热带海洋学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 124-136.doi: 10.11978/2024117CSTR: 32234.14.2024117
基于微卫星标记9个缢蛏群体的遗传多样性分析
吴贵清1( ), 李瑞华1, 肖意豪1, 陈彦林1, 罗璇2, 刘相全3, 朱佳杰1, 吴雪萍1(
), 李瑞华1, 肖意豪1, 陈彦林1, 罗璇2, 刘相全3, 朱佳杰1, 吴雪萍1( )
)
- 1.广西民族大学海洋与生物技术学院, 广西 南宁 530007
2.广西壮族自治区水产技术推广站, 广西 南宁 530016
3.山东省海洋生态修复重点实验室(山东省海洋资源与环境研究院), 山东 烟台 264006
-
收稿日期:2024-06-01修回日期:2024-08-19出版日期:2025-03-10发布日期:2025-04-11 -
通讯作者:吴雪萍 -
作者简介:吴贵清(2000—), 男, 广西壮族自治区柳州市人, 硕士研究生, 从事贝类遗传与育种研究。email: 18077267931@163.com
-
基金资助:广西民族大学引进人才启动基金(2017KJQD007); 广西自然科学基金资助项目(2020GXNSFBA159010); 2022年广西壮族自治区大学生创新创业训练计划项目(S202210608162); 2022年广西壮族自治区大学生创新创业训练计划项目(S202210608163); 2023年广西壮族自治区大学生创新创业训练计划项目(S202310608040)
Analysis of genetic diversity in 9 populations of Sinonovacula constricta using microsatellite markers
WU Guiqing1( ), LI Ruihua1, XIAO Yihao1, CHEN Yanlin1, LUO Xuan2, LIU Xiangquan3, ZHU Jiajie1, WU Xueping1(
), LI Ruihua1, XIAO Yihao1, CHEN Yanlin1, LUO Xuan2, LIU Xiangquan3, ZHU Jiajie1, WU Xueping1( )
)
- 1. School of Marine Science and Biotechnology, Guangxi Minzu University, Nanning 530007, China
2. Guangxi Fisheries Technical Extension Station, Nanning 530016, China
3. Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Restoration for Marine Ecology (Shandong Marine Resource and Environment Research Institute), Yantai 264006, China
-
Received:2024-06-01Revised:2024-08-19Online:2025-03-10Published:2025-04-11 -
Contact:WU Xueping -
Supported by:High Level Introduction of Talent Research Start-up Projects of Guangxi Minzu University(2017KJQD007); Guangxi Natural Science Foundation Grant(2020GXNSFBA159010); Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for College Students of Guangxi in 2022(S202210608162); Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for College Students of Guangxi in 2022(S202210608163); Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for College Students of Guangxi in 2023(S202310608040)
摘要:
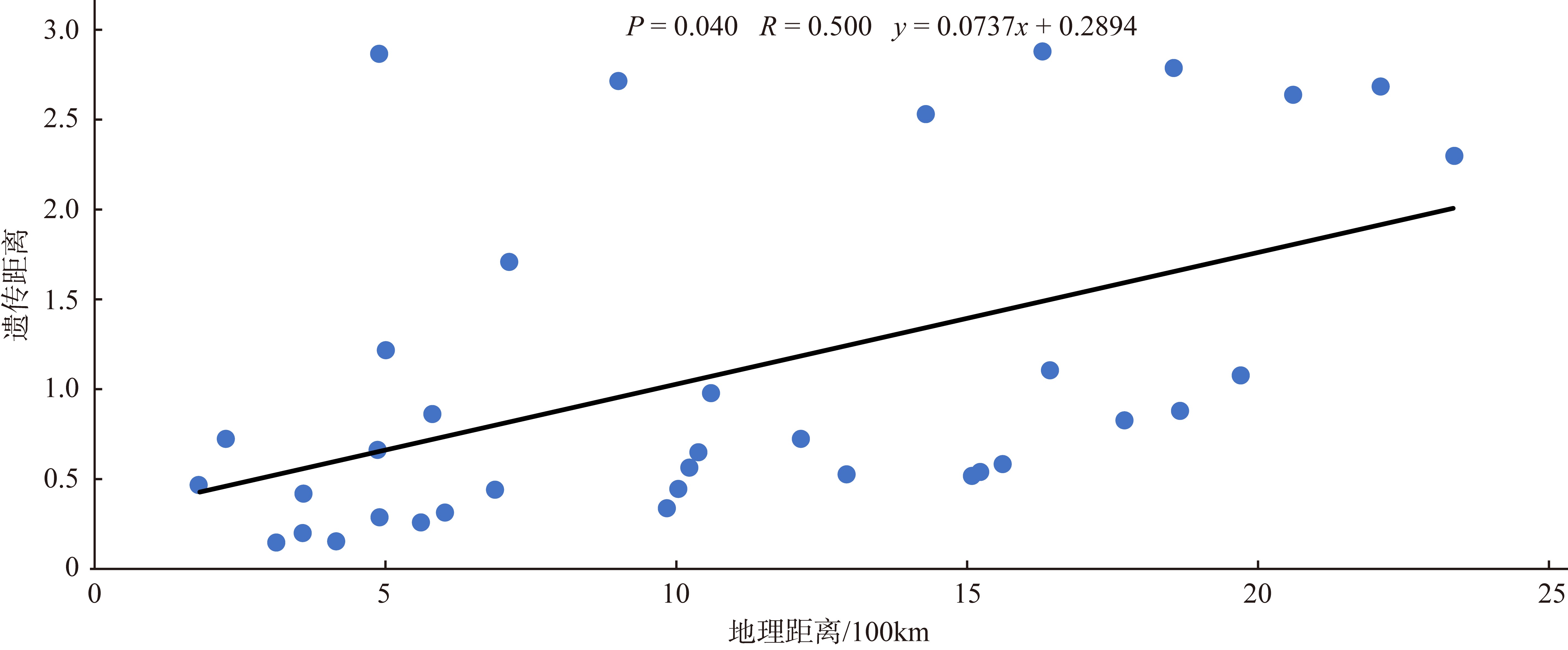
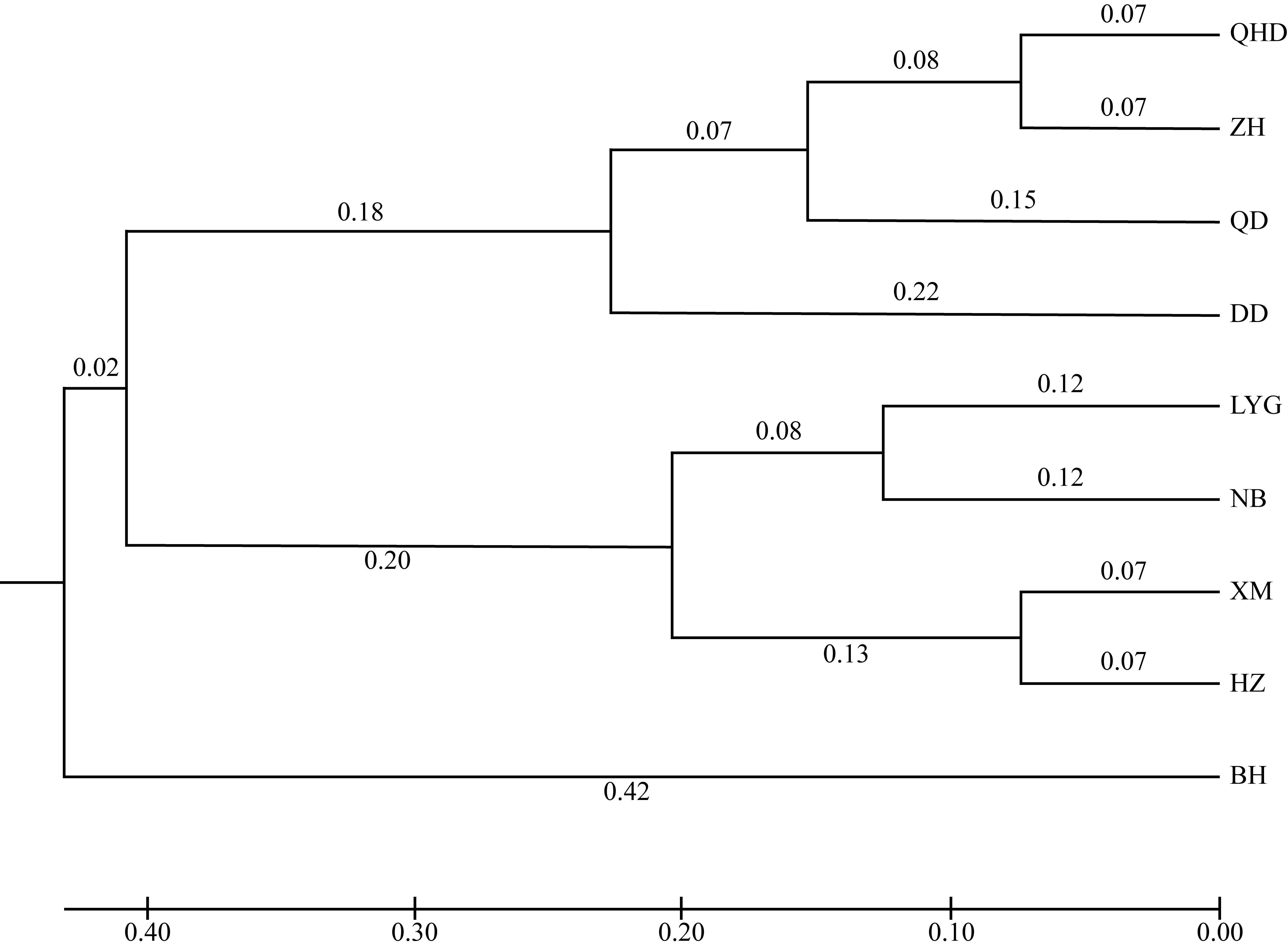
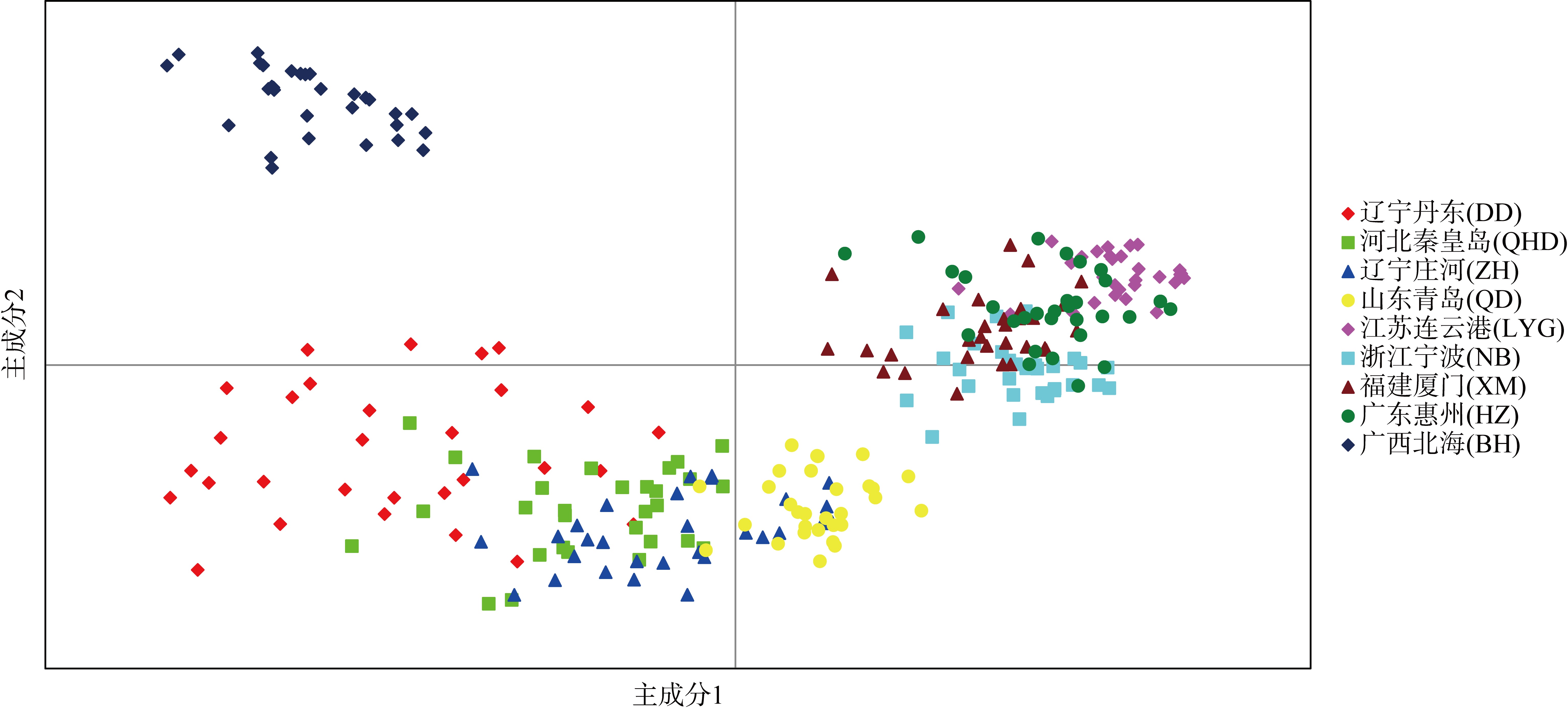
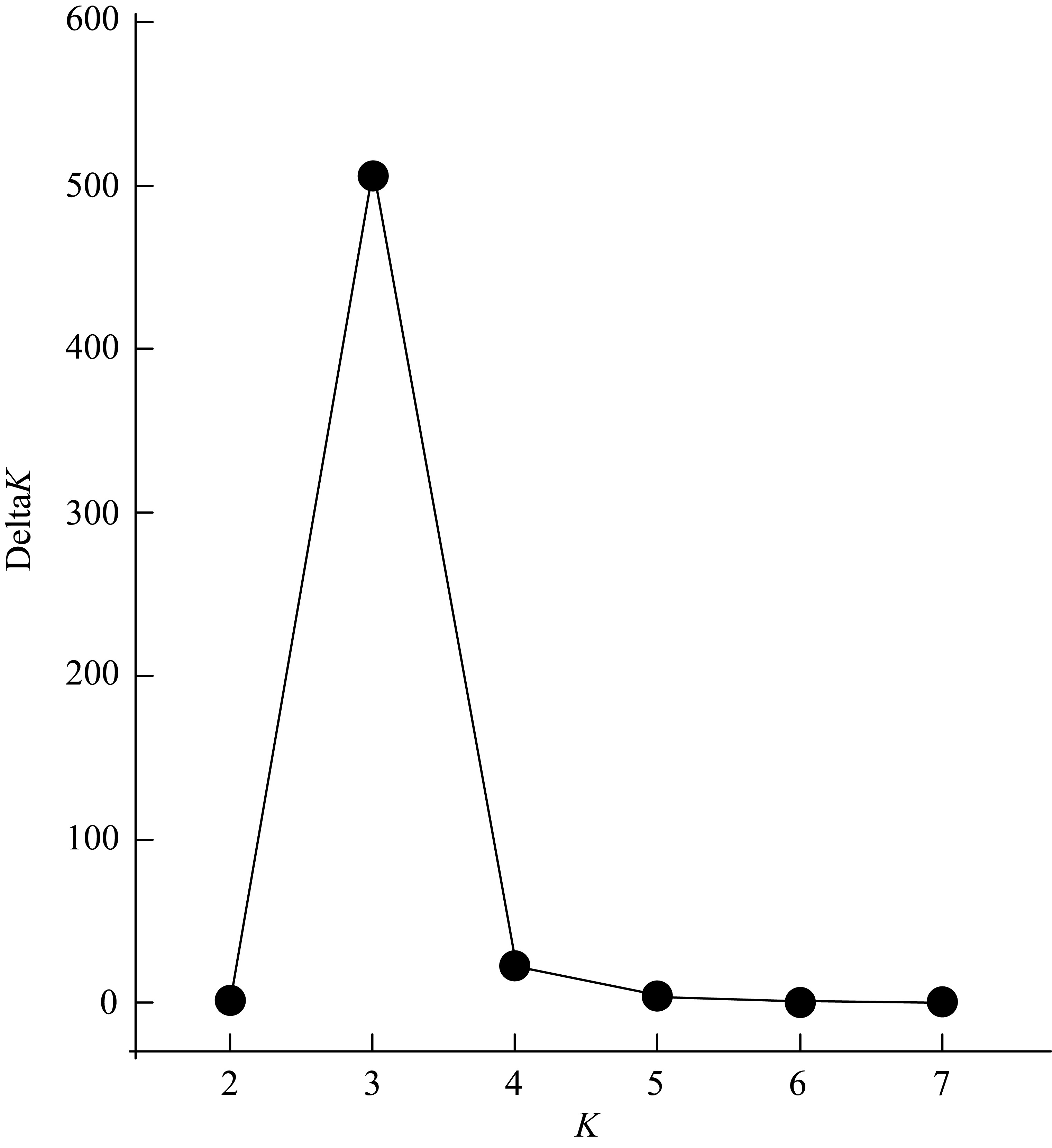
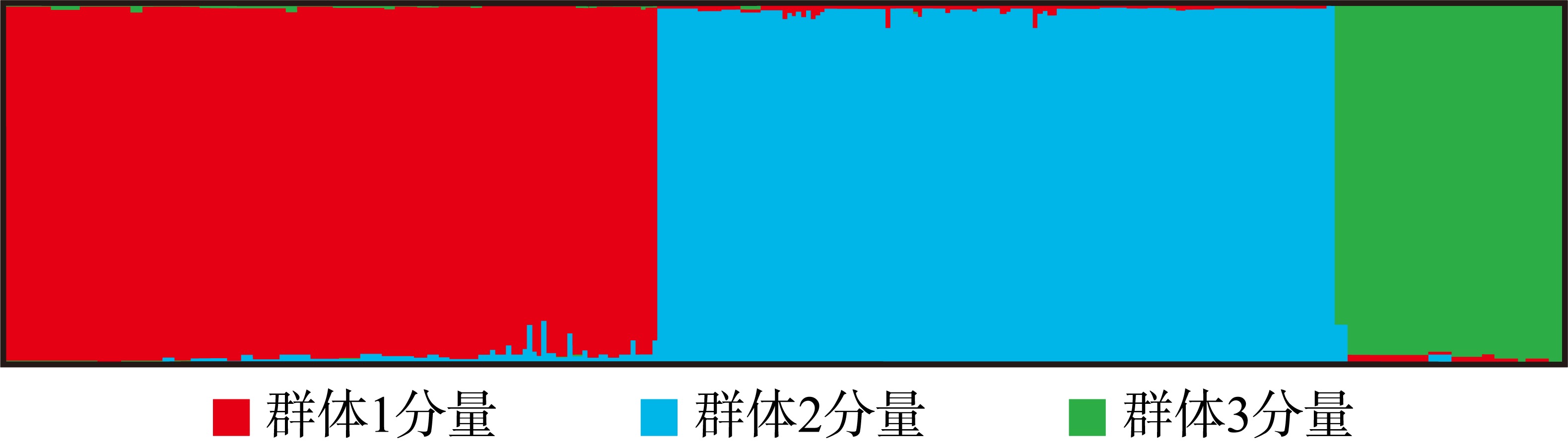
利用基于简化基因组测序(restriction site associated DNA sequencing, RAD-seq)技术开发了10对新的多态性微卫星引物, 对辽宁丹东(DD)、河北秦皇岛(QHD)、辽宁庄河(ZH)、山东青岛(QD)、江苏连云港(LYG)、浙江宁波(NB)、福建厦门(XM)、广东惠州(HZ)和广西北海(BH)共9个缢蛏群体进行了遗传多样性分析, 在270个缢蛏个体中共检测到了352个等位基因。平均等位基因数(Na, number of alleles)在3.2000~4.3000之间、平均有效等位基因数(Ne, effective number of alleles)在1.8789~2.5433之间; 观测杂合度(Ho, observed heterozygosity)范围为0.0000~0.9667、平均观测杂合度在0.3088~0.5533之间; 期望杂合度(He, expected heterozygosity)范围为0.0000~0.7945、平均期望杂合度在0.3456~0.5715之间; 平均多态信息含量(PIC, polymorphic information content)在0.3373~0.5989之间。遗传多样性评估显示, 9个缢蛏群体的遗传多样性水平属于中等。群体间的遗传分化系数(Fst, genetic differentiation coefficient)在0.0547~0.3511之间, 其中QHD和ZH群体之间的Fst值最低为0.0547, 而LYG和BH群体之间的Fst值最高为0.3511。基因流(Nm, gene flow)在0.4620至4.3204之间, 其中QHD和ZH群体之间的Nm值最高为4.3204, 而LYG和BH群体之间的Nm值最低为0.4620。分子方差分析(analysis of molecular variance, AMOVA)分析结果显示, 群体间的遗传变异占总变异的33.04% (p < 0.01), 而群体内的遗传变异占总变异的66.96% (p < 0.01), 表明遗传变异不仅存在于个体间, 也存在于群体间, 但个体间的遗传变异大于群体间的遗传变异。非加权组平均法(unweighted pair-group method with arithmetic means, UPGMA)、Structure软件的聚类结果以及主坐标分析(principal coordinate analysis, PCoA)结果一致。研究结果显示, 9个缢蛏群体可分为3大支: 第一支由QHD、ZH、QD、DD 4个群体组成; 第二支由LYG、NB、XM、HZ 4个群体组成; 第三支由BH群体独立成支。
中图分类号:
- P735.542
引用本文
吴贵清, 李瑞华, 肖意豪, 陈彦林, 罗璇, 刘相全, 朱佳杰, 吴雪萍. 基于微卫星标记9个缢蛏群体的遗传多样性分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(2): 124-136.
WU Guiqing, LI Ruihua, XIAO Yihao, CHEN Yanlin, LUO Xuan, LIU Xiangquan, ZHU Jiajie, WU Xueping. Analysis of genetic diversity in 9 populations of Sinonovacula constricta using microsatellite markers[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(2): 124-136.
表1
9个缢蛏群体采样信息"
| 采样地点 | 经度 | 纬度 | 样本量/个 | 采样时间 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DD | 124°16′54′′E | 39°56′15′′N | 30 | 2022年11月22日 |
| QHD | 119°26′11′′E | 39°47′47′′N | 30 | 2022年11月05日 |
| ZH | 122°38′59′′E | 39°31′36′′N | 30 | 2022年10月23日 |
| QD | 120°67′16′′E | 36°16′06′′N | 30 | 2022年10月15日 |
| LYG | 119°17′08′′E | 34°46′50′′N | 30 | 2022年9月27日 |
| NB | 121°43′55′′E | 29°32′01′′N | 30 | 2022年9月18日 |
| XM | 118°11′50′′E | 24°29′18′′N | 30 | 2022年8月25日 |
| HZ | 114°38′26′′E | 22°45′40′′N | 30 | 2022年8月12日 |
| BH | 109°06′33′′E | 21°25′25′′N | 30 | 2022年7月10日 |
表2
10对缢蛏微卫星引物的信息"
| 位点 | 序列号 | 引物序列(5′-3′) | 退火温度/℃ | 片段大小/bp |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC03 | PP409554 | F: CTTATCTTTATCCTCCTCGCCAT R: TGATGATAATGTTGAGGCTGTTG | 54 | 120~160 |
| SC04 | PP409555 | F: AGATAAAGCCAGGAAAACACAGA R: GTTTACAATGAAAAGACAGATGGC | 52 | 110~150 |
| SC05 | PP409556 | F: TCTTGGTTAGAGTGGGTTGTTGT R: TGCTTTCTAATGTGCCTTTCATT | 52 | 130~170 |
| SC06 | PP409557 | F: TTTCATGTTGTTGGTTGTTTGTT R: AATGTTGCCAAATCAAAACATTC | 54 | 110~150 |
| SC07 | PP409558 | F: CATCATCATTAACCGTCCTCCTA R:AGAAATTGGCATTGATAGCAAAA | 52 | 120~160 |
| SC08 | PP409559 | F: CCATGCATGAGAGTTAAGTAACAAA R: CCAAGAATGCACAATAAAATTGA | 52 | 120~160 |
| SC11 | PP409560 | F: GACAATTATGATTGCGATTGGTT R: TTGATACCCTTCATTCCAGCTTA | 53 | 120~150 |
| SC13 | PP409560 | F: ACAACGCCAGCAGTAACCTATAA R: CGGTTGTGGAAGCAGTAGTAGTAG | 54 | 100~140 |
| SC17 | PP409562 | F: CACCTCTGTCTGAAAAACAAAAA R: AGGGACACCCAGTACACATCTAT | 50 | 130~170 |
| SC19 | PP409563 | F: CAAAACCGGTTGGTAATGAATAA R: TTTTGTTGTTGTTTTGTTGTTGC | 55 | 120~160 |
表3
9个缢蛏群体的平均遗传多样参数"
| 群体 | 参数 | SC03 | SC04 | SC05 | SC06 | SC07 | SC08 | SC11 | SC13 | SC17 | SC19 | 均值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DD | Na | 3.0000 | 3.0000 | 4.0000 | 5.0000 | 6.0000 | 5.0000 | 4.0000 | 4.0000 | 4.0000 | 4.0000 | 4.2000 |
| Ne | 1.7527 | 1.9674 | 2.3810 | 4.3239 | 2.9268 | 3.4118 | 3.2200 | 1.8127 | 1.4207 | 2.2161 | 2.5433 | |
| Ho | 0.6000 | 0.0357 | 0.1000 | 0.4138 | 0.3333 | 0.6207 | 0.7667 | 0.2667 | 0.2333 | 0.0690 | 0.3439 | |
| He | 0.4367 | 0.5006 | 0.5898 | 0.7822 | 0.6695 | 0.7193 | 0.7011 | 0.4559 | 0.3011 | 0.5584 | 0.5715 | |
| PIC | 0.4510 | 0.4130 | 0.7330 | 0.7730 | 0.6070 | 0.9080 | 0.6650 | 0.4390 | 0.2870 | 0.4580 | 0.5734 | |
| P-value | 1.0000 | 0.0000* | 0.0000* | 0.0000* | 0.0033 | 0.0042 | 0.8245 | 0.0002* | 0.0561 | 0.0000* | 0.1888 | |
| QHD | Na | 5.0000 | 3.0000 | 5.0000 | 5.0000 | 4.0000 | 5.0000 | 3.0000 | 5.0000 | 4.0000 | 2.0000 | 4.1000 |
| Ne | 2.2416 | 1.4551 | 3.5644 | 4.4888 | 2.9851 | 3.3835 | 2.0619 | 1.6949 | 1.2721 | 1.9627 | 2.5110 | |
| Ho | 0.7333 | 0.0333 | 0.5333 | 0.3667 | 0.4667 | 0.6000 | 0.9667 | 0.4000 | 0.2333 | 0.0345 | 0.4368 | |
| He | 0.5633 | 0.3181 | 0.7316 | 0.7904 | 0.6763 | 0.7164 | 0.5237 | 0.4169 | 0.2175 | 0.4991 | 0.5453 | |
| PIC | 0.5690 | 0.2860 | 0.7040 | 0.7550 | 0.6230 | 0.8260 | 0.3980 | 0.4050 | 0.2050 | 0.3700 | 0.5141 | |
| P-value | 0.9964 | 0.0000* | 0.0000* | 0.0641 | 0.0025 | 1.0000 | 0.0459 | 1.0000 | 0.0000* | 0.0205 | 0.3129 | |
| ZH | Na | 4.0000 | 3.0000 | 6.0000 | 5.0000 | 4.0000 | 6.0000 | 3.0000 | 5.0000 | 3.0000 | 3.0000 | 4.2000 |
| Ne | 2.5388 | 1.1450 | 2.9561 | 4.1570 | 2.5678 | 4.5113 | 2.3866 | 1.9759 | 1.2685 | 1.4019 | 2.4909 | |
| Ho | 0.2667 | 0.0000 | 0.4138 | 0.3667 | 0.2000 | 0.6000 | 0.6071 | 0.4000 | 0.2333 | 0.0000 | 0.3088 | |
| He | 0.6164 | 0.1288 | 0.6733 | 0.7723 | 0.6209 | 0.7915 | 0.5916 | 0.5023 | 0.2153 | 0.2915 | 0.5204 | |
| PIC | 0.5360 | 0.1230 | 0.6750 | 0.7330 | 0.5300 | 0.8940 | 0.5080 | 0.4630 | 0.1990 | 0.2600 | 0.4921 | |
| P-value | 0.0205 | 0.0003* | 0.0022 | 0.0000* | 0.0001* | 0.0000* | 0.0386 | 0.2979 | 1.0000 | 0.0000* | 0.1359 | |
| QD | Na | 5.0000 | 2.0000 | 4.0000 | 5.0000 | 3.0000 | 4.0000 | 3.0000 | 5.0000 | 2.0000 | 4.0000 | 3.7000 |
| Ne | 1.6559 | 1.0689 | 3.4682 | 4.5421 | 1.3072 | 3.4221 | 2.0202 | 1.3206 | 1.0339 | 1.6408 | 2.1480 | |
| Ho | 0.4000 | 0.0000 | 0.5333 | 0.2963 | 0.2000 | 0.7000 | 0.8667 | 0.2000 | 0.0333 | 0.1333 | 0.3363 | |
| He | 0.4028 | 0.0655 | 0.7237 | 0.7945 | 0.239 | 0.7198 | 0.5136 | 0.2469 | 0.0333 | 0.3972 | 0.4136 | |
| PIC | 0.3770 | 0.0620 | 0.0730 | 0.7560 | 0.2220 | 0.8590 | 0.3930 | 0.2340 | 0.0320 | 0.3650 | 0.3373 | |
| P-value | 0.0316 | 0.0169 | 0.0036 | 0.0000* | 0.2409 | 0.0000* | 1.0000 | 0.0146 | 0.0000* | 0.0002* | 0.1308 | |
| LYG | Na | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 5.0000 | 2.0000 | 2.0000 | 6.0000 | 4.0000 | 5.0000 | 3.0000 | 3.0000 | 3.2000 |
| Ne | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.9956 | 1.2596 | 1.9978 | 4.2254 | 3.1634 | 1.7787 | 1.2237 | 1.1443 | 1.8789 | |
| Ho | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.3667 | 0.2333 | 0.9667 | 0.7333 | 0.6333 | 0.3667 | 0.1333 | 0.0667 | 0.3500 | |
| He | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.5073 | 0.2096 | 0.5079 | 0.7763 | 0.6955 | 0.4452 | 0.1859 | 0.1282 | 0.3456 | |
| PIC | 0.0000 | 0.0320 | 0.6650 | 0.1850 | 0.3750 | 0.8710 | 0.6190 | 0.4160 | 0.1800 | 0.1240 | 0.3467 | |
| P-value | 0.0000* | 1.0000 | 0.0000* | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.1941 | 0.2597 | 0.0006* | 0.0669 | 0.0169 | 0.3538 | |
| NB | Na | 5.0000 | 2.0000 | 5.0000 | 5.0000 | 2.0000 | 5.0000 | 3.0000 | 5.0000 | 2.0000 | 4.0000 | 3.8000 |
| Ne | 3.1746 | 1.0689 | 3.3835 | 3.1142 | 1.4274 | 4.0909 | 2.2727 | 2.2814 | 1.0339 | 1.4718 | 2.3319 | |
| Ho | 0.4667 | 0.0000 | 0.4667 | 0.4333 | 0.3667 | 0.5333 | 0.9333 | 0.4000 | 0.0333 | 0.1000 | 0.3733 | |
| He | 0.6966 | 0.0655 | 0.7164 | 0.6904 | 0.3045 | 0.7684 | 0.5695 | 0.5712 | 0.0333 | 0.3260 | 0.4742 | |
| PIC | 0.6560 | 0.0620 | 0.8160 | 0.6430 | 0.2550 | 0.9030 | 0.4610 | 0.5500 | 0.0640 | 0.3050 | 0.4715 | |
| P-value | 0.1371 | 0.0169 | 0.0000* | 0.0058 | 1.0000 | 0.0217 | 0.9827 | 0.0000* | 1.0000 | 0.0000* | 0.3164 | |
| XM | Na | 2.0000 | 1.0000 | 4.0000 | 5.0000 | 5.0000 | 5.0000 | 3.0000 | 4.0000 | 4.0000 | 5.0000 | 3.8000 |
| Ne | 1.6000 | 1.0000 | 2.2876 | 3.5573 | 1.9063 | 3.8793 | 2.2032 | 2.1102 | 1.4634 | 1.8653 | 2.1873 | |
| Ho | 0.4333 | 0.0000 | 0.3462 | 0.3667 | 0.4333 | 0.8000 | 0.9333 | 0.4333 | 0.2000 | 0.1000 | 0.4046 | |
| He | 0.3814 | 0.0000 | 0.5739 | 0.7311 | 0.4836 | 0.7548 | 0.5554 | 0.5350 | 0.3220 | 0.4718 | 0.4809 | |
| PIC | 0.6720 | 0.4410 | 0.8840 | 0.4420 | 0.4410 | 0.8840 | 0.4420 | 0.5260 | 0.2950 | 0.4440 | 0.5471 | |
| P-value | 0.0000* | 0.0044 | 0.6226 | 0.8616 | 0.0044 | 0.6226 | 0.8616 | 0.0068 | 0.0048 | 0.0000* | 0.2989 | |
| HZ | Na | 5.0000 | 3.0000 | 5.0000 | 5.0000 | 2.0000 | 5.0000 | 4.0000 | 4.0000 | 2.0000 | 4.0000 | 3.9000 |
| Ne | 2.2939 | 1.2649 | 2.4931 | 3.4417 | 1.5139 | 3.8710 | 2.8257 | 1.3657 | 1.0339 | 1.5139 | 2.1618 | |
| Ho | 0.5333 | 0.0333 | 0.2333 | 0.5667 | 0.4333 | 0.6333 | 0.7667 | 0.3000 | 0.0333 | 0.1333 | 0.3667 | |
| He | 0.5734 | 0.2130 | 0.6090 | 0.7215 | 0.3452 | 0.7542 | 0.6571 | 0.2723 | 0.0333 | 0.3452 | 0.4524 | |
| PIC | 0.5880 | 0.2130 | 0.7830 | 0.7260 | 0.3520 | 0.9010 | 0.6570 | 0.2450 | 0.0330 | 0.3460 | 0.4844 | |
| P-value | 0.0937 | 0.0001* | 0.0000* | 0.0683 | 1.0000 | 0.0000* | 0.6531 | 1.0000 | 0.0000* | 0.0263 | 0.2841 | |
| BH | Na | 5.0000 | 3.0000 | 5.0000 | 3.0000 | 5.0000 | 5.0000 | 5.0000 | 5.0000 | 3.0000 | 4.0000 | 4.3000 |
| Ne | 2.2032 | 1.2270 | 2.4658 | 1.3943 | 4.5226 | 1.8927 | 2.8939 | 2.8571 | 1.9231 | 1.7561 | 2.3136 | |
| Ho | 0.6333 | 0.2000 | 0.4333 | 0.3333 | 0.7667 | 0.5333 | 0.6667 | 0.7667 | 0.6667 | 0.5333 | 0.5533 | |
| He | 0.5554 | 0.1881 | 0.6045 | 0.2876 | 0.7921 | 0.4797 | 0.6655 | 0.6610 | 0.4881 | 0.4379 | 0.5160 | |
| PIC | 0.5030 | 0.1770 | 0.7760 | 0.2510 | 0.8590 | 0.6010 | 0.7320 | 0.7160 | 0.6220 | 0.7520 | 0.5989 | |
| P-value | 0.9440 | 1.0000 | 0.0181 | 1.0000 | 0.4223 | 0.7689 | 0.9183 | 1.0000 | 0.9940 | 0.9761 | 0.8042 |
表4
9个缢蛏群体间的遗传分化系数(对角线下)和基因流(对角线以上)"
| 群体 | DD | QHD | ZH | QD | LYG | NB | XM | HZ | BH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DD | — | 2.7297 | 1.6497 | 1.0460 | 0.5298 | 0.8741 | 0.8756 | 0.8188 | 0.8586 |
| QHD | 0.0839 | — | 4.3204 | 1.5281 | 0.6187 | 1.1282 | 1.4507 | 0.9450 | 0.7350 |
| ZH | 0.1316 | 0.0547 | — | 2.6981 | 0.7194 | 1.5093 | 1.2707 | 0.8271 | 0.8508 |
| QD | 0.1929 | 0.1406 | 0.0848 | — | 0.7186 | 1.2951 | 0.9248 | 1.0665 | 0.5406 |
| LYG | 0.3206 | 0.2878 | 0.2579 | 0.2581 | — | 1.7892 | 1.0146 | 1.0294 | 0.4620 |
| NB | 0.2224 | 0.1814 | 0.1421 | 0.1618 | 0.1226 | — | 2.1219 | 1.1939 | 0.6296 |
| XM | 0.2221 | 0.1470 | 0.1644 | 0.2128 | 0.1977 | 0.1054 | — | 3.4211 | 0.6309 |
| HZ | 0.2339 | 0.2092 | 0.2321 | 0.1899 | 0.1954 | 0.1142 | 0.0681 | — | 0.6009 |
| BH | 0.2255 | 0.2538 | 0.2721 | 0.3162 | 0.3511 | 0.2842 | 0.2838 | 0.2938 | — |
表6
9个群体间的Nei’s遗传距离(对角线下)和遗传相似指数(对角线上)"
| 群体 | DD | QHD | ZH | QD | LYG | NB | XM | HZ | BH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DD | — | 0.7501 | 0.6262 | 0.5149 | 0.1806 | 0.3759 | 0.3309 | 0.3403 | 0.1000 |
| QHD | 0.2875 | — | 0.8632 | 0.6573 | 0.2957 | 0.5220 | 0.5833 | 0.4370 | 0.0712 |
| ZH | 0.4681 | 0.1471 | — | 0.8187 | 0.4218 | 0.6405 | 0.5575 | 0.4148 | 0.0680 |
| QD | 0.6637 | 0.4196 | 0.2000 | — | 0.4845 | 0.6434 | 0.4846 | 0.5954 | 0.0613 |
| LYG | 1.7115 | 1.2185 | 0.8631 | 0.7247 | — | 0.7722 | 0.5684 | 0.5911 | 0.0559 |
| NB | 0.9785 | 0.6501 | 0.4455 | 0.4411 | 0.2586 | — | 0.7310 | 0.7133 | 0.0792 |
| XM | 1.1059 | 0.5391 | 0.5843 | 0.7244 | 0.5649 | 0.3134 | — | 0.8574 | 0.0659 |
| HZ | 1.0780 | 0.8278 | 0.8798 | 0.5185 | 0.5257 | 0.3378 | 0.1538 | — | 0.0566 |
| BH | 2.3022 | 2.6421 | 2.6885 | 2.7917 | 2.8838 | 2.5353 | 2.7198 | 2.8723 | — |
| [1] |
包文斌, 束婧婷, 许盛海, 等, 2007. 样本量和性比对微卫星分析中群体遗传多样性指标的影响[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 43(1): 6-9.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
范士琦, 冯婧昀, 苗晓敏, 等, 2023. 重庆养殖场鳜群体微卫星遗传多样性研究[J]. 水产养殖, 44(7): 18-23.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
谷德贤, 王婷, 许玉甫, 等, 2021. 利用微卫星分子标记分析渤海湾的口虾蛄遗传多样性[J]. 水产科学, 40(5): 693-699.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
郭香, 曾志南, 郑雅友, 等, 2018. 福建牡蛎选育群体的遗传多样性[J]. 中国水产科学, 25(5): 1131-1136.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
黄小林, 李文俊, 林黑着, 等, 2018. 基于线粒体DNA D-loop序列的黄斑篮子鱼群体遗传多样性分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 37(4): 45-51.
doi: 10.11978/2017109 |
|
|
|
| [6] |
黄新芯, 刘玉萍, 宁子君, 等, 2025. 基于微卫星标记的中国近海龙头鱼群体遗传结构分析[J]. 水生态学杂志, 46(1): 90-98.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
李成华, 2004. 泥蚶分子系统分化及缢蛏遗传多样性的研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所): 53-62 (in Chinese).
|
| [8] |
李景芬, 夏正龙, 栾生, 等, 2020. 五个罗氏沼虾群体遗传多样性的微卫星分析[J]. 水生生物学报, 44(6): 1208-1214.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
李鸥, 赵莹莹, 郭娜, 等, 2009. 草鱼种群SSR分析中样本量及标记数量对遗传多度的影响[J]. 动物学研究, 30(2): 121-130.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
李妍, 姚健涛, 张恩烁, 等, 2024. 长牡蛎(Crassostrea gigas)野生与选育群体的微卫星遗传多样性分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 55(2): 462-470.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
李镒民, 丁琳琳, 谭杰, 等, 2019. 马氏珠母贝F8代黑壳色选育系群体与普通养殖群体遗传多样性分析[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 38(11): 4961-4967.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
梁园, 付敬强, 沈铭辉, 等, 2022. 方斑东风螺3个选育世代遗传多样性和遗传结构的微卫星分析[J]. 海洋科学, 46(10): 85-93.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
刘博, 邵艳卿, 王侃, 等, 2013. 4个缢蛏群体遗传多样性和系统发生关系的微卫星分析[J]. 海洋科学, 37(8): 96-102.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
刘达博, 牛东红, 冯冰冰, 等, 2011. 乐清湾和三沙湾缢蛏群体遗传多样性的微卫星分析[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 20(3): 350-357.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
牛东红, 李家乐, 冯冰冰, 等, 2009. 缢蛏6个群体遗传结构的ISSR分析[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 15(3): 332-336.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
牛东红, 陈慧, 林国文, 等, 2010. 缢蛏群体微卫星分析中样本量对遗传多样性指标的影响[J]. 海洋科学进展, 28(2): 203-208.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
牛东红, 冯冰冰, 刘达博, 等, 2011. 浙闽沿海缢蛏群体遗传结构的微卫星和线粒体CO Ⅰ序列分析[J]. 水产学报, 35(12): 1805-1813.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
彭敏, 肖珊, 洪传远, 等, 2022. 华南沿海长鳍篮子鱼不同地理群体的遗传多样性分析[J]. 水生态学杂志, 43(5): 127-133.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
阮惠婷, 徐姗楠, 李敏, 等, 2020. 飘鱼微卫星位点的筛选及珠江流域5个地理群体的遗传多样性分析[J]. 水生生物学报, 44(3): 501-508.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
邵艳卿, 方军, 柏艳, 等, 2015. 缢蛏(Sinonovacula constricta) EST-SSR标记与生长性状的相关性分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 46(5): 1146-1152.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
苏晓盈, 代永仙, 谭杰, 等, 2021. 马氏珠母贝(Pinctada martensii)黑壳色养殖群体SSR遗传多样性分析[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 40(2): 615-621.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
孙志鹏, 鲁翠云, 那荣滨, 等, 2023. 利用线粒体序列比较分析梭鲈鸭绿江和乌伦古湖群体的遗传结构[J]. 水产学杂志, 36(5): 10-16, 26.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
唐芳, 温贝妮, 刘红, 2021. 不同凡纳滨对虾养殖群体的微卫星遗传多样性分析[J]. 南方农业学报, 52(4): 1108-1115.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
滕爽爽, 胡高宇, 范建勋, 等, 2021. 缢蛏5个群体遗传多样性和遗传分化的SNP分析[J]. 水生生物学报, 45(4): 861-870.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
田镇, 陈爱华, 曹奕, 等, 2021. 红壳色文蛤选育群体遗传多样性的微卫星分析[J]. 南方农业学报, 52(9): 2582-2589.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
王冬群, 李太武, 苏秀榕, 2005. 象山缢蛏养殖群体和野生群体遗传多样性的比较[J]. 中国水产科学, 12(2): 138-143.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
吴玲, 2013. 马氏珠母贝和缢蛏的遗传多样性研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学: 49-86.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
徐义平, 许会宾, 金凯, 等, 2017. 浙江乐清湾缢蛏的形态和遗传多样性[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 26(1): 31-37.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
于思梦, 高磊, 王伟, 等, 2017. 辽宁黄渤海沿岸长牡蛎遗传多样性分析[J]. 经济动物学报, 21(4): 215-220.
|
|
|
|
| [30] |
于颖, 孟祥盈, 王秀利, 等, 2007. 缢蛏遗传多样性的RAPD分析[J]. 生物技术通报, (6): 138-140.
|
|
|
|
| [31] |
张帝, 强俊, 傅建军, 等, 2022. 基于微卫星标记和线粒体D-loop序列的5个大口黑鲈群体遗传变异分析[J]. 中国水产科学, 29(9): 1277-1289.
|
|
|
|
| [32] |
张秀英, 张晓军, 赵翠, 等, 2012. 栉孔扇贝BES-SSR的开发及遗传多样性分析[J]. 水产学报, 36(6): 815-824.
|
|
|
|
| [33] |
赵文浩, 易少奎, 周琼, 等, 2023. 新疆塔里木河叶尔羌高原鳅群体遗传学研究[J]. 水产科学, 42(4): 664-673.
|
|
|
|
| [34] |
pmid: 6247908 |
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.302370 pmid: 31537622 |
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
doi: 10.1126/science.3576198 pmid: 3576198 |
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
doi: 10.1016/j.margen.2012.06.003 pmid: 23904061 |
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [1] | 黄红伟, 张志新, 仲嘉, 林强, 郭宝英, 严小军. 印太交汇区八种鱼类群体遗传结构和连通性分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(1): 9-23. |
| [2] | 黄雯, 冯逸, 李明, 武茜, 罗燕秋, 陈胤民, 王丽荣, 余克服. 造礁石珊瑚群体遗传学研究进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(6): 13-26. |
| [3] | 付成冲, 李福宇, 陈丹丹, 侯敬, 王珺, 李元超, 王道儒, 王嫣. 海南岛岸礁澄黄滨珊瑚(Porites lutea)集合种群的遗传结构和连通性[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(2): 64-77. |
| [4] | 邹聪聪, 王丽娟, 吴志昊, 尤锋. 基于线粒体控制区序列的黄海日本鳀(Engraulis japonicus)的群体遗传结构*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(5): 25-35. |
| [5] | 李敏, 孔啸兰, 许友伟, 陈作志. 基于线粒体控制区序列的花斑蛇鲻遗传多态性分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(4): 42-49. |
| [6] | 季莹莹,徐磊,黎红,王亮根,杜飞雁. 基于28S rDNA的南海刺长腹剑水蚤(Oithona setigera)种群遗传多样性研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(3): 89-97. |
| [7] | 黄小林, 李文俊, 林黑着, 杨育凯, 李涛, 虞为, 黄忠. 基于线粒体DNA D-loop序列的黄斑篮子鱼群体遗传多样性分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(4): 45-51. |
| [8] | 赵志英, 梁丽运, 白丽蓉. 斑节对虾3个野生群体遗传多样性的微卫星标记分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(3): 65-72. |
| [9] | 杜蕴超, 谢淑媚, 何圣耀, 牛东红, 李家乐. 缢蛏多巴胺受体基因及其在损伤修复中的作用[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(3): 45-54. |
| [10] | 施晓峰, 苏永全, 王文成, 王军. 基于mtDNA控制区序列的3个黑棘鲷群体遗传结构特性研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2015, 34(1): 56-63. |
| [11] | 刘丽, 赵洁, 郭昱嵩, 刘楚吾. 4种笛鲷AFLP引物筛选及其遗传多样性分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(4): 112-116. |
| [12] | 李莉好,喻达辉,黄桂菊,杜博,符云,童馨,郭奕惠,叶卫. 尼罗罗非鱼 Oreochromis niloticus 、 奥利亚罗非鱼 O. aureus 和红罗非鱼 O. sp. 群体遗传多样性的比较[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(2): 102-109. |
| [13] | 吉磊 ,区又君 ,李加儿 . 卵形鲳鲹 3 个养殖群体的微卫星多态性分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2011, 30(3): 62-68. |
| [14] | 郭昱嵩,王中铎,刘楚吾,陈志明,刘筠. 9种常见笛鲷微卫星位点筛选与遗传多样性分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2010, 29(3): 82-86. |
| [15] | 曲妮妮,龚世园,黄桂菊,童金苟,喻达辉. 基于FIASCO技术的合浦珠母贝微卫星标记分离与筛选研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2010, 29(3): 47-54. |
|
||