热带海洋学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 18-29.doi: 10.11978/2024095CSTR: 32234.14.2024095
基于水文气象参数的南海西部叶绿素a估算*
郑媛宁1,2( ), 李彩1(
), 李彩1( ), 周雯1, 许占堂1, 施震1, 张现清1,2, 刘聪1,2, 赵金成1,2
), 周雯1, 许占堂1, 施震1, 张现清1,2, 刘聪1,2, 赵金成1,2
- 1.热带海洋国家重点实验室(中国科学院南海海洋研究所), 广东 广州 510301
2.中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
-
收稿日期:2024-04-26修回日期:2024-06-19出版日期:2025-03-10发布日期:2025-04-11 -
通讯作者:李彩 -
作者简介:郑媛宁(1999—), 女, 河南省邓州市人, 硕士研究生, 研究方向是海洋环境监测。email: zhengyuanning21@mails.ucas.ac.cn
*感谢国家自然科学基金共享航次, 感谢中国科学院南海海洋研究所海洋光学学科组全体成员对于本次实验数据获取做出的贡献。
-
基金资助:广东省基础与应用基础研究基金项目(2023A1515240073); 广州市南沙区科技规划项目(2022ZD001); 国家重点研发计划项目(2016YFC1400603); 国家重点研发计划项目(2017YFC0506305)
Estimation of Chlorophyll-a in the western South China Sea based on hydro-meteorological parameters*
ZHENG Yuanning1,2( ), LI Cai1(
), LI Cai1( ), ZHOU Wen1, XU Zhantang1, SHI Zhen1, ZHANG Xianqing1,2, LIU Cong1,2, ZHAO Jincheng1,2
), ZHOU Wen1, XU Zhantang1, SHI Zhen1, ZHANG Xianqing1,2, LIU Cong1,2, ZHAO Jincheng1,2
- 1. State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography (South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2024-04-26Revised:2024-06-19Online:2025-03-10Published:2025-04-11 -
Contact:LI Cai -
Supported by:Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation(2023A1515240073); Science and Technology Planning Project of Science and Technology Planning Project of Nansha District, Guangzhou(2022ZD001); National Key Research and Development Program of China(2016YFC1400603); National Key Research and Development Program of China(2017YFC0506305)
摘要:
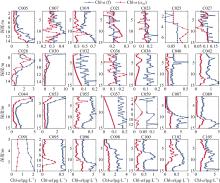
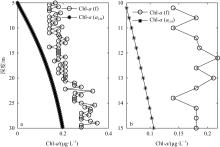
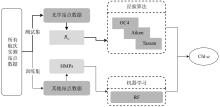
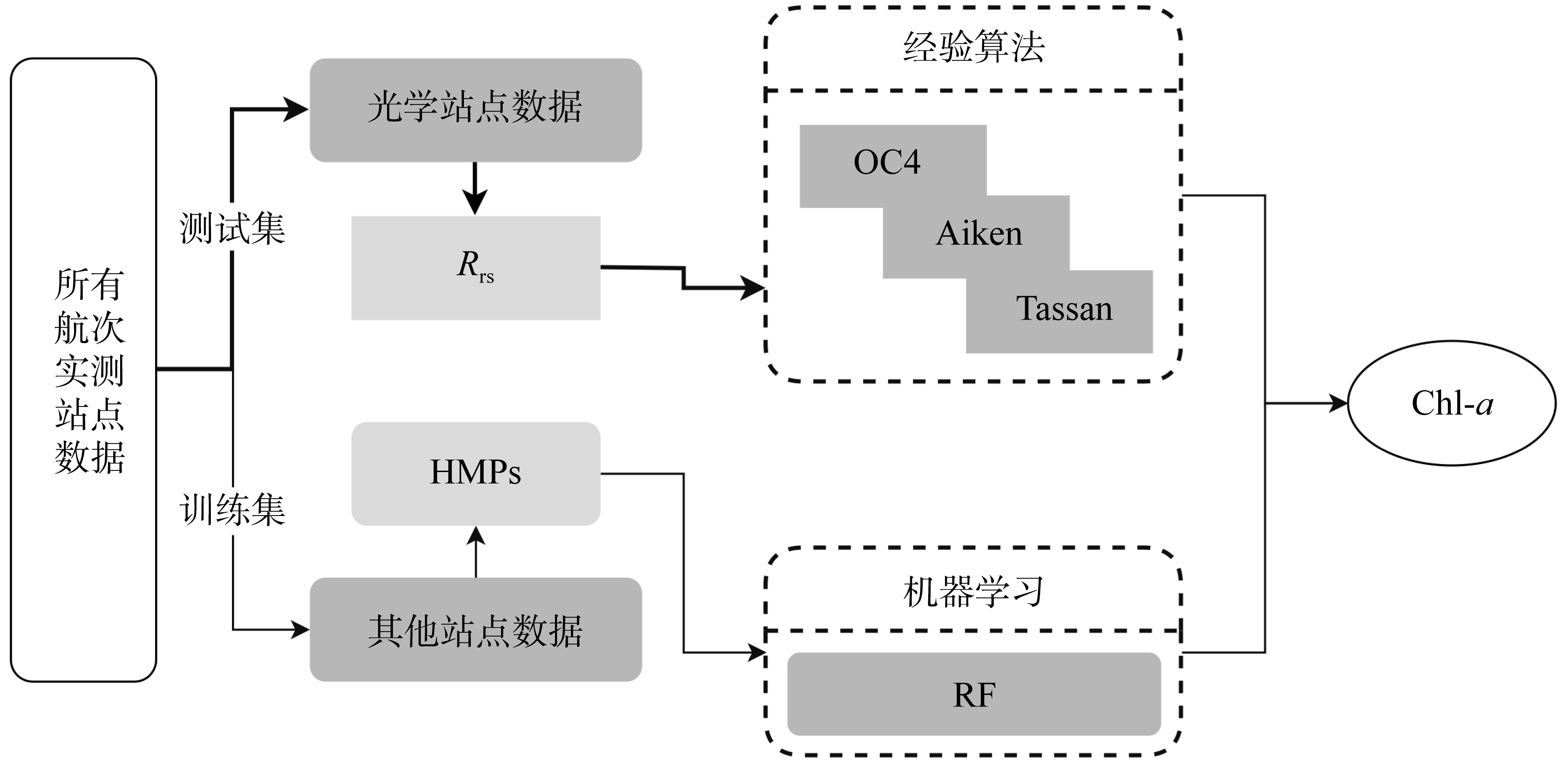
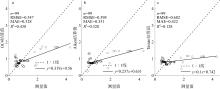
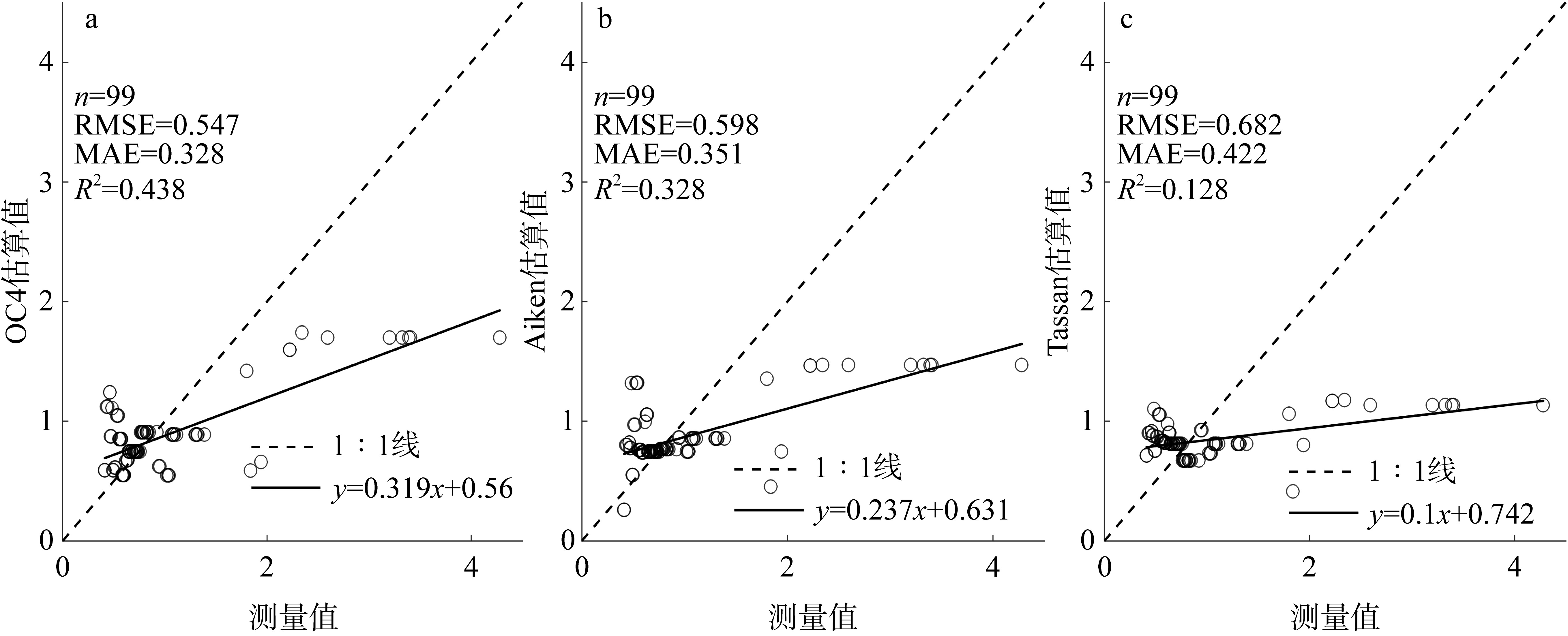
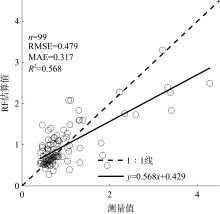
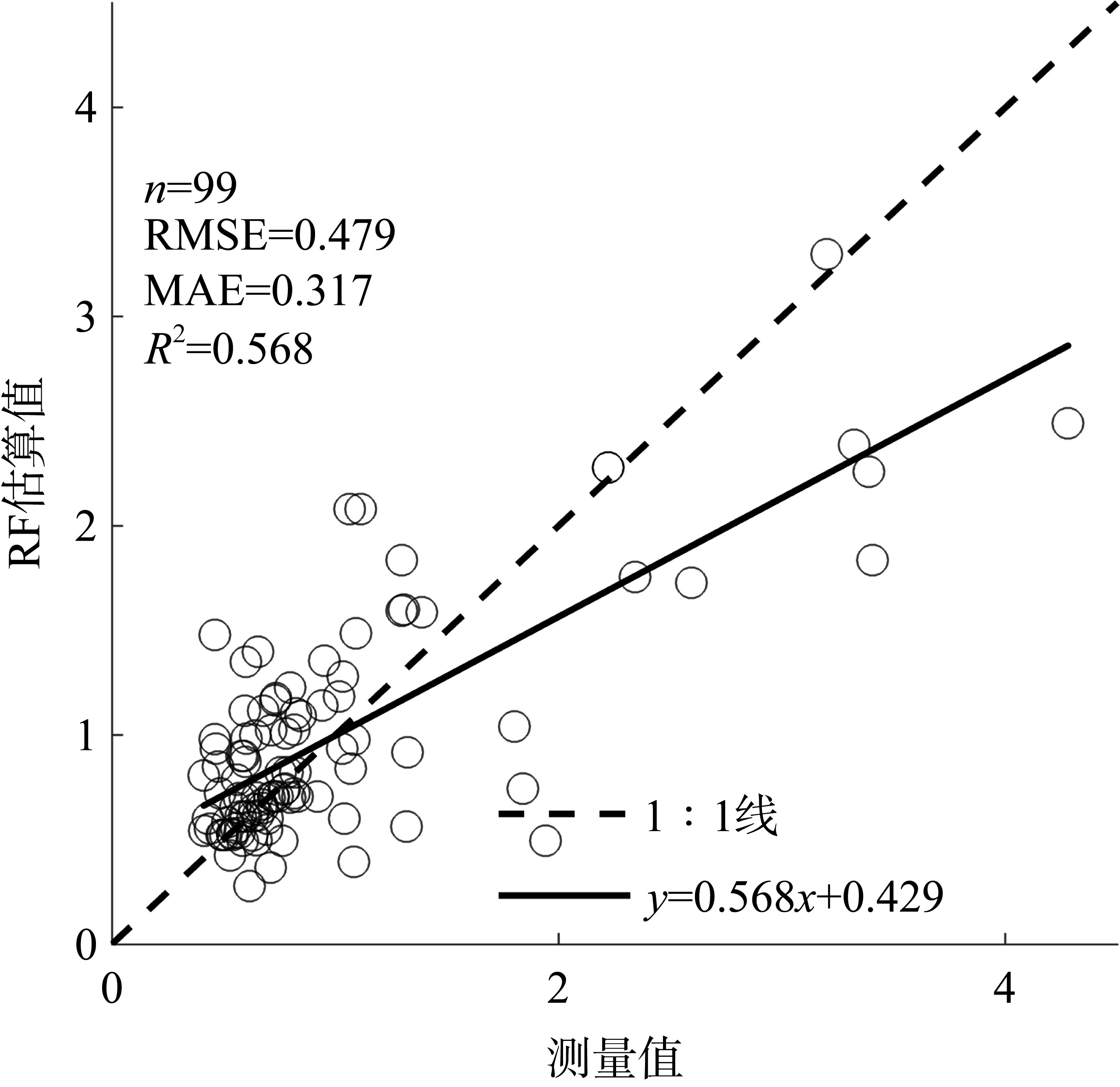
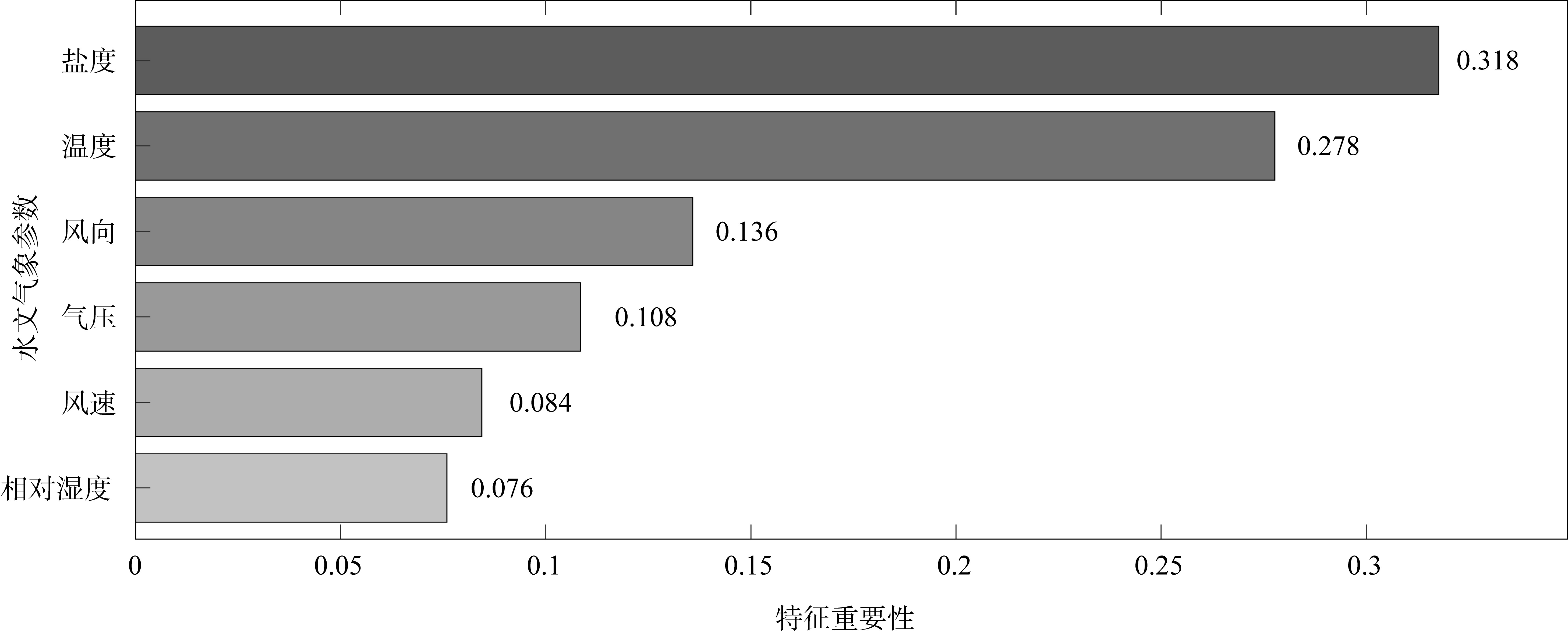
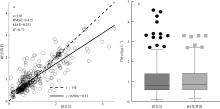
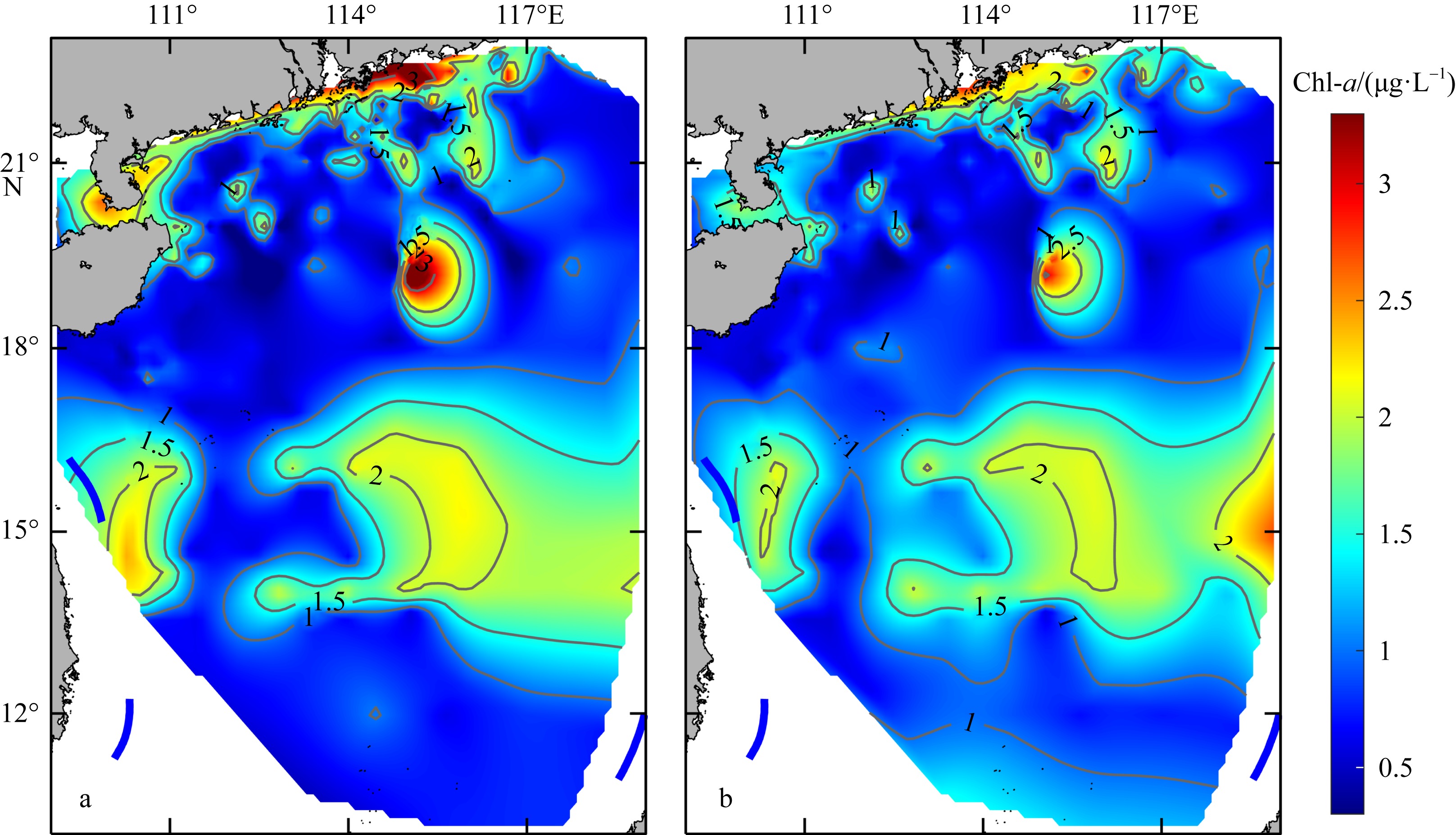
文章以叶绿素a (Chlorophyll-a, Chl-a)的低成本、高精度估算为目标, 利用近十年南海西部调查航次数据, 基于随机森林(random forest, RF)算法, 以水文气象条件的变化对海洋生化过程的影响及贡献为基础, 以水文气象参数(hydro-meteorological parameters, HMPs)作为输入数据, 构建Chl-a的低成本估算模型对南海西部表层Chl-a进行了估算。为验证基于水文气象参数估算Chl-a的可靠性, 利用准分析算法(quasi-analytical algorithm, QAA)以实测固有光学特性参数为基础, 推导得到原位遥感反射率(remote sensing reflectance, Rrs)。在此基础上, 结合海洋颜色4 (ocean color 4, OC4)、Aiken和Tassan等经典水色产品经验算法对 Chl-a进行了估算及评价, 评价结果表明OC4算法的估算精度最高, R2可达0.438。与RF模型0.568的R2比较不难看出, 得益于HMPs的大数据量, 基于HMPs的RF模型其Chl-a估算结果表现出较为优秀的稳定性和泛化性, 与实测结果的空间分布一致性更好。通过对特征参数重要性进行研究发现, 盐度是基于HMPs估算Chl-a的机器学习模型中最重要的特征变量, 其次依次是温度、风与气压, 贡献率最低的是相对湿度。
中图分类号:
- P731.3
引用本文
郑媛宁, 李彩, 周雯, 许占堂, 施震, 张现清, 刘聪, 赵金成. 基于水文气象参数的南海西部叶绿素a估算*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(2): 18-29.
ZHENG Yuanning, LI Cai, ZHOU Wen, XU Zhantang, SHI Zhen, ZHANG Xianqing, LIU Cong, ZHAO Jincheng. Estimation of Chlorophyll-a in the western South China Sea based on hydro-meteorological parameters*[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(2): 18-29.
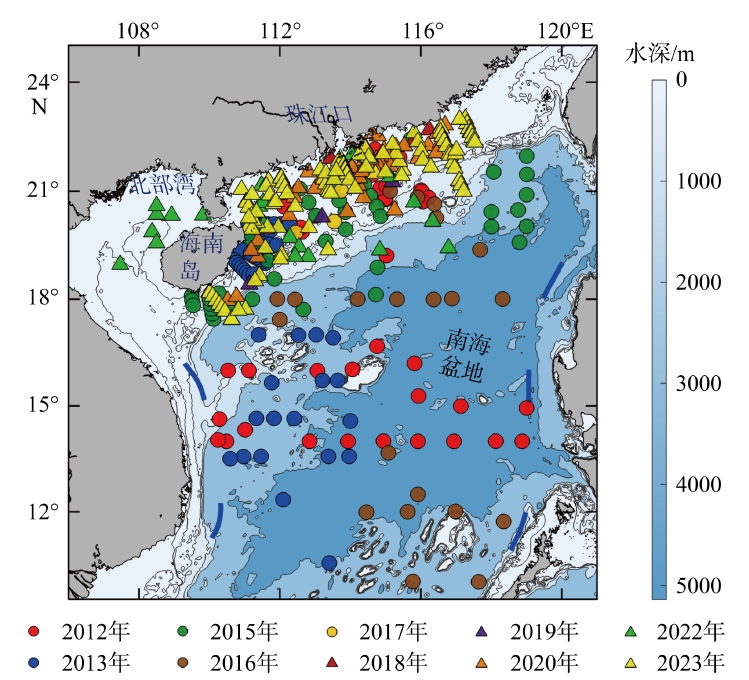
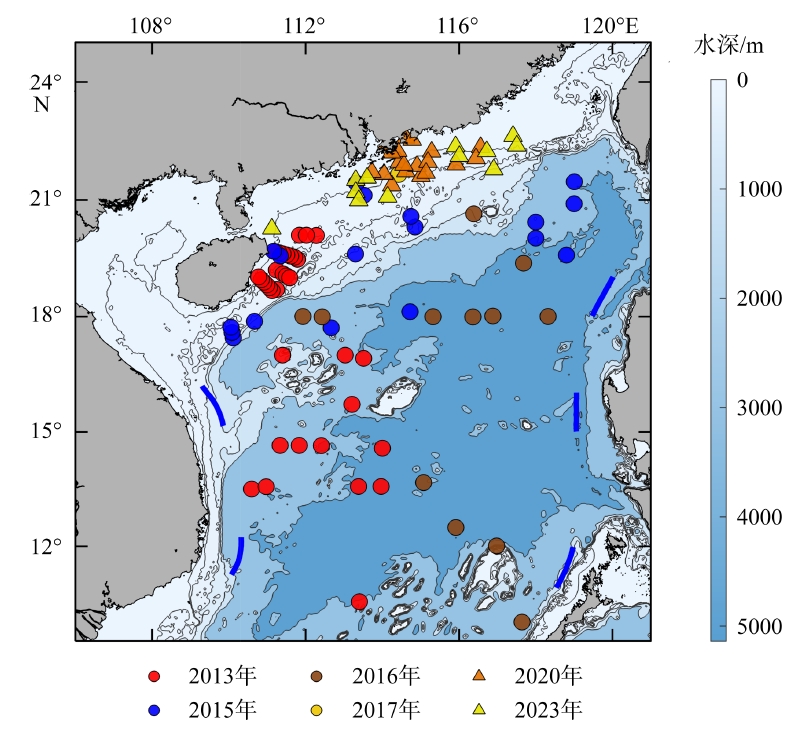
表1
2012年至2023年12次巡航收集的信息概要"
| 年份 | 数据采集时间 | 覆盖范围 | 站点数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 9月30日—10月25日 | 14°00′—22°12′N, 110°12′—119°00′E | 37 |
| 2013 | 8月9日—9月2日 | 10°00′—20°06′N, 110°30′—114°00′E | 61 |
| 2015 | 6月21日—7月17日 | 17°24′—22°30′N, 109°30′—119°00′E | 43 |
| 2016 | 9月3日—9月23日 | 10°00′—21°00′N, 111°30′—119°00′E | 23 |
| 2017 | 10月1日—10月23日 | 18°24′—21°54′N, 110°18′—114°54′E | 4 |
| 2018 | 6月12日—6月22日 | 21°30′—23°06′N, 113°12′—116°54′E | 7 |
| 8月18日—8月25日 | 17°54′—21°18′N, 110°36′—115°18′E | 1 | |
| 2019 | 9月27日—10月5日 | 17°42′—23°00′N, 110°30′—117°06′E | 3 |
| 2020 | 8月28日—9月4日 | 18°42′—22°00′N, 107°24′—117°00′E | 32 |
| 6月1日—6月29日 | 17°24′—23°06′N, 110°00′—117°36′E | 22 | |
| 2022 | 8月14日—6月22 日 | 14°00′—22°24′N, 110°12′—119°00′E | 27 |
| 2023 | 6月23日—7月20日 | 10°00′—20°06′N, 110°30′—114°00′E | 129 |
| [1] |
李建鸿, 黄昌春, 查勇, 等, 2021. 长江干流表层水体悬浮物的空间变化特征及遥感反演[J]. 环境科学, 42(11): 5239-5249.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
柳青青, 孟朔羽, 徐茗, 等, 2021. 随机森林反演卫星遥感海表面盐度研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 48(9): 1538-1545.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
王春玲, 史锴源, 明星, 等, 2022. 基于机器学习的水体化学需氧量高光谱反演模型对比研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 42(8): 2353-2358.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
张莹, 谢仕义, 邓伟彬, 等, 2019. 基于机器学习理论的海洋水质评价模型[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 41(6): 819-825.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
doi: 10.1007/s10661-023-11492-3 pmid: 37354319 |
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39507-0 pmid: 37355684 |
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
doi: 10.1364/AO.33.002369 pmid: 20885588 |
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
doi: 10.1007/s11707-016-0585-0 |
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
doi: 10.1364/OE.503850 pmid: 38178466 |
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [1] | 刘慧, 张辉贤, 刘馨蔓, 林强, 沈萍萍. 南海小叶海蛞蝓(Phyllidiella nanhaiensis sp. nov.)线粒体基因组特征与系统进化[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(1): 1-8. |
| [2] | 刘杰, 闫桐, 经志友. 南海西北部连续台风激发的近惯性内波观测研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(1): 66-81. |
| [3] | 徐超, 龙丽娟, 李莎, 袁丽, 徐晓璐. 南海及其附属岛礁海洋科学考察历史资料系统整编3. 数据共享服务及应用[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 158-165. |
| [4] | 徐超, 龙丽娟, 李莎, 何云开, 袁丽, 徐晓璐. 南海及其附属岛礁海洋科学考察历史资料系统整编1. 资料整编技术及应用[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 143-149. |
| [5] | 徐超, 龙丽娟, 李莎, 徐晓璐, 袁丽. 南海及其附属岛礁海洋科学考察历史资料系统整编2. 数据治理技术与应用[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 150-157. |
| [6] | 齐焕东, 朱程, 李序春, 景昕蒂, 宋德瑞. 基于规则集和多层感知机的Argo温度数据质量控制方法*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 190-202. |
| [7] | 柳原, 柯志新, 李开枝, 谭烨辉, 梁竣策, 周伟华. 人类活动和沿岸流影响下的粤东近海浮游动物群落特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [8] | 刘玓玓, 张喜洋, 孙富林, 王明壮, 谭飞, 施祺, 王冠, 杨红强. 南海海滩岩微生物群落结构和特定菌株对其成因机制的启示*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 112-122. |
| [9] | 江绿苗, 陈天然, 赵宽, 张婷, 许莉佳. 南海北部涠洲岛边缘珊瑚礁的生物侵蚀实验研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 155-165. |
| [10] | 许莉佳, 廖芝衡, 陈辉, 王永智, 黄柏强, 林巧云, 甘健锋, 杨静. 南海北部珊瑚群落结构特征及其对海洋热浪事件的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 58-71. |
| [11] | 邱燕, 鞠东, 黄文凯, 王英民, 聂鑫. 南海中央海盆海底初始扩张时间的重新认定[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 154-165. |
| [12] | 赵明辉, 袁野, 张佳政, 张翠梅, 高金尉, 王强, 孙珍, 程锦辉. 南海北部被动陆缘洋陆转换带张裂-破裂研究新进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 173-183. |
| [13] | 黄谕, 王琳, 麦志茂, 李洁, 张偲. 南海热带岛礁生物土壤结皮中细菌的分离及其固砂特性初步研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(6): 101-110. |
| [14] | 王辰燕, 史敬文, 颜安南, 康亚茹, 王煜轩, 覃素丽, 韩民伟, 张瑞杰, 余克服. 有机磷酸酯在南海长棘海星中的生物富集特征及来源解析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(5): 30-37. |
| [15] | 李牛, 邸鹏飞, 冯东, 陈多福. 冷泉渗漏对海洋沉积物氧化还原环境地球化学识别的影响——以南海东北部F站位活动冷泉为例*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(5): 144-153. |
|
||