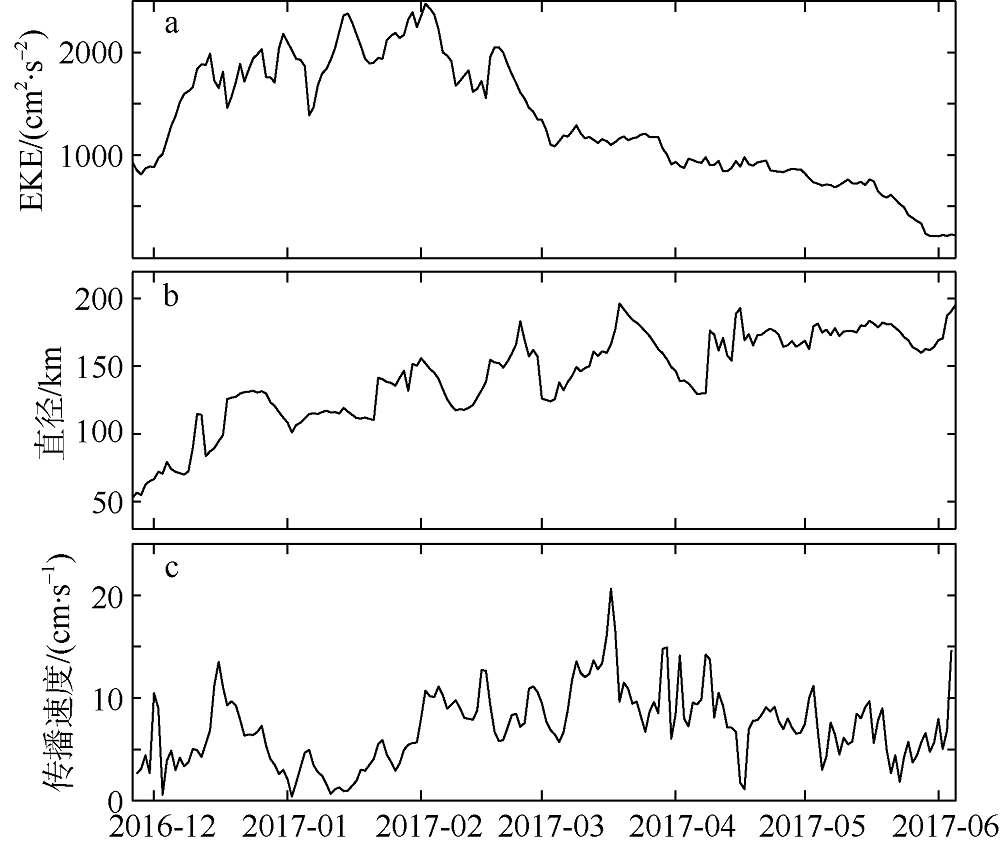
| [1] |
程旭华, 齐义泉, 王卫强 , 2005. 南海中尺度涡的季节和年际变化特征分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 24(4):51-59.
|
|
CHENG XUHUA, QI YIQUAN, WANG WEIQIANG , 2005. Seasonal and interannual variabilities of mesoscale eddies in South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 24(4):51-59 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
李立, 许金电, 靖春生 , 等, 2002. 南海海面高度、动力地形和环流的周年变化——TOPEX/Poseidon卫星测高应用研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 32(12):978-986.
|
|
LI LI, XU JINDIAN, JING CHUNSHENG , et al, 2003. Annual variation of sea surface height, dynamic topography and circulation in the South China Sea: a TOPEX/Poseidon satellite altimetry study[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 46(2):127-138.
|
| [3] |
李燕初, 蔡文理, 李立 , 等, 2003. 南海东北部海域中尺度涡的季节和年际变化[J]. 热带海洋学报, 22(3):61-70.
|
|
LI YANCHU, CAI WENLI, LI LI , et al, 2003. Seasonal and interannual variabilities of mesoscale eddies in northeastern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 22(3):61-70 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
王桂华, 苏纪兰, 齐义泉 , 2005. 南海中尺度涡研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 20(8):882-886.
|
|
WANG GUIHUA, SU JILAN, QI YIQUAN , 2005. Advances in studying mesoscale eddies in South China Sea[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 20(8):882-886 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
魏凤英 , 2007. 现代气候统计诊断与预测技术[M]. 2版. 北京: 气象出版社: 1-296.
|
| [6] |
CHELTON D B, SCHLAX M G, SAMELSON R M , 2011. Global observations of nonlinear mesoscale eddies[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 91(2):167-216.
doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2011.01.002
|
| [7] |
CHEN GENGXIN, HOU YIJUN, CHU XIAOQING , et al, 2009. The variability of eddy kinetic energy in the South China Sea deduced from satellite altimeter data[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 27(4):943-954.
doi: 10.1007/s00343-009-9297-6
|
| [8] |
CHEN GENGXIN, HOU YIJUN, CHU XIAOQING , et al, 2010. Vertical structure and evolution of the Luzon Warm Eddy[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 28(5):955-961.
doi: 10.1007/s00343-010-9040-3
|
| [9] |
CHEN GENGXIN, HOU YIJUN, CHU XIAOQING , 2011. Mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea: mean properties, spatiotemporal variability, and impact on thermohaline structure[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 116(C6):C06018.
|
| [10] |
CHOW C-H, HU J-H, CENTURIONI L R , et al, 2008. Mesoscale Dongsha Cyclonic Eddy in the northern South China Sea by drifter and satellite observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 113(C4):C04018.
doi: 10.1029/2007JC004542
|
| [11] |
CHU XIAOQING, XUE HUIJIE, QI YIQUAN , et al, 2014. An exceptional anticyclonic eddy in the South China Sea in 2010[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 119(2):881-897.
doi: 10.1002/2013JC009314
|
| [12] |
FANG GUOHONG, FANG WENDONG, FANG YUE , et al, 1998. A survey of studies on the South China Sea upper ocean circulation[J]. Acta Oceanographica Taiwanica, 37(1):1-16.
|
| [13] |
FANG WENDONG, GUO JUNJIAN, SHI PING , et al, 2006. Low frequency variability of South China Sea surface circulation from 11 years of satellite altimeter data[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 33(22):L22612.
doi: 10.1029/2006GL027431
|
| [14] |
FANG WENDONG, QIU FUWEN, GUO PU , 2014. Summer circulation variability in the South China Sea during 2006-2010[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 137:47-54.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2014.04.014
|
| [15] |
HAUSMANN U, MCGILLICUDDY D J JR, MARSHALL J , 2017. Observed mesoscale eddy signatures in Southern Ocean surface mixed-layer depth[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 122(1):617-635.
doi: 10.1002/jgrc.v122.1
|
| [16] |
HE QINGYOU, ZHAN HAIGANG, CAI SHUQUN , et al, 2018. A new assessment of mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea: surface features, three-dimensional structures, and thermohaline transports[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 123(7):4906-4929.
doi: 10.1029/2018JC014054
|
| [17] |
HE YINGHUI, CAI SHUQUN, WANG DONGXIAO , et al, 2015. A model study of Luzon Cold Eddies in the northern South China Sea[J]. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 97:107-123.
doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2014.12.007
|
| [18] |
HE YINGHUI, XIE JIESHUO, CAI SHUQUN , 2016. Interannual variability of winter eddy patterns in the eastern South China Sea[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 43(10):5185-5193.
doi: 10.1002/grl.v43.10
|
| [19] |
HU JIANYU, KAWAMURA H, HONG HUASHENG , et al, 2001. 3≈6 months variation of sea surface height in the South China Sea and its adjacent ocean[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 57(1):69-78.
doi: 10.1023/A:1011126804461
|
| [20] |
LYU KEWEI, YANG XIAOYI, ZHENG QUANAN , et al, 2016. Intraseasonal variability of the winter western boundary current in the South China Sea using satellite data and mooring observations[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 9(11):5079-5088.
doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2553049
|
| [21] |
MAO JIANGYU, WANG MING , 2018. The 30-60-day intraseasonal variability of sea surface temperature in the South China Sea during May-September[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 35(5):550-566.
doi: 10.1007/s00376-017-7127-x
|
| [22] |
NAN FENG, XUE HUIJIE, XIU PENG , et al, 2011. Oceanic eddy formation and propagation southwest of Taiwan[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 116(C12):C12045.
doi: 10.1029/2011JC007386
|
| [23] |
QIU CHUNHUA, MAO HUABIN, WANG YANHUI , et al, 2019. An irregularly shaped warm eddy observed by Chinese underwater gliders[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 75(2):139-148.
doi: 10.1007/s10872-018-0490-0
|
| [24] |
WANG DONGXIAO, XU HONGZHOU, LIN JING , et al, 2008. Anticyclonic eddies in the northeastern South China Sea during winter 2003/2004[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 64(6):925-935.
doi: 10.1007/s10872-008-0076-3
|
| [25] |
WANG XIA, FANG WENDONG, CHEN RONGYU , et al, 2017. The summer-fall anticyclonic eddy west of Luzon: structure and evolution in 2012 and interannual variability[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 172:84-92.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2017.03.004
|
| [26] |
WILKIN J L, ZHANG W G , 2007. Modes of mesoscale sea surface height and temperature variability in the East Australian Current[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 112(C1):C01013.
|
| [27] |
WILLIAMS S, PETERSEN M, BREMER P-T , et al, 2011. Adaptive extraction and quantification of geophysical vortices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 17(12):2088-2095.
doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2011.162
pmid: 22034327
|
| [28] |
WU C R, TANG T Y, LIN S F , 2005. Intra-seasonal variation in the velocity field of the northeastern South China Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 25(17):2075-2083.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2005.03.005
|
| [29] |
XIU PENG, CHAI FEI, SHI LEI , et al, 2010. A census of eddy activities in the South China Sea during 1993-2007[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 115(C3):C03012.
|
| [30] |
YANG HAIJUN, LIU QINYU , 2003. Forced Rossby wave in the northern South China Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 50(7):917-926.
doi: 10.1016/S0967-0637(03)00074-8
|
| [31] |
YUAN DONGLIANG, HAN WEIQING, HU DUNXIN , 2006. Surface Kuroshio path in the Luzon Strait area derived from satellite remote sensing data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 111(C11):C11007.
doi: 10.1029/2005JC003412
|
| [32] |
YUAN DONGLIANG, HAN WEIQING, HU DUNXIN , 2007. Anti-cyclonic eddies northwest of Luzon in summer-fall observed by satellite altimeters[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 34(13):L13610.
doi: 10.1029/2007GL029401
|
| [33] |
ZHUANG WEI, DU YAN, WANG DONGXIAO , et al, 2010a. Pathways of mesoscale variability in the South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 28(5):1055-1067.
doi: 10.1007/s00343-010-0035-x
|
| [34] |
ZHUANG WEI, XIE SHANGPING, WANG DONGXIAO , et al, 2010b. Intraseasonal variability in sea surface height over the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2010,115(C4):C04010.
|
| [35] |
ZHAO RUIXIANG, ZHU XIAOHUA, GUO XINYU , 2017. The impact of monsoon winds and mesoscale eddies on thermohaline structures and circulation patterns in the northern South China Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 143:240-256.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2016.06.009
|
 ),Rongyu CHEN2
),Rongyu CHEN2