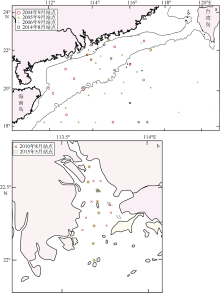
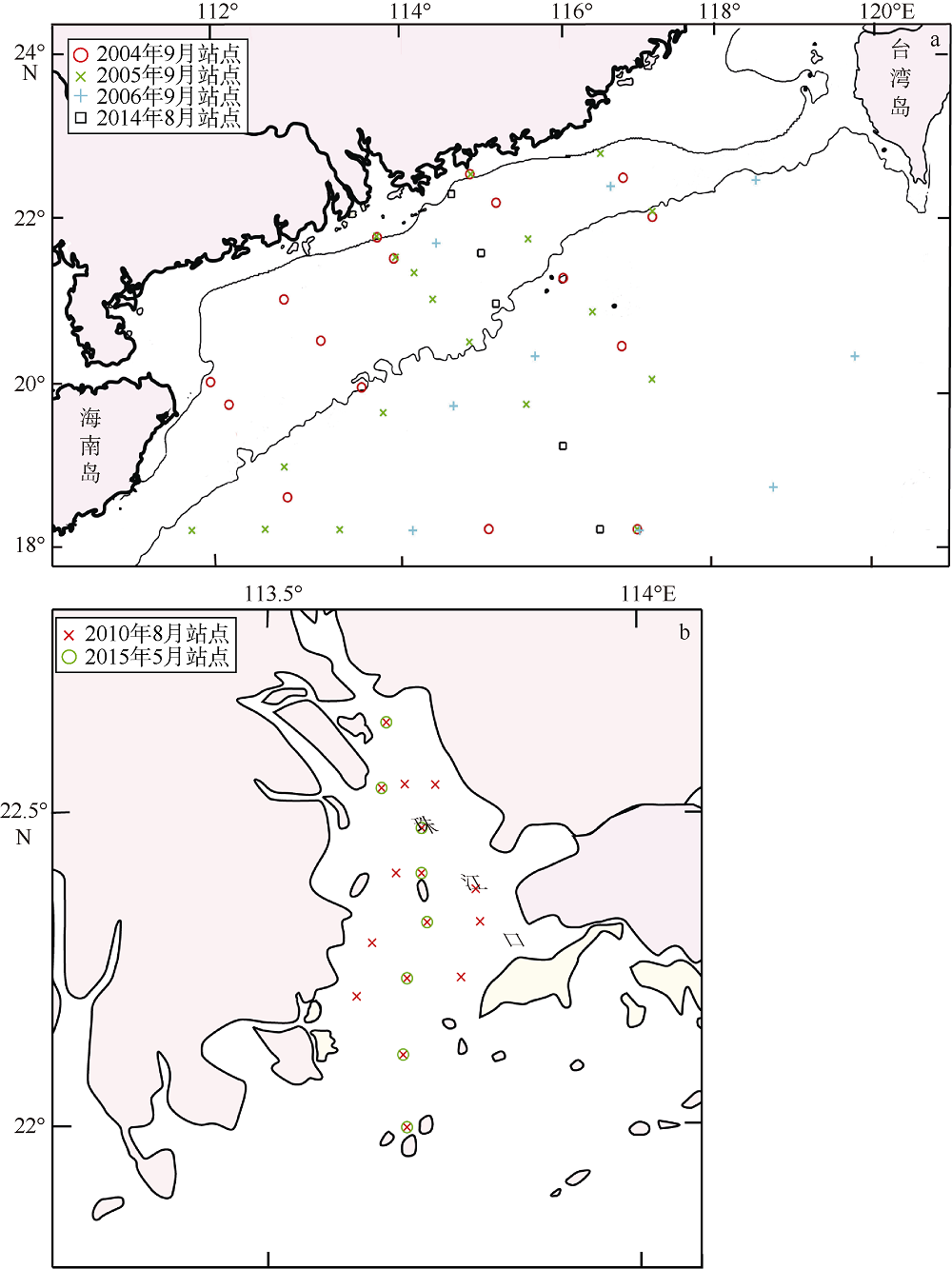
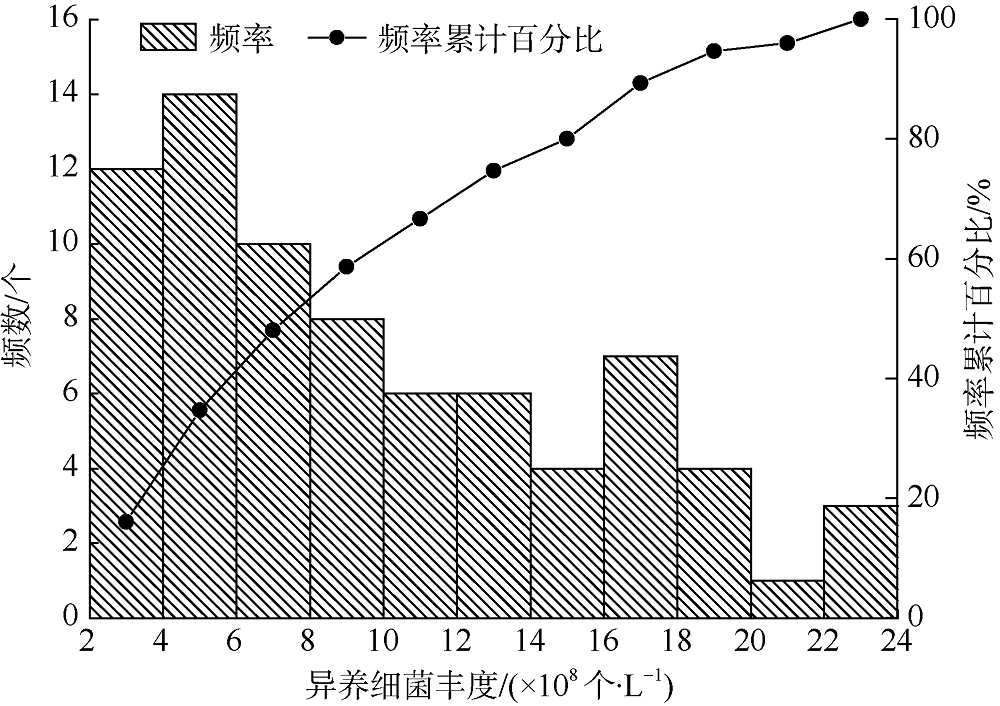
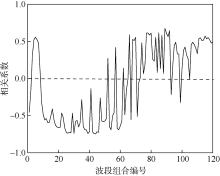
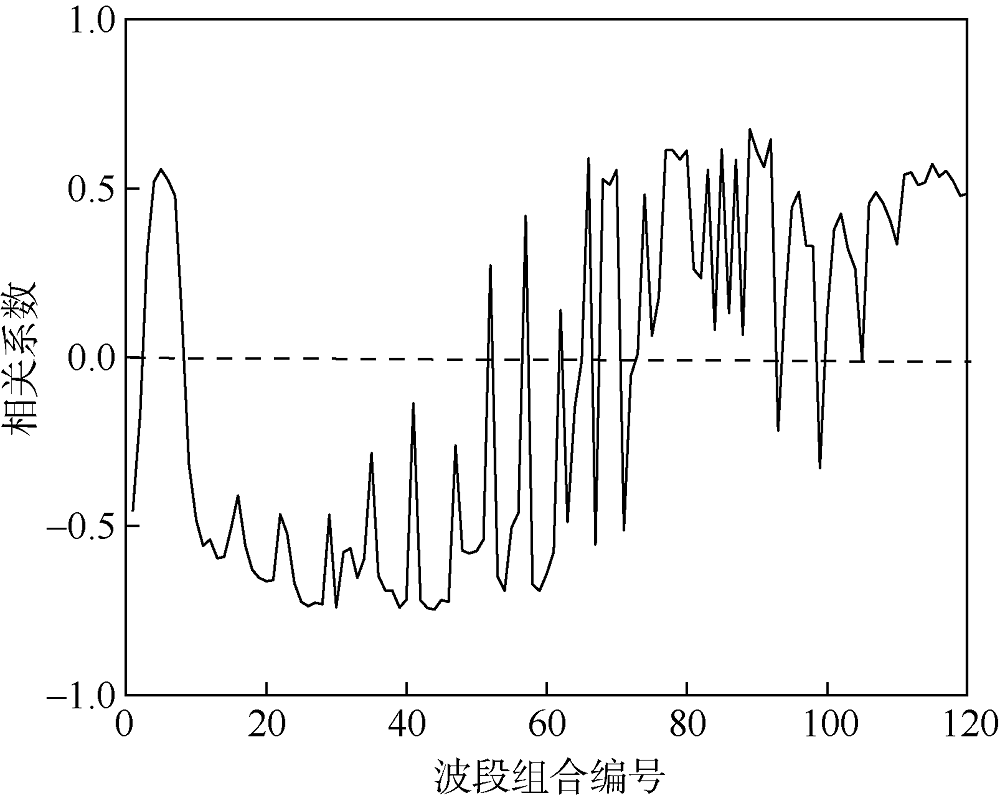
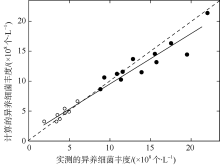
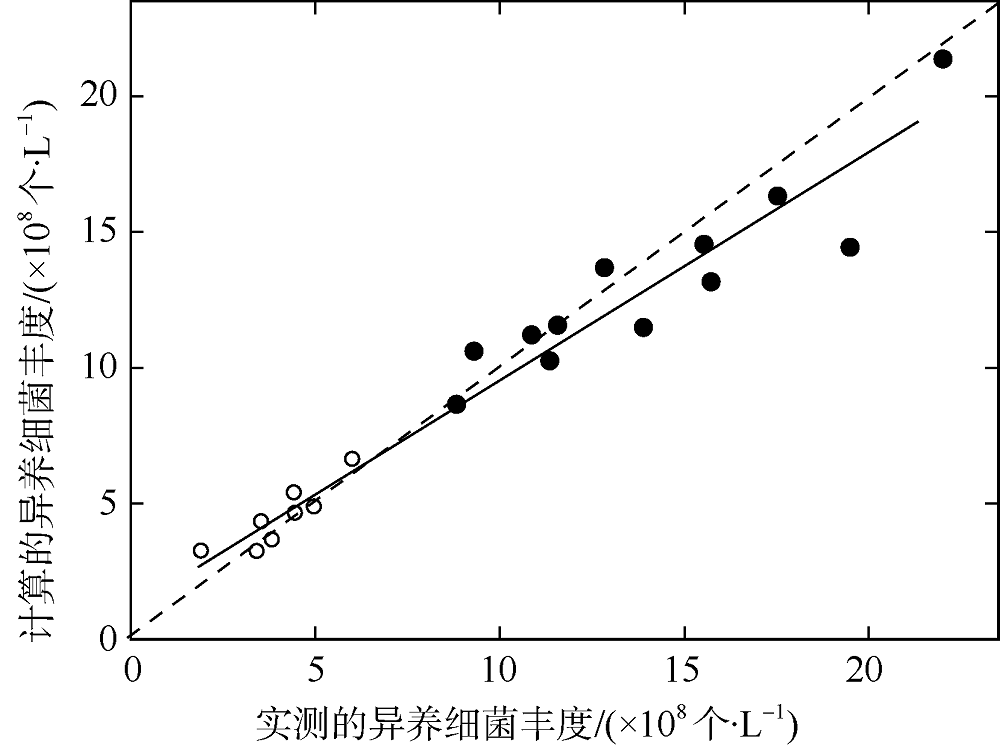
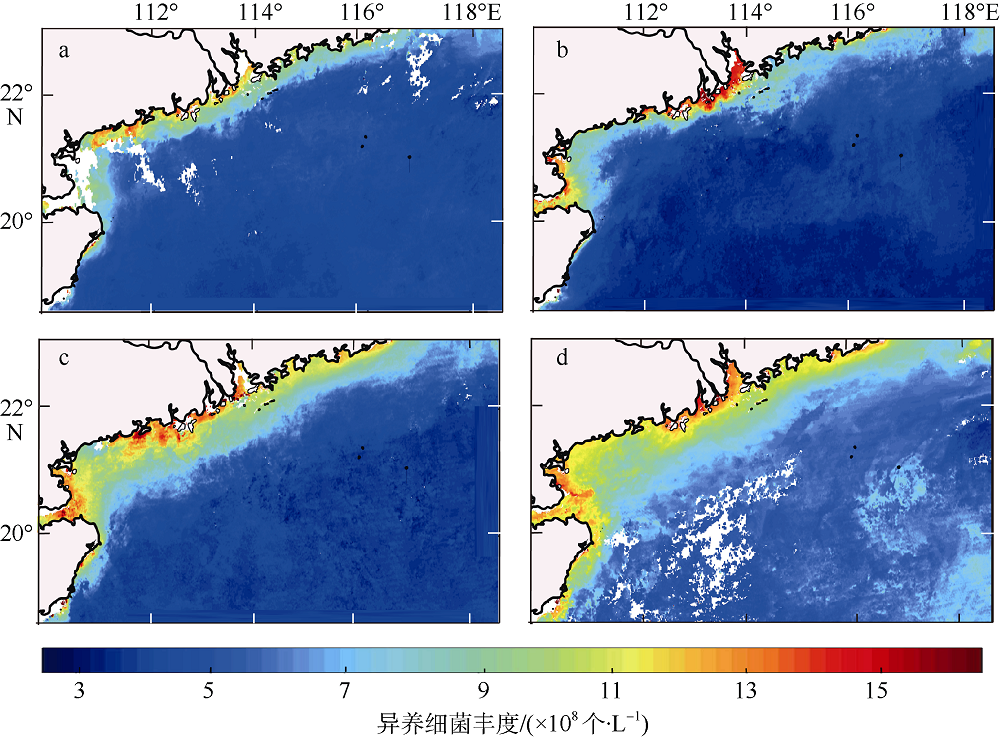
| [1] |
陈楚群, 施平, 毛庆文, 1996. 应用TM数据估算沿岸海水表层叶绿素浓度模型研究[J]. 环境遥感, 11(3):168-176.
|
|
CHEN CHUQUN, SHI PING, MAO QINGWEN, 1996. Study on modeling chlorophyll concentration of surface coastal water using TM data[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment China, 11(3):168-176 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
杜成功, 李云梅, 王桥, 等, 2016. 面向GOCI数据的太湖总磷浓度反演及其日内变化研究[J]. 环境科学, 37(3):862-872.
|
|
DU CHENGGONG, LI YUNMEI, WANG QIAO, et al, 2016. Inversion model and daily variation of total phosphorus concentrations in Taihu lake based on GOCI data[J]. Environmental Science, 37(3):862-872 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
季凤云, 郭立梅, 李洪波, 等, 2017. 南海北部细菌丰度和细菌生产力分布及其与环境因子相关性[J]. 海洋环境科学, 36(3):354-359.
|
|
JI FENGYUN, GUO LIMEI, LI HONGBO, et al, 2017. Abundance and production of bacteria and their correlations with environmental factor[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 36(3):354-359 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
荆红梅, 韦誉, 郑丽平, 等, 2018. 三亚海域浮游病毒与细菌丰度的时空变化规律以及相关环境因子[J]. 热带海洋学报, 37(2):36-46.
|
|
JING HONGMEI, WEI YU, ZHENG LIPING, et al, 2018. Spatiotemporal variations of virioplankton and bacterioplankton abundance in Sanya waters and their related environmental factors[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 37(2):36-46 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
李祥付, 徐杰, 施震, 等, 2018. 珠江口异养细菌时空分布特征及其调控机制[J]. 热带海洋学报, 37(1):27-36.
|
|
LI XIANGFU, XU JIE, SHI ZHEN, et al, 2018. Spatial and temporal variation in heterotrophic bacteria and their regulators in the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 37(1):27-36 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
逄淑娜, 朱渭宁, 陈江, 等, 2019. Landsat-8的舟山近岸海域总悬浮物遥感反演与时空变异研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 39(12):3826-3832.
|
|
PANG SHUNA, ZHU WEINING, CHEN JIANG, et al, 2019. Using Landsat-8 to remotely estimate and observe spatio-temporal variations of total suspended matter in Zhoushan coastal regions[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 39(12):3826-3832 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
王生福, 宋星宇, 黄良民, 等, 2013. 南海北部夏季浮游细菌生长效率初步研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 32(6):73-79.
|
|
WANG SHENGFU, SONG XINGYU, HUANG LIANGMIN, et al, 2013. Preliminary study on marine bacterial growth efficiency in the northern South China Sea in summer[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 32(6):73-79 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
张霞, 黄小平, 施震, 等, 2012. 珠江口异养细菌丰度与环境因子的耦合关系[J]. 海洋学报, 34(6):228-237.
|
|
ZHANG XIA, HUANG XIAOPING, SHI ZHEN, et al, 2012. Coupling of heterotrophic bacteria abundance and environmental variables of the Zhujiang (Pearl) River Estuary[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 34(6):228-237 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
BAILEY S, WANG MENGHUA, 2001. Satellite aerosol optical thickness match-up procedures[M]// FARGION G S, BARNES R, MCCLAIN C. In situ aerosol optical thickness collected by the SIMBIOS program (1997—2000): protocols, and data QC and analysis. NASA/TM-2001-209982. Greenbelt: Goddard Space Flight Center: 70-72.
|
| [10] |
BAILEY S W, WERDELL P J, 2006. A multi-sensor approach for the on-orbit validation of ocean color satellite data products[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 102(1-2):12-23.
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2006.01.015
|
| [11] |
CAO ZHIGANG, DUAN HONGTAO, FENG LIAN, et al, 2017. Climate- and human-induced changes in suspended particulate matter over Lake Hongze on short and long timescales[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 192:98-113.
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2017.02.007
|
| [12] |
CHEN BINGZHANG, LIU HONGBIN, WANG ZONGLING, 2009. Trophic interactions within the microbial food web in the South China Sea revealed by size-fractionation method[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 368:59-66.
doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2008.10.012
|
| [13] |
CHEN JUN, WANG BAOJUN, SUN JIHONG, 2012. Scale correction of two-band ratio of red to near-infrared using imagery histogram approach: a case study on indian remote sensing satellite in yellow river estuary[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 5(2):663-668.
doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.4609443
|
| [14] |
CRUMP B C, FINE L M, FORTUNATO C S, et al, 2017. Quantity and quality of particulate organic matter controls bacterial production in the Columbia River estuary[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 62(6):2713-2731.
doi: 10.1002/lno.v62.6
|
| [15] |
DUARTE C M, AGUSTI S, VAQUÉ D, et al, 2005. Experimental test of bacteria-phytoplankton coupling in the Southern Ocean[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 50(6):1844-1854.
doi: 10.4319/lo.2005.50.6.1844
|
| [16] |
HE QUANJUN, CHEN CHUQUN, 2014. A new approach for atmospheric correction of MODIS imagery in turbid coastal waters: a case study for the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 5(3):249-257.
doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2014.898192
|
| [17] |
HE XIANQIANG, PAN DELU, MAO ZHIHUA, 2004. Atmospheric correction of SeaWiFS imagery for turbid coastal and inland waters[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 23(4):609-615.
|
| [18] |
HU SHUIBO, CAO WENXI, WANG GUIFEN, et al, 2015. Empirical ocean color algorithm for estimating particulate organic carbon in the South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 33(3):764-778.
doi: 10.1007/s00343-015-4203-x
|
| [19] |
LI W K W, HEAD E J H, GLEN HARRISON W, 2004. Macroecological limits of heterotrophic bacterial abundance in the ocean[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅰ: Oceanographic Research Papers, 51(11):1529-1540.
|
| [20] |
LIU DONG, PAN DELU, BAI YAN, et al, 2015. Remote sensing observation of particulate organic carbon in the pearl river estuary[J]. Remote Sensing, 7(7):8683-8704.
doi: 10.3390/rs70708683
|
| [21] |
MOBLEY C D, STRAMSKI D, 1997. Effects of microbial particles on oceanic optics: Methodology for radiative transfer modeling and example simulations[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 42(3):550-560.
doi: 10.4319/lo.1997.42.3.0550
|
| [22] |
MONTES-HUGO M A, REYNOLDS R A, VERNET M, et al, 2007. Particulate beam attenuation coefficient, bacteria abundance, and production in marine nearshore waters[C] // Proceedings of SPIE 6680, coastal ocean remote sensing. San Diego: SPIE.
|
| [23] |
PAN XIAOJU, WONG G T F, HO T-Y, et al, 2018. Remote sensing of surface [nitrite + nitrate] in river-influenced shelf-seas: the northern South China Sea shelf-sea[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 210:1-11.
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2018.03.012
|
| [24] |
PRIYAJA P, DWIVEDI R, SINI S, et al, 2016. Remote sensing of bacterial response to degrading phytoplankton in the Arabian Sea[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188(12):662.
doi: 10.1007/s10661-016-5666-8
|
| [25] |
RUDDICK K G, OVIDIO F, RIJKEBOER M, 2000. Atmospheric correction of SeaWiFS imagery for turbid coastal and inland waters[J]. Applied Optics, 39(6):897-912.
doi: 10.1364/AO.39.000897
|
| [26] |
STRAMSKI D, REYNOLDS R A, KAHRU M, et al, 1999. Estimation of particulate organic carbon in the ocean from satellite remote sensing[J]. Science, 285(5425):239-242.
doi: 10.1126/science.285.5425.239
|
| [27] |
STRAMSKI D, BRICAUD A, MOREL A, 2001. Modeling the inherent optical properties of the ocean based on the detailed composition of the planktonic community[J]. Applied Optics, 40(18):2929-2945.
doi: 10.1364/AO.40.002929
|
| [28] |
WANG MENGHUA, SHI WEI. 2007. The NIR-SWIR combined atmospheric correction approach for MODIS ocean color data processing[J]. Optics Express, 15(24):15722-15733.
doi: 10.1364/OE.15.015722
|
| [29] |
WONG G T F, KU T-L, LIU HONGBIN, et al, 2015. The oceanography of the Northern south China Sea Shelf-Sea (NoSoCS) and its adjacent Waters-overview and Highlights[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 117:3-9.
|
| [30] |
YE HAIBIN, CHEN CHUQUN, YANG CHAOYU, 2017. Atmospheric correction of landsat-8/OLI imagery in turbid estuarine waters: a case study for the pearl river estuary[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 10(1):252-261.
doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.4609443
|
| [31] |
YUAN XIANGCHENG, HE LEI, YIN KEDONG, et al, 2011. Bacterial distribution and nutrient limitation in relation to different water masses in the coastal and northwestern South China Sea in late summer[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 31(11):1214-1223.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2011.04.012
|
| [32] |
ZHANG XIA, SHI ZHEN, LIU QINGXIA, et al, 2013. Spatial and temporal variations of picoplankton in three contrasting periods in the Pearl River Estuary, South China[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 56:1-12.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2013.01.015
|
| [33] |
ZHOU WEIHUA, LONG AIMIN, JIANG TAO, et al, 2011. Bacterioplankton dynamics along the gradient from highly eutrophic Pearl River Estuary to oligotrophic northern South China Sea in wet season: implication for anthropogenic inputs[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62(4):726-733.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.01.018
|
| [34] |
ZUBKOV M V, FUCHS B M, TARRAN G A, et al, 2002. Mesoscale distribution of dominant bacterioplankton groups in the northern North Sea in early summer[J]. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 29(2):135-144.
doi: 10.3354/ame029135
|
 ), 陈楚群1,2,3(
), 陈楚群1,2,3( ), 周伟华4, 李祥付1, 吴颉1, 叶海彬1, 唐世林1,3
), 周伟华4, 李祥付1, 吴颉1, 叶海彬1, 唐世林1,3
 ), CHEN Chuqun1,2,3(
), CHEN Chuqun1,2,3( ), ZHOU Weihua4, LI Xiangfu1, WU Jie1, YE Haibin1, TANG Shilin1,3
), ZHOU Weihua4, LI Xiangfu1, WU Jie1, YE Haibin1, TANG Shilin1,3