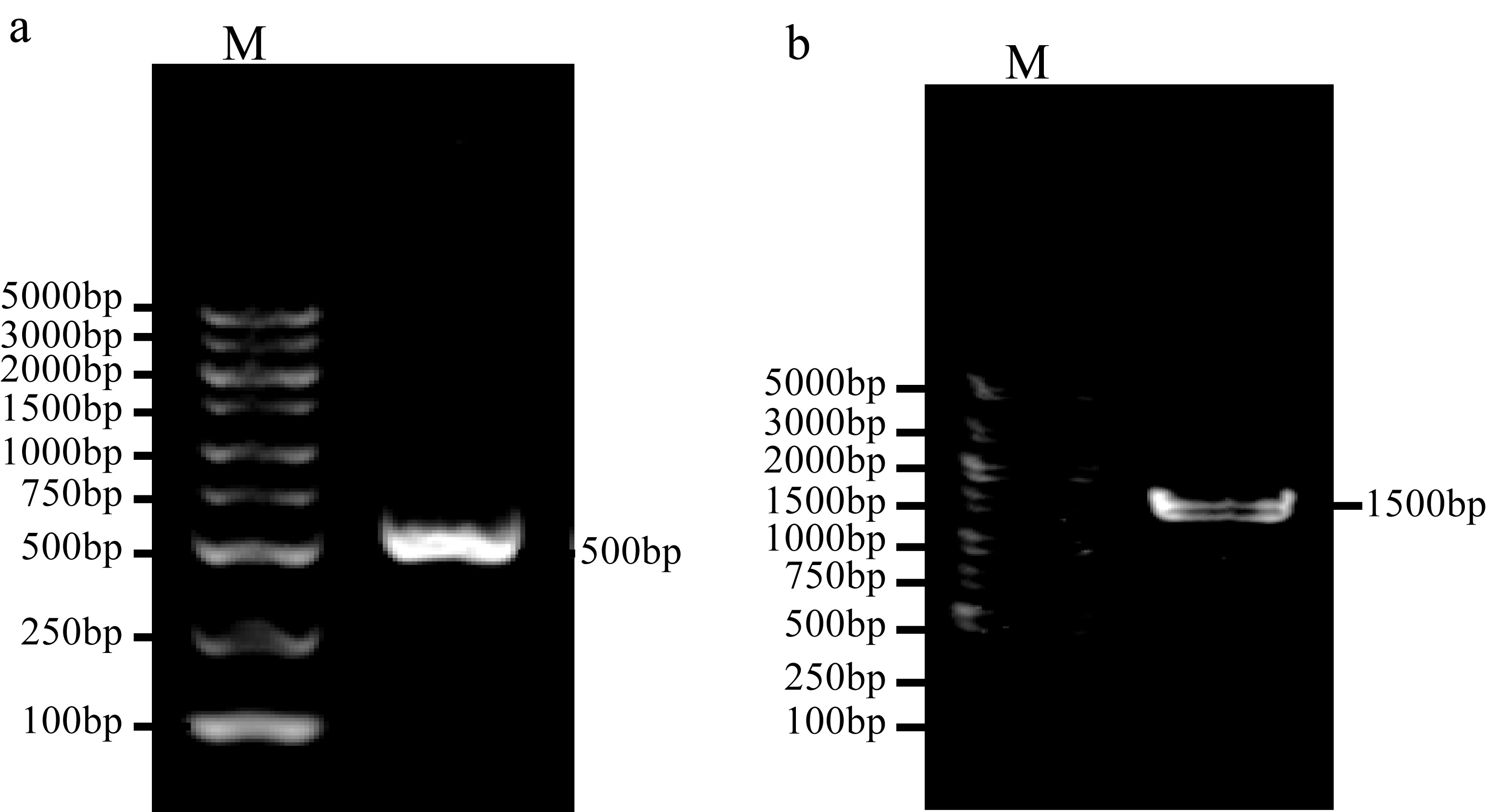
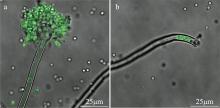
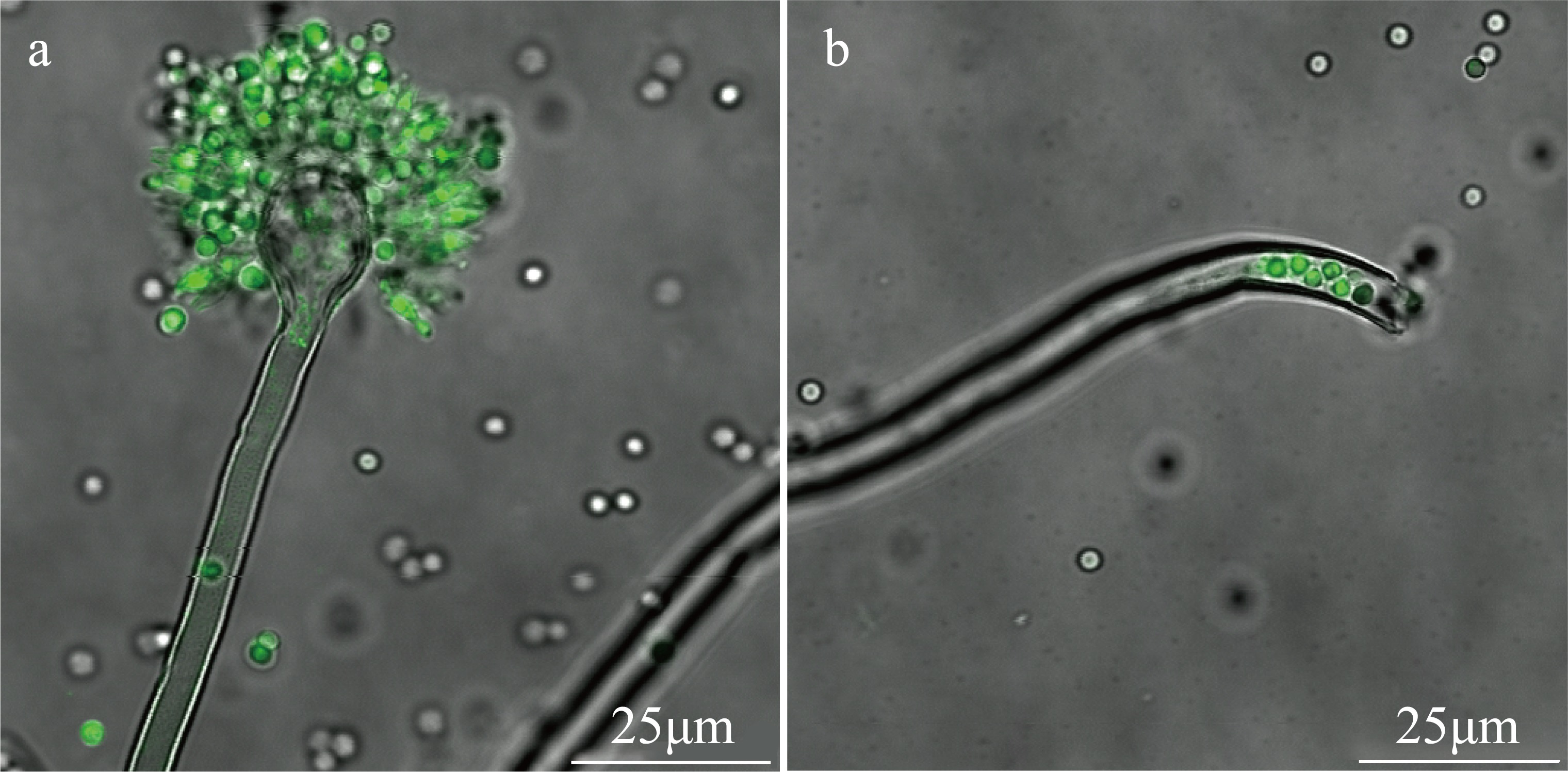
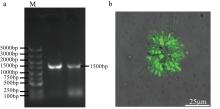
| [1] |
高亚欣, 王昊, 戴好富, 等, 2023. 西沙短指软珊瑚Sinularia flexibilis中具有肿瘤细胞毒活性的甾体化合物[J]. 热带海洋学报, 42(5): 56-63.
|
|
GAO YAXIN, WANG HAO, DAI HAOFU, et al, 2023. Cytotoxic steroids from the soft coral Sinularia flexibilis collected off the Xisha[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 42(5): 56-63 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
鞠建华, 邵明伟, 孙长利, 等, [2022-05-06]. 一种海洋真菌-细菌共生体及其代谢产物和在制备抗菌药物中的应用: 中国, CN112694983B[P].
|
|
JU JIANHUA, SHAO MINGWEI, SUN CHANGLI, et al, [2022-05-06]. Marine fungus-bacterium symbiont, metabolite of marine fungus-bacterium symbiont and application of metabolite in preparation of antibacterial drugs: China, CN112694983B[P] (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
凌娟, 梁童茵, 岳维忠, 等, 2023. 热带海草泰来草沉积物真菌的群落结构、功能与分子生态网络研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 42(5): 64-75.
|
|
LING JUAN, LIANG TONGYIN, YUE WEIZHONG, et al, 2023. Community structure, function, and molecular ecological network of fungi in the tropical seagrass Thalassia hemprichii sediment[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 42(5): 64-75 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
马丽丽, 田新朋, 李桂菊, 等, 2021. 海洋微生物来源天然产物研究现状与态势[J]. 热带海洋学报, 40(5): 134-146.
doi: 10.11978/2020104
|
|
MA LILI, TIAN XINPENG, LI GUIJU, et al, 2021. Research status and development trends of natural products from marine microorganisms[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 40(5): 134-146 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.11978/2020104
|
| [5] |
张涵, 谭雁鸿, 杨斌, 等, 2021. 中国南海软珊瑚附生真菌Acremonium sp. SCSIO41216的次级代谢产物研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 40(6): 135-139.
doi: 10.11978/2020103
|
|
ZHANG HAN, TAN YANHONG, YANG BIN, et al, 2021. Study on the secondary metabolites from the South China Sea soft coral-derived fungus Acremonium sp. SCSIO41216[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 40(6): 135-139 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.11978/2020103
|
| [6] |
CHENG SHENG, JIANG JIANWEI, TAN LITAO, et al, 2022. Plant growth-promoting ability of mycorrhizal fusarium strain KB-3 enhanced by its IAA producing endohyphal bacterium, Klebsiella aerogenes[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 13: 855399.
|
| [7] |
DE CASTRO M V, IÓCA L P, WILLIAMS D E, et al, 2016. Condensation of macrocyclic polyketides produced by Penicillium sp. DRF2 with mercaptopyruvate represents a new fungal detoxification pathway[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 79(6): 1668-1678.
|
| [8] |
DING GANG, CHEN LIN, CHEN AMANDAJUAN, et al, 2012. Trichalasins C and D from the plant endophytic fungus Trichoderma gamsii[J]. Fitoterapia, 83(3): 541-544.
|
| [9] |
FRANK J A, REICH C I, SHARMA S, et al, 2008. Critical evaluation of two primers commonly used for amplification of bacterial 16S rRNA genes[J]. Applied and environmental microbiology, 74(8): 2461-2470.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.02272-07
pmid: 18296538
|
| [10] |
FÜRSTNER A, CASTANET A S, RADKOWSKI K, et al, 2003. Total synthesis of (S)-(+)-citreofuran by ring closing alkyne metathesis[J]. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 68(4): 1521-1528.
|
| [11] |
GUO ZHE, HUO RUIYUN, NIU SHUBIN, et al, 2021. Alternariasin A, new pentacyclic cytochalasin from the fungus Alternaria alternate[J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 74(9): 596-600.
|
| [12] |
HAO JUNDI, ZHENG JUANJUAN, CHEN MIN, et al, 2017. Cytochalasins from the gorgonian-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. XS-2009-0B15[J]. Chemistry of Natural Compounds, 53(4): 732-735.
|
| [13] |
HOFFMAN M T, ARNOLD A E, 2010. Diverse bacteria inhabit living hyphae of phylogenetically diverse fungal endophytes[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 76(12): 4063-4075.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.02928-09
pmid: 20435775
|
| [14] |
OKRASIŃSKA A, BOKUS A, DUK K, et al, 2021. New endohyphal relationships between Mucoromycota and Burkholderiaceae representatives[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 87(7): e02707-20.
|
| [15] |
PANG XU, ZHAO JIANYUAN, FANG XIAOMEI, et al, 2017. Metabolites from the plant endophytic fungus Aspergillus sp. CPCC 400735 and their anti-HIV activities[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 80(10): 2595-2601.
|
| [16] |
PARTIDA-MARTINEZ L P, HERTWECK C, 2005. Pathogenic fungus harbours endosymbiotic bacteria for toxin production[J]. Nature, 437(7060): 884-888.
|
| [17] |
SHAO MINGWEI, SUN CHANGLI, LIU XIAOXIAO, et al, 2020. Upregulation of a marine fungal biosynthetic gene cluster by an endobacterial symbiont[J]. Communications Biology, 3(1): 527.
doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-01239-y
pmid: 32968175
|
| [18] |
SHARMIN D, GUO YONG, NISHIZAWA T, et al, 2018. Comparative genomic insights into endofungal lifestyles of two bacterial endosymbionts, Mycoavidus cysteinexigens and Burkholderia rhizoxinica[J]. Microbes and Environments, 33(1): 66-76.
|
| [19] |
SI YINGYING, TANG MINGXU, LIN SHUANG, et al, 2018. Cytotoxic cytochalasans from Aspergillus flavipes PJ03-11 by OSMAC method[J]. Tetrahedron Letters, 59(18): 1767-1771.
|
| [20] |
STIEFEL P, SCHMIDT-EMRICH S, MANIURA-WEBER K, et al, 2015. Critical aspects of using bacterial cell viability assays with the fluorophores SYTO9 and propidium iodide[J]. BMC Microbiology, 15(1): 36.
|
| [21] |
TOMIKAWA T, SHIN-YA K, SETO H, et al, 2002. Structure of aspochalasin H, a new member of the aspochalasin family[J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 55(7): 666-668.
|
| [22] |
XU XIAO, SHAO MINGWEI, YIN CAIPIN, et al, 2020. Diversity, bacterial symbionts, and antimicrobial potential of termite-associated fungi[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 11(3): 300.
|
| [23] |
YE XUEWEI, ANJUM K, SONG TENGFEI, et al, 2016. A new curvularin glycoside and its cytotoxic and antibacterial analogues from marine actinomycete Pseudonocardia sp. HS7[J]. Natural Product Research, 30(10): 1156-1161.
|
| [24] |
YU CHUNXUE, XIA ZIXUAN, XU ZHIPENG, et al, 2025. Curvularin derivatives from hydrothermal vent sediment fungus Penicillium sp. HL-50 guided by molecular networking and their anti-inflammatory activity[J]. Chinese Journal of Natural Medicines, 23(01): 119-128.
|
| [25] |
ZHENG CAIJUAN, SHAO CHANGLUN, WU LUYONG, et al, 2013. Bioactive phenylalanine derivatives and cytochalasins from the soft coral-derived fungus, Aspergillus elegans[J]. Marine Drugs, 11(6): 2054-2068.
|
| [26] |
ZHOU GUANGXIONG, WIJERATNE E M K, BIGELOW D, et al, 2004. Aspochalasins I, J, and K: three new cytotoxic cytochalasans of Aspergillus flavipes from the rhizosphere of Ericameria laricifolia of the Sonoran desert[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 67(3): 328-332.
|
 ), 姚飞华1,2, 李晓燕1,2, 石婕妤2,3, 易湘茜2,3, 高程海1,2(
), 姚飞华1,2, 李晓燕1,2, 石婕妤2,3, 易湘茜2,3, 高程海1,2( )
)
 ), YAO Feihua1,2, LI Xiaoyan1,2, SHI Jieyu2,3, YI Xiangxi2,3, GAO Chenghai1,2(
), YAO Feihua1,2, LI Xiaoyan1,2, SHI Jieyu2,3, YI Xiangxi2,3, GAO Chenghai1,2( )
)