| [1] |
方精云, 王襄平, 沈泽昊, 等, 2009. 植物群落清查的主要内容、方法和技术规范[J]. 生物多样性, 17(6): 533-548.
|
|
FANG JINGYUN, WANG XIANGPING, SHEN ZEHAO, et al, 2009. Methods and protocols for plant community inventory[J]. Biodiversity Science, 17(6): 533-548 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09253
|
| [2] |
黄良民, 林强, 谭烨辉, 等, 2024. 热带海洋特色生态系统恢复重构与保护思考[J]. 热带海洋学报, 43(6): 1-12.
|
|
HUANG LIANGMIN, LIN QIANG, TAN YEHUI, et al, 2024. Thoughts on the restoration, reconstruction and protection of typical tropical marine ecosystems[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 43(6): 1-12 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
黄晓敏, 卢昌义, 2019. 无瓣海桑人工混交林结构及幼苗天然更新能力[J]. 福建林业科技, 46(1): 1-5, 61.
|
|
HUANG XIAOMIN, LU CHANGYI, 2019. The stand structure of artificial mixed forest of Sonneratia apetala and the ability of natural regeneration of Seedlings in Xiamen Bay, China[J]. Journal of Fujian Forestry Science and Technology, 46(1): 1-5, 61 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
李元熙, 2020. 不同退塘还湿方式下红树林鱼类生物多样性差异及影响因素[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学.
|
|
LI YUANXI, 2020. Differences and influencing factors of fish biodiversity under different ways of pond-to-mangrove reversion[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
廖宝文, 郑德璋, 郑松发, 等, 2000. 海南岛清澜港红树林群落演替系列的物种多样性特征[J]. 生态科学, 19(3): 17-22.
|
|
LIAO BAOWEN, ZHENG DEZHANG, ZHENG SONGFA, et al, 2000. The characteristics of species diversity for the successional series of mangrove community in Qinglan Harbor of Hainan Island[J]. Ecologic Science, 19(3): 17-22 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
廖宝文, 李玫, 郑松发, 等, 2003. 外来种无瓣海桑种内、种间竞争关系研究[J]. 林业科学研究, 16(4): 418-422.
|
|
LIAO BAOWEN, LI MEI, ZHENG SONGFA, et al, 2003. Study on intraspecific and interspecific competition in exotic species Sonneratia apetala[J]. Forest Research, 16(4): 418-422 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
罗文, 李艳朋, 许涵, 等, 2023. 海南热带雨林国家公园极小种群野生植物坡垒适生群落特征研究[J]. 林业资源管理, (4): 98-106.
|
|
LUO WEN, LI YANPENG, XU HAN, et al, 2023. Characteristics of suitable communities of Hopea hainanensis, a wild plant with extremely small populations in national park of Hainan tropical rainforest[J]. Forest Resources Management, (4): 98-106 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
吕晓波, 钟才荣, 张孟文, 等, 2023. 海南东寨港秋茄种群结构与数量动态变化特征研究[J]. 广东农业科学, 50(3): 39-48.
|
|
LYU XIAOBO, ZHONG CAIRONG, ZHANG MENGWEN, et al, 2023. Dynamic change characteristics of population structure and quantity of Kandelia obovata in Dongzhai harnor of Hainan[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 50(3): 39-48 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
彭潔莹, 谢缘铭, 刘文帧, 等, 2021. 小陇山锐齿栎林木本植物物种丰富度与生产力关系研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 43(11): 11-19.
|
|
PENG JIEYING, XIE YUANMING, LIU WENZHEN, et al, 2021. Relationship between tree species richness and productivity of Quercus aliena var. acutiserrata forest in Xiaolongshan Mountain, Gansu Province of northwestern China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 43(11): 11-19 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
生农, 辛琨, 廖宝文, 2021. 红树林湿地生态功能及其价值研究文献学分析[J]. 湿地科学与管理, 17(1): 47-50.
|
|
SHENG NONG, XIN KUN, LIAO BAOWEN, 2021. Literature analysis concerning studies of ecological functions and values of mangrove wetland[J]. Wetland Science & Management, 17(1): 47-50 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
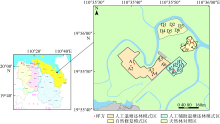
田蜜, 钟才荣, 方赞山, 等, 2023. 基于多源遥感的东寨港不同模式退塘还林红树林演变分析[J]. 湿地科学与管理, 19(3): 4-8.
|
|
TIAN MI, ZHONG CAIRONG, FANG ZANSHAN, et al, 2023. An analysis of the evolution of mangrove forests in Dongzhaigang with different models of reclaim of fishing ponds for forest based on multi-source remote sensing[J]. Wetland Science & Management, 19(3): 4-8 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
王瑁, 王文卿, 林贵生, 2019. 三亚红树林[M]. 北京: 科学出版社 (in Chinese).
|
| [13] |
王仁恩, 陈玉军, 黄勃, 等, 2011. 无瓣海桑人工林下乡土树种自然更新的初步研究[J]. 热带生物学报, 2(4): 342-348.
|
|
WANG RENEN, CHEN YUJUN, HUANG BO, et al, 2011. Natural regeneration of indigenous mangroves in Sonneratia apetala Buch. -Ham. plantations[J]. Journal of Tropical Organisms, 2(4): 342-348 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [14] |
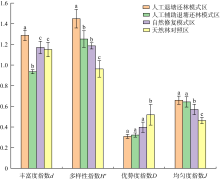
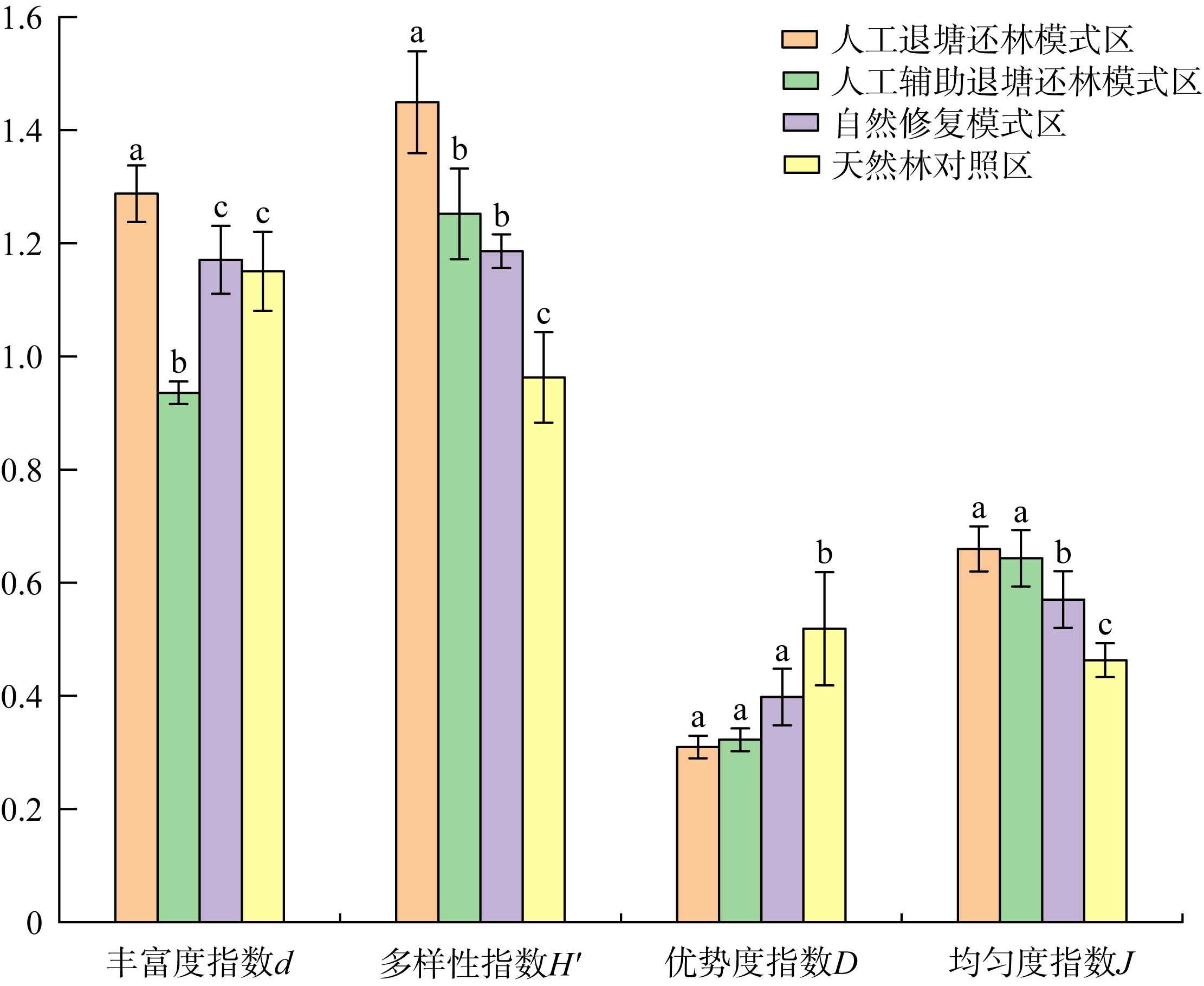
王文卿, 张林, 张雅棉, 等, 2021. 红树林退塘还林研究进展[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 60(2): 348-354.
|
|
WANG WENQING, ZHANG LIN, ZHANG YAMIAN, et al, 2021. Research progress of pond-to-mangrove restoration[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 60(2): 348-354 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [15] |
谢瑞红, 2007. 海南岛红树林资源与生态适宜性区划研究[D]. 儋州: 华南热带农业大学.
|
|
XIE RUIHONG, 2007. Study on the mangroves resource and ecological suitability regionalization in Hainan Island, China[D]. Danzhou: South China University of Tropical Agriculture (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [16] |
熊燕梅, 吴晓东, 陈玉军, 等, 2023. 退塘还林中地形和植被恢复方式对红树林恢复效果影响[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 43(4): 122-128.
|
|
XIONG YANMEI, WU XIAODONG, CHEN YUJUN, et al, 2023. Effects of landform and vegetation restoration method on mangroves restoration in ponds[J]. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 43(4): 122-128 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [17] |
杨德瑞, 2007. 内蒙古多伦县植被工程修复对植物多样性影响的研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院.
|
|
YANG DERUI, 2007. Study on the effect of vegetation restoration on the plants diversity in Duolun County of Inner Mongolia[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [18] |
张晓君, 管伟, 廖宝文, 等, 2014. 珠海人工红树林与天然红树林群落特征比较研究[J]. 生态科学, 33(2): 321-326.
|
|
ZHANG XIAOJUN, GUAN WEI, LIAO BAOWEN, et al, 2014. Comparison on the community characteristics between artificial and natural mangroves in Zhuhai City[J]. Ecological Science, 33(2): 321-326 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [19] |
GUSMAWATI N, SOULARD B, SELMAOUI-FOLCHER N, et al, 2018. Surveying shrimp aquaculture pond activity using multitemporal VHSR satellite images-case study from the Perancak estuary, Bali, Indonesia[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 131: 49-60.
|
| [20] |
SAJJAD M, LI YANGFAN, TANG ZHENGHONG, et al, 2018. Assessing hazard vulnerability, habitat conservation, and restoration for the enhancement of mainland China's coastal resilience[J]. Earth’s Future, 6(3): 326-338.
|
| [21] |
XIONG YANMEI, JIANG ZHONGMAO, XIN KUN, et al, 2021. Factors influencing mangrove forest recruitment in rehabilitated aquaculture ponds[J]. Ecological Engineering, 168: 106272.
|
| [22] |
ZHANG YAMIAN, ZHANG LIN, KANG YIYANG, et al, 2022. Biotic homogenization increases with human intervention: implications for mangrove wetland restoration[J]. Ecography, 2022(4): e05835.
|
 ), 钟才荣1,2(
), 钟才荣1,2( ), 吕晓波1,2, 方赞山1,2, 黄丹慜1
), 吕晓波1,2, 方赞山1,2, 黄丹慜1
 ), ZHONG Cairong1,2(
), ZHONG Cairong1,2( ), LYU Xiaobo1,2, FANG Zanshan1,2, HUANG Danmin1
), LYU Xiaobo1,2, FANG Zanshan1,2, HUANG Danmin1