热带海洋学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 89-97.doi: 10.11978/2018112CSTR: 32234.14.2018112
所属专题: 南海专题
基于28S rDNA的南海刺长腹剑水蚤(Oithona setigera)种群遗传多样性研究
- 1. 上海海洋大学海洋科学学院, 上海 201306
2. 中国水产科学研究院南海水产研究所, 广东省渔业生态环境重点实验室, 农业部南海渔业资源开发利用重点实验室, 广东 广州 510300
-
收稿日期:2018-10-25修回日期:2018-12-20出版日期:2019-05-20发布日期:2019-06-17 -
通讯作者:杜飞雁 -
作者简介:季莹莹(1994—), 女, 江苏省南京市人, 硕士研究生, E-mail:15705117350@163.com -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(41406188);中国水产科学研究院南海水产研究所中央级公益性科研院所基本科研业务费专项资金(2017YB26、2016TS24)(2017YB26);中国水产科学研究院南海水产研究所中央级公益性科研院所基本科研业务费专项资金(2017YB26、2016TS24)(2016TS24)
Genetic structure of Oithona setigera from South China Sea based on 28S rDNA gene
Yingying JI1,2,Lei XU2,Hong LI2,Lianggen WANG2,Feiyan DU2( )
)
- 1. College of Marine Sciences, Shanghai ocean university, Shanghai 201306, China
2. South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Fishery Ecology and Environment, Guangzhou 510300, China
-
Received:2018-10-25Revised:2018-12-20Online:2019-05-20Published:2019-06-17 -
Contact:Feiyan DU -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(41406188);South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, Scientific Research Funds for Central Non-profit Institutes(2017YB26);South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, Scientific Research Funds for Central Non-profit Institutes(2016TS24)
摘要:
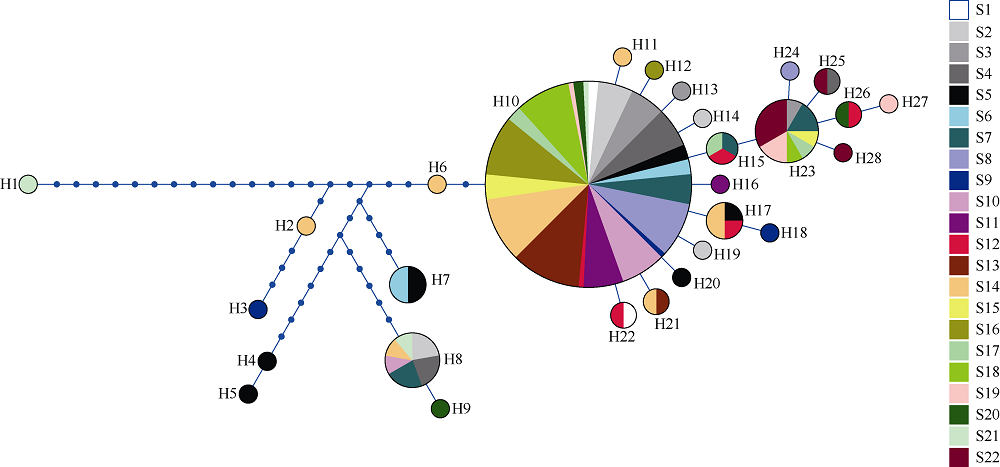
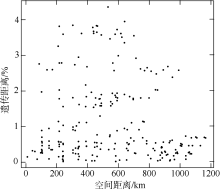
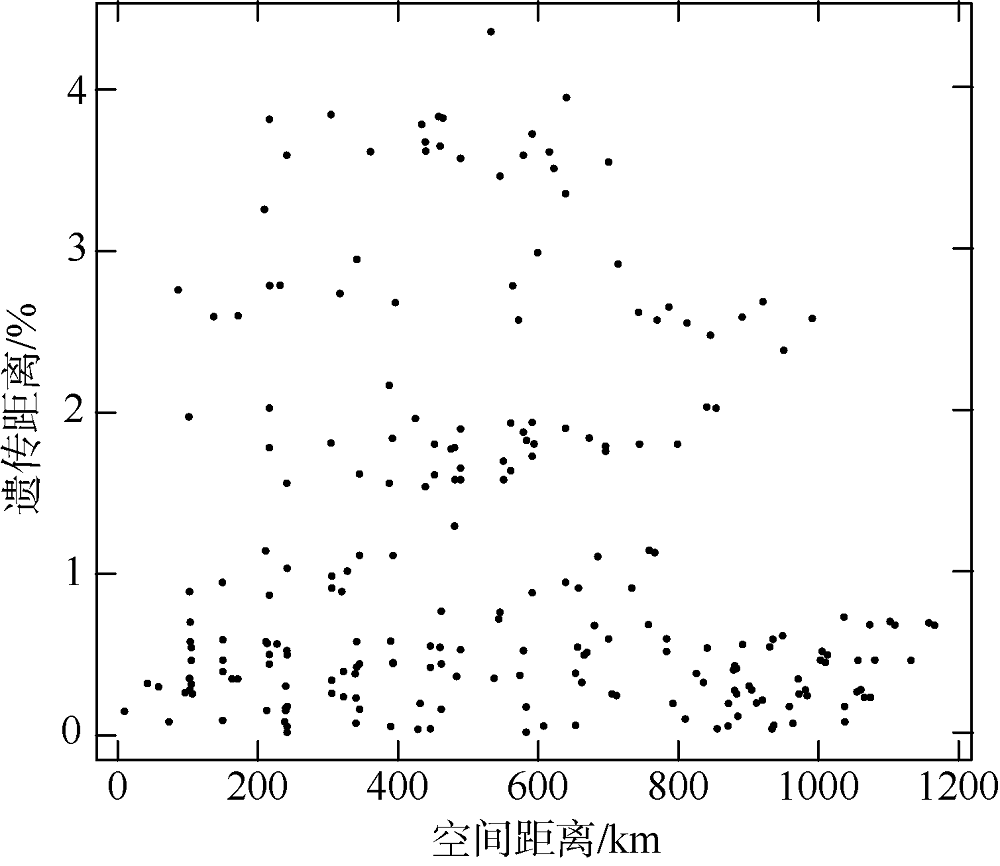
长腹剑水蚤属是海洋中小型浮游动物中最为丰富的类群之一, 在生物地理学与海洋生态学研究中均具有重要地位。本研究基于28S rDNA分析了南海长腹剑水蚤属中较为常见的刺长腹剑水蚤Oithona setigera的单倍型多样性和种群遗传结构。结果显示, 792bp长度的核苷酸片段中, 碱基G+C的平均含量为58.2%, 高于A+T含量(41.8%)。种群平均遗传距离ΦST为0.011。在22个种群共计186个个体中, 发现了28个单倍型, 其中单倍型H10在21个种群中均被发现, 最远距离超过1000km, 说明刺长腹剑水蚤可以实现远距离的扩散且受到南海海流影响。Mantel检验结果显示, 刺长腹剑水蚤种群遗传距离和地理距离无线性相关性(R=-0.04615, P=0.678); RDA变差分解结果显示, 空间变量全模型对种群遗传结构的解释率为53.3%, 结合种群平均遗传距离ΦST为0.011, 我们判断目前观测到的刺长腹剑水蚤的种群遗传结构可能由历史上种群扩展带来的拓殖隔离造成。
中图分类号:
- Q179.1
引用本文
季莹莹,徐磊,黎红,王亮根,杜飞雁. 基于28S rDNA的南海刺长腹剑水蚤(Oithona setigera)种群遗传多样性研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(3): 89-97.
Yingying JI,Lei XU,Hong LI,Lianggen WANG,Feiyan DU. Genetic structure of Oithona setigera from South China Sea based on 28S rDNA gene[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(3): 89-97.
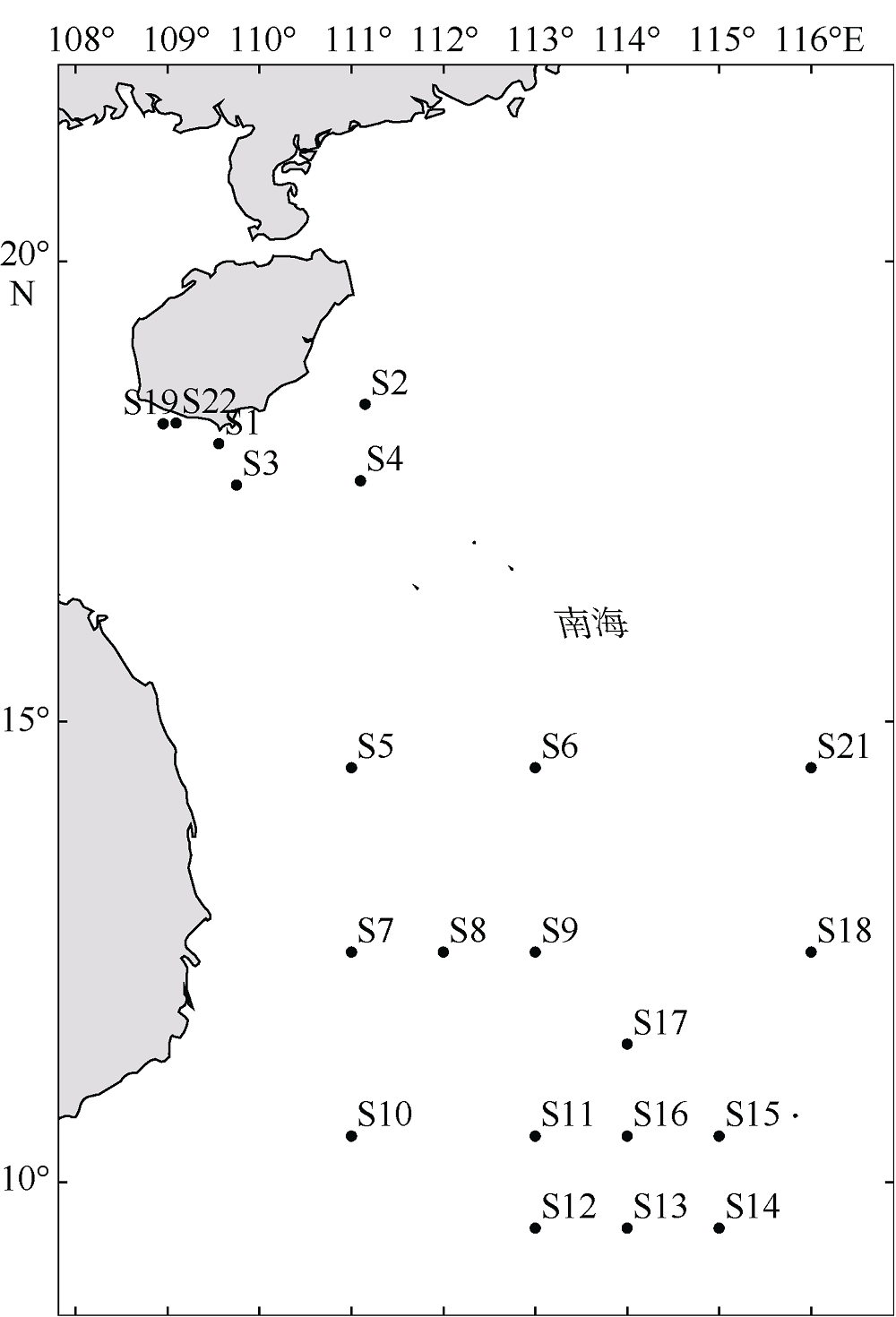
表1
刺长腹剑水蚤(Oithona setigera) 种群采集站点及其基本信息"
| 站位 | 纬度 | 经度 | 平均水温/℃ | 风速/(m·s-1) | 盐度/‰ | 叶绿素a/(mg·m-3) | 样本 数量 | 单倍型 数量 | 单倍型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 18°15′36″N | 109°33'36"E | 24.49 | 8.19 | NaN | 0.23 | 3 | 2 | H10、H22 |
| S2 | 18°26'59N | 111°9'E | 24.44 | 8.95 | NaN | 0.12 | 11 | 4 | H8、H10、H14、H19 |
| S3 | 17°34'12"N | 109°45'E | 24.60 | 8.71 | NaN | 0.13 | 9 | 3 | H8、H10、H13 |
| S4 | 17°37'12"N | 111°5'59"E | 24.71 | 9.35 | 33.24 | 0.11 | 11 | 2 | H10、H25 |
| S5 | 14°30'N | 111°E | 26.54 | 10.78 | 33.36 | 0.08 | 9 | 5 | H4、H5、H7、H10、H20 |
| S6 | 14°30'N | 113°E | 26.93 | 11.04 | 33.25 | 0.08 | 5 | 2 | H7、H10 |
| S7 | 12°30'N | 111°E | 26.84 | 10.73 | 34.12 | 0.11 | 11 | 4 | H8、H10、H15、H13 |
| S8 | 12°30'N | 112°E | 27.09 | 10.39 | 33.67 | 0.10 | 12 | 1 | H10、H24 |
| S9 | 12°30'N | 113°E | 27.23 | 10.13 | 33.50 | 0.08 | 3 | 2 | H10、H18 |
| S10 | 10°30'N | 111°E | 27.20 | 5.05 | 33.14 | 0.08 | 10 | 4 | H8、H10、H23、H27 |
| S11 | 10°30'N | 113°E | 27.36 | 4.35 | 33.53 | 0.10 | 9 | 2 | H10、H16 |
| S12 | 9°30'N | 113°E | 27.39 | 3.43 | 33.57 | 0.09 | 5 | 5 | H10、H22、H17、H15、H26 |
| S13 | 9°30'N | 114°E | 27.92 | 3.57 | 33.21 | 0.09 | 15 | 2 | H10、H21 |
| S14 | 9°30'N | 115°E | 28.13 | 5.88 | 33.36 | 0.11 | 20 | 6 | H2、H6、H8、H10、H11、H17、H21 |
| S15 | 10°30'N | 115°E | 27.97 | 7.62 | 33.32 | 0.10 | 6 | 2 | H10、H23 |
| S16 | 10°30'N | 114°E | 27.77 | 6.48 | 33.06 | 0.09 | 12 | 2 | H10、H12 |
| S17 | 11°30'N | 114°E | 27.57 | 9.17 | 33.25 | 0.11 | 6 | 4 | H1、H10、H15、H23 |
| S18 | 12°30'N | 116°E | 27.83 | 10.00 | 33.46 | 0.08 | 12 | 2 | H10、H23 |
| S19 | 18°14'23"N | 108°57'E | 25.06 | 7.77 | NaN | 0.98 | 4 | 1 | H10 |
| S20 | 14°30'N | 117°E | 27.50 | 10.60 | 33.42 | 0.10 | 4 | 2 | H9、H10、H26 |
| S21 | 14°30'N | 116°E | 27.55 | 10.90 | 33.36 | 0.09 | 2 | 2 | H8、H10 |
| S22 | 18°15'N | 109°5'59"E | 24.76 | 7.89 | NaN | 0.59 | 7 | 3 | H23、H25、H28 |
表2
部分站位之间刺长腹剑水蚤(Oithona setigera)的遗传距离(%)"
| S8 | S9 | S10 | S11 | S12 | S13 | S14 | S15 | S16 | S17 | S18 | S19 | S20 | S21 | S22 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S9 | 0.89 | ||||||||||||||
| S10 | 0.18 | 0.99 | |||||||||||||
| S11 | 0.02 | 0.87 | 0.16 | ||||||||||||
| S12 | 0.16 | 1.02 | 0.30 | 0.16 | |||||||||||
| S13 | 0.45 | 1.12 | 0.58 | 0.43 | 0.58 | ||||||||||
| S14 | 0.45 | 1.12 | 0.56 | 0.42 | 0.57 | 0.70 | |||||||||
| S15 | 0.06 | 0.91 | 0.20 | 0.04 | 0.17 | 0.47 | 0.47 | ||||||||
| S16 | 0.26 | 1.04 | 0.40 | 0.24 | 0.40 | 0.55 | 0.59 | 0.28 | |||||||
| S17 | 0.09 | 0.95 | 0.23 | 0.08 | 0.18 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.09 | 0.32 | ||||||
| S18 | 0.04 | 0.89 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.16 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.06 | 0.26 | 0.09 | |||||
| S19 | 0.25 | 1.13 | 0.42 | 0.26 | 0.29 | 0.69 | 0.68 | 0.24 | 0.50 | 0.22 | 0.25 | ||||
| S20 | 0.53 | 1.30 | 0.60 | 0.52 | 0.60 | 0.95 | 0.89 | 0.53 | 0.76 | 0.55 | 0.53 | 0.62 | |||
| S21 | 1.78 | 2.17 | 1.79 | 1.76 | 1.90 | 1.94 | 1.94 | 1.81 | 1.90 | 1.84 | 1.78 | 2.03 | 1.98 | ||
| S22 | 0.26 | 1.15 | 0.43 | 0.28 | 0.27 | 0.71 | 0.70 | 0.24 | 0.52 | 0.20 | 0.26 | 0.15 | 0.60 | 2.04 |
表3
部分站位之间刺长腹剑水蚤(Oithona setigera)的空间距离(km)"
| S8 | S9 | S10 | S11 | S12 | S13 | S14 | S15 | S16 | S17 | S18 | S19 | S20 | S21 | S22 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 660 | 740 | 878 | 940 | 1043 | 1087 | 1138 | 1044 | 987 | 891 | 943 | 65 | 898 | 805 | 49 |
| S2 | 669 | 691 | 885 | 907 | 1016 | 1043 | 1079 | 977 | 937 | 832 | 842 | 234 | 764 | 679 | 218 |
| S3 | 614 | 664 | 799 | 862 | 965 | 1009 | 1063 | 970 | 911 | 816 | 877 | 113 | 847 | 751 | 102 |
| S4 | 578 | 605 | 793 | 819 | 927 | 957 | 997 | 897 | 852 | 749 | 776 | 238 | 720 | 629 | 223 |
| S5 | 248 | 311 | 445 | 495 | 598 | 645 | 707 | 622 | 552 | 466 | 585 | 470 | 647 | 539 | 464 |
| S6 | 248 | 223 | 495 | 445 | 557 | 567 | 598 | 495 | 458 | 351 | 394 | 600 | 431 | 323 | 590 |
| S7 | 109 | 217 | 223 | 312 | 399 | 468 | 550 | 490 | 396 | 345 | 543 | 676 | 687 | 585 | 672 |
| S8 | 109 | 248 | 248 | 351 | 399 | 468 | 396 | 312 | 245 | 435 | 718 | 585 | 487 | 712 | |
| S9 | 312 | 223 | 334 | 351 | 399 | 312 | 248 | 156 | 326 | 773 | 487 | 394 | 765 | ||
| S10 | 219 | 246 | 347 | 452 | 438 | 328 | 346 | 589 | 889 | 789 | 702 | 887 | |||
| S11 | 246 | 347 | 452 | 452 | 328 | 346 | 589 | 889 | 789 | 702 | 887 | ||||
| S12 | 110 | 220 | 246 | 156 | 248 | 468 | 1067 | 707 | 645 | 1061 | |||||
| S13 | 110 | 156 | 111 | 223 | 399 | 1115 | 645 | 598 | 1108 | ||||||
| S14 | 111 | 156 | 248 | 351 | 1172 | 598 | 567 | 1164 | |||||||
| S15 | 109 | 156 | 248 | 1080 | 495 | 458 | 1072 | ||||||||
| S16 | 111 | 312 | 1019 | 552 | 495 | 1011 | |||||||||
| S17 | 245 | 926 | 466 | 398 | 918 | ||||||||||
| S18 | 990 | 248 | 223 | 979 | |||||||||||
| S19 | 955 | 860 | 16 | ||||||||||||
| S20 | 108 | 941 | |||||||||||||
| S21 | 847 |
表4
空间变量与环境变量的RDA变差分解结果"
| RDA | R2 | R2adj | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S (空间变量) | Global model(全模型) | 0.759 | 0.638 | 0.003 |
| dbMEM2 | 0.281 | 0.015 | ||
| dbMEM4 | 0.190 | 0.010 | ||
| dbMEM6 | 0.120 | 0.025 | ||
| dbMEM7 | 0.099 | 0.019 | ||
| E(环境变量) | Global model(全模型) | 0.304 | 0.141 | 0.05 |
| FS(前向选择) | 0.181 | 0.094 | 0.03 | |
| Wind speed(风速) | 0.170 | 0.048 | ||
| S+E(环境与空间变量) | 0.722 | 0.611 | 0.002 | |
| S|E(单纯空间变量) | 0.557 | 0.533 | 0.003 | |
| E|S(单纯环境变量) | 0.165 | 0.077 | NS | |
| Shard(环境与空间变量共享) | 0.084 | |||
| Residuals(残差) | 0.389 |
| [1] | 杜飞雁, 王亮根, 王雪辉 , 等, 2016. 南沙群岛海域长腹剑水蚤(Oithona spp.)的种类组成、数量分布及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 47(6):1176-1184. |
| DU FEIYAN, WANG LIANGGEN, WANG XUEHUI , et al, 2016. Assemblage and abundance of Oithona and environmental factors in Nansha Islands Waters, South China Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 47(6):1176-1184 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [2] |
范启, 何舜平 , 2014. 长江流域䱗种群遗传多样性和遗传结构分析[J]. 水生生物学报, 38(4):627-635.
doi: 10.7541/2014.89 |
|
FAN QI, HE SHUNPING , 2014. The pattern of upper and Middle Yangtze drainages shapes the genetic structure and diversity of Hemiculter leucisculus revealed by mitochondrial DNA locus[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 38(4):627-635 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.7541/2014.89 |
|
| [3] | 黄琦, 徐少林, 徐磊 , 等, 2017. 广东流溪河水库盔型溞(Daphnia galeata)休眠种群与现生种群的单倍型多样性和遗传分化[J]. 湖泊科学, 29(5):1209-1216. |
| HUANG QI, XU SHAOLIN, XU LEI , et al, 2017. Haplotype diversity and genetic differentiation of dormant and active populations of Daphnia galeata in Liuxihe reservoir of Guangdong Province, southern China[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 29(5):1209-1216 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [4] | 李纯厚, 贾晓平, 蔡文贵 , 2004. 南海北部浮游动物多样性研究[J]. 中国水产科学, 11(2):139-146. |
| LI CHUNHOU, JIA XIAOPING, CAI WENGUI , 2004. Diversity of marine zooplankton in the north of South China Sea[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 11(2):139-146 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [5] | 林元烧 , 2005. 中华哲水蚤种群遗传学研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学. |
| LIN YUANSHAO , 2005. Population genetics of a marine copepod, Calanus sinicus Brodsky[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [6] | 刘光兴, 林坚 , 2007. 遗传标记技术在海洋桡足类生物多样性和系统发生研究中的应用[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 37(1):33-37. |
| LIU GUANGXING, LIN JIAN , 2007. Application of genetic marker technique to the study of systematics, biodiversity and phylogenetics for marine copepods[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 37(1):33-37 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [7] | 曲若竹, 侯林, 吕红丽 , 等, 2004. 群体遗传结构中的基因流[J]. 遗传, 26(3):377-382. |
| QUN RUOZHU, HOU LIN, LV HONGLI , et al, 2004. The gene flow of population genetic structure[J]. Hereditas, 26(3):377-382 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [8] |
孙柔鑫, 王彦国, 连光山 , 等, 2014. 海南岛西北沿岸海域浮游桡足类的分布及群落特征[J]. 生物多样性, 22(3):320-328.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13137 |
|
SUN ROUXIN, WANG YANGUO, LIAN GUANGSHAN , et al, 2014. Distribution and community characteristics of planktonic copepods in the northwest coastal waters off Hainan Island[J]. Biodiversity Science, 22(3):320-328 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13137 |
|
| [9] | 田志富 , 2012. 基于RDA的白洋淀浮游植物群落结构动态特征分析[D]. 保定: 河北大学. |
| TIAN ZHIFU , 2012. Structure and dynamics of phytoplankton community based on the redundancy analysis (RDA)[D]. Baoding: Hebei University (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [10] | 王敏晓 , 2010. 分子标记在中国近海浮游桡足类研究中的应用 [D]. 青岛:中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所). |
| WANG MINXIAO , 2010. Application of molecular markers to the researches on pelagic copepods in the Chinese coastal regions[D]. Qingdao:The Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [11] | 王兴霞, 徐磊, 王亮根 , 等, 2018. 基于COI基因序列的长腹剑水蚤系统进化关系[J]. 海洋学报, 40(6):92-103. |
| WANG XINGXIA, XU LEI, WANG LIANGGEN , et al, 2018. Molecular phylogenetic of Oithona based on COI sequence[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 40(6):92-103 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [12] | 徐兆礼 , 2006. 中国海洋浮游动物研究的新进展[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 45(S2):16-23. |
| XU ZHAOLI , 2006. Advance and future of our study on marine zooplankton[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 45(S2):16-23 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [13] | 薛亚东, 李丽, 吴巩胜 , 等, 2011. 景观遗传学: 概念与方法[J]. 生态学报, 31(6):1756-1762. |
| XUE YADONG, LI LI, WU GONGSHENG , et al, 2011. Concepts and techniques of landscape genetics[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(6):1756-1762 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [14] | 杨海军, 刘秦玉 , 1998. 南海海洋环流研究综述[J]. 地球科学进展, 13(4):364-368. |
| YANG HAIJUN, LIU QINYU , 1998. A summary on ocean circulation study of the South China Sea[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 13(4):364-368 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [15] | 张才学, 龚玉艳, 王学锋 , 等, 2011. 湛江港湾浮游桡足类群落结构的季节变化和影响因素[J]. 生态学报, 31(23):7086-7096. |
| ZHANG CAIXUE, GONG YUYAN, WANG XUEFENG , et al, 2011. The effects of season and environmental factors on community structure of planktonic copepods in Zhanjiang Bay, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(23):7086-7096 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [16] | 张武昌, 赵楠, 陶振铖 , 等, 2010. 中国海浮游桡足类图谱[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 800. |
| ZHANG WUCHANG, ZHAO NAN, TAO ZHENCHENG , et al, 2010. An illustrated guide to marine planktonic copepods in China seas[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 800 (in Chinese). | |
| [17] | 赵静, 孙洋, 谭永安 , 等, 2014. 基于COI及28S rDNA序列分析的扶桑绵粉蚧地理科群的遗传分化研究[J]. 棉花学报, 26(2):130-137. |
| ZHAO JING, SUN YANG, TAN YONG’AN , et al, 2014. Genetic differentiation among different geographic populations of Phenacoccus solenopsis based on sequences of COI and 28S rDNA[J]. Cotton Science, 26(2):130-137 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [18] | 朱伟军, 孙照渤, 齐卫宁 , 1997. 南海季风爆发及其环流特征[J]. 南京气象学院学报, 20(4):440-446. |
| ZHU WEIJUN, SUN ZHAOBO, QI WEINING , 1997. South-China-Sea monsoon onset with its circulation structure[J]. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology, 20(4):440-446 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [19] |
AJIBOYE O O, YAKUBU A F, ADAMS T E , et al, 2011. A review of the use of copepods in marine fish larviculture[J]. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 21(2):225-246.
doi: 10.1007/s11160-010-9169-3 |
| [20] |
BAUS E, DARROCK D J, BRUFORD M W , 2005. Gene-flow pattern in Atlantic and Mediterranean populations of the Lusitanian sea star Asterina gibbosa[J]. Molecular Ecology, 14(11):3373-3382.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2005.02681.x pmid: 16156809 |
| [21] |
BARATTI M, GOTI E, MESSANA G G , 2005. High level of genetic differentiation in the marine isopod Sphaeroma terebrans (Crustacea Isopoda Sphaeromatidae) as inferred by mitochondrial DNA analysis[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 315(2):225-234.
doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2004.09.020 |
| [22] | CHEN GANG , 2006. Cryptic biodiversity and speciation in marine populations: The holoplankton paradox[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 45(S2):68-76. |
| [23] |
CASTELIN M, FEUTRY P, HAUTECOEUR M , et al, 2013. New insight on population genetic connectivity of widespread amphidromous prawn Macrobrachium lar (fabricius, 1798) (Crustacea: Decapoda: Palaemonidae)[J]. Marine Biology, 160(6):1395-1406.
doi: 10.1007/s00227-013-2191-y |
| [24] |
CORNILS A, WEND-HECKMANN B, HELD C , 2017. Global phylogeography of Oithona similis s.l. (Crustacea, Copepoda, Oithonidae) - A cosmopolitan plankton species or a complex of cryptic lineages?[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 107:473-485.
doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2016.12.019 |
| [25] |
COSTA F O, DEWAARD J R, BOUTILLIER J , et al, 2007. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes: the case of the Crustacea[J]. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 64(2):272-295.
doi: 10.1139/f07-008 |
| [26] |
ELLIS C D, HODGSON D J, DANIELS C L , et al, 2017. Population genetic structure in European lobsters: implications for connectivity, diversity and hatchery stocking[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 563:123-137.
doi: 10.3354/meps11957 |
| [27] |
GOETZE E , 2003. Cryptic speciation on the high seas; global phylogenetics of the copepod family Eucalanidae[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences, 270(1531):2321-2331.
doi: 10.1098/rspb.2003.2505 |
| [28] |
GILG M R, HOWARD R, TURNER R , et al, 2014. Estimating the dispersal capacity of the introduced green mussel, Perna viridis (Linnaeus, 1758), from field collections and oceanographic modeling[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 461:233-242.
doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2014.08.004 |
| [29] | HALL T A , 1999. BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT[J]. Nucleic Acids Symposium Series, 41:95-98. |
| [30] |
HILBISH T J, KOEHN R K , 1985. The Physiological Basis of Natural Selection at the Lap Locus[J]. Evolution, 39(6):1302-1317.
doi: 10.2307/2408787 pmid: 28564261 |
| [31] |
HAYE P A, SEGOVIA N I, MUNOZHERRERA N C , et al, 2014. Phylogeographic structure in benthic marine invertebrates of the southeast pacific coast of Chile with differing dispersal potential[J]. Plos One, 9(2):e88613
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088613 |
| [32] |
HORNE J B, VAN HERWERDEN L, CHOAT J H , et al, 2008. High population connectivity across the Indo-Pacific: congruent lack of phylogeographic structure in three reef fish congeners[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 49(2):629-638.
doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2008.08.023 |
| [33] | IZZARD R, DRAY L, KARAKAS A , et al, 2006. Population nucleosynjournal in single and binary stars I. Model[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 460(2):565-572. |
| [34] |
KUMAR S, NEI M, DUDLEY J , et al, 2008. MEGA: a biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences[J]. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 9(4):299-306.
doi: 10.1093/bib/bbn017 |
| [35] |
KENCHINGTON E L, PATWARY M U, ZOUROS E , et al, 2006. Genetic differentiation in relation to marine landscape in a broadcast spawning bivalve mollusc (Placopecten magellanicus)[J]. Molecular Ecology, 15(7):1781-1796.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2006.02915.x |
| [36] |
LUTTIKHUIZEN P C, DRENT J, BAKER A J , 2003. Disjunct distribution of highly diverged mitochondrial lineage clade and population subdivision in a marine bivalve with pelagic larval dispersal[J]. Molecular Ecology, 12(8):2215-2229.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-294X.2003.01872.x |
| [37] | NIELSEN E E, KENCHINGTON E . 2001. Prioritising marine fish and shellfish populations for conservation: A useful concept?[J]. Fish Fisher, 7:328-343. |
| [38] |
NAKAMURA Y, TURNER J T , 1997. Predation and respiration by the small cyclopoid copepod Oithona similisr: How important is feeding on ciliates and heterotrophic flagellates?[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 19(9):1275-1288.
doi: 10.1093/plankt/19.9.1275 |
| [39] |
PALUMBI S R , 1994. Genetic divergence, reproductive isolation, and marine speciation[J]. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 25:547-572.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.es.25.110194.002555 |
| [40] |
ROZAS J, SÁNCHEZ-DELBARRIO J C, MESSEGUER X , et al, 2003. DnaSP, DNA polymorphism analyses by the coalescent and other methods[J]. Bioinformatics, 19(18):2496-2497.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btg359 |
| [41] |
SALZBURGER W, EWING G B, VON HAESELER A , 2011. The performance of phylogenetic algorithms in estimating haplotype genealogies with migration[J]. Molecular Ecology, 20(9):1952-1963.
doi: 10.1111/mec.2011.20.issue-9 |
| [42] |
TAYLOR M S, HELLBERG M E , 2006. Comparative phylogeography in a genus of coral reef fishes: biogeographic and genetic concordance in the Caribbean[J]. Molecular Ecology, 15(3):695-707.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2006.02820.x |
| [43] |
WANG LIANGGEN, DU FEIYAN, WANG XUEHUI , et al, 2017. Distribution and role of the genus Oithona (Copepoda: Cyclopoida) in the South China Sea[J]. Oceanologia, 59(3):300-310.
doi: 10.1016/j.oceano.2017.03.009 |
| [44] |
WAPLES R S , 1998. Separating the wheat from the chaff: Patterns of genetic differentiation in high gene flow species[J]. Journal of Heredity, 89(5):438-450.
doi: 10.1093/jhered/89.5.438 |
| [45] |
Ward R D, WOODWARK M, SKIBINSK D O F , 1994. A comparison of genetic diversity levels in marine, fresh-water, and anadromous fishes[J]. Journal Fish Biology, 44(2):213-232.
doi: 10.1111/jfb.1994.44.issue-2 |
| [46] |
WEERSING K, TOONEN R J , 2009. Population genetics, larval dispersal, and connectivity in marine systems[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 393:1-12.
doi: 10.3354/meps08287 |
| [47] |
WHITE C, SELKOE K A, WATSON J , et al, 2010. Ocean currents help explain population genetic structure[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences, 277(1688):1685-1694.
doi: 10.1098/rspb.2009.2214 pmid: 2871860 |
| [1] | 徐超, 龙丽娟, 李莎, 袁丽, 徐晓璐. 南海及其附属岛礁海洋科学考察历史资料系统整编3. 数据共享服务及应用[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 158-165. |
| [2] | 徐超, 龙丽娟, 李莎, 何云开, 袁丽, 徐晓璐. 南海及其附属岛礁海洋科学考察历史资料系统整编1. 资料整编技术及应用[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 143-149. |
| [3] | 徐超, 龙丽娟, 李莎, 徐晓璐, 袁丽. 南海及其附属岛礁海洋科学考察历史资料系统整编2. 数据治理技术与应用[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 150-157. |
| [4] | 柳原, 柯志新, 李开枝, 谭烨辉, 梁竣策, 周伟华. 人类活动和沿岸流影响下的粤东近海浮游动物群落特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [5] | 刘玓玓, 张喜洋, 孙富林, 王明壮, 谭飞, 施祺, 王冠, 杨红强. 南海海滩岩微生物群落结构和特定菌株对其成因机制的启示*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 112-122. |
| [6] | 江绿苗, 陈天然, 赵宽, 张婷, 许莉佳. 南海北部涠洲岛边缘珊瑚礁的生物侵蚀实验研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 155-165. |
| [7] | 许莉佳, 廖芝衡, 陈辉, 王永智, 黄柏强, 林巧云, 甘健锋, 杨静. 南海北部珊瑚群落结构特征及其对海洋热浪事件的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 58-71. |
| [8] | 邱燕, 鞠东, 黄文凯, 王英民, 聂鑫. 南海中央海盆海底初始扩张时间的重新认定[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 154-165. |
| [9] | 赵明辉, 袁野, 张佳政, 张翠梅, 高金尉, 王强, 孙珍, 程锦辉. 南海北部被动陆缘洋陆转换带张裂-破裂研究新进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 173-183. |
| [10] | 黄谕, 王琳, 麦志茂, 李洁, 张偲. 南海热带岛礁生物土壤结皮中细菌的分离及其固砂特性初步研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(6): 101-110. |
| [11] | 王辰燕, 史敬文, 颜安南, 康亚茹, 王煜轩, 覃素丽, 韩民伟, 张瑞杰, 余克服. 有机磷酸酯在南海长棘海星中的生物富集特征及来源解析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(5): 30-37. |
| [12] | 李牛, 邸鹏飞, 冯东, 陈多福. 冷泉渗漏对海洋沉积物氧化还原环境地球化学识别的影响——以南海东北部F站位活动冷泉为例*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(5): 144-153. |
| [13] | 张智晟, 谢玲玲, 李君益, 李强. 边缘海与开阔海中尺度涡生命周期演化规律对比分析: 以南海和黑潮延伸体为例[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(4): 63-76. |
| [14] | 杨磊, 温金辉, 王强, 罗希, 黄华明, 何云开, 陈举. 热带气旋影响吕宋海峡输运的研究进展与展望*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 40-51. |
| [15] | 赵中贤, 孙珍, 毛云华, 张伙带. 南海北部陆缘不均匀伸展及脉动式构造升降史*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 96-115. |
|
||